vue处理get/post的http请求
一、使用Vue.http/this.$http
在发起请求的时候,为了减少作用域链的搜索,建议使用一个局部变量来接受this
1. GET请求
// 基于全局Vue对象使用http
Vue.http.get('/someUrl', [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);
// 在一个Vue实例内使用$http
this.$http.get('/someUrl', [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);
示例
//不带参数的get请求
this.$http.get('/someUrl').then(function(res){
console.log('请求成功处理');
},function(res){
console.log('请求失败处理');
});
//需要传递数据的get请求
this.$http.get('/someUrl',{param:jsonData}).then(function(res){
console.log('请求成功处理');
},function(res){
console.log('请求失败处理');
});
//ES6的Lambda写法
this.$http.get('/someUrl', [options]).then((response) => {
console.log('请求成功处理');
}, (response) => {
console.log('请求失败处理');
});
2.POST请求
post 发送数据到后端,需要第三个参数 {emulateJSON:true}。
emulateJSON 的作用: 如果Web服务器无法处理编码为 application/json 的请求,你可以启用 emulateJSON 选项。启用该选项后,请求会以application/x-www-form-urlencoded作为MIME type,就像普通的HTML表单一样。
// 基于全局Vue对象使用http
Vue.http.post('/someUrl', [body], [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);
// 在一个Vue实例内使用$http
this.$http.post('/someUrl', [body], [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);
示例
this.$http.post('/try/ajax/demo_test_post.php',{name:"菜鸟教程",url:"http://www.runoob.com"},{emulateJSON:true}).then(function(res){
document.write(res.body);
},function(res){
console.log(res.status);
});
二、使用Vue.resource/this.$resource
vue-resource提供了另外一种方式访问HTTP——resource服务,resource服务包含以下几种默认的action:
get: {method: 'GET'},
save: {method: 'POST'},
query: {method: 'GET'},
update: {method: 'PUT'},
remove: {method: 'DELETE'},
delete: {method: 'DELETE'}
访问resource对象的两种方式:
//全局访问
Vue.resource
//实例访问
this.$resource
GET请求
//使用一个局部变量来接受this
var vm = this;
this.$resource('apiUrl').get().then((response) => {
console.log("调用成功");
})
.catch(function(response) {
console.log("调用失败");
})
}
POST请求
使用save方法发送POST请求
//使用一个局部变量来接受this
var vm = this;
this.$resource('apiUrl').save('apiUrl',Target).then((response) => {
console.log("调用成功");
})
.catch(function(response) {
console.log("调用失败");
})
}
inteceptor – 在请求前和请求后附加行为
用法
//Lambda函数写法
Vue.http.interceptors.push((request, next) => {
// ...
// 请求发送前的处理逻辑
// ...
next((response) => {
// ...
// 请求发送后的处理逻辑
// ...
// 根据请求的状态,response参数会返回给successCallback或errorCallback
return response
})
})
//普通写法
Vue.http.interceptors.push(function(request, next) {
// ...
// 请求发送前的处理逻辑
// ...
next(function(response) {
// ...
// 请求发送后的处理逻辑
// ...
// 根据请求的状态,response参数会返回给successCallback或errorCallback
return response
})
})
实例 – 为所有的请求处理加一个loading
请求发送前显示loading,接收响应后隐藏loading或显示指定的loading信息;
- 添加
loading.vue组件
<template id="loading-template">
<div class="loading-overlay">
<div class="sk-three-bounce">
<div class="sk-child sk-bounce1"></div>
<div class="sk-child sk-bounce2"></div>
<div class="sk-child sk-bounce3"></div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
- 在父组件中引入loading组件
<template>
<div class="father">
//loading 发起请求时显示
<loading v-show="showLoading"</loading>
//modal-dialog 请求失败时显示
<modal-dialog :show="showDialog">
<header class="dialog-header" slot="header">
<h1 class="dialog-title">Server Error</h1>
</header>
<div class="dialog-body" slot="body">
<p class="error">Oops,server has got some errors, error code: {{errorCode}}.</p>
</div>
</modal-dialog>
</div>
</template>
- 在父组件中添加inteceptor
data: {
showLoading: false,
showDialog: false,
errorCode: ''
},
//在生命周期中添加inteceptor
Vue.http.interceptors.push((request, next) => {
help.showLoading = true
next((response) => {
if(!response.ok){
help.errorCode = response.status
help.showDialog = true
}
help.showLoading = false
return response
});
});
拓展
vue-resource 提供了 7 种请求 API(REST 风格):
get(url, [options])
head(url, [options])
delete(url, [options])
jsonp(url, [options])
post(url, [body], [options])
put(url, [body], [options])
patch(url, [body], [options])
除了 jsonp 以外,另外 6 种的 API 名称是标准的 HTTP 方法。其中,options参数说明如下:
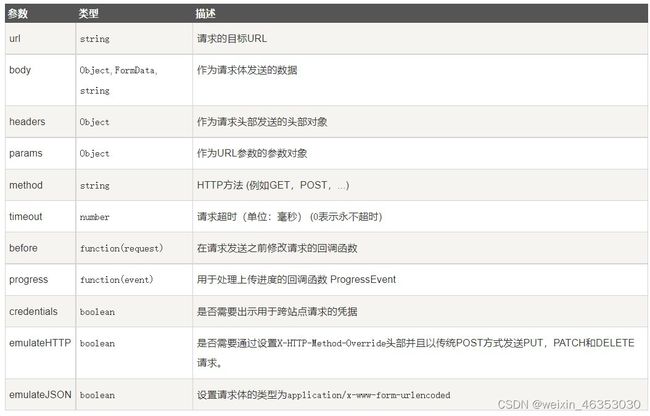
可以通过如下属性和方法处理一个请求获取到的响应对象:
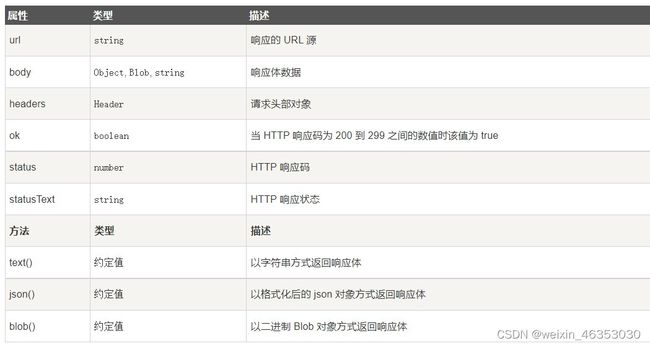
参考文章
- 菜鸟教程
- 完整代码示例及其他请求方法的使用
代码是参考上面两篇文章写出来的,没有实际运行过;且只记录了GET/POST两种请求方式,其它请求方式以及完整代码需要参考第二篇文章
