原型是JS中继承的基础,JS的继承主要依靠原型链来实现
用图来表示:
原型链:让一个原型对象等于另一个类型的实例,层层递进,就构成了实例与原型的链条
继承
- 原型链继承: 子类的原型等于父类的实例
function Parent(){
this.color = 'blue'
// this.getParentValue = function(){
// return this.color
// }
}
// 将方法添加在原型中,避免每次new,方法都被反复添加到this中,浪费内存
Parent.prototype.getParentValue = function(){
return this.color
}
function Child(){
this.childColor = 'yellow'
}
Child.prototype = new Parent()
Child.prototype.getChildValue = function(){
return this.childColor
}
const exp = new Child()
console.log('pColor:',exp.getParentValue(),'color:',exp.getChildValue());
//pColor: blue color: yellow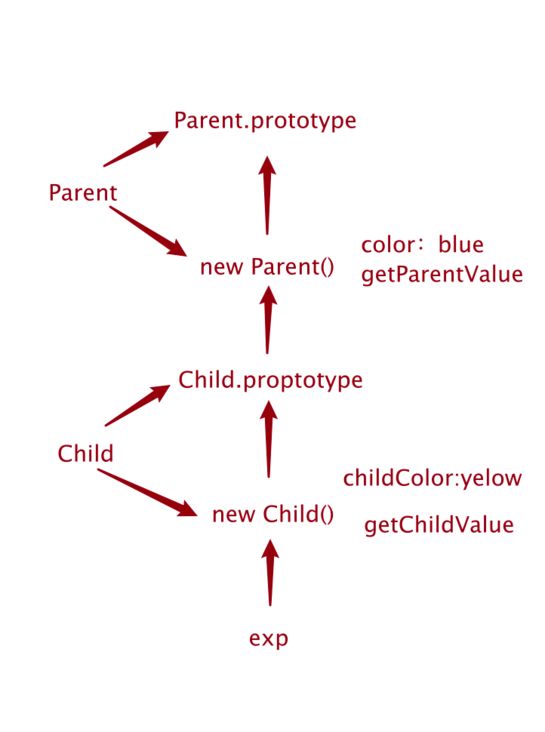
优点:继承了构造函数及其原型的所有属性和方法。
缺点:1、在创建子类实例时,无法向超类型的构造函数传参,继承单一。
2、所有新实例都会共享父类实例的属性。(原型上的属性是共享的,一个实例修改了原型引用类型的属性,另一个实例的原型属性也会被修改!)
function Parent() {
this.info = {
name:"lin",
age:42
}}
function Child(){
this.childinfo = {
name:"meng",
age:18
}
}
Child.prototype = new Parent()
const exp = new Child()
exp.info.name = "qqqq"
const exp1 = new Child()
console.log('info',exp1.info);//info {name: 'qqqq', age: 42}
- 构造函数继承: 在子类的内部调用父类,通过call改变父类中this的指向
优点:可以在子类构造函数中,向超类型构造函数传递参数。
缺点:只继承了父类构造函数的属性,没有继承父类原型的属性。
function Parent(){
this.info = {
name:'lin',
age:42
}
}
function Child(){
Parent.call(this)
}
const exp1 = new Child()
exp1.info.name = 'qqqqq'
console.log('exp1.info',exp1.info);//exp1.info {name: 'qqqqq', age: 42}
const exp2 = new Child()
console.log('exp2.info',exp2.info);//exp2.info {name: 'lin', age: 42}- 组合继承:原型链+构造函数
使用原型链实现对原型属性和方法的继承,通过构造函数来实现对实例属性的继承。这样既通过在原型上定义方法实现了函数的复用,又能够保证每个实例都有它自己的属性。
缺点:调用两次父类构造函数。
function Parent(name){
this.name = name;
this.colors = ['red','blue','green']
}
Parent.prototype.sayName = function(){
console.log('Pname',this.name);
}
function Child(name,age){
Parent.call(this,name)
this.age = age
}
Child.prototype = new Parent()
//Child.prototype.constructor = Child
Child.prototype.sayAge = function(){
console.log('Cage:',this.age);
}
const exp1 = new Child('lin',18)
exp1.colors.push('black')
console.log('exp1.colors',exp1.colors);//exp1.colors (4) ['red', 'blue', 'green', 'black']
exp1.sayName() //Pname lin
exp1.sayAge()//Cage: 18
const exp2 = new Child('meng',20)
console.log('exp2.colors',exp2.colors); //exp2.colors (3) ['red', 'blue', 'green']
Q:为什么要设置prototype.constructor?
A:建立原型链主要靠proto属性,因此constructor对原型链毫无影响。prototype.constructor仅仅可以用于识别对象是由哪个构造函数初始化的,仅此而已。
- 原型式继承:Object.create()
创建一个构造函数,构造函数的原型指向对象,然后调用 new 操作符创建实例,并返回这个实例,本质是一个浅拷贝,引用类型的数据共享在不同的实例之间
function newObj(o){
const Object = function(){}
Object.prototype = o
return new Object()
}
const obj = {
name:"lin",
age:18,
skills:['js','java'],
show:function(){
return `${this.name},${this.age}`
}
}
const obj2 = newObj(obj)
obj2.skills.push('c')
console.log('obj2.skills',obj2.skills);//obj2.skills (3) ['js', 'java', 'c']
const obj3 = newObj(obj)//obj3.skills (3) ['js', 'java', 'c']
console.log('obj3.skills',obj3.skills);- 寄生式继承:在原型式继承基础上进行封装,在对象上扩展新的方法,
function newerObj(o){
const Obj = Object.create(o)
Obj.sayName = function(){
return this.name
}
return Obj
}
const obj = {
name:"lin",
age:18,
skills:['js','java'],
show:function(){
return `${this.name},${this.age}`
}
}
const obj2 = newerObj(obj)
console.log('obj2',obj2.sayName());//obj2 lin寄生组合式继承:借用构造函数继承属性,通过原型链继承方法
只调用了一次超类(父类)的构造,并且避免了在子类prototype上面创建不必要,多余的属性function Inherit(child,parent){ const protoT = Object.create(parent.prototype) protoT.constructor = child child.prototype = protoT } // 使用 function Parent(name){ this.name = name, this.colors = ['red','blue','green'] } Parent.prototype.sayName = function(){ console.log('Pname',this.name); } function Child(name,age){ Parent.call(this,name) this.age = age } Inherit(Child,Parent) Child.prototype.sayAge = function(){ console.log('Cage',this.age); } const exp1 = new Child('lin',18) exp1.colors.push('black') console.log('exp1',exp1);//exp1 Child {name: 'lin', colors: Array(4), age: 18} const exp2 = new Child('meng',20) console.log('exp2',exp2);//exp2 Child {name: 'meng', colors: Array(3), age: 20}开发人员普遍认为寄生组合式继承是引用类型最理想的继承范式。