1. 前言
在SQL开发当中,多表联查是绝对绕不开的一种技能。同样的查询结果不同的写法其运行效率也是千差万别。
在实际开发当中,我见过(好像还写过~)不少又长又臭的查询SQL,数据量一上来查个十几分钟那是家常便饭。
因此,深入理解SQL的多表查询机制,少写一些慢查询,应该可以少挨点骂。
2. 等值连接和非等值连接
2.1 等值连接
等值连接是在多表查询中最基础,也最简单的一种,其值为所有满足条件的笛卡尔积。
在from后面,哪个表写在前面结果中哪个表的值就先出现,
如下:
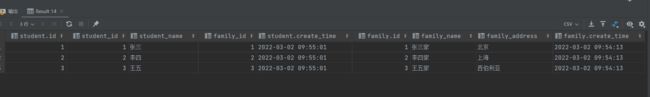
select * from student, family where student.family_id = family.id;
等值连接查询结果:
阿里在最新发布的Java开发手册中强制要求,只要涉及多个表,必须在列名前加表的别名(或表名)进行限定
2.2 非等值连接
非等值连接是通过a表中的值在b表中的某一个范围来进行的,能够很好的满足预设定好的分段统计需求。
非等值连接有两种写法,使用between...and...或大于号小于号
第一种写法:使用between...and...
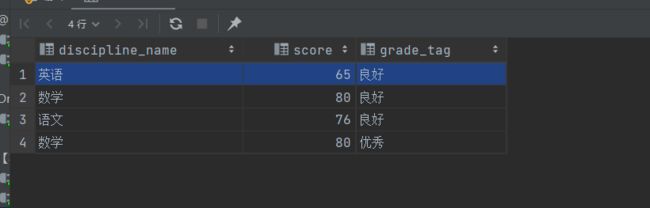
select a.discipline_name, a.score, b.grade_tag from achievement a, achievement_grade b where a.score between b.lowest_score and b.highest_score;
第二种写法:使用>=或<=
select a.discipline_name, a.score, b.grade_tag from achievement a, achievement_grade b where a.score >= b.lowest_score and a.score <= b.highest_score;
非等值连接查询结果:
3. 自连接和非自连接
3.1 自连接
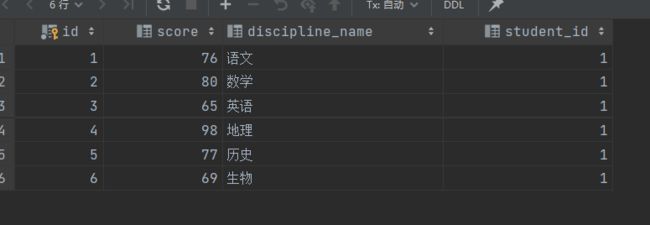
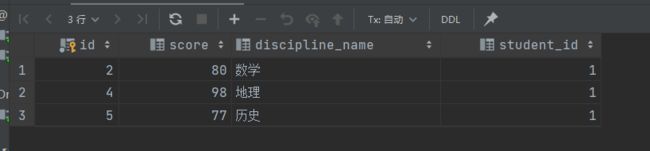
自连接,顾名思义就是同一张表自己跟自己连接,为了区分需要给表取不同的别名。如一张成绩表,需要查询所有分数比“语文”高的数据:
分数表:
若不使用自连接,需要先通过查询语文的分数,然后再查询大于这个分数的数据。
具体可以按如下步骤进行查询:
-- 先查询语文的分数 select score from achievement where discipline_name = '语文'; -- 再查询分数比语文分数更高的数据 select * from achievement where score > 76;
而使用自连接,则可以在一条sq语句里完成查询:
select a.* from achievement a, achievement b where b.discipline_name = '语文' and a.score > b.score;
自连接查询结果:
3.2 非自连接
除自连接外,其他的都叫非自连接~~~
4. 内连接和外连接
内连接和外连接的区分本质上是另一种分类方法,如内连接就是等值连接。
- 内连接:合并具有同一列的两个或两个以上的表的行, 结果集中不包含一个表与另一个表不匹配的行
- 外连接:两个表在连接过程中除了返回满足连接条件的行以外还返回左(或右)表中不满足条件的
行 ,这种连接称为左(或右) 外连接。没有匹配的行时, 结果表中相应的列为空(NULL)。
- 左外连接:连接条件中左边的表也称为主表 ,右边的表称为从表 。
- 右外连接:连接条件中右边的表也称为主表 ,左边的表称为从表 。
- 全外连接
4.1 测试数据
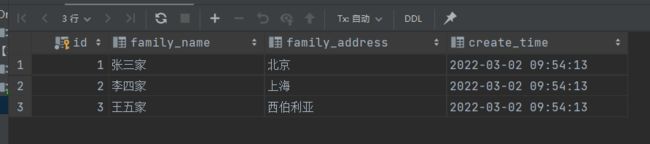
测试用学生表student和家庭表family数据如下:
学生表数据:
家庭表数据:
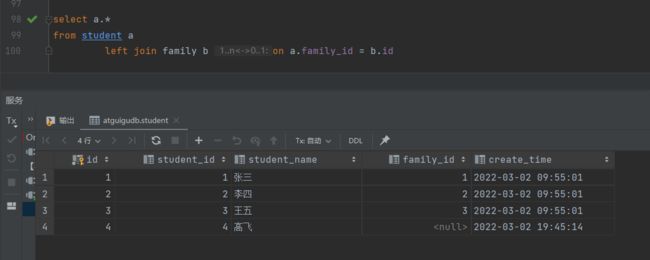
4.2 左外连接
-- 查出student中的所有数据,不满足的显示为null -- 这里student在前面 select a.* from student a left join family b on a.family_id = b.id
左外连接查询结果:
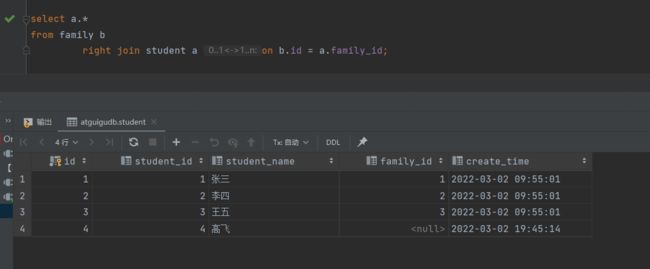
4.3 右外连接
-- 查出student中的所有数据,不满足的显示为null -- 这里student在后面 select a.* from family b right join student a on b.id = a.family_id;
右外连接查询结果:
4.4 全外连接
很遗憾,MySQL不支持全外连接。
附录:测试数据SQL脚本
-- auto-generated definition create table student ( id int auto_increment primary key, student_id int null comment '学号', student_name varchar(40) null comment '姓名', family_id int null comment '家庭ID', create_time datetime default CURRENT_TIMESTAMP null comment '创建时间' ) comment '学生表'; create table family ( id int auto_increment primary key, family_name varchar(40) null comment '家庭名称', family_address varchar(40) null comment '家庭地址', create_time datetime default CURRENT_TIMESTAMP null comment '创建时间' ) comment '家庭表'; create table achievement ( id int auto_increment primary key, score int null comment '分数', discipline_name varchar(40) null comment '学科名称', student_id int null comment '学号' ) comment '成绩表'; create table achievement_grade ( id int auto_increment primary key, grade_tag varchar(10) null comment '档次', lowest_score int null comment '最低分', highest_score int null comment '最高分', create_time datetime default CURRENT_TIMESTAMP null comment '创建时间' ) comment '分数档次表'; INSERT INTO achievement_grade (id, grade_tag, lowest_score, highest_score, create_time) VALUES (1, '不及格', 0, 60, '2022-03-02 11:44:01'); INSERT INTO achievement_grade (id, grade_tag, lowest_score, highest_score, create_time) VALUES (2, '良好', 60, 80, '2022-03-02 11:44:01'); INSERT INTO achievement_grade (id, grade_tag, lowest_score, highest_score, create_time) VALUES (3, '优秀', 80, 100, '2022-03-02 11:44:01'); INSERT INTO student (id, student_id, student_name, family_id, create_time) VALUES (1, 1, '张三', 1, '2022-03-02 09:55:01'); INSERT INTO student (id, student_id, student_name, family_id, create_time) VALUES (2, 2, '李四', 2, '2022-03-02 09:55:01'); INSERT INTO student (id, student_id, student_name, family_id, create_time) VALUES (3, 3, '王五', 3, '2022-03-02 09:55:01'); INSERT INTO student (id, student_id, student_name, family_id, create_time) VALUES (4, 4, '高飞', null, '2022-03-02 19:45:14'); INSERT INTO family (id, family_name, family_address, create_time) VALUES (1, '张三家', '北京', '2022-03-02 09:54:13'); INSERT INTO family (id, family_name, family_address, create_time) VALUES (2, '李四家', '上海', '2022-03-02 09:54:13'); INSERT INTO family (id, family_name, family_address, create_time) VALUES (3, '王五家', '西伯利亚', '2022-03-02 09:54:13'); INSERT INTO achievement (id, score, discipline_name, student_id) VALUES (1, 76, '语文', 1); INSERT INTO achievement (id, score, discipline_name, student_id) VALUES (2, 80, '数学', 1); INSERT INTO achievement (id, score, discipline_name, student_id) VALUES (3, 65, '英语', 1); INSERT INTO achievement (id, score, discipline_name, student_id) VALUES (4, 98, '地理', 1); INSERT INTO achievement (id, score, discipline_name, student_id) VALUES (5, 77, '历史', 1); INSERT INTO achievement (id, score, discipline_name, student_id) VALUES (6, 69, '生物', 1);
到此这篇关于MySQL多表查询机制的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关MySQL多表查询内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!