第一题 多数元素
题目
简单的思路
简单的想法是使用哈希表或者排序完成
遍历一次数组,将每个数出现的次数存入哈希表,当次数大于n/2时返回即可
然而该方案空间复杂度为O(n),不符合要求O(1)
将数组排成有序数组,计算每个元素出现的次数,当次数大于n/2时返回即可
然而排序的时间复杂度为O(nlogn),大于题目要求O(n)
随机法
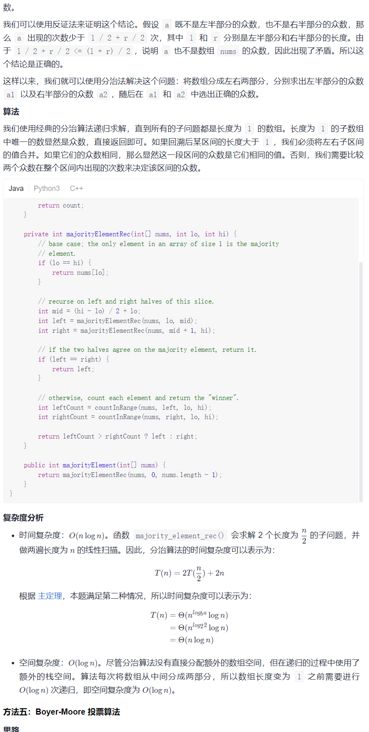
分治法
代码.3
func majorityElement(nums []int) int {
return majorityElementRec(nums, 0, len(nums) - 1)
}
//判断众数
func countInRange(nums []int, target int,lo int, hi int) int{
count := 0
for i := lo; i <= hi; i++ {
if nums[i] == target {
count++
}
}
return count
}
//二分查找
func majorityElementRec( nums []int, lo int, hi int) int{
//左边界等于右边界,只有一个元素,即为该数组众数
if lo == hi {
return nums[lo]
}
mid := (lo + hi) / 2
//左右众数
leftMajority := majorityElementRec(nums, lo, mid)
rightMajority := majorityElementRec(nums, mid + 1, hi)
//返回真正的众数
if countInRange(nums, leftMajority, lo, hi) > (hi - lo + 1) / 2 {
return leftMajority
}
if countInRange(nums, rightMajority, lo, hi) > (hi - lo + 1) / 2 {
return rightMajority
}
return -1
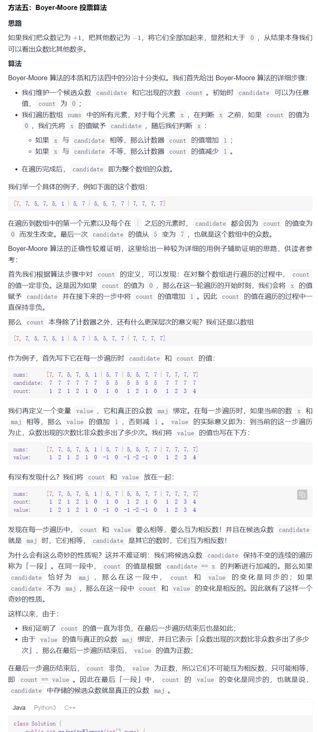
}摩尔投票法
代码
func majorityElement(nums []int) int {
//初始化
candidate := -1
count := 0
for _, num :=range nums {
//如果相等,计数器加一
if num == candidate {
count++
}else {
//否则计数器减一,消去一个非众数
count--
}
//初始化候选众数
if count < 0 {
candidate = num
count = 1
}
}
return candidate
}
效果
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n)。Boyer-Moore 算法只对数组进行了一次遍历。
空间复杂度:O(1)。Boyer-Moore 算法只需要常数级别的额外空间。