Spring源码系列——手撸一个@EnableXXX
一. 前言
耍了一个国庆节,感觉好累~~ 必须写一篇文章休息一下!
通过前面几篇源码系列的学习之后,有必要进行一个阶段性总结了。基于前面的学习,我们已经非常清楚了Spring是如何基于BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanDefinitionRegistoryPostProcessor来插手BeanFactory的扩展的原理;@Configuration/@Import/@ComponentScan/@Bean等注解的解析原理。在这个过程中,还初步窥探了Spring是如何基于动态代理技术来实现AOP。
应用过Spring技术的都应该晓得在Spring当中,有很多功能都是通过@EnableXXX来实现某种特殊的能力,比如@EnableCache等。而这一些吊炸天的技术其实就是基于Spring的基础能力实现的。本片文章将基于目前对这些知识的掌握,自己手撸一个简单的@EnableLeon来巩固源码的学习成果以及应用。
二. 实现
设计目标
通过在配置类上开启@EnableLeon注解,让指定类的所有方法在执行之前都先打印Hello Leon!。
注解实现
package com.leon.funddatahouse.spring;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
/**
* @author created by leon on 2020-10-06
* @since v1.0
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Import(MyImportSeletor.class)
public @interface EnableLeon {
}
@Import的应用
通过上面的注解类可以发现一行关键代码:@Import(MyImportSeletor.class)
MyImportSeletor类的代码如下:
package com.leon.funddatahouse.spring;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportSelector;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author created by leon on 2020-10-06
* @since v1.0
*/
public class MyImportSeletor implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
// 获取当前所有的注解名称
Set<String> annotationTypes = importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationTypes();
// 判断是否包含@EnableLeon注解
boolean contains = annotationTypes.contains("com.leon.funddatahouse.spring.EnableLeon");
// 如果包含,则返回指定的类的全限定名数组,这里我只指定MyDao.
if (contains) {
return new String[]{MyDao.class.getName()};
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
后置处理器的应用
后置处理器可以插足Bean的实例化过程,因此自定义一个后置处理器来对我们指定的bean进行增强(就是上面指定的MyDao类)。增强的方法当然是基于动态代理啦。
package com.leon.funddatahouse.spring;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/**
* @author created by leon on 2020-10-06
* @since 版本号
*/
@Component
public class HelloLeonBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 判断当前bean是不是MyDao类,如果是,则基于JDK动态代理来进行增强(当然也可以基于CGLIB动态代理)
if (bean.getClass().getName().equals(MyDao.class.getName())) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(bean.getClass().getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Dao.class}, new HelloLeonInvokeHandler(bean));
}
return bean;
}
}
JDK动态代理的HelloLeonInvokeHandler的代码如下:
package com.leon.funddatahouse.spring;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author created by leon on 2020-10-06
* @since 版本号
*/
public class HelloLeonInvokeHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private Object obj;
public HelloLeonInvokeHandler(Object obj) {
this.obj = obj;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 在目标方法执行之前打印 hello leon
System.out.println("Hello Leon!");
return method.invoke(obj, args);
}
}
MyDao的代码
由于我们是基于JDK动态代理的,因此必须实现接口。 具体代码如下:
package com.leon.funddatahouse.spring;
/**
* @author created by leon on 2020-10-06
* @since 版本号
*/
public interface Dao {
void test();
}
package com.leon.funddatahouse.spring;
/**
* @author created by leon on 2020-10-06
* @since 版本号
*/
public class MyDao implements Dao {
@Override
public void test() {
System.out.println("test method exe.");
}
}
配置类
在配置类上开启@EnableLeon注解。
package com.leon.funddatahouse.spring;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author created by leon on 2020-10-06
* @since 版本号
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.leon.funddatahouse.spring")
@EnableLeon
public class Config {
}
启动类
package com.leon.funddatahouse.spring;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
/**
* @author created by leon on 2020-10-06
* @since 版本号
*/
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 基于配置类启动Spring容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class);
// 获取bean。由于开启了@EnableLeon注解,这里拿到的一定是一个代理类
Dao indexDao = context.getBean(Dao.class);
indexDao.test();
}
}
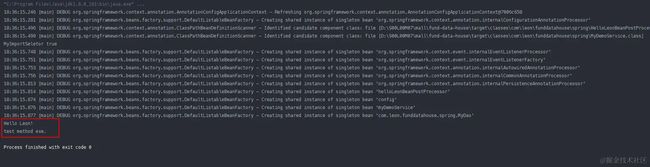
执行结果
可以看到,@EnableLeon注解起作用了。
三. 技术总结
这个例子虽然简单,但却应用了后置处理器、@Configuration和@Import的配置型注解的应用以及动态代理的应用。这些应用点的背后都是强大且复杂的源码体系。能够做到看到这些点就能够知道背后的原理才是我们学习的目标。
本文虽然是一个例子,但如果对这个例子能够理解透,那么后续学习AOP、Mybatis-Spring等其他组件时将会发现:这个例子和它们的实现思路是很相似的。再实际工程中,我们甚至可以实现自己的组件并集成到Spring框架中。