随着Vue3的普及,已经有越来越多的项目开始使用Vue3。为了快速进入开发状态,在这里向大家推荐一套开箱即用的企业级开发脚手架,框架使用:Vue3+Vite2+TypeScript+JSX+Pinia(Vuex)+Antd。废话不多话,直接上手开撸。
该脚手架根据使用状态库的不同分为两个版本Vuex版、Pinia版,下面是相关代码地址:
Vuex版、
Pinia版
搭建需准备
- Vscode : 前端人必备写码神器
- Chrome :对开发者非常友好的浏览器(程序员标配浏览器)
- Nodejs & npm :配置本地开发环境,安装 Node 后你会发现 npm 也会一起安装下来 (V12+)
使用npm安装依赖包时会发现非常慢,在这里推荐使用cnpm、yarn代替。
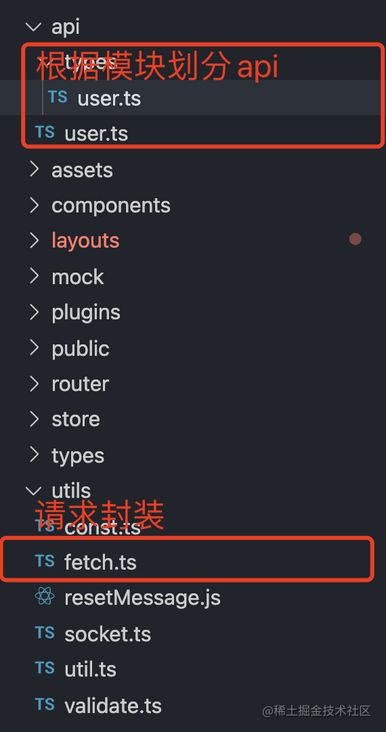
脚手架目录结构
├── src
│ ├── App.tsx
│ ├── api # 接口管理模块
│ ├── assets # 静态资源模块
│ ├── components # 公共组件模块
│ ├── mock # mock接口模拟模块
│ ├── layouts # 公共自定义布局
│ ├── main.ts # 入口文件
│ ├── public # 公共资源模块
│ ├── router # 路由
│ ├── store # vuex状态库
│ ├── types # 声明文件
│ ├── utils # 公共方法模块
│ └── views # 视图模块
├── tsconfig.json
└── vite.config.js什么是Vite
下一代前端开发与构建工具
Vite(法语意为 "快速的",发音/vit/,发音同 "veet")是一种新型前端构建工具,能够显著提升前端开发体验。它主要由两部分组成:
- 一个开发服务器,它基于 原生 ES 模块 提供了 丰富的内建功能,如速度快到惊人的 模块热更新(HMR)。
- 一套构建指令,它使用 Rollup 打包你的代码,并且它是预配置的,可输出用于生产环境的高度优化过的静态资源。
Vite 意在提供开箱即用的配置,同时它的 插件 API 和 JavaScript API 带来了高度的可扩展性,并有完整的类型支持。
你可以在 为什么选 Vite 中了解更多关于项目的设计初衷。
什么是Pinia
Pinia.js 是新一代的状态管理器,由 Vue.js团队中成员所开发的,因此也被认为是下一代的 Vuex,即 Vuex5.x,在 Vue3.0 的项目中使用也是备受推崇
Pinia.js 有如下特点:
- 相比Vuex更加完整的 typescript 的支持;
- 足够轻量,压缩后的体积只有1.6kb;
- 去除 mutations,只有 state,getters,actions(支持同步和异步);
- 使用相比Vuex更加方便,每个模块独立,更好的代码分割,没有模块嵌套,store之间可以自由使用
安装
npm install pinia --save创建Store
新建 src/store 目录并在其下面创建 index.ts,并导出store
import { createPinia } from 'pinia' const store = createPinia() export default store- 在main.ts中引入
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import store from './store'
const app = createApp(App)
app.use(store)定义State
在新建src/store/modules,根据模块划分在modules下新增common.ts
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const CommonStore = defineStore('common', {
// 状态库
state: () => ({
userInfo: null, //用户信息
}),
})获取State
获取state有多种方式,最常用一下几种:
import { CommonStore } from '@/store/modules/common'
// 在此省略defineComponent
setup(){
const commonStore = CommonStore()
return ()=>(
{commonStore.userInfo}
)
}使用computed获取
const userInfo = computed(() => common.userInfo)使用Pinia提供的storeToRefs
import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'
import { CommonStore } from '@/store/modules/common'
...
const commonStore = CommonStore()
const { userInfo } = storeToRefs(commonStore)修改State
修改state的三种方式:
- 直接修改(不推荐)
commonStore.userInfo = '曹操'- 通过$patch
commonStore.$patch({
userInfo:'曹操'
})- 通过actions修改store
export const CommonStore = defineStore('common', {
// 状态库
state: () => ({
userInfo: null, //用户信息
}),
actions: {
setUserInfo(data) {
this.userInfo = data
},
},
})import { CommonStore } from '@/store/modules/common'
const commonStore = CommonStore()
commonStore.setUserInfo('曹操')Getters
export const CommonStore = defineStore('common', {
// 状态库
state: () => ({
userInfo: null, //用户信息
}),
getters: {
getUserInfo: (state) => state.userInfo
}
})使用同State获取
Actions
Pinia赋予了Actions更大的职能,相较于Vuex,Pinia去除了Mutations,仅依靠Actions来更改Store状态,同步异步都可以放在Actions中。
同步action
export const CommonStore = defineStore('common', {
// 状态库
state: () => ({
userInfo: null, //用户信息
}),
actions: {
setUserInfo(data) {
this.userInfo = data
},
},
})异步actions
...
actions: {
async getUserInfo(params) {
const data = await api.getUser(params)
return data
},
}内部actions间相互调用
...
actions: {
async getUserInfo(params) {
const data = await api.getUser(params)
this.setUserInfo(data)
return data
},
setUserInfo(data){
this.userInfo = data
}
}modules间actions相互调用
import { UserStore } from './modules/user'
...
actions: {
async getUserInfo(params) {
const data = await api.getUser(params)
const userStore = UserStore()
userStore.setUserInfo(data)
return data
},
}pinia-plugin-persist 插件实现数据持久化
安装
npm i pinia-plugin-persist --save使用
// src/store/index.ts
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
import piniaPluginPersist from 'pinia-plugin-persist'
const store = createPinia().use(piniaPluginPersist)
export default store对应store中的使用
export const CommonStore = defineStore('common', {
// 状态库
state: () => ({
userInfo: null, //用户信息
}),
// 开启数据缓存
persist: {
enabled: true,
strategies: [
{
storage: localStorage, // 默认存储在sessionStorage里
paths: ['userInfo'], // 指定存储state,不写则存储所有
},
],
},
})Fetch
为了更好的支持TypeScript,统计Api请求,这里将axios进行二次封装
结构目录:
// src/utils/fetch.ts
import axios, { AxiosRequestConfig, AxiosResponse, AxiosInstance } from 'axios'
import { getToken } from './util'
import { Modal } from 'ant-design-vue'
import { Message, Notification } from '@/utils/resetMessage'
// .env环境变量
const BaseUrl = import.meta.env.VITE_API_BASE_URL as string
// create an axios instance
const service: AxiosInstance = axios.create({
baseURL: BaseUrl, // 正式环境
timeout: 60 * 1000,
headers: {},
})
/**
* 请求拦截
*/
service.interceptors.request.use(
(config: AxiosRequestConfig) => {
config.headers.common.Authorization = getToken() // 请求头带上token
config.headers.common.token = getToken()
return config
},
(error) => Promise.reject(error),
)
/**
* 响应拦截
*/
service.interceptors.response.use(
(response: AxiosResponse) => {
if (response.status == 201 || response.status == 200) {
const { code, status, msg } = response.data
if (code == 401) {
Modal.warning({
title: 'token出错',
content: 'token失效,请重新登录!',
onOk: () => {
sessionStorage.clear()
},
})
} else if (code == 200) {
if (status) {
// 接口请求成功
msg && Message.success(msg) // 后台如果返回了msg,则将msg提示出来
return Promise.resolve(response) // 返回成功数据
}
// 接口异常
msg && Message.warning(msg) // 后台如果返回了msg,则将msg提示出来
return Promise.reject(response) // 返回异常数据
} else {
// 接口异常
msg && Message.error(msg)
return Promise.reject(response)
}
}
return response
},
(error) => {
if (error.response.status) {
switch (error.response.status) {
case 500:
Notification.error({
message: '温馨提示',
description: '服务异常,请重启服务器!',
})
break
case 401:
Notification.error({
message: '温馨提示',
description: '服务异常,请重启服务器!',
})
break
case 403:
Notification.error({
message: '温馨提示',
description: '服务异常,请重启服务器!',
})
break
// 404请求不存在
case 404:
Notification.error({
message: '温馨提示',
description: '服务异常,请重启服务器!',
})
break
default:
Notification.error({
message: '温馨提示',
description: '服务异常,请重启服务器!',
})
}
}
return Promise.reject(error.response)
},
)
interface Http {
fetch(params: AxiosRequestConfig): Promise>
}
const http: Http = {
// 用法与axios一致(包含axios内置所有请求方式)
fetch(params) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
service(params)
.then((res) => {
resolve(res.data)
})
.catch((err) => {
reject(err.data)
})
})
},
}
export default http['fetch']
使用
// src/api/user.ts
import qs from 'qs'
import fetch from '@/utils/fetch'
import { IUserApi } from './types/user'
const UserApi: IUserApi = {
// 登录
login: (params) => {
return fetch({
method: 'post',
url: '/login',
data: params,
})
}
}
export default UserApi
类型定义
/**
* 接口返回结果Types
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
// 登录返回结果
export interface ILoginData {
token: string
userInfo: {
address: string
username: string
}
}
/**
* 接口参数Types
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
// 登录参数
export interface ILoginApiParams {
username: string // 用户名
password: string // 密码
captcha: string // 验证码
uuid: string // 验证码uuid
}
/**
* 接口定义Types
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
export interface IUserApi {
login: (params: ILoginApiParams) => Promise>
}
Router4
基础路由
// src/router/router.config.ts const Routes: Array= [ { path: '/403', name: '403', component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "403" */ '@/views/exception/403'), meta: { title: '403', permission: ['exception'], hidden: true }, }, { path: '/404', name: '404', component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "404" */ '@/views/exception/404'), meta: { title: '404', permission: ['exception'], hidden: true }, }, { path: '/500', name: '500', component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "500" */ '@/views/exception/500'), meta: { title: '500', permission: ['exception'], hidden: true }, }, { path: '/:pathMatch(.*)', name: 'error', component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "404" */ '@/views/exception/404'), meta: { title: '404', hidden: true }, }, ] title: 导航显示文字;hidden: 导航上是否隐藏该路由 (true: 不显示 false:显示)
- 动态路由(权限路由)
// src/router/router.ts
router.beforeEach(
async (
to: RouteLocationNormalized,
from: RouteLocationNormalized,
next: NavigationGuardNext,
) => {
const token: string = getToken() as string
if (token) {
// 第一次加载路由列表并且该项目需要动态路由
if (!isAddDynamicMenuRoutes) {
try {
//获取动态路由表
const res: any = await UserApi.getPermissionsList({})
if (res.code == 200) {
isAddDynamicMenuRoutes = true
const menu = res.data
// 通过路由表生成标准格式路由
const menuRoutes: any = fnAddDynamicMenuRoutes(
menu.menuList || [],
[],
)
mainRoutes.children = []
mainRoutes.children?.unshift(...menuRoutes, ...Routes)
// 动态添加路由
router.addRoute(mainRoutes)
// 注:这步很关键,不然导航获取不到路由
router.options.routes.unshift(mainRoutes)
// 本地存储按钮权限集合
sessionStorage.setItem(
'permissions',
JSON.stringify(menu.permissions || '[]'),
)
if (to.path == '/' || to.path == '/login') {
const firstName = menuRoutes.length && menuRoutes[0].name
next({ name: firstName, replace: true })
} else {
next({ path: to.fullPath })
}
} else {
sessionStorage.setItem('menuList', '[]')
sessionStorage.setItem('permissions', '[]')
next()
}
} catch (error) {
console.log(
`%c${error} 请求菜单列表和权限失败,跳转至登录页!!`,
'color:orange',
)
}
} else {
if (to.path == '/' || to.path == '/login') {
next(from)
} else {
next()
}
}
} else {
isAddDynamicMenuRoutes = false
if (to.name != 'login') {
next({ name: 'login' })
}
next()
}
},
)Layouts布局组件
脚手架提供多种排版布局,目录结构如下:
- BlankLayout.tsx: 空白布局,只做路由分发
- RouteLayout.tsx: 主体布局,内容显示部分,包含面包屑
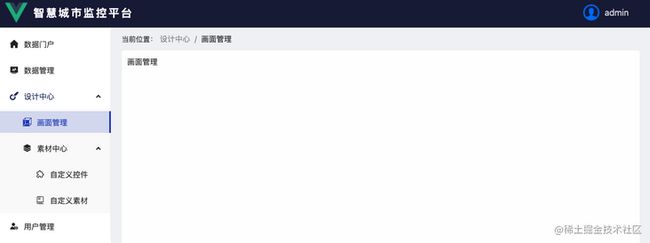
- LevelBasicLayout.tsx 多级展示布局,适用于2级以上路由
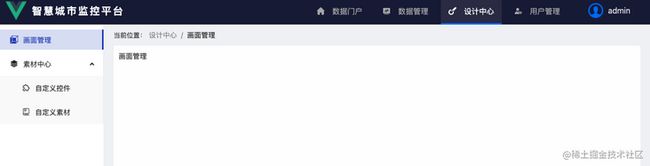
- SimplifyBasicLayout.tsx 简化版多级展示布局,适用于2级以上路由
相关参考链接
最后
文章暂时就写到这,后续会增加JSX语法部分,如果本文对您有什么帮助,别忘了动动手指点个赞❤️。
本文如果有错误和不足之处,欢迎大家在评论区指出,多多提出您宝贵的意见!