【前端面试题】Vue2 和 Vue3 中computed和watch的使用和区别
Vue2 和 Vue3 中computed和watch的使用和区别
- 一、computed
- 二、watch
- 三、区别
-
- 1、是否支持缓存
- 2、是否支持异步
一、computed
Vue2:
<template>
<div>
<span>姓:{{ firstName }}</span>
<br />
<span>名:{{ lastName }}</span>
<br />
<span>全名:{{ fullName }}</span>
<br />
全名:<input type="text" v-model="fullName" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
firstName: "戴",
lastName: "Dai",
};
},
computed: {
/*简写(如果不需要对fullName进行修改) */
// fullName: function () {
// return this.firstName + "-" + this.lastName;
// },
/*完整方式 */
fullName: {
get() {
return this.firstName + "-" + this.lastName;
},
set(val) {
const nameArr = val.split("-");
this.firstName = nameArr[0];
this.lastName = nameArr[1];
},
},
},
};
</script>
<template>
<div>
<span>姓:{{ firstName }}</span>
<br />
<span>名:{{ lastName }}</span>
<br />
<span>全名:{{ fullName }}</span>
<br />
全名:<input type="text" v-model="fullName" />
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { computed, defineComponent, reactive, toRefs } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
const state = reactive({
firstName: "戴",
lastName: "Dai",
});
/*简易写法(不需要对内容进行修改) */
// let fullName = computed(() => state.firstName + "-" + state.lastName);
/*完整写法 */
let fullName = computed({
get() {
return state.firstName + "-" + state.lastName;
},
set(val: any) {
const nameArr = val.split("-");
state.firstName = nameArr[0];
state.lastName = nameArr[1];
},
});
return {
...toRefs(state),
fullName,
};
},
});
</script>
二、watch
Vue2:
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{ weather }}</h1>
<button @click="isHot = !isHot">切换</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
weather: "炎热",
isHot: true,
};
},
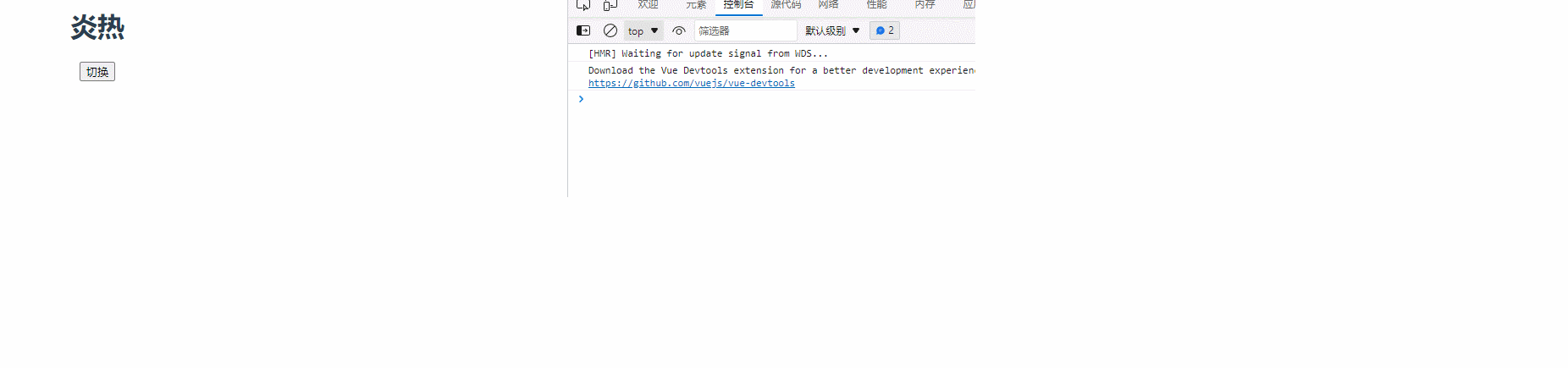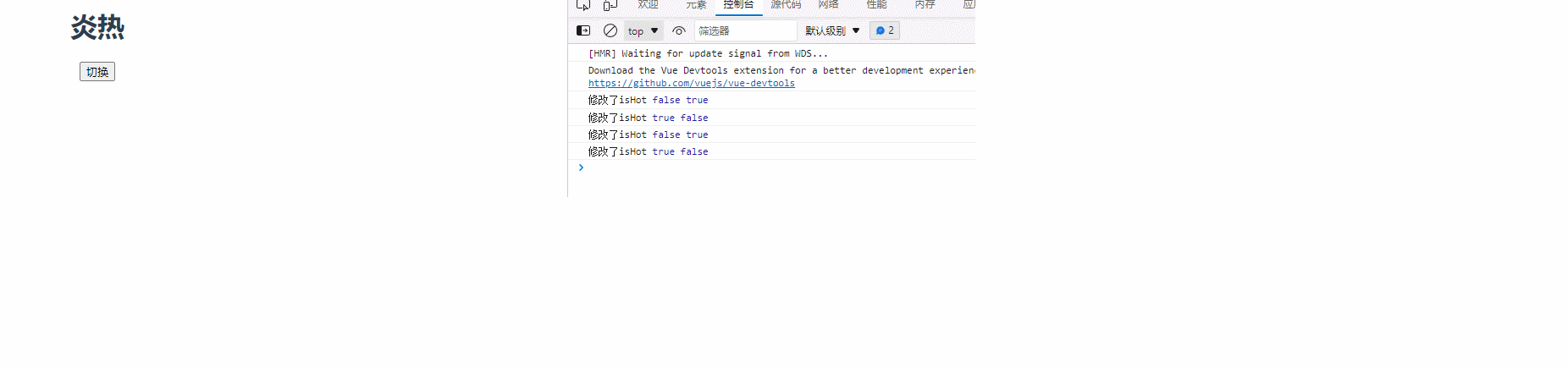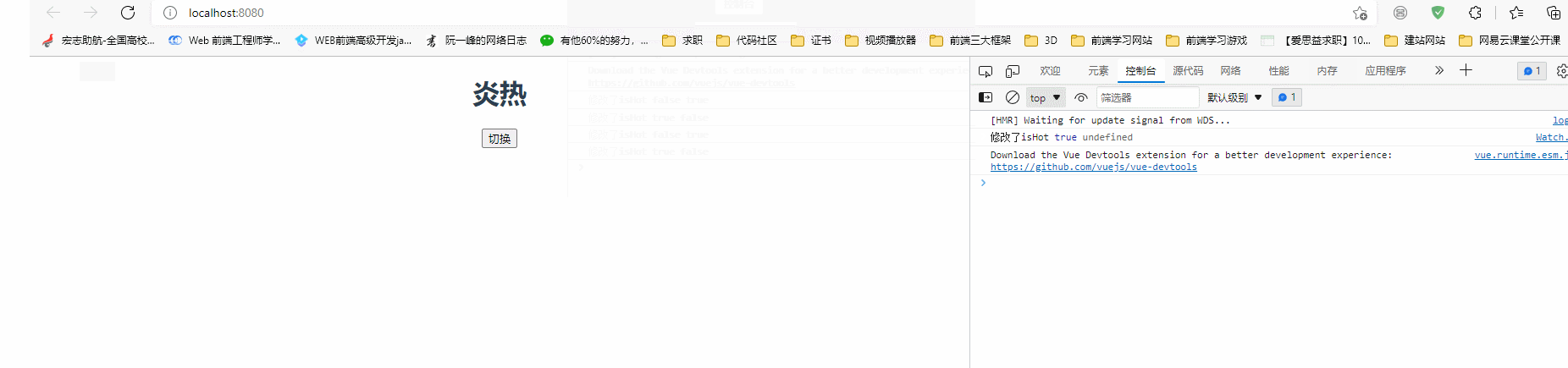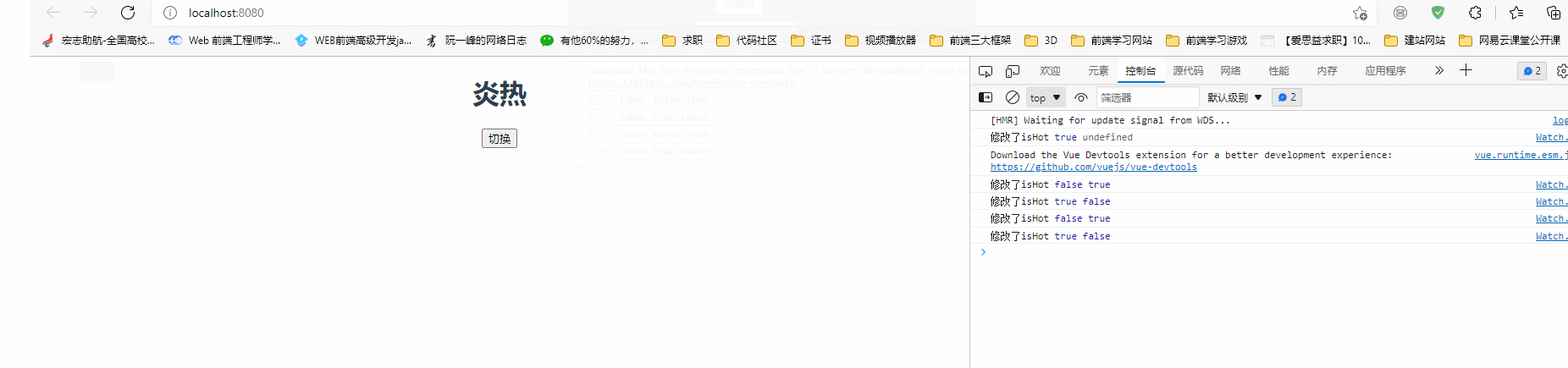
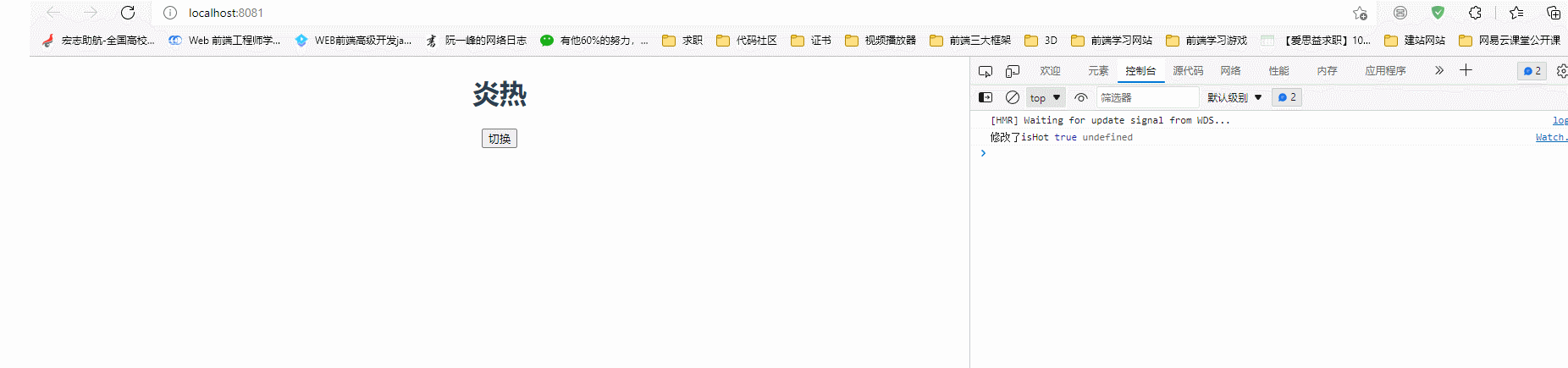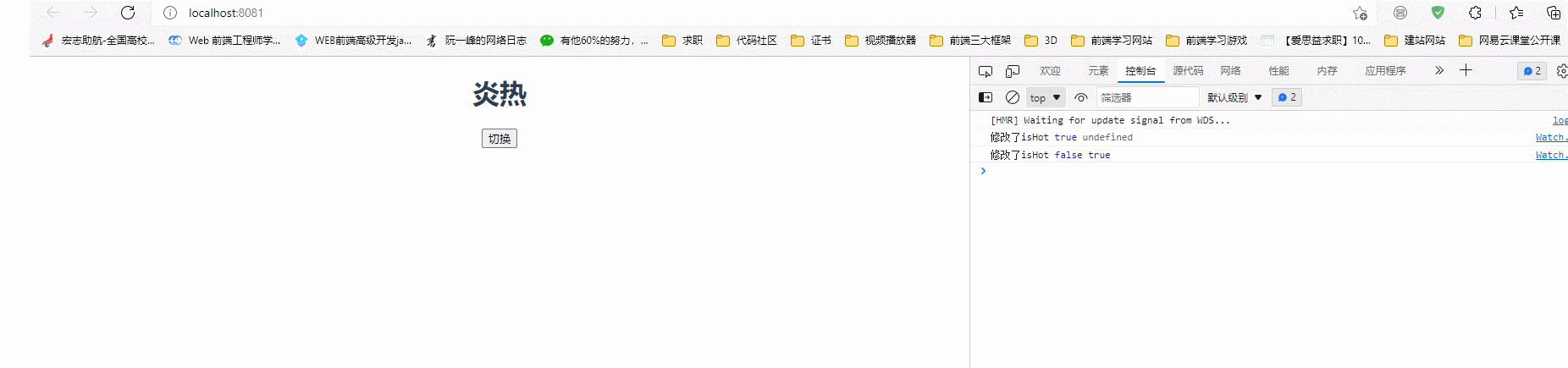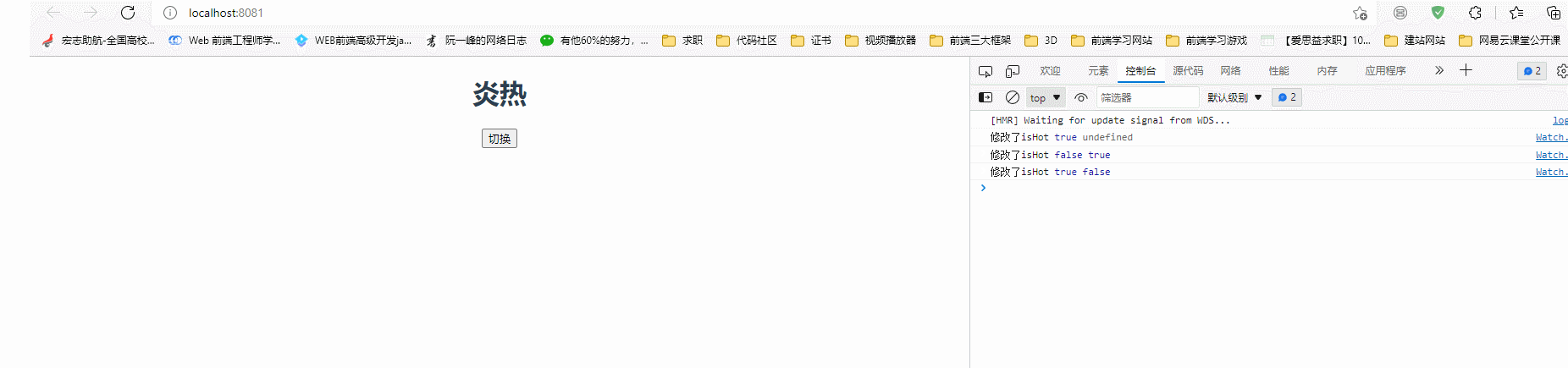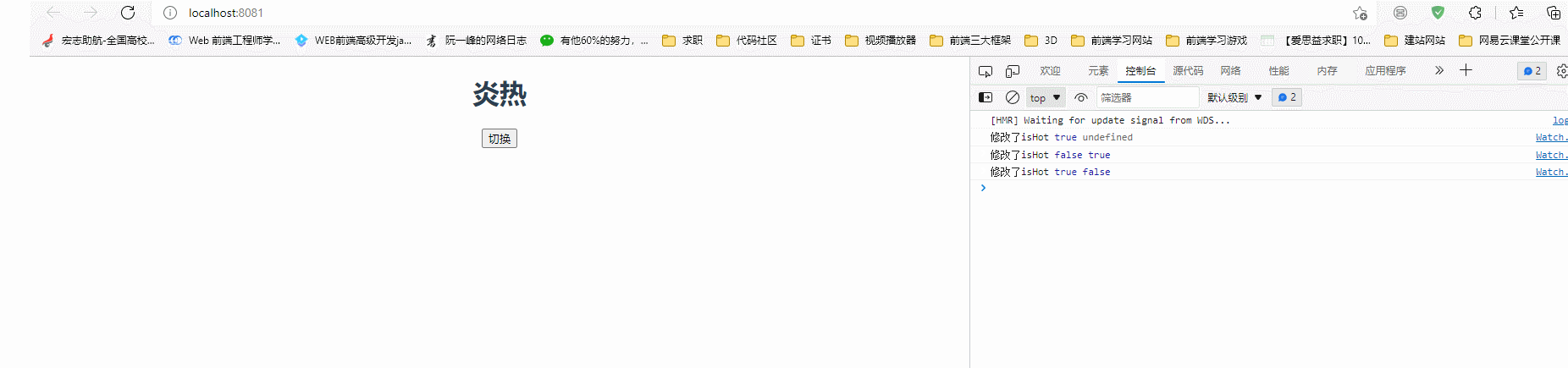
watch: {
/**简写 */
// isHot(newValue, oldValue){
// console.log("修改了isHot", newValue, oldValue);
// },
/*完整写法*/
isHot: {
immediate: true,
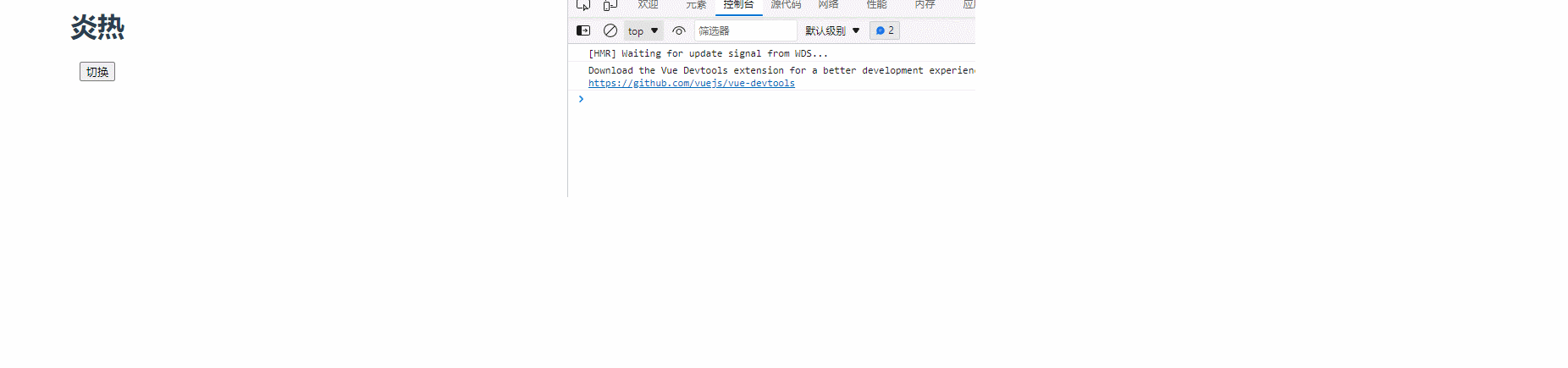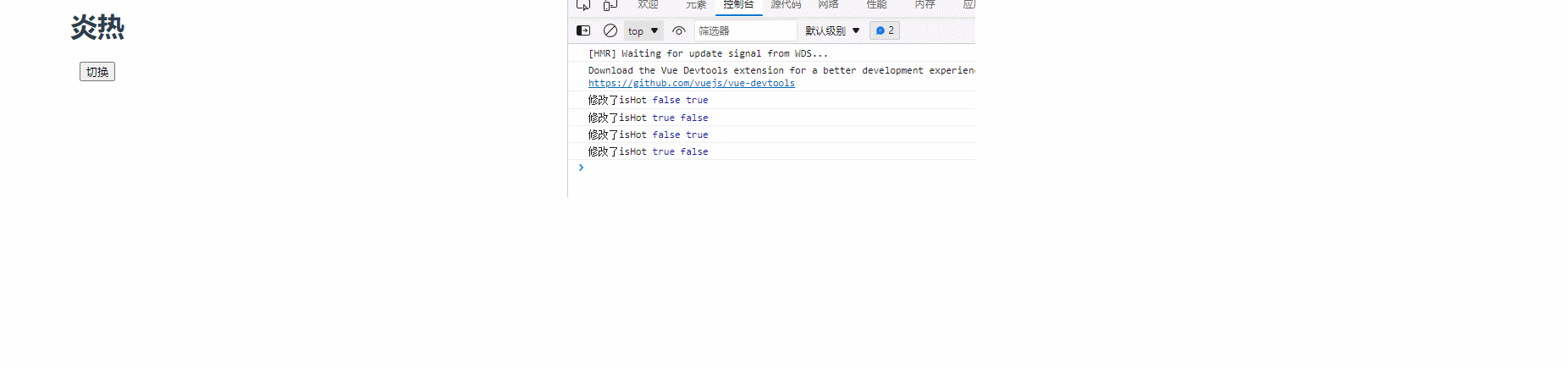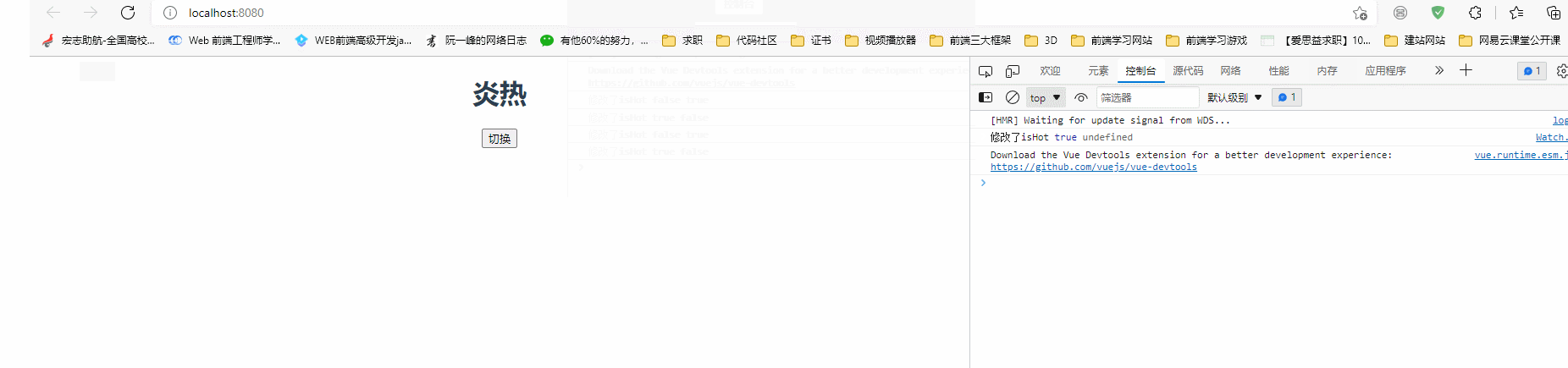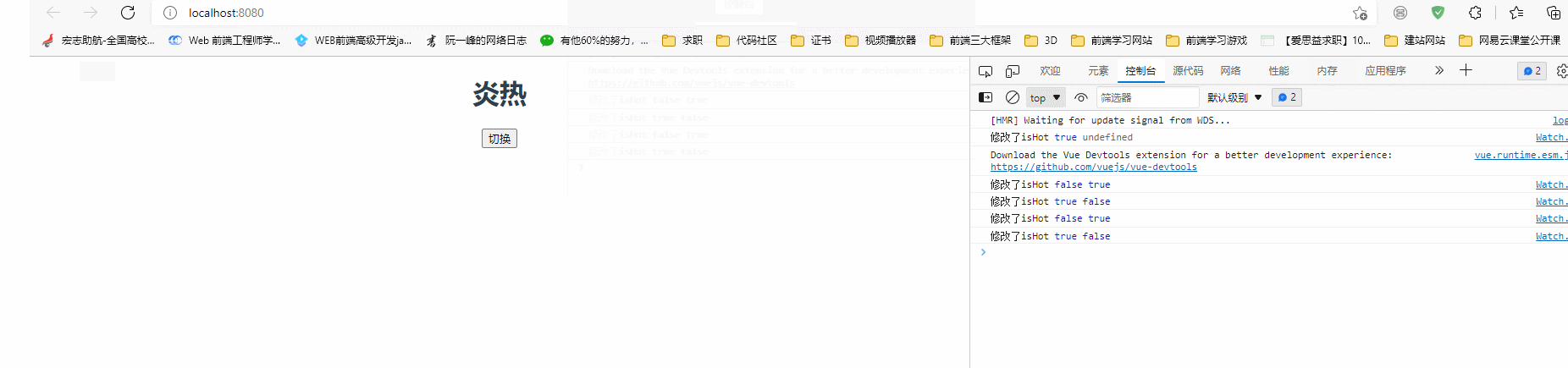
handler(newValue, oldValue) {
console.log("修改了isHot", newValue, oldValue);
this.weather = this.isHot === true ? "炎热" : "寒冷";
},
},
},
};
</script>
Vue3:
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{ weather }}</h1>
<button @click="isHot = !isHot">切换</button>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, reactive, toRefs, watch } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
const state = reactive({
weather: "炎热",
isHot: true,
});
watch(
() => state.isHot,
(newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log("修改了isHot", newValue, oldValue);
state.weather = state.isHot === true ? "炎热" : "寒冷";
},
{
//属性定义
immediate: true,
}
);
return {
...toRefs(state),
};
},
});
</script>
三、区别
1、是否支持缓存
computed(计算属性)支持缓存:当依赖的数据没有发生改变的时候就直接从缓存中读取;当依赖的数据发生变化的时候就重新进行计算。
watch(监听属性)不支持缓存:当数据变或者重新进行渲染的时候都会触发相应的操作,没有缓存。
2、是否支持异步
computed能完成的操作,watch都能完成,但是异步操作,只有watch能完成。
/*Vue3*/
watch(
() => state.isHot,
(newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log("修改了isHot", newValue, oldValue);
setTimeout(() => {
state.weather = state.isHot === true ? "炎热" : "寒冷";
}, 1000);
},
{
//属性定义
immediate: true,
}
);
/*Vue3*/
/*简易写法(不需要对内容进行修改) */
let fullName = computed(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
state.firstName + "-" + state.lastName;
}, 1000);
});
以上就是Vue2 和 Vue3 中computed和watch的使用和区别,请关注《前端面试题》专栏。
我会将自己平时项目中常见的问题以及笔试面试的知识在CSDN与大家分享,一起进步,加油。