YOLOV5实战训练自己的数据集,包含数据集转换,训练~
YOLOV5实战检测
1.下载YOLOV5
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git
2.安装环境
cd yolov5
pip install -r requirements.txt
(本机环境全部为最新,测试支持:3080 CUDA11.2 )
3.创建VOC数据集
@1.创建自己项目文件夹:我的项目文件夹命名为paper_data
@2.将标注好或者转换好的xml文件放入文件/paper_data/Annotations中。将图片放入/paper_data/images。同时在/paper_data中创建文件夹ImageSets,labels。
本项目使用的xml是通过csv转换而成,csv格式,生成xml格式,转换代码如下:
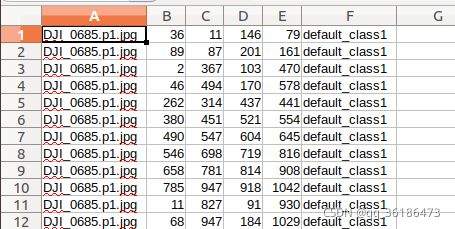
A列为图片名称,BCDE列为目标物坐标,F列为类别(本项目只有一类)

@3.生成的XML格式,一定要是这样的!!!
import glob
from PIL import Image
import csv
#xml保存的位置
save_xml_dir = "/home/kemove/shumiao/save_path/Annotations/" #修改为你自己的路径
src_img_dir = "/home/kemove/shumiao" #修改为你自己的路径
#img_Lists = glob.glob(src_img_dir + '/*.jpg')
# read csv
file_path = "/home/kemove/shumiao/5.26SM.csv"
width = 1920
height = 1080 #图片大小也修为自己数据集
with open(file_path) as csvfile:
#读取csv数据
csv_reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
#去掉第一行(第一行是列名)
csv_header = next(csv_reader)
#因为csv数据中有许多行其实是同一个照片,因此需要pre_img
pre_img = ''
for row in csv_reader:
#C:/Users/Timothy/Desktop/keras-retinanet/images/test/Subset_1_450x450_001.jpg
#只要文件名Subset_1_450x450_001
img = row[0].split("/")[-1].split(".")[0]
#遇到的是一张新图片
if img != pre_img:
#非第一张图片,在上一个xml中写下
if pre_img != '':
xml_file1 = open((save_xml_dir + pre_img + '.xml'), 'a')
xml_file1.write('')
xml_file1.close()
#新建xml文件
xml_file = open((save_xml_dir + img + '.xml'), 'w')
xml_file.write('\n' )
xml_file.write(' VOC2007 \n')
xml_file.write(' ' + str(img) + '.jpg' + '\n')
xml_file.write(' ' +'/home/kemove/shumiao/'+str(img) + '.jpg'+'\n')#+
xml_file.write('\n' )
xml_file.write('Unknown \n')
xml_file.write('\n')
xml_file.write(' \n' )
xml_file.write(' ' + str(width) + '\n')
xml_file.write(' ' + str(height) + '\n')
xml_file.write(' 3 \n')
xml_file.write(' \n')
xml_file.write(' 0 \n') #+
xml_file.write(' )
xml_file.write('' +str(row[-1])+'\n')
xml_file.write('' +'Unspecified'+'\n')#+
xml_file.write('' +'0'+'\n')#+
xml_file.write('' +'0'+'\n')#+
xml_file.write(' \n' )
xml_file.write(' ' + str(row[1]) + '\n')
xml_file.write(' ' + str(row[2]) + '\n')
xml_file.write(' ' + str(row[3]) + '\n')
xml_file.write(' ' + str(row[4]) + '\n')
xml_file.write(' \n')
xml_file.write(' \n')
xml_file.close()
pre_img = img
else:
#同一张图片,只需要追加写入object
xml_file = open((save_xml_dir + pre_img + '.xml'), 'a')
xml_file.write(' )
xml_file.write('' +str(row[-1])+'\n')
xml_file.write(' Unspecified \n')
xml_file.write(' 0 \n')
xml_file.write(' 0 \n')
xml_file.write(' \n' )
xml_file.write(' ' + str(row[1]) + '\n')
xml_file.write(' ' + str(row[2]) + '\n')
xml_file.write(' ' + str(row[3]) + '\n')
xml_file.write(' ' + str(row[4]) + '\n')
xml_file.write(' \n')
xml_file.write(' \n')
xml_file.close()
pre_img = img
#最后一个xml需要写入
xml_file1 = open((save_xml_dir + pre_img + '.xml'), 'a')
xml_file1.write('')
xml_file1.close()
4.在YOLOV5/paper_data中创建立split_train_val.py 以生成train.txt,val.txt,tranval.txt等绝对路径的图片名称地址。代码如下:
import os
import random
trainval_percent = 1.0
train_percent = 0.9
xmlfilepath = 'Annotations'
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(num * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
# ImageSets目录不存在,就创建
if not os.path.exists('ImageSets/'):
os.makedirs('ImageSets/')
# ImageSets/Main目录不存在,就创建
if not os.path.exists('ImageSets/Main/'):
os.makedirs('ImageSets/Main/')
ftrainval = open('ImageSets/Main/trainval.txt', 'w')
ftest = open('ImageSets/Main/test.txt', 'w')
ftrain = open('ImageSets/Main/train.txt', 'w')
fval = open('ImageSets/Main/val.txt', 'w')
for i in list:
name = '/home/kemove/yolov5/paper_data/images/' + total_xml[i][:-4] + '.jpg' + '\n'
if i in trainval:
ftrainval.write(name)
if i in train:
ftrain.write(name)
else:
fval.write(name)
else:
ftest.write(name)
ftrainval.close()
ftrain.close()
fval.close()
ftest.close()
运行python split_train_val.py后,会在yolov5/paper_data中生成/ImageSets/Main两个文件夹,Main文件夹中包含
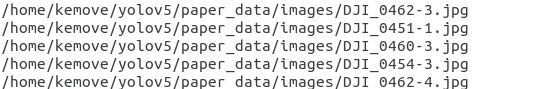
内容为绝对路径地址:
5.在/yolov5/paper_data中创建voc_label.py文件,以生成yolo训练需要的txt文件。代码如下:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import pickle
import os
from os import listdir, getcwd
from os.path import join
image_sets = ['train', 'val', 'test']
classes = ["??"]#??为自己类的名称
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / (size[0]) #中心点做坐标
dh = 1. / (size[1]) #中心点做坐标
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1 #若生成txt中包含负数,可将此处的‘-1’删除
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1 #若生成txt中包含负数,可将此处的‘-1’删除
w = box[1] - box[0] #size的max-min
h = box[3] - box[2] #size的max-min
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
isValid = True
if x == 0 or y == 0 or w == 0 or h == 0:
print(f'x :{x} y:{y} w:{w} h:{h}')
isValid = False
if box[0] == 0 or box[1] == 0 or box[2] == 0 or box[3] == 0:
print(f'box[0] :{box[0]} box[1]:{box[1]} box[2]:{box[2]} box[3]:{box[3]}')
isValid = False
return (x, y, w, h), isValid
def convert_annotation(image_id):
in_file = open('Annotations/%s.xml' % (image_id.split("/").pop().split(".")[0]))
out_file = open('labels/%s.txt' % (image_id.split("/").pop().split(".")[0]), 'w')
print(out_file)
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
# print(root['object'])
# return
objList = root.findall('object')
# for obj in objList:
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
print('-------')
if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
bb, isValid = convert((w, h), b)
if isValid == False:
# out_file.close()
print(image_id)
return False
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
print("文件内容:")
print(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
out_file.flush()
out_file.close()
return True
if not os.path.exists('labels/'):
os.makedirs('labels/')
for image_set in image_sets:
# strip() 移除字符串的首尾字符,默认为空格
# split() 字符串分割,默认为所有空字符,包含空格、换行、制表符
image_ids = open('ImageSets/Main/%s.txt' % (image_set)).read().strip().split()
list_file = open('%s.txt' % (image_set), 'w')
for image_id in image_ids:
isValid = convert_annotation(image_id)
if isValid == True:
list_file.write('%s\n' % (image_id))
else:
print(f'存在无效值:{image_id}')
list_file.close()
运行python voc_label.py后,labels文件中会生成类别 + 坐标的数字,以及在本级目录下会生成同样的train.txt等。如下: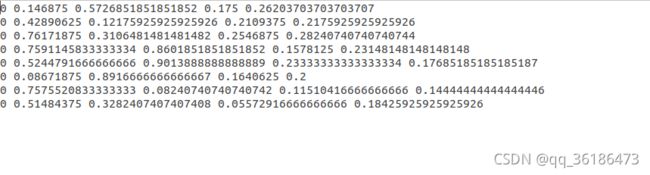
6.配置文件。在yolov5/model中有文件yolov5l.yaml 等,修改部分
# YOLOv5 by Ultralytics, GPL-3.0 license
# Parameters
nc: 1 # 修改为自己的类别数字
depth_multiple: 1.0 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 1.0 # layer channel multiple
anchors:
- [10,13, 16,30, 33,23] # P3/8
- [30,61, 62,45, 59,119] # P4/16
- [116,90, 156,198, 373,326] # P5/32
# YOLOv5 v6.0 backbone
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 6, 2, 2]], # 0-P1/2
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, C3, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 6, C3, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, C3, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 3, C3, [1024]],
[-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]], # 9
]
# YOLOv5 v6.0 head
head:
[[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 13
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, C3, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large)
[[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]
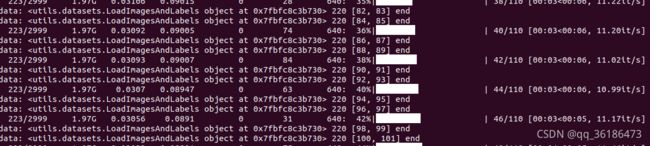
7.下面就可以开始训练了
将train.py中的训练参数修改为自己项目的。或者直接在终端输入也是一样的,如果使用CPU训练直接在下面代码后加一句:–device ‘cpu’ 即可。其他参数均可修改。
python3 train.py --img-size 256 --batch-size 8 --epoch 300 --data data/corn.yaml --cfg models/yolov5s.yaml --weights weights/yolov5s.pt
PS:在yolov5/data文件夹中创建自己项目的yaml 代码如下:
train: /home/kemove/yolov5/paper_data/train.txt #自己的txt路径
val: /home/kemove/yolov5/paper_data/val.txt #自己的txt路径
# number of classes自己类别数
nc: 1
# class names 自己类别名称
names: ['corn']
第一次写完整的训练过程(平时太懒了),大家有不明白的可以留言~~,科研顺利!