1. Pyplot Simple
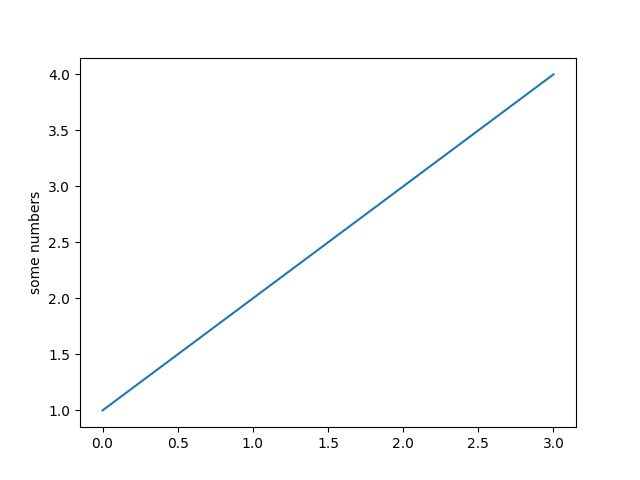
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot([1,2,3,4])
plt.ylabel('some numbers')
plt.show()
2. Pyplot Formatstr
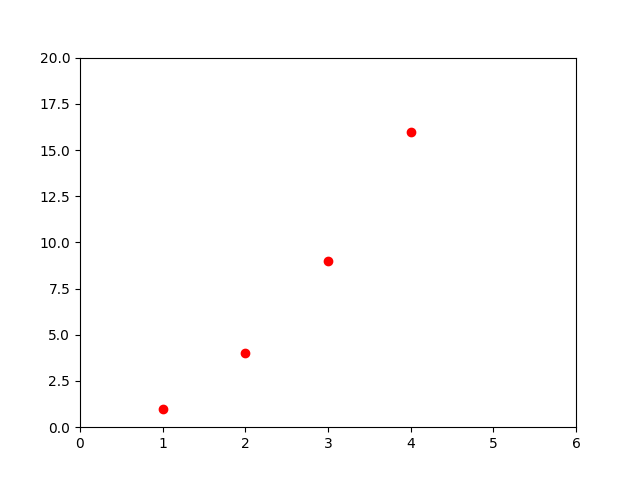
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot([1,2,3,4], [1,4,9,16], 'ro')
plt.axis([0, 6, 0, 20])
plt.show()
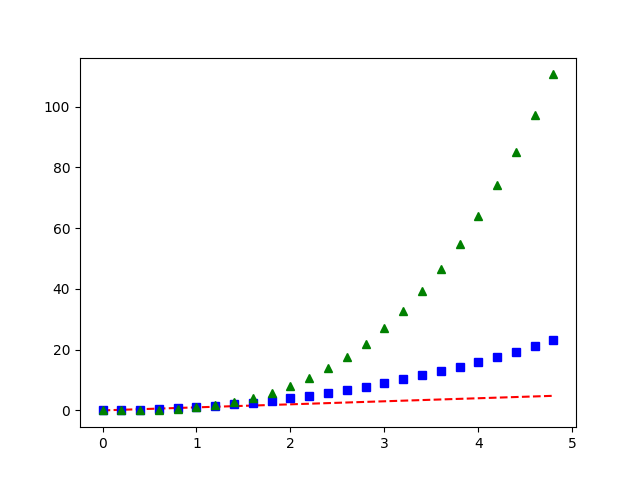
3. Pyplot Three
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# evenly sampled time at 200ms intervals
t = np.arange(0., 5., 0.2)
# red dashes, blue squares and green triangles
plt.plot(t, t, 'r--', t, t**2, 'bs', t, t**3, 'g^')
plt.show()
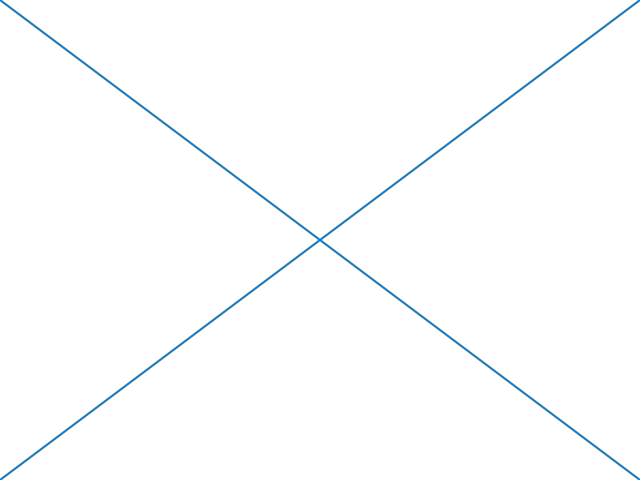
4. Fig X
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.lines as lines
fig = plt.figure()
l1 = lines.Line2D([0, 1], [0, 1], transform=fig.transFigure, figure=fig)
l2 = lines.Line2D([0, 1], [1, 0], transform=fig.transFigure, figure=fig)
fig.lines.extend([l1, l2])
plt.show()
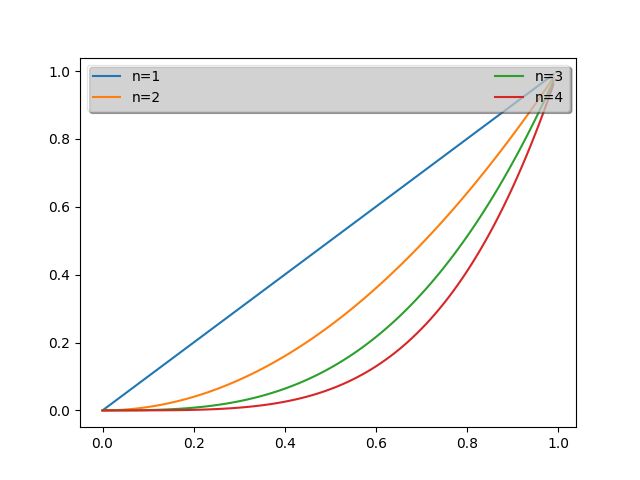
5. Whats New 0.98.4 Legend
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
ax = plt.subplot(111)
t1 = np.arange(0.0, 1.0, 0.01)
for n in [1, 2, 3, 4]:
plt.plot(t1, t1**n, label="n=%d"%(n,))
leg = plt.legend(loc='best', ncol=2, mode="expand", shadow=True, fancybox=True)
leg.get_frame().set_alpha(0.5)
plt.show()
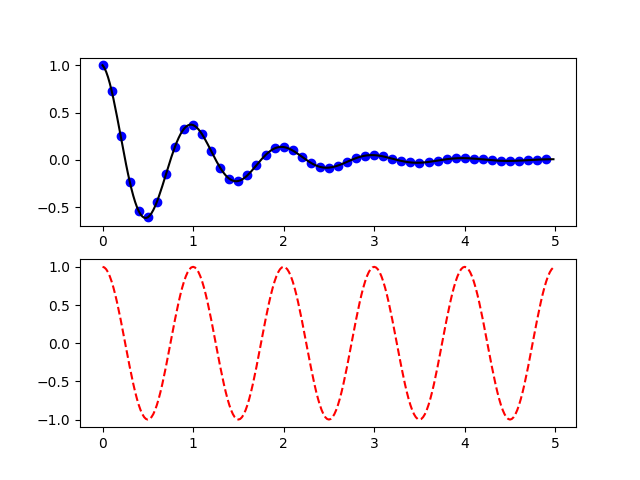
6. Pyplot Two Subplots
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def f(t):
return np.exp(-t) * np.cos(2*np.pi*t)
t1 = np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.1)
t2 = np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.02)
plt.figure(1)
plt.subplot(211)
plt.plot(t1, f(t1), 'bo', t2, f(t2), 'k')
plt.subplot(212)
plt.plot(t2, np.cos(2*np.pi*t2), 'r--')
plt.show()
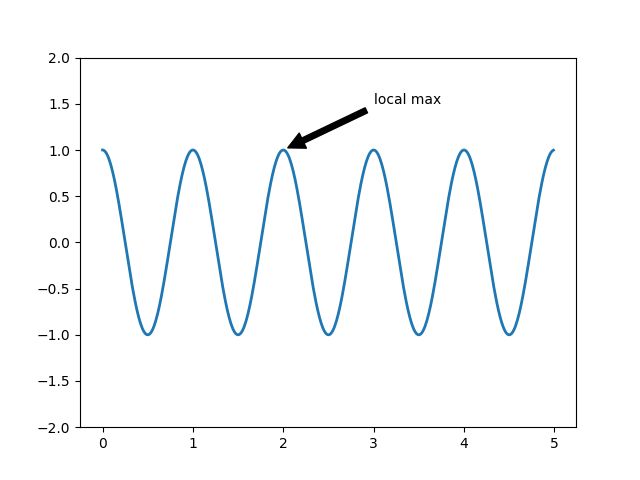
7. Annotating a plot
此示例演示如何用指向提供的坐标的箭头对绘图进行批注。我们修改箭头的默认值,以 "缩小" 它。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
t = np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.01)
s = np.cos(2*np.pi*t)
line, = ax.plot(t, s, lw=2)
ax.annotate('local max', xy=(2, 1), xytext=(3, 1.5),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05),
)
ax.set_ylim(-2, 2)
plt.show()
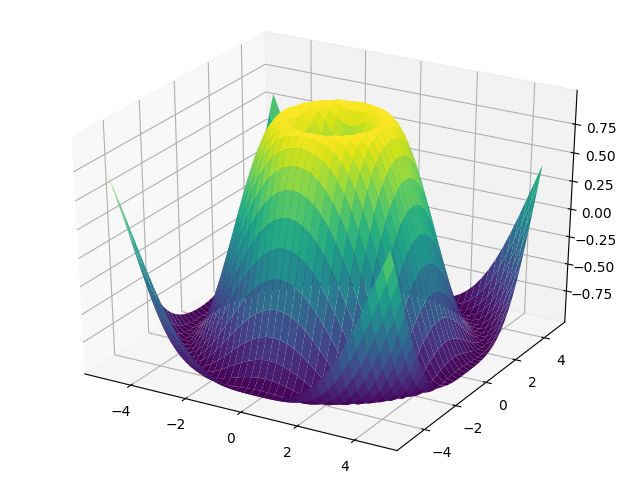
8. Whats New 0.99 Mplot3d
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
X = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
Y = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
R = np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2)
Z = np.sin(R)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = Axes3D(fig)
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=cm.viridis)
plt.show()
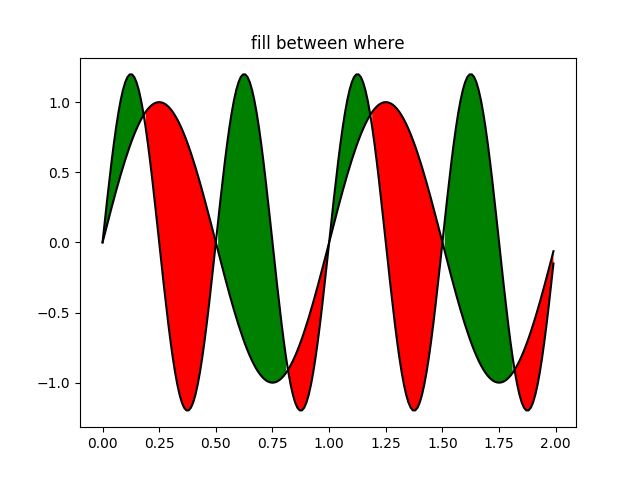
9. Whats New 0.98.4 Fill Between
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.arange(0.0, 2, 0.01)
y1 = np.sin(2*np.pi*x)
y2 = 1.2*np.sin(4*np.pi*x)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, y1, x, y2, color='black')
ax.fill_between(x, y1, y2, where=y2>y1, facecolor='green')
ax.fill_between(x, y1, y2, where=y2<=y1, facecolor='red')
ax.set_title('fill between where')
plt.show()
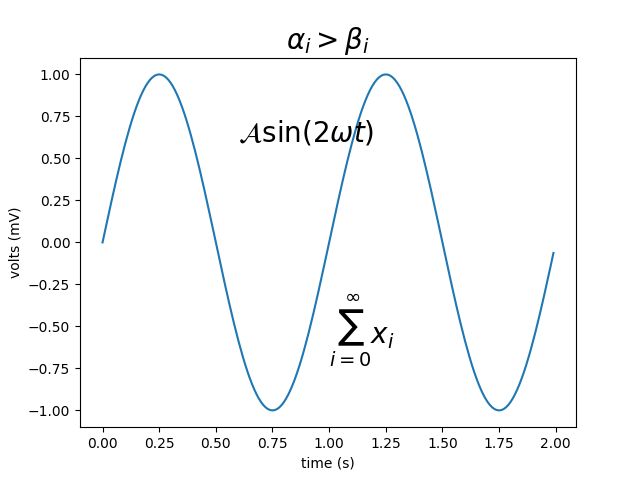
10. Pyplot Mathtext
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
t = np.arange(0.0, 2.0, 0.01)
s = np.sin(2*np.pi*t)
plt.plot(t,s)
plt.title(r'$\alpha_i > \beta_i$', fontsize=20)
plt.text(1, -0.6, r'$\sum_{i=0}^\infty x_i$', fontsize=20)
plt.text(0.6, 0.6, r'$\mathcal{A}\mathrm{sin}(2 \omega t)$',
fontsize=20)
plt.xlabel('time (s)')
plt.ylabel('volts (mV)')
plt.show()
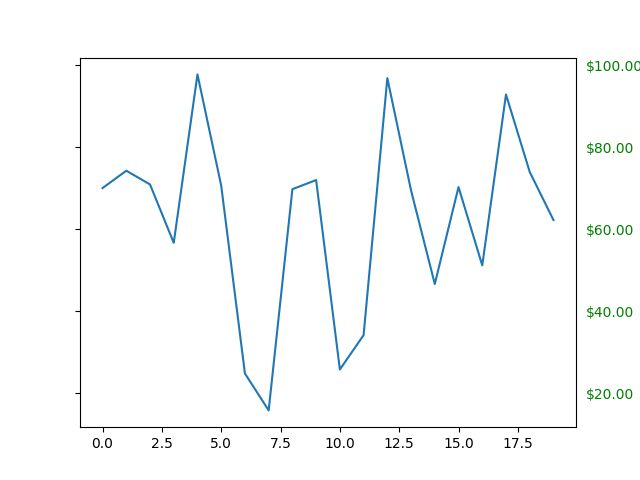
11. Dollar Ticks
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.ticker as ticker
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(100*np.random.rand(20))
formatter = ticker.FormatStrFormatter('$%1.2f')
ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(formatter)
for tick in ax.yaxis.get_major_ticks():
tick.label1On = False
tick.label2On = True
tick.label2.set_color('green')
plt.show()
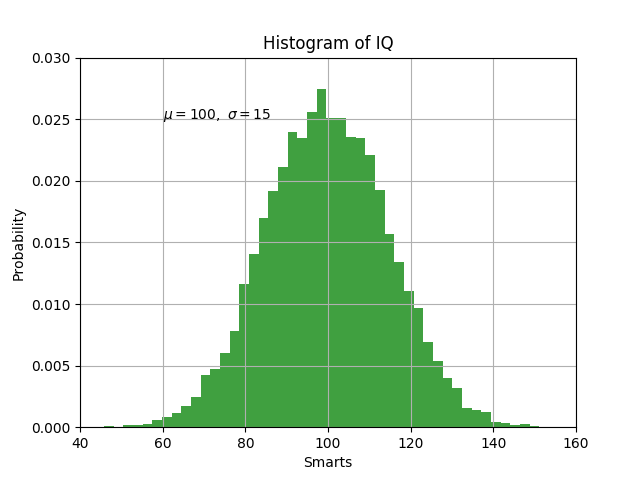
12. Pyplot Text
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
mu, sigma = 100, 15
x = mu + sigma * np.random.randn(10000)
# the histogram of the data
n, bins, patches = plt.hist(x, 50, density=True, facecolor='g', alpha=0.75)
plt.xlabel('Smarts')
plt.ylabel('Probability')
plt.title('Histogram of IQ')
plt.text(60, .025, r'$\mu=100,\ \sigma=15$')
plt.axis([40, 160, 0, 0.03])
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
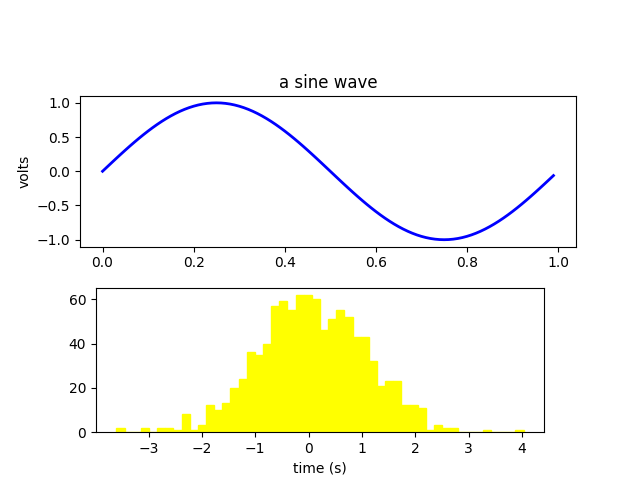
13. Fig Axes Labels Simple
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
fig.subplots_adjust(top=0.8)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(211)
ax1.set_ylabel('volts')
ax1.set_title('a sine wave')
t = np.arange(0.0, 1.0, 0.01)
s = np.sin(2*np.pi*t)
line, = ax1.plot(t, s, color='blue', lw=2)
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
ax2 = fig.add_axes([0.15, 0.1, 0.7, 0.3])
n, bins, patches = ax2.hist(np.random.randn(1000), 50,
facecolor='yellow', edgecolor='yellow')
ax2.set_xlabel('time (s)')
plt.show()
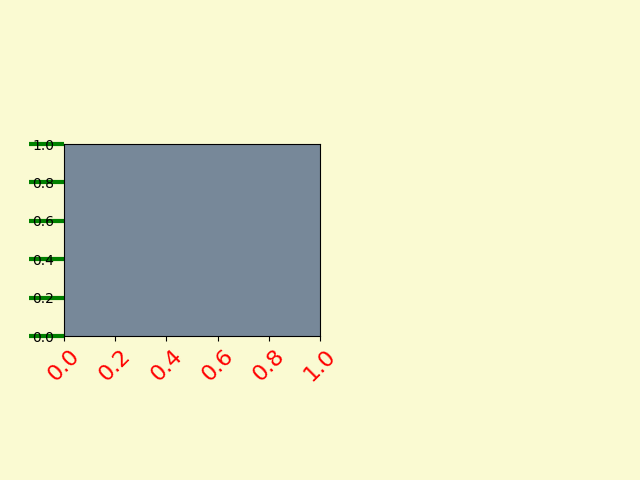
14. Fig Axes Customize Simple
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure 创建一个 matplotlib.figure.Figure 实例
fig = plt.figure()
rect = fig.patch # a rectangle instance
rect.set_facecolor('lightgoldenrodyellow')
ax1 = fig.add_axes([0.1, 0.3, 0.4, 0.4])
rect = ax1.patch
rect.set_facecolor('lightslategray')
for label in ax1.xaxis.get_ticklabels():
# label is a Text instance
label.set_color('red')
label.set_rotation(45)
label.set_fontsize(16)
for line in ax1.yaxis.get_ticklines():
# line is a Line2D instance
line.set_color('green')
line.set_markersize(25)
line.set_markeredgewidth(3)
plt.show()
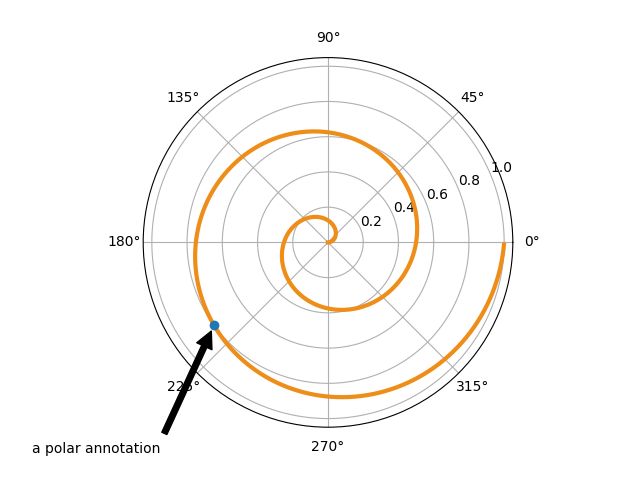
15. Annotation Polar
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, polar=True)
r = np.arange(0,1,0.001)
theta = 2 * 2*np.pi * r
line, = ax.plot(theta, r, color='#ee8d18', lw=3)
ind = 800
thisr, thistheta = r[ind], theta[ind]
ax.plot([thistheta], [thisr], 'o')
ax.annotate('a polar annotation',
xy=(thistheta, thisr), # theta, radius
xytext=(0.05, 0.05), # fraction, fraction
textcoords='figure fraction',
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05),
horizontalalignment='left',
verticalalignment='bottom',
)
plt.show()
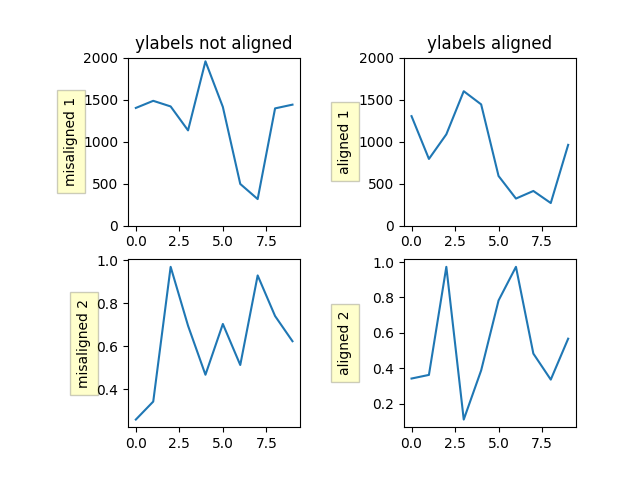
16. Align Ylabels
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
box = dict(facecolor='yellow', pad=5, alpha=0.2)
fig, ((ax1, ax2), (ax3, ax4)) = plt.subplots(2, 2)
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.2, wspace=0.6)
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
ax1.plot(2000*np.random.rand(10))
ax1.set_title('ylabels not aligned')
ax1.set_ylabel('misaligned 1', bbox=box)
ax1.set_ylim(0, 2000)
ax3.set_ylabel('misaligned 2',bbox=box)
ax3.plot(np.random.rand(10))
labelx = -0.3 # axes coords
ax2.set_title('ylabels aligned')
ax2.plot(2000*np.random.rand(10))
ax2.set_ylabel('aligned 1', bbox=box)
ax2.yaxis.set_label_coords(labelx, 0.5)
ax2.set_ylim(0, 2000)
ax4.plot(np.random.rand(10))
ax4.set_ylabel('aligned 2', bbox=box)
ax4.yaxis.set_label_coords(labelx, 0.5)
plt.show()
17. Whats New 0.99 Axes Grid
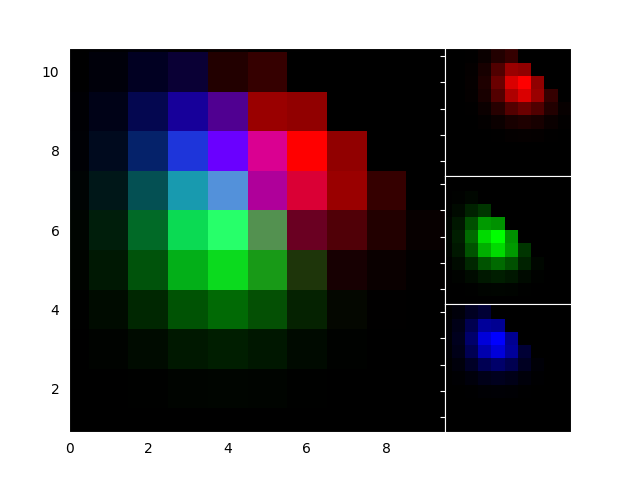
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.axes_rgb import RGBAxes
def get_demo_image():
# prepare image
delta = 0.5
extent = (-3, 4, -4, 3)
x = np.arange(-3.0, 4.001, delta)
y = np.arange(-4.0, 3.001, delta)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
Z1 = np.exp(-X**2 - Y**2)
Z2 = np.exp(-(X - 1)**2 - (Y - 1)**2)
Z = (Z1 - Z2) * 2
return Z, extent
def get_rgb():
Z, extent = get_demo_image()
Z[Z < 0] = 0.
Z = Z / Z.max()
R = Z[:13, :13]
G = Z[2:, 2:]
B = Z[:13, 2:]
return R, G, B
fig = plt.figure(1)
ax = RGBAxes(fig, [0.1, 0.1, 0.8, 0.8])
r, g, b = get_rgb()
kwargs = dict(origin="lower", interpolation="nearest")
ax.imshow_rgb(r, g, b, **kwargs)
ax.RGB.set_xlim(0., 9.5)
ax.RGB.set_ylim(0.9, 10.6)
plt.draw()
plt.show()
18. Text Commands
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
fig.suptitle('bold figure suptitle', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
fig.subplots_adjust(top=0.85)
ax.set_title('axes title')
ax.set_xlabel('xlabel')
ax.set_ylabel('ylabel')
ax.text(3, 8, 'boxed italics text in data coords', style='italic',
bbox={'facecolor':'red', 'alpha':0.5, 'pad':10})
ax.text(2, 6, r'an equation: $E=mc^2$', fontsize=15)
ax.text(3, 2, u'unicode: Institut f\374r Festk\366rperphysik')
ax.text(0.95, 0.01, 'colored text in axes coords',
verticalalignment='bottom', horizontalalignment='right',
transform=ax.transAxes,
color='green', fontsize=15)
ax.plot([2], [1], 'o')
ax.annotate('annotate', xy=(2, 1), xytext=(3, 4),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05))
ax.axis([0, 10, 0, 10])
plt.show()
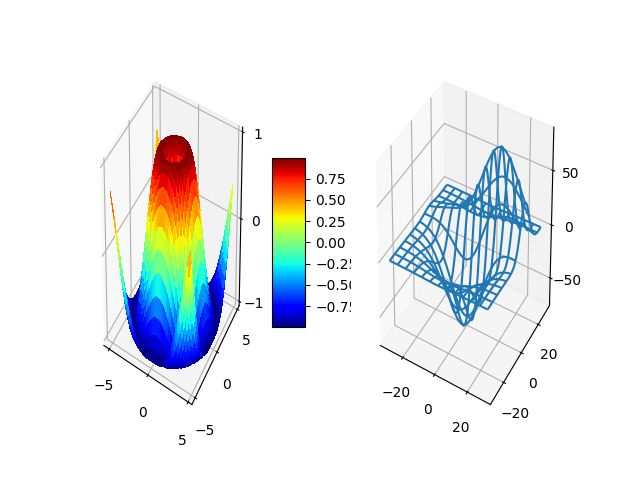
19. Whats New 1 Subplot3d
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.axes3d import Axes3D
from matplotlib import cm
#from matplotlib.ticker import LinearLocator, FixedLocator, FormatStrFormatter
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1, projection='3d')
X = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
Y = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
R = np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2)
Z = np.sin(R)
surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=cm.jet,
linewidth=0, antialiased=False)
ax.set_zlim3d(-1.01, 1.01)
#ax.w_zaxis.set_major_locator(LinearLocator(10))
#ax.w_zaxis.set_major_formatter(FormatStrFormatter('%.03f'))
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.axes3d import get_test_data
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2, projection='3d')
X, Y, Z = get_test_data(0.05)
ax.plot_wireframe(X, Y, Z, rstride=10, cstride=10)
plt.show()
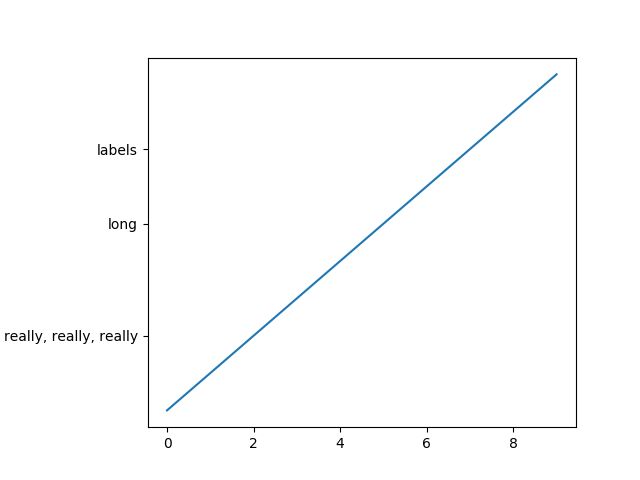
20. Auto Subplots Adjust
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.transforms as mtransforms
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.plot(range(10))
ax.set_yticks((2,5,7))
labels = ax.set_yticklabels(('really, really, really', 'long', 'labels'))
def on_draw(event):
bboxes = []
for label in labels:
bbox = label.get_window_extent()
# the figure transform goes from relative coords->pixels and we
# want the inverse of that
bboxi = bbox.inverse_transformed(fig.transFigure)
bboxes.append(bboxi)
# this is the bbox that bounds all the bboxes, again in relative
# figure coords
bbox = mtransforms.Bbox.union(bboxes)
if fig.subplotpars.left < bbox.width:
# we need to move it over
fig.subplots_adjust(left=1.1*bbox.width) # pad a little
fig.canvas.draw()
return False
fig.canvas.mpl_connect('draw_event', on_draw)
plt.show()
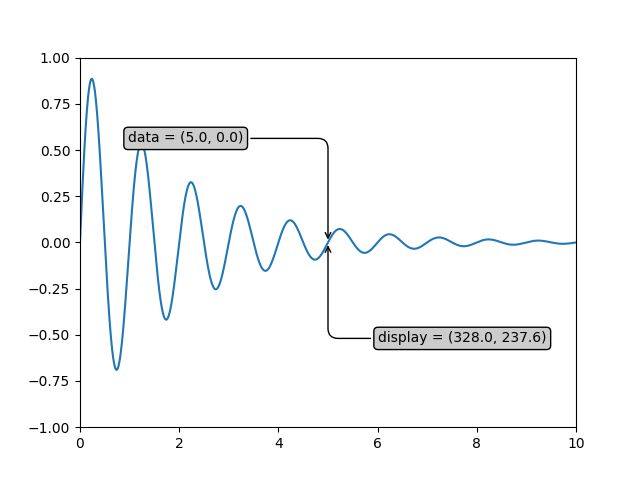
21. Annotate Transform
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.arange(0, 10, 0.005)
y = np.exp(-x/2.) * np.sin(2*np.pi*x)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_xlim(0, 10)
ax.set_ylim(-1, 1)
xdata, ydata = 5, 0
xdisplay, ydisplay = ax.transData.transform_point((xdata, ydata))
bbox = dict(boxstyle="round", fc="0.8")
arrowprops = dict(
arrowstyle = "->",
connectionstyle = "angle,angleA=0,angleB=90,rad=10")
offset = 72
ax.annotate('data = (%.1f, %.1f)'%(xdata, ydata),
(xdata, ydata), xytext=(-2*offset, offset), textcoords='offset points',
bbox=bbox, arrowprops=arrowprops)
disp = ax.annotate('display = (%.1f, %.1f)'%(xdisplay, ydisplay),
(xdisplay, ydisplay), xytext=(0.5*offset, -offset),
xycoords='figure pixels',
textcoords='offset points',
bbox=bbox, arrowprops=arrowprops)
plt.show()
22. Whats New 0.99 Spines
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def adjust_spines(ax,spines):
for loc, spine in ax.spines.items():
if loc in spines:
spine.set_position(('outward',10)) # outward by 10 points
else:
spine.set_color('none') # don't draw spine
# turn off ticks where there is no spine
if 'left' in spines:
ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left')
else:
# no yaxis ticks
ax.yaxis.set_ticks([])
if 'bottom' in spines:
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
else:
# no xaxis ticks
ax.xaxis.set_ticks([])
fig = plt.figure()
x = np.linspace(0,2*np.pi,100)
y = 2*np.sin(x)
ax = fig.add_subplot(2,2,1)
ax.plot(x,y)
adjust_spines(ax,['left'])
ax = fig.add_subplot(2,2,2)
ax.plot(x,y)
adjust_spines(ax,[])
ax = fig.add_subplot(2,2,3)
ax.plot(x,y)
adjust_spines(ax,['left','bottom'])
ax = fig.add_subplot(2,2,4)
ax.plot(x,y)
adjust_spines(ax,['bottom'])
plt.show()
23. Compound Path Demo
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
import matplotlib.path as path
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
# histogram our data with numpy
data = np.random.randn(1000)
n, bins = np.histogram(data, 100)
# get the corners of the rectangles for the histogram
left = np.array(bins[:-1])
right = np.array(bins[1:])
bottom = np.zeros(len(left))
top = bottom + n
nrects = len(left)
nverts = nrects*(1+3+1)
verts = np.zeros((nverts, 2))
codes = np.ones(nverts, int) * path.Path.LINETO
codes[0::5] = path.Path.MOVETO
codes[4::5] = path.Path.CLOSEPOLY
verts[0::5,0] = left
verts[0::5,1] = bottom
verts[1::5,0] = left
verts[1::5,1] = top
verts[2::5,0] = right
verts[2::5,1] = top
verts[3::5,0] = right
verts[3::5,1] = bottom
barpath = path.Path(verts, codes)
patch = patches.PathPatch(barpath, facecolor='green', edgecolor='yellow', alpha=0.5)
ax.add_patch(patch)
ax.set_xlim(left[0], right[-1])
ax.set_ylim(bottom.min(), top.max())
plt.show()
24. Pyplot Scales
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.ticker import NullFormatter # useful for `logit` scale
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
# make up some data in the interval ]0, 1[
y = np.random.normal(loc=0.5, scale=0.4, size=1000)
y = y[(y > 0) & (y < 1)]
y.sort()
x = np.arange(len(y))
# plot with various axes scales
plt.figure(1)
# linear
plt.subplot(221)
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.yscale('linear')
plt.title('linear')
plt.grid(True)
# log
plt.subplot(222)
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.yscale('log')
plt.title('log')
plt.grid(True)
# symmetric log
plt.subplot(223)
plt.plot(x, y - y.mean())
plt.yscale('symlog', linthreshy=0.01)
plt.title('symlog')
plt.grid(True)
# logit
plt.subplot(224)
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.yscale('logit')
plt.title('logit')
plt.grid(True)
# Format the minor tick labels of the y-axis into empty strings with
# `NullFormatter`, to avoid cumbering the axis with too many labels.
plt.gca().yaxis.set_minor_formatter(NullFormatter())
# Adjust the subplot layout, because the logit one may take more space
# than usual, due to y-tick labels like "1 - 10^{-3}"
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.92, bottom=0.08, left=0.10, right=0.95, hspace=0.25,
wspace=0.35)
plt.show()
25. Boxplot Demo
示例箱线图代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
# fake up some data
spread = np.random.rand(50) * 100
center = np.ones(25) * 50
flier_high = np.random.rand(10) * 100 + 100
flier_low = np.random.rand(10) * -100
data = np.concatenate((spread, center, flier_high, flier_low), 0)

fig1, ax1 = plt.subplots()
ax1.set_title('Basic Plot')
ax1.boxplot(data)
fig2, ax2 = plt.subplots()
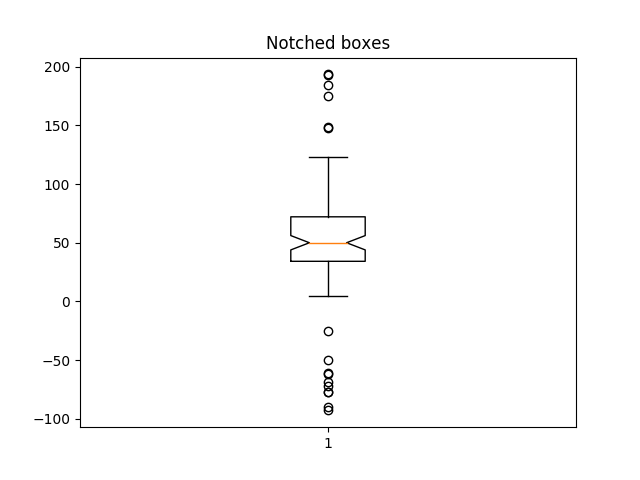
ax2.set_title('Notched boxes')
ax2.boxplot(data, notch=True)
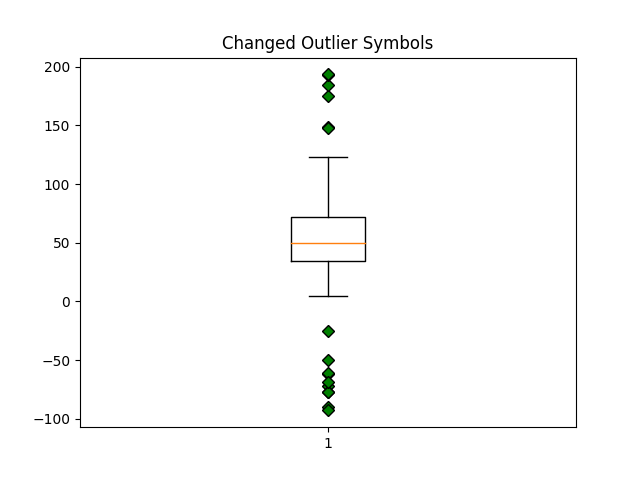
green_diamond = dict(markerfacecolor='g', marker='D')
fig3, ax3 = plt.subplots()
ax3.set_title('Changed Outlier Symbols')
ax3.boxplot(data, flierprops=green_diamond)
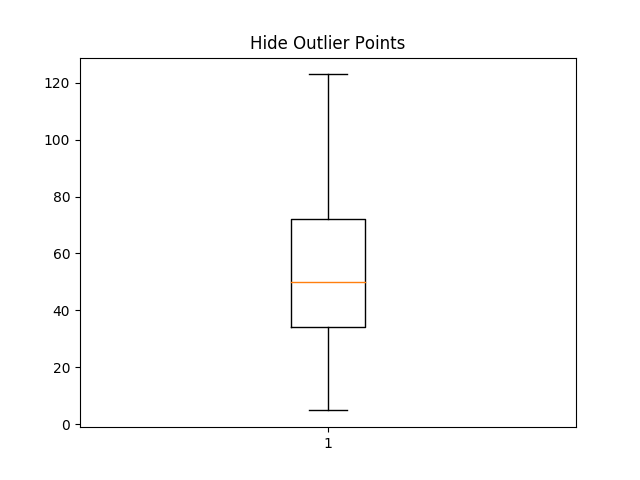
fig4, ax4 = plt.subplots()
ax4.set_title('Hide Outlier Points')
ax4.boxplot(data, showfliers=False)
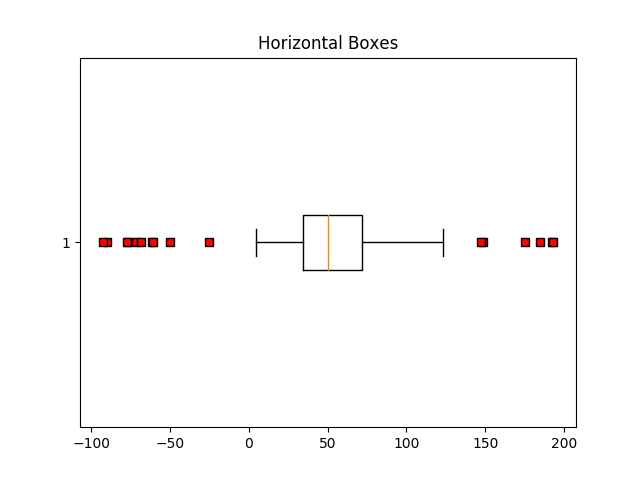
red_square = dict(markerfacecolor='r', marker='s')
fig5, ax5 = plt.subplots()
ax5.set_title('Horizontal Boxes')
ax5.boxplot(data, vert=False, flierprops=red_square)
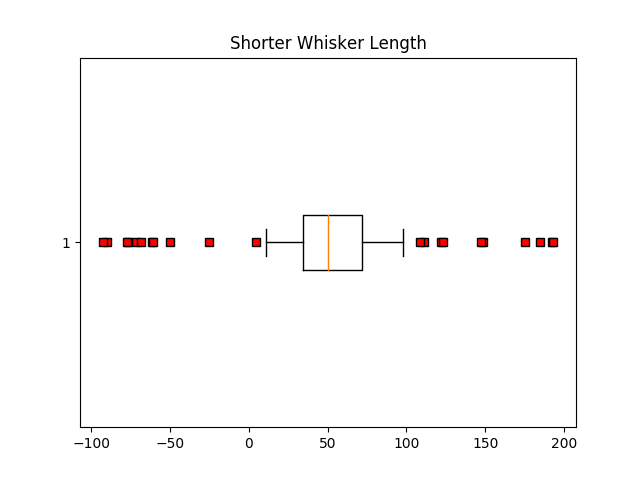
fig6, ax6 = plt.subplots()
ax6.set_title('Shorter Whisker Length')
ax6.boxplot(data, flierprops=red_square, vert=False, whis=0.75)
伪造更多的数据
spread = np.random.rand(50) * 100
center = np.ones(25) * 40
flier_high = np.random.rand(10) * 100 + 100
flier_low = np.random.rand(10) * -100
d2 = np.concatenate((spread, center, flier_high, flier_low), 0)
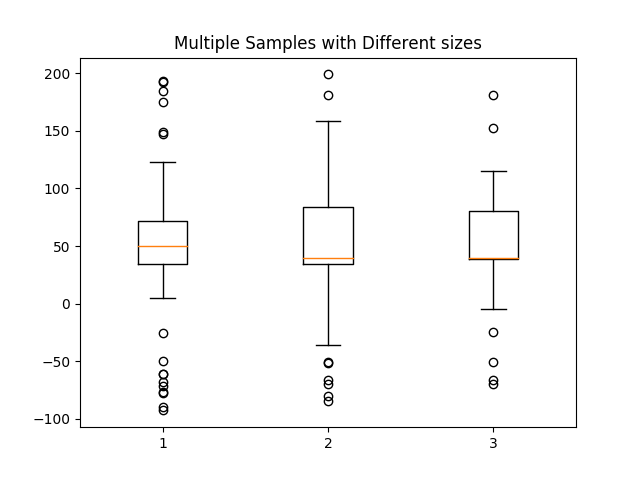
data.shape = (-1, 1)
d2.shape = (-1, 1)
如果所有列的长度相同,则使2维数组有效。如果不是,则使用列表代替。这实际上更有效,因为箱线图无论如何将2维数组转换为向量列表。
data = [data, d2, d2[::2,0]]
fig7, ax7 = plt.subplots()
ax7.set_title('Multiple Samples with Different sizes')
ax7.boxplot(data)
plt.show()
26. Whats New 0.98.4 Fancy
import matplotlib.patches as mpatch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
figheight = 8
fig = plt.figure(1, figsize=(9, figheight), dpi=80)
fontsize = 0.4 * fig.dpi
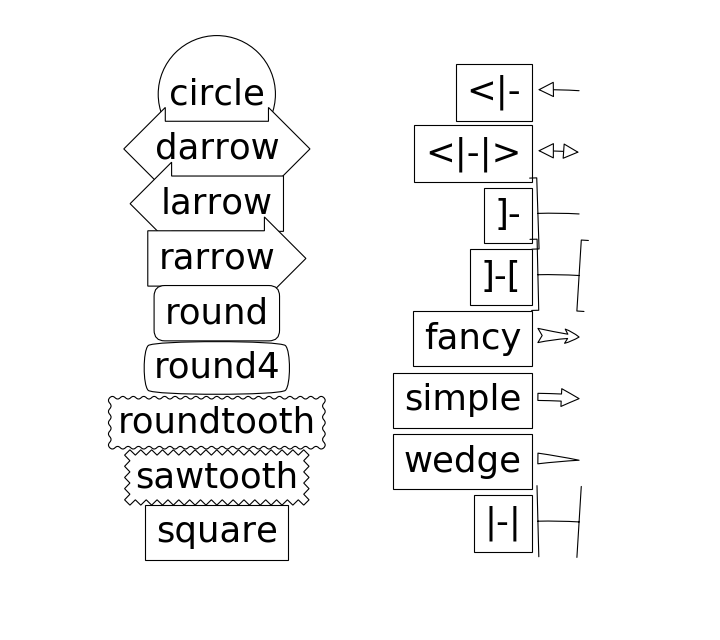
def make_boxstyles(ax):
styles = mpatch.BoxStyle.get_styles()
for i, (stylename, styleclass) in enumerate(sorted(styles.items())):
ax.text(0.5, (float(len(styles)) - 0.5 - i)/len(styles), stylename,
ha="center",
size=fontsize,
transform=ax.transAxes,
bbox=dict(boxstyle=stylename, fc="w", ec="k"))
def make_arrowstyles(ax):
styles = mpatch.ArrowStyle.get_styles()
ax.set_xlim(0, 4)
ax.set_ylim(0, figheight)
for i, (stylename, styleclass) in enumerate(sorted(styles.items())):
y = (float(len(styles)) -0.25 - i) # /figheight
p = mpatch.Circle((3.2, y), 0.2, fc="w")
ax.add_patch(p)
ax.annotate(stylename, (3.2, y),
(2., y),
#xycoords="figure fraction", textcoords="figure fraction",
ha="right", va="center",
size=fontsize,
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle=stylename,
patchB=p,
shrinkA=5,
shrinkB=5,
fc="w", ec="k",
connectionstyle="arc3,rad=-0.05",
),
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square", fc="w"))
ax.xaxis.set_visible(False)
ax.yaxis.set_visible(False)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121, frameon=False, xticks=[], yticks=[])
make_boxstyles(ax1)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122, frameon=False, xticks=[], yticks=[])
make_arrowstyles(ax2)
plt.show()
27. Text Layout
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
# build a rectangle in axes coords
left, width = .25, .5
bottom, height = .25, .5
right = left + width
top = bottom + height
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_axes([0,0,1,1])
# axes coordinates are 0,0 is bottom left and 1,1 is upper right
p = patches.Rectangle(
(left, bottom), width, height,
fill=False, transform=ax.transAxes, clip_on=False
)
ax.add_patch(p)
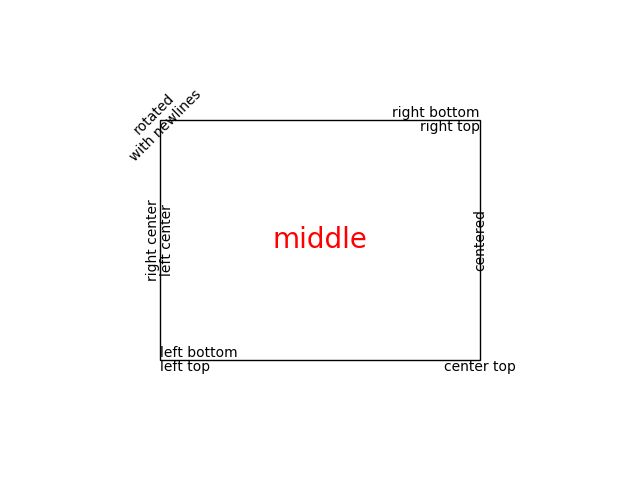
ax.text(left, bottom, 'left top',
horizontalalignment='left',
verticalalignment='top',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(left, bottom, 'left bottom',
horizontalalignment='left',
verticalalignment='bottom',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(right, top, 'right bottom',
horizontalalignment='right',
verticalalignment='bottom',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(right, top, 'right top',
horizontalalignment='right',
verticalalignment='top',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(right, bottom, 'center top',
horizontalalignment='center',
verticalalignment='top',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(left, 0.5*(bottom+top), 'right center',
horizontalalignment='right',
verticalalignment='center',
rotation='vertical',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(left, 0.5*(bottom+top), 'left center',
horizontalalignment='left',
verticalalignment='center',
rotation='vertical',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(0.5*(left+right), 0.5*(bottom+top), 'middle',
horizontalalignment='center',
verticalalignment='center',
fontsize=20, color='red',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(right, 0.5*(bottom+top), 'centered',
horizontalalignment='center',
verticalalignment='center',
rotation='vertical',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(left, top, 'rotated\nwith newlines',
horizontalalignment='center',
verticalalignment='center',
rotation=45,
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.set_axis_off()
plt.show()