更多算法(语言为JavaScript) 持续更新...
戳我去GitHub看更多算法问题>>>>目录
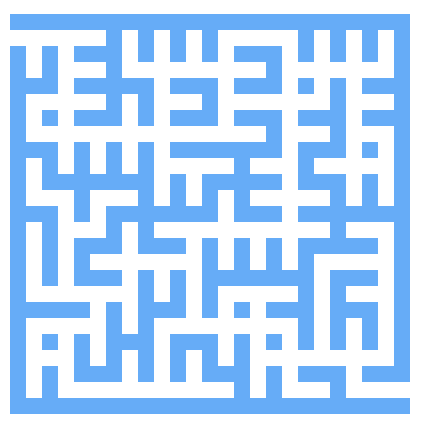
迷宫生成
戳我去GitHub看详细代码以及生成动画>>>>迷宫生成
下文所涉及的迷宫代码为:
- 只有一个出口,一个入口
- 解有且只有一个
- 方形画布,行与列均为奇数
- 墙与路径均占一个格子
- 路径连续
思路
-
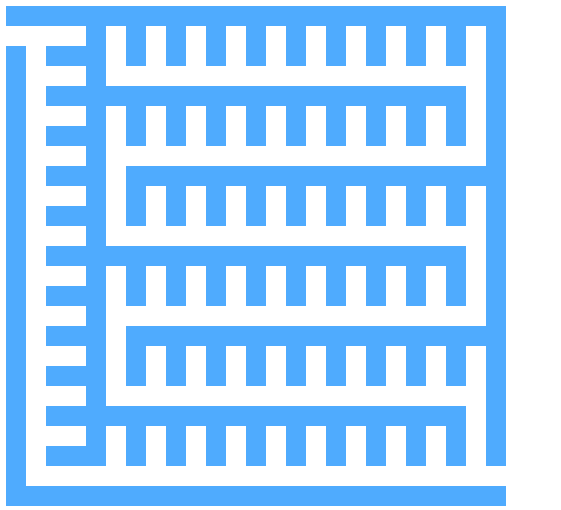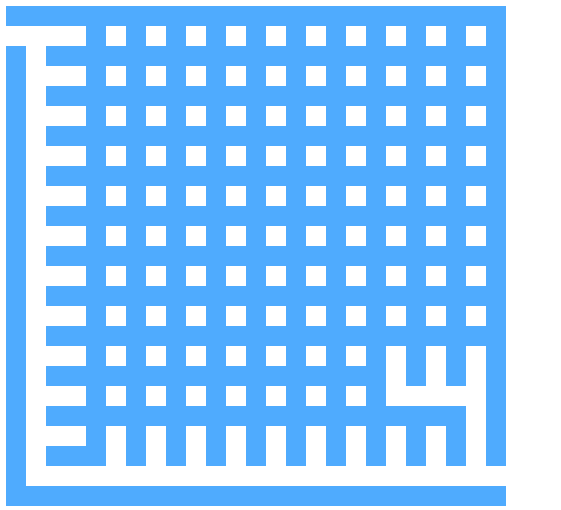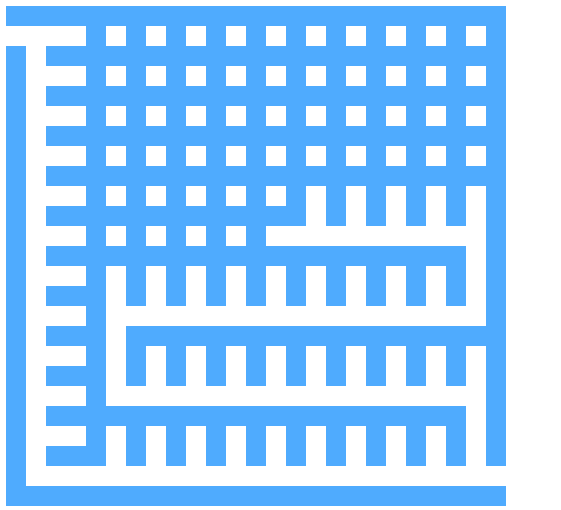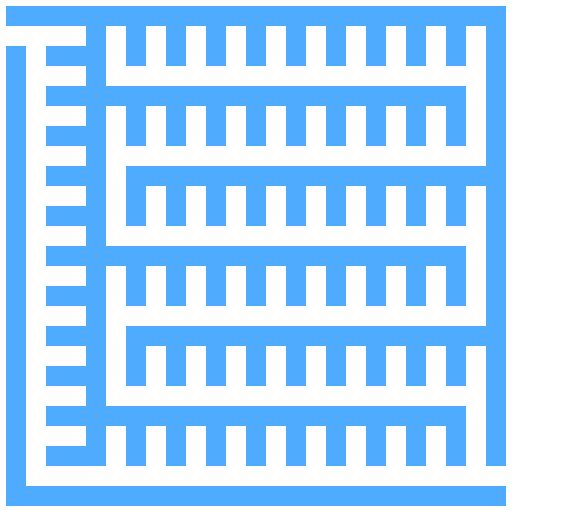
初始化出如下图所示的图形,然后进行图的遍历
通过遍历目前的白色方块,然后按照某种方法连通两个方块(即把两者之间的蓝色方块变成白色)
// row, col, 迷宫的行数 列数
// paintProgressTime, 开启可视化展示时的间隔
// width = 500, height = 500 迷宫的宽高 默认500px
// 此demo所实现的迷宫为固定出口,固定入口, 解有且只有一个,行与列均为奇数
// demo中所有坐标相关的变量均代表的是第几行 第几列 从0开始
constructor(row, col, paintProgressTime, width = 500, height = 500) {
// 类名
this.class = Math.random().toFixed(2)
// Maze行列
this.row = row
this.col = col
// 迷宫的长宽
this.width = width
this.height = height
// 设置路与墙
this.road = ' '
this.wall = '#'
// 入口坐标(1, 0)
this.entryX = 1
this.entryY = 0
// 出口坐标(倒数第二行, 最后一列)
this.outX = row - 2
this.outY = col - 1
// 迷宫数据
this.maze = []
// 各节点的遍历情况
this.visited = []
// 设置上下左右的偏移坐标值(上右下左)
this.offset = [[-1, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1]]
// 可视化展示间隔
this.paintProgressTime = paintProgressTime
this.i = 0 // 可视化展示索引
}
// 初始化迷宫数据
initData(maze) {
for (let i = 0; i < this.row; i++) {
maze[i] = new Array(this.col).fill(this.wall) // 初始化二维数组
this.visited[i] = new Array(this.col).fill(false) // 初始化访问状态为false
for (let j = 0; j < this.col; j++) {
// 横纵坐标均为奇数 则是路
if (i % 2 === 1 && j % 2 === 1) {
maze[i][j] = this.road
}
}
}
// 入口及出口 则是路
maze[this.entryX][this.entryY] = this.road
maze[this.outX][this.outY] = this.road
return maze
}
// 初始化迷宫DOM
initDOM(maze) {
let oDiv = document.createElement('div')
oDiv.style.width = this.width + 'px'
oDiv.style.height = this.height + 'px'
oDiv.style.display = 'flex'
oDiv.style.flexWrap = 'wrap'
oDiv.style.marginBottom = '20px'
for (let i = 0; i < maze.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < maze[i].length; j++) {
let oSpan = document.createElement('span')
oSpan.dataset.index = i + '-' + j + '-' + this.class
oSpan.style.width = (this.width / this.col).toFixed(2) + 'px'
oSpan.style.height = (this.height / this.row).toFixed(2) + 'px'
// 加边框
// oSpan.style.border = '1px solid #ccc'
// oSpan.style.boxSizing = 'border-box'
oSpan.style.background = maze[i][j] === this.wall ? '#4facfe' : '#fff'
oDiv.appendChild(oSpan)
}
}
document.body.appendChild(oDiv)
}
// 重新渲染迷宫 改变的格子坐标为(i, j)
resetMaze(x, y, type) {
// 只有不越界的点才做后续处理
if (this.isArea(x, y)) {
// 改变this.maze中对应的数据
this.maze[x][y] = type
// 改变dom中对应的节点颜色
let changeSpan = document.querySelector(`span[data-index='${x}-${y}-${this.class}']`)
changeSpan.style.background = type === this.wall ? '#4facfe' : '#fff'
}
}
// 判断坐标是否越界
isArea(x, y) {
return x > 0 && x < this.row - 1 && y > 0 && y < this.col - 1
}
深度优先遍历_递归
// 渲染迷宫
paintMaze() {
this.initMaze()
this.go(this.entryX, this.entryY + 1) // 执行遍历 起点是入口右侧的点
}
// 遍历
go(x, y) {
this.visited[x][y] = true
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
let newX = x + this.offset[i][0] * 2 // 两步是 *2
let newY = y + this.offset[i][1] * 2
// console.log(newX, newY);
// 坐标没有越界 而且 没有被访问过
if (this.isArea(newX, newY) && !this.visited[newX][newY]) {
this.resetMazeShow((newX + x) / 2, (newY + y) / 2, this.road) // 打通两个方块之间的墙
this.go(newX, newY)
}
}
}
深度优先遍历_非递归(通过栈实现)
// 模拟栈
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.stack = []
}
push(pos) {
this.stack.push(pos)
}
pop() {
return this.stack.pop()
}
empty() {
return !this.stack.length
}
}
// 渲染迷宫
paintMaze() {
this.initMaze()
let stack = new Stack()
stack.push({x: this.entryX, y: this.entryY + 1})
this.visited[this.entryX][this.entryY + 1] = true
while (!stack.empty()) {
let curPos = stack.pop()
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
let newX = curPos.x + this.offset[i][0] * 2 // 两步是 *2
let newY = curPos.y + this.offset[i][1] * 2
// 坐标没有越界 而且 没有被访问过
if (this.isArea(newX, newY) && !this.visited[newX][newY]) {
// this.resetMazeShow((newX + curPos.x) / 2, (newY + curPos.y) / 2, this.road) // 打通两个方块之间的墙
stack.push({x: newX, y: newY})
this.visited[newX][newY] = true
}
}
}
}
广度优先遍历(在深度优先遍历的基础上将栈改为队列即可实现)
只需要将原来的栈的实现改为队列,主要是pop()的更改
// 模拟队列
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.queue = []
}
push(pos) {
this.queue.push(pos)
}
pop() {
return this.queue.shift()
}
empty() {
return !this.queue.length
}
}
随机队列生成迷宫
更改队列的pop()实现即可。随机选一个元素与队列的头交换,实现随机出队一个元素。
// 模拟队列
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.queue = []
}
push(pos) {
this.queue.push(pos)
}
pop() {
// 随机选出一个与队列的头交换
let randomIndex = Math.floor(Math.random() * this.queue.length)
let temp = this.queue[0]
this.queue[0] = this.queue[randomIndex]
this.queue[randomIndex] = temp
return this.queue.shift()
}
empty() {
return !this.queue.length
}
}
更加随机的迷宫
// 模拟队列
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.queue = []
}
push(pos) {
if ( Math.random() < 0.5) {
this.queue.push(pos)
} else {
this.queue.unshift(pos)
}
}
pop() {
if ( Math.random() < 0.5) {
return this.queue.pop()
} else {
return this.queue.shift()
}
}
empty() {
return !this.queue.length
}
}
// 多解
if (this.isArea(newX, newY)) {
if (!this.visited[newX][newY]) {
this.resetMazeShow((newX + curPos.x) / 2, (newY + curPos.y) / 2, this.road) // 打通两个方块之间的墙
queue.push({x: newX, y: newY})
this.visited[newX][newY] = true
} else if (Math.random() < 0.05) {
this.resetMazeShow((newX + curPos.x) / 2, (newY + curPos.y) / 2, this.road) // 打通两个方块之间的墙
}
}
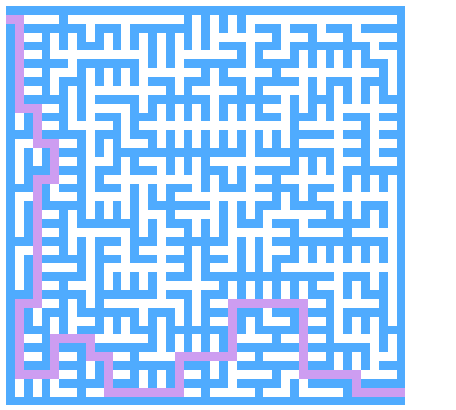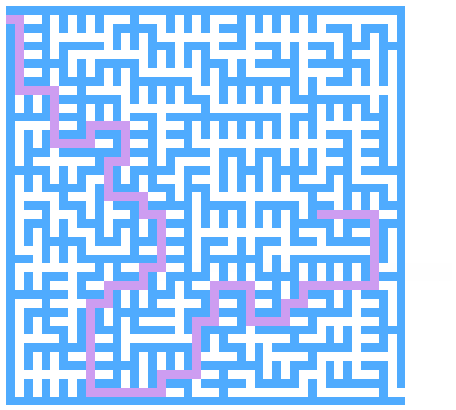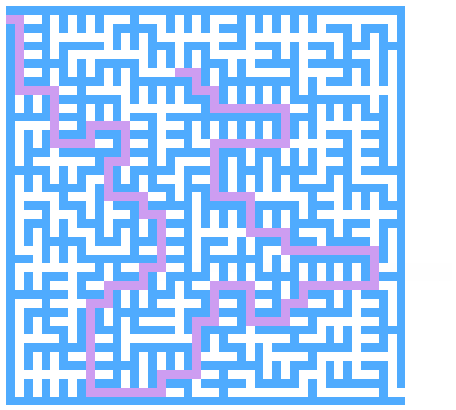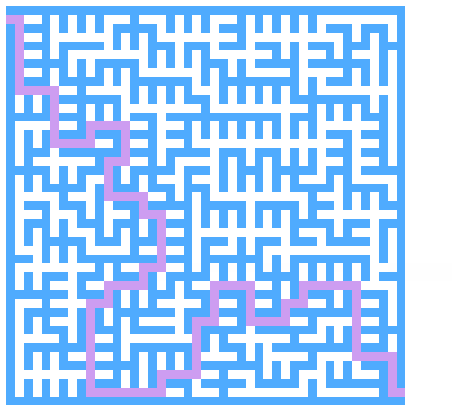
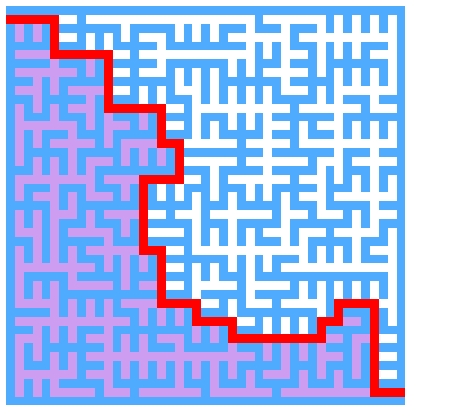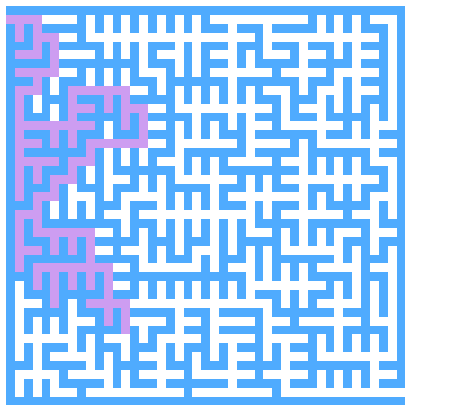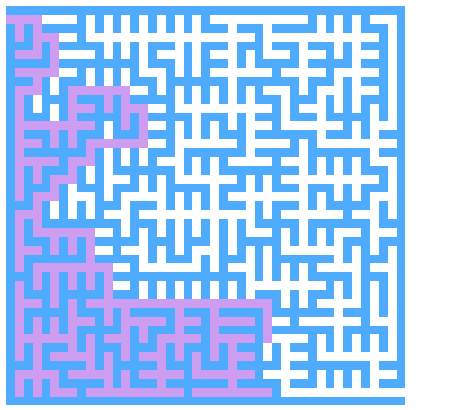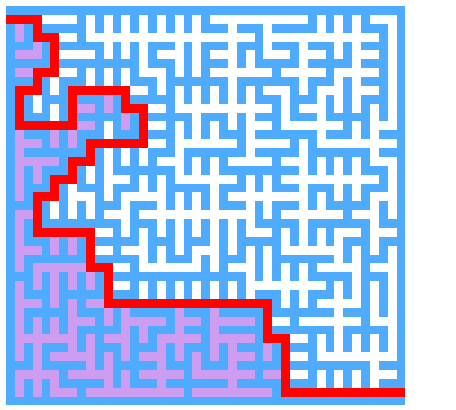
迷宫求解
戳我去GitHub看详细代码以及求解动画>>>>迷宫求解
以下求解的迷宫为迷宫生成中随机生成的迷宫 代码只得出一个解
思路
求解迷宫(x, y)
- 尝试向上走,继续求解迷宫
- 尝试向右走,继续求解迷宫
- 尝试向下走,继续求解迷宫
- 尝试向左走,继续求解迷宫
求解
新增解迷宫需要的属性
// 求解迷宫时各节点的遍历情况
this.findPathVisited = []
// 迷宫是否生成完成
this.hasDown = false
// 迷宫自动求解
findPath() {
if (!this.hasDown) throw new Error('请等待迷宫生成后再求解!')
if (!this.findPathGo(this.entryX, this.entryY)) throw new Error('迷宫无解!')
}
// 渲染迷宫指定位置
findPathSpan(x, y, color) {
// 只有不越界的点才做后续处理
if (this.isArea(x, y)) {
// 改变dom中对应的节点颜色
let changeSpan = document.querySelector(`span[data-index='${x}-${y}-${this.class}']`)
changeSpan.style.background = color
}
}
findPathReset(x, y, color = '#cd9cf2') {
if (!this.paintProgressTime) {
this.findPathSpan(x, y, color)
return
}
this.i++ // 可视化展示
setTimeout(() => { // 可视化展示
this.findPathSpan(x, y, color)
}, this.i * this.paintProgressTime);
}
深度优先递归+回溯
// 递归遍历 渲染迷宫求解路径
findPathGo(x, y) {
if (this.isArea(x, y)) {
this.findPathVisited[x][y] = true // 求解时访问过
this.findPathReset(x, y) // 渲染当前点
if (x == this.outX && y == this.outY) return true // 已找到出口 递归终止
// 遍历该点的四个方向是否可继续遍历
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
let newX = x + this.offset[i][0]
let newY = y + this.offset[i][1]
if (this.isArea(newX, newY) && this.maze[newX][newY] === this.road && !this.findPathVisited[newX][newY]) {
if (this.findPathGo(newX, newY)) return true
}
}
// 回溯 遍历完四个方向的点均没有找到出口 则表示该点不是解的路径上的点 变回路的颜色
this.findPathReset(x, y, '#fff')
return false
}
}
深度优先非递归
新增需要属性,由于非递归无法像递归一样轻易回溯,所以通过记录每次遍历到的节点是从哪个节点过来的可以再找到出口时,找到出口的前一个元素,依次找到入口,即可完成路径的寻找。
// 迷宫是否有解
this.hasFindPath = false
// 存储迷宫某点的上一点位置
this.path = []
// 迷宫自动求解
findPath() {
if (!this.hasDown) throw new Error('请等待迷宫生成后再求解!')
let stack = new Stack()
stack.push({x: this.entryX, y: this.entryY}) // 入栈
while (!stack.empty()) {
let curPos = stack.pop()
this.findPathVisited[curPos.x][curPos.y] = true // 求解时访问过
this.findPathReset(curPos.x, curPos.y) // 渲染当前点
// 找到出口
if (curPos.x === this.outX && curPos.y === this.outY) {
this.hasFindPath = true
// 绘制解
this.findPathReset(curPos.x, curPos.y, 'red') // 绘制出口
let prePos = this.path[curPos.x][curPos.y] // 获取上一个点
while(prePos != null) {
this.findPathReset(prePos.x, prePos.y, 'red') // 渲染上一个点
prePos = this.path[prePos.x][prePos.y] // 获取上一个点的上一个点
}
break;
}
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
let newX = curPos.x + this.offset[i][0]
let newY = curPos.y + this.offset[i][1]
if (this.isArea(newX, newY) && this.maze[newX][newY] === this.road && !this.findPathVisited[newX][newY]) {
this.path[newX][newY] = {x: curPos.x, y: curPos.y} // 记录新的点以及该点由谁走过来
stack.push({x: newX, y: newY}) // 入栈
}
}
}
if(!this.hasFindPath) throw new Error('迷宫无解!')
}
广度优先
与深度优先遍历非递归逻辑完全相同,只需要将模拟的栈替换成模拟的队列即可
// 模拟队列 -- 自动寻解
class QueueFindPath {
constructor() {
this.queue = []
}
push(pos) {
this.queue.push(pos)
}
pop() {
return this.queue.shift()
}
empty() {
return !this.queue.length
}
}
// 迷宫自动求解
findPath() {
if (!this.hasDown) throw new Error('请等待迷宫生成后再求解!')
let queueFindPath = new QueueFindPath()
queueFindPath.push({x: this.entryX, y: this.entryY}) // 入栈
while (!queueFindPath.empty()) {
let curPos = queueFindPath.pop()
this.findPathVisited[curPos.x][curPos.y] = true // 求解时访问过
this.findPathReset(curPos.x, curPos.y) // 渲染当前点
// 找到出口
if (curPos.x === this.outX && curPos.y === this.outY) {
this.hasFindPath = true
// 绘制解
this.findPathReset(curPos.x, curPos.y, 'red') // 绘制出口
let prePos = this.path[curPos.x][curPos.y] // 获取上一个点
while(prePos != null) {
this.findPathReset(prePos.x, prePos.y, 'red') // 渲染上一个点
prePos = this.path[prePos.x][prePos.y] // 获取上一个点的上一个点
}
break;
}
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
let newX = curPos.x + this.offset[i][0]
let newY = curPos.y + this.offset[i][1]
if (this.isArea(newX, newY) && this.maze[newX][newY] === this.road && !this.findPathVisited[newX][newY]) {
this.path[newX][newY] = {x: curPos.x, y: curPos.y} // 记录新的点以及该点由谁走过来
queueFindPath.push({x: newX, y: newY}) // 入栈
}
}
}
if(!this.hasFindPath) throw new Error('迷宫无解!')
}
更多算法(语言为JavaScript) 持续更新...
戳我去GitHub看更多算法问题>>>>目录