数据结构和算法
一、时间复杂度和空间复杂度
1.时间复杂度
常数阶O(1)
对数阶O(logN)
线性阶O(n)
线性对数阶O(nlogN)
平方阶O(n²)
立方阶O(n³)
K次方阶O(n^k)
指数阶(2^n)
上面从上至下依次的时间复杂度越来越大,执行的效率越来越低。
2.空间复杂度
二、数据结构
1. 线性表
a.数组
b.单链表
c.双向链表
d.循环链表
e.双向循环链表
f.静态链表
2.栈
a.顺序栈
数组实现静态栈
public class ArrayStack {
//栈的大小
private int maxStack;
//底层用数组实现,本次使用int数组;
private int[] stack;
//栈顶位置,默认为-1,表示此时栈中没有数据
private int top = -1;
public ArrayStack(int maxStack){
this.maxStack=maxStack;
}
//判断是否是满栈
public boolean isFull(){
return this.maxStack-1==this.top;
}
//判断是否是空栈
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.top==-1;
}
//压栈
public void push(int num){
//表示栈已经满了,无法继续压栈
if (isFull()){
throw new RuntimeException("此栈已满,无法压栈");
}
top++;
stack[top]=num;
}
//弹栈
public int pop(){
//表示此时栈为空,无法弹栈
if (isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("此栈已空,无法弹栈");
}
int val = stack[top];
top--;
return val;
}
//查看栈中所有元素
public void list(){
if (isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("此栈已空,无法弹栈");
}
for (int i = 0; i < stack.length; i++) {
System.out.println("stack[" + i + "]=" + stack[i]);
}
}
}
b.链式栈
3.队列
a.普通队列
public class ArrayQueue {
private int[] array;
private int maxSize;
private int frontPoint;
private int rearPoint;
public ArrayQueue(int maxSize){
this.maxSize=maxSize;
array=new int[maxSize];
frontPoint=-1;
rearPoint=-1;
}
//判断当前队列是否已满
public boolean isFull(){
return rearPoint==maxSize-1;
}
//判断是否是空队列
public boolean isEmpty(){
return rearPoint==frontPoint;
}
//添加元素
public void add(int n){
if (isFull()){
System.out.println("队列已满");
return;
}
rearPoint++;
array[rearPoint]=n;
}
//出队列
public int get(){
if (isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("空队列");
}
frontPoint++;
return array[frontPoint];
}
}
b.双端队列
c.阻塞队列
d.并发队列
e.阻塞并发队列
3.散列表
a.散列函数
b.冲突解决
链法表
开放地址
c.动态扩容
d.位图
4.树
a.二叉树
平衡二叉树
二叉查找树
平衡二叉查找树
完全二叉树
满二叉树
b.多路查找树
b树
b+树
2-3树
2-3-4树
c.堆
小顶堆
大顶堆
优先级队列
斐波那契堆
二项堆
d.树状数组
e.线段树
5.图
a.图的存储
邻接矩阵
邻接表
b.拓扑排序
c.最短路径
d.关键路径
e.最小生成树
f.二分图
g.最大流
三、算法
1.基本算法思想
a.贪心算法
b.分治算法
汉诺塔
public static void move(int n,char x,char y,char z){
if (n==1){
System.out.println(x+"---->" + z);
}else {
move(n-1,x,z,y); //将n-1个盘子从x借助z移动到y
System.out.println(x+"---->" + z); //将n-1个盘子从x借助z移动到y
move(n-1,y,x,z); //将第n-1个盘子从x借助z移动到y
}
}
c.动态规划
d.回溯算法
e.枚举算法
2.排序算法
a.冒泡排序
冒泡排序只会操作相邻的两个数据。每次冒泡操作都会对相邻的两个元素进行比较,看是否满足大小关系要求,如果不满足就让它俩互换。
时间复杂度:O(n² )

public int[] bubbleSort(int[] a) {
int n = a.length;
if (n<=1) {
return a;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n-i-1; j++) {
if (a[j]>a[j+1]) {//
int temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j+1];
a[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
return a;
}
b.插入排序
插入排序将数组数据分成已排序区间和未排序区间。初始已排序区间只有一个元素,即数组第一个元素。在未排序区间取出一个元素插入到已排序区间的合适位置,直到未排序区间为空。
时间复杂度:O(n² )

public int[] insertionSort(int[] a) {
int n = a.length;
if (n<=1) return a;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int value = a[i];
int j = i-1;
for (; j >=0; j--) {
if (a[j] > value) {
a[j+1] = a[j];//移动数据
}else {
break;
}
}
a[j+1] = value;//插入数据
}
return a;
}
c.选择排序
选择排序将数组分成已排序区间和未排序区间。初始已排序区间为空。每次从未排序区间中选出最小的元素插入已排序区间的末尾,直到未排序区间为空。
时间复杂度:O(n² )
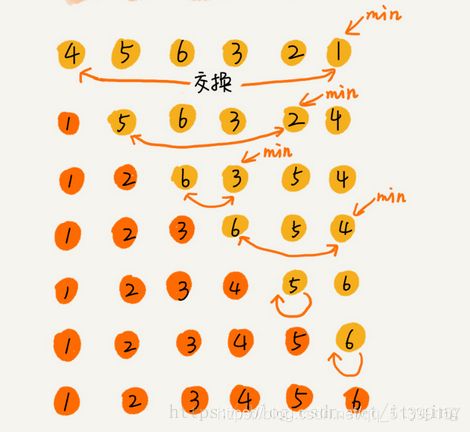
public int[] selectionSort(int[] a) {
int n = a.length;
for (int i = 0; i a[j]) {
k = j;
count=a[j];
}
}
//交换
if(i != k){
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[k];
a[k] = temp;
}
}
return a;
}
d.希尔排序
时间复杂度:O(n² )
public int[] sort(int[] nums){
for (int gap = nums.length/2;gap>0;gap/=2){
for (int i = gap; i =0;j-=gap){
if (nums[j]>nums[j+gap]){
int temp = nums[j];
nums[j] = nums[j+gap];
nums[j+gap]=temp;
}
}
}
}
return nums;
}
e.归并排序
时间复杂度:O(nlogn )
public int[] sort(int[] nums){
int[] temp = new int[nums.length];
group(nums,0,nums.length-1,temp);
return nums;
}
public int[] group(int[] nums,int left,int right,int[] temp){
if (leftf.快速排序
时间复杂度:O(n² )
public void sort(int[] array, int left, int right) {
if (left > right) {
return;
}
// base中存放基准数
int base = array[left];
int l = left, r = right;
while (l != r) {
// 顺序很重要,先从右边开始往左找,直到找到比base值小的数
while (array[r] >= base && l < r) {
r--;
}
// 再从左往右边找,直到找到比base值大的数
while (array[l] <= base && l < r) {
l++;
}
// 上面的循环结束表示找到了位置或者(i>=j)了,交换两个数在数组中的位置
if (l < r) {
int tmp = array[l];
array[l] = array[r];
array[r] = tmp;
}
}
// 将基准数放到中间的位置(基准数归位)
array[left] = array[l];
array[l] = base;
// 递归,继续向基准的左右两边执行和上面同样的操作
// i的索引处为上面已确定好的基准值的位置,无需再处理
sort(array, left, l - 1);
sort(array, l + 1, right);
}
g.堆排序
时间复杂度:O(nlogn )
h.计数排序
时间复杂度:O(n+k )
i.基数排序
思想:找出所有数据中最长的,将所有数据保持与之一样长度,不够的前面补0,借助10个桶从个位开始排序,到十位,百位。
为什么不从高位开始排序?举例12和21。
时间复杂度:O(N*M)N:数组长度,M:最大的数字的位数
public int[] sort(int[] arrays){
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) {
max=Math.max(max,arrays[i]);
}
int maxLength = (max+"").length();
int[][] bucket = new int[10][arrays.length];
int[] bucketElementCount = new int[10];
int k = 1;
while (k<=maxLength){
for (int i = 0; i j.桶排序
3.搜索
a.深度优化搜索
b.广度优先搜索
c.启发式搜索
4.查找
a.线性表查找
b.树结构查找
c.散列表查找
5.字符串匹配
a.朴素
暴力算法:是将目标串S的第一个字符与模式串T的第一个字符进行匹配,若相等,则继续比较S的第二个字符和 T的第二个字符;若不相等,则比较S的第二个字符和T的第一个字符,依次比较下去,直到得出最后的匹配结果。BF算法是一种蛮力算法。
b.KMP
public class Test {
/**
* 求出一个字符数组的next数组
* @param t 字符数组
* @return next数组
*/
public static int[] getNext(String s) {
int[] next = new int[s.length()];
next[0] = -1;
int j = 0;
int k = -1;
while (j < s.length() - 1) {
if (k == -1 || s.charAt(j) == s.charAt(k)) {
next[++j] = ++k;
} else {
k = next[k];
}
}
return next;
}
/**
* 对主串s和模式串t进行KMP模式匹配
* @param s 主串
* @param t 模式串
* @return 若匹配成功,返回t在s中的位置(第一个相同字符对应的位置),若匹配失败,返回-1
*/
public static int kmpMatch(String s, String t){
int[] next = getNextArray(t);
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i