5、Hive数据仓库——Hive分区及动态分区
文章目录
- Hive分区
-
- 建立分区表
- 增加分区
- 删除分区
- 查看某个表的所有分区
- 往分区中插入数据
- 查询某个分区的数据
- Hive动态分区
-
- 开启Hive的动态分区支持
- 建立原始表并加载数据
- 建立分区表并加载数据
- 使用动态分区插入数据
- 多级分区
Hive分区
分区的概念和分区表:
分区表指的是在创建表时指定分区空间,实际上就是在hdfs上表的目录下再创建子目录。
在使用数据时如果指定了需要访问的分区名称,则只会读取相应的分区,避免全表扫描,提高查询效率。
作用:进行分区裁剪,避免全表扫描,减少MapReduce处理的数据量,提高效率。
一般在公司的hive中,所有的表基本上都是分区表,通常按日期分区、地域分区。
分区表在使用的时候记得加上分区字段。
分区也不是越多越好,一般不超过3级,根据实际业务衡量。
建立分区表
建立外部表的时候external一般和LOCATION一同使用
create external table students_pt1
(
id bigint
,name string
,age int
,gender string
,clazz string
)
PARTITIONED BY(pt string)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ','
LOCATION '/student/input1';
这个时候多了一个字段:# Partition Information
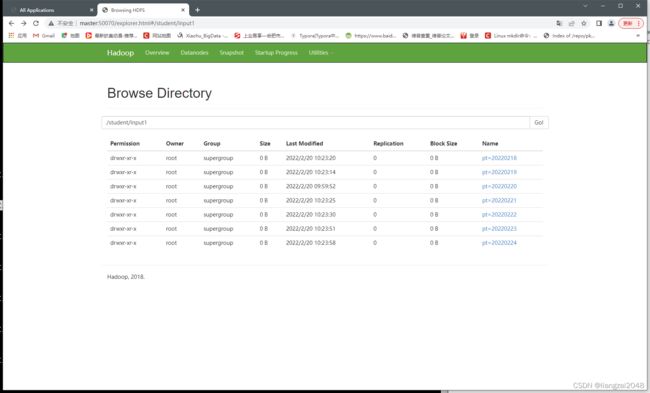
增加分区
alter table students_pt1 add partition(pt='20220220');
alter table students_pt1 add partition(pt='20220219');
alter table students_pt1 add partition(pt='20220218');
alter table students_pt1 add partition(pt='20220221');
alter table students_pt1 add partition(pt='20220222');
alter table students_pt1 add partition(pt='20220223');
alter table students_pt1 add partition(pt='20220224');
删除分区
alter table students_pt1 drop partition(pt='20200218');
alter table students_pt1 drop if exists partition(pt='20220218');
查看某个表的所有分区
推荐这种方式(直接从元数据中获取分区信息)
show partitions students_pt1;
不推荐(这种方式会执行MapReduce)
select distinct pt from students_pt1;
往分区中插入数据
insert into table students_pt1 partition(pt='20220220') select * from student1;
load data local inpath '/usr/local/soft/data/students.txt' into table students_pt1 partition(pt='20200221');
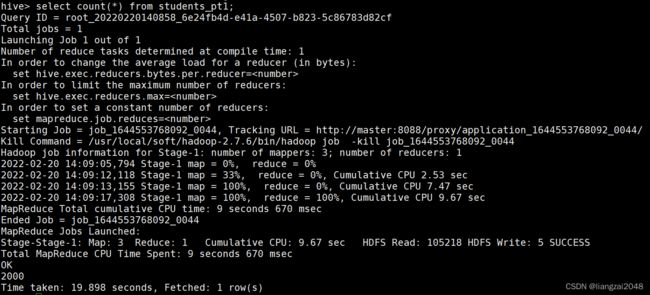
查询某个分区的数据
全盘扫描,不推荐,效率低。
select count(*) from students_pt1;
使用where条件进行分区裁剪,避免了全表扫描,效率高。
select count(*) from students_pt1 where pt='20220220';
也可以在where条件中使用非等值判断。
select count(*) from students_pt1 where pt<='20220224' and pt>='20220219';
Hive动态分区
有的时候我们原始表中的数据里面包含了“日期字段dt”,我们需要根据dt中不同的时期,分为不同的分区,将原始表改造成分区表。
hive默认不开启动态分区。
动态分区:根据数据中某几列的不同的取值 划分 不同的分区。
开启Hive的动态分区支持
# 表示开启动态分区
set hive.exec.dynamic.partition=true;
# 表示动态分区模式:strict(需要配合静态分区一起使用)、nostrict
# strict: insert into table students_pt partition(dt='anhui',pt) select ......,pt from students;
set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nostrict;
# 表示支持的最大的分区数量为1000,可以根据业务自己调整
set hive.exec.max.dynamic.partitions.pernode=1000;
建立原始表并加载数据
create table students_dt
(
id bigint,
name string,
age int,
gender string,
clazz string,
dt string
)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',';
load data local inpath '/usr/local/soft/data/students_dt.txt' into table students_dt;
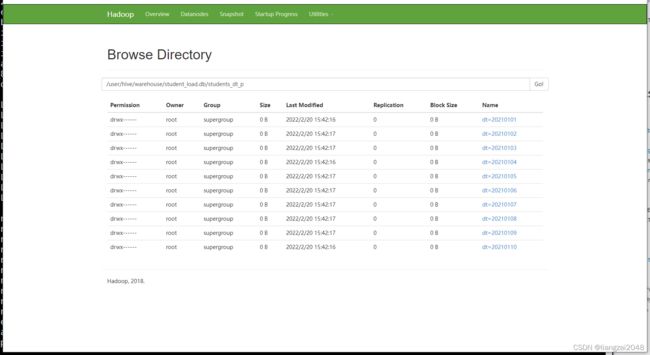
建立分区表并加载数据
create table students_dt_p
(
id bigint,
name string,
age int,
gender string,
clazz string
)
PARTITIONED BY(dt string)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',';
使用动态分区插入数据
分区字段需要放在 select 的最后,如果有多个分区字段 同理,它是按位置匹配,不是按名字匹配
insert into students_dt_p partition(dt) select id,name,age,gender,clazz,dt from students_dt;
比如下面这条语句会使用age作为分区字段,而不会使用student_dt中的dt作为分区字段
insert into table students_dt_p partition(dt) select id,name,age,gender,dt,age from students_dt;
多级分区
create table students_year_month
(
id bigint,
name string,
age int,
gender string,
clazz string,
year string,
month string
)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',';
create table students_year_month_pt
(
id bigint,
name string,
age int,
gender string,
clazz string
)
PARTITIONED BY(year string,month string)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',';
insert into table students_year_month_pt partition(year,month) select id,name,age,gender,clazz,year,month from students_year_month;
到底啦!关注靓仔学习更多的大数据知识 (❁´◡`❁)