介绍
近期发布了 webpack 4.0.0 的 beta 版本,如果想了解和之前版本的区别,不妨先自己搭建一个webpack的简单应用体验一下。
1.简单案例
安装 npm i webpack --webpack-cli -D
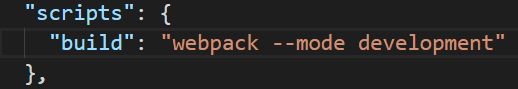
1.1 为了使用命令行进行打包,需要在package.json中配置
1.2 webpack.config.js配置
let path = require('path');
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',//入口配置
output:{
path:path.join(__dirname,'dist'),//只能写绝对路径,输出文件夹
filename:'bundle.js'//输出文件名
},
module:{
},
plugins:[
]
}
执行
npx webpack或者npm run build压缩 src文件夹下的index.js
1.3 对打包后的js解读
- 在bundle.js中,生成一个字执行函数,把要打包的js定义为实参,传入到自执行函数当中。
- 首先会先构建模块的缓存,目的是为了提高模块的加载速度,下次直接从缓存中取
1.4 使用http服务自动访问项目
- 在dist文件夹下创建index.html文件 引入bundle.js
- 在src目录下创建index.css 并在index.js中引入index.css
require('./index.css');
- 执行
npm install style-loader css-loader并在webpack-config.js 中配置loader
rules:[
{
test:/\.css$/,
loader:["style-loader","css-loader"]
}
]
},
- 执行
npm install webpack-dev-server -D - 在package.json中 配置
"dev": "webpack-dev-server --open --mode development",在配置--open 后,最后执行npm run dev会自动启动服务打开预览。 - 在webpack.config.js配置静态文件服务器,可以预览打包后的项目
devServer:{
contentBase:'./dist',//静态文件跟目录
host:'localhost',//配置主机
port:8080,//主机名
compress:true//服务器返回给浏览器是否使用gzip压缩
}
-
npm run dev成功启动项目
webpack-dev-server是一个小型的Node.jsExpress服务器,它使用webpack-dev-middleware来服务于webpack的包,我们可以看到产出的文件(bundle.js),但是webpack-dev-server打包的文件会放到内存中,不可见。
1.5 使用动态模板产出项目
-
npm i html-webpack-plugin -D根据模板生成一个html文件 - 配置webpack-config.js
output:{
path:path.join(__dirname,'dist'),//只能写绝对路径
filename: '[name].[hash].js'//打包后的文件名
},
输出文件名,改为变量加上哈希值,避免页面引入js有缓存的情况
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
plugins:[
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index.html',
filename: 'index.html',
title: 'hello world!'
}),
],
src下创建index.html 模板文件,并且配置参数。
E:\韩佳骏\FF\test\webpack\dist\index.html
<%=htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title%>
-
npm run builddist目录下会自动生成打包后的文件,插入js和传入的title属性
1.6 多入口配置
首先为了每次build后dist下的目录重新打包,方便查看,我们使用
npm i clean-webpack-plugin -D
引入webpack.config.js中
const CleanWebpackPlugin = require('clean-webpack-plugin');
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin([path.join(__dirname, 'dist')]),
...
],
如果我们多个页面,并且每个页面引入的模块不相同,该如何配置?
entry: {
index:'./src/index.js',
base:'./src/base.js'
},
entry 中配置的key相当于每一个代码块chunk,配置多个页面时,每个页面配置需要的模块
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin([path.join(__dirname, 'dist')]),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index.html',//指定产的HTML模板
filename: 'index.html',
title: 'hello index!',
chunks:['index']
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index.html',//指定产的HTML模板
filename: 'base.html',
title: 'hello base!',
chunks: ['base']
}),
],
假如我们需要引入一个公共模块common.js,比如是jquery,我们还要其他模块内部引用jquery,这时
$这个变量被封装在模块内部,其他模块无法拿到jquery对象$,这时需要在plugin中使用一个模块
plugins: [
//用来自动向模块内部注入变量
new webpack.ProvidePlugin({
$: 'jquery'
}),...
假如我们想把
$变成全局变量,那么要引入expose-loader, 它会先加载此模块,然后得到模块的导出对象,并且挂载到window
写法:
expose-loader?全局变量名:模块名
let $ = require('expose-loader?$!jquery');
或者
rules: [
{
test: require.resolve('jquery'),
use: {
loader: 'expose-loader',
options: '$'
}
},
1.7 多个页面配置
let pages = ['index', 'base'];
pages = pages.map(page => new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index.html',//指定产的HTML模板
filename: `${page}.html`,//产出的HTML文件名
title: `${page}`,
chunks: [`${page}`],//在产出的HTML文件里引入哪些代码块
hash: true,// 会在引入的js里加入查询字符串避免缓存,
minify: {
removeAttributeQuotes: true
}
}))
//....
plugins:[
//....
...pages
]