2022前端应该掌握的10个 JS 小技巧
正文
1. 用??代替||,用于判断运算符左侧的值为null或undefined时,才返回右侧的值
??运算符是 ES2020 引入,也被称为null判断运算符( Nullish coalescing operator)
它的行为类似||,但是更严
||运算符是左边是空字符串或false或0等falsy值,都会返回后侧的值。而??必须运算符左侧的值为null或undefined时,才会返回右侧的值。因此0||1的结果为1,0??1的结果为0
例如
const response = {
settings: {
nullValue: null,
height: 400,
animationDuration: 0,
headerText: '',
showSplashScreen: false
}
};
const undefinedValue = response.settings.undefinedValue ?? 'some other default'; // result: 'some other default'
const nullValue = response.settings.nullValue ?? 'some other default'; // result: 'some other default'
const headerText = response.settings.headerText ?? 'Hello, world!'; // result: ''
const animationDuration = response.settings.animationDuration ?? 300; // result: 0
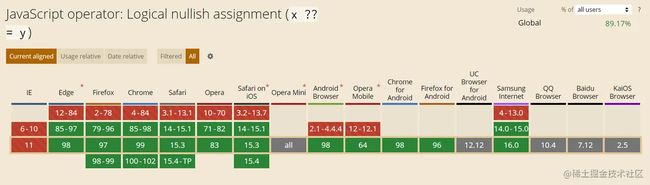
const showSplashScreen = response.settings.showSplashScreen ?? true; // result: false浏览器支持情况
2. 使用?.简化&&和三元运算符
?.也是ES2020 引入,有人称为链判断运算符(optional chaining operator)
?.直接在链式调用的时候判断,判断左侧的对象是否为null或undefined,如果是的,就不再往下运算,返回undefined,如果不是,则返回右侧的值
例如
var street = user.address && user.address.street;
var fooInput = myForm.querySelector('input[name=foo]')
var fooValue = fooInput ? fooInput.value : undefined
// 简化
var street = user.address?.street
var fooValue = myForm.querySelector('input[name=foo]')?.value注: 常见写法
obj?.prop对象属性obj?.[expr]对象属性func?.(...args)函数或对象方法的调用
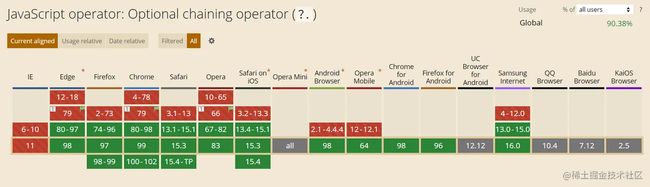
浏览器支持情况
3. 使用动态导入import()实现按需加载(优化静态import)
我们可以使用 import 语句初始化的加载依赖项
import defaultExport from "module-name";
import * as name from "module-name";
//...但是静态引入的import 语句需要依赖于 type="module" 的script标签,而且有的时候我们希望可以根据条件来按需加载模块,比如以下场景:
- 当静态导入的模块很明显的降低了代码的加载速度且被使用的可能性很低,或者并不需要马上使用它
- 当静态导入的模块很明显的占用了大量系统内存且被使用的可能性很低
- 当被导入的模块,在加载时并不存在,需要异步获取
- 当被导入的模块有副作用,这些副作用只有在触发了某些条件才被需要时
这个时候我们就可以使用动态引入import(),它跟函数一样可以用于各种地方,返回的是一个 promise
基本使用如下两种形式
//形式 1
import('/modules/my-module.js')
.then((module) => {
// Do something with the module.
});
//形式2
let module = await import('/modules/my-module.js');
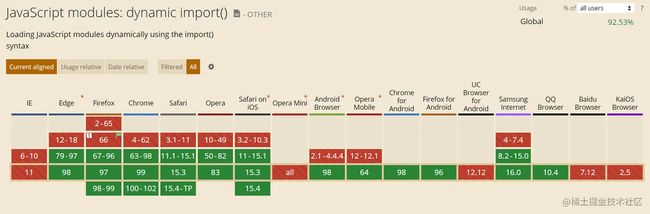
浏览器支持情况
4. 使用顶层 await(top-level await)简化 async 函数
其实上面的代码就有用到
let module = await import('/modules/my-module.js');
顶层 await 允许开发者在 async 函数外部使用 await 字段
因此
//以前
(async function () {
await Promise.resolve(console.log(''));
// →
})();
//简化后
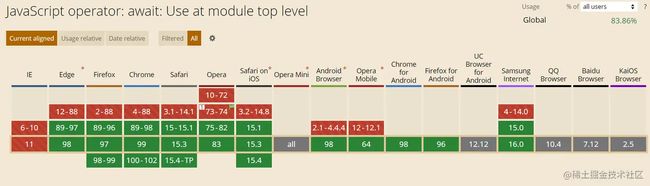
await Promise.resolve(console.log(''));浏览器支持情况
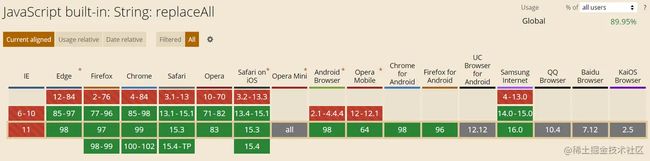
5. 使用String.prototype.replaceAll()简化replace一次性替换所有子字符串
String.prototype.replaceAll()用法与String.prototype.replace()类似
但是replace仅替换第一次出现的子字符串,而replaceAll会替换所有
例如需要替换所有a为A:
// 以前
console.log('aaa'.replace(/a/g,'A')) //AAA
// 简化后
console.log('aaa'.replaceAll('a','A')) //AAA浏览器支持情况
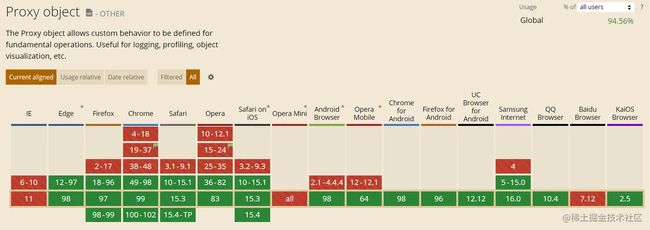
6. 使用Proxy替代Object.defineProperty
为什么使用 Proxy 替代 Object.defineProperty,简单总结Proxy的几点优势
- Proxy 是对整个对象的代理,而 Object.defineProperty 只能代理某个属性
- 对象上新增属性,Proxy 可以监听到,Object.defineProperty 不能
- 数组新增修改,Proxy 可以监听到,Object.defineProperty 不能
- 若对象内部属性要全部递归代理,Proxy 可以只在调用的时候递归,而 Object.definePropery 需要一次完成所有递归,性能比 Proxy 差
使用也很简单,Proxy本质是构造函数,通过new即可产生对象,它接收两个参数:
target表示的就是要拦截(代理)的目标对象handler是用来定制拦截行为(13种)
例如响应式reactive的基本实现:
function reactive(obj) {
return new Proxy(obj, {
get(target, key) {
// 可以做依赖收集
track(target, key)
return target[key]
},
set(target, key, val) {
target[key] = val
// 触发依赖
trigger(target, key)
}
})
}浏览器支持情况
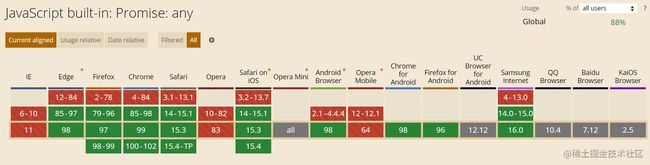
7. Promise.any快速获取一组Promise实例中第一个fulfilled的promise
Promise.any 接收一组Promise实例作为参数
- 只要其中的一个
promise成功,就返回那个已经成功的promise - 如果这组可迭代对象中,没有一个
promise成功,就返回一个失败的promise和AggregateError类型的实例
写法推荐
try {
const first = await Promise.any(promises);
// Any of the promises was fulfilled.
} catch (error) {
// All of the promises were rejected.
}或者
Promise.any(promises).then(
(first) => {
// Any of the promises was fulfilled.
},
(error) => {
// All of the promises were rejected.
}
);浏览器支持情况
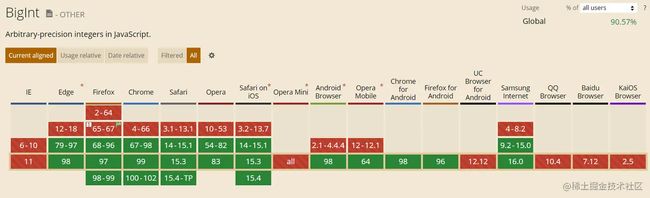
8. 使用BigInt支持大整数计算问题
ES2020 引入了一种新的数据类型 BigInt,用来表示任意位数的整数
例如
// 超过 53 个二进制位的数值(相当于 16 个十进制位),无法保持精度
Math.pow(2, 53) === Math.pow(2, 53) + 1 // true
// BigInt
BigInt(Math.pow(2, 53)) === BigInt(Math.pow(2, 53)) + BigInt(1) // false
除了使用BigInt来声明一个大整数,还可以使用数字后面加n的形式,如
1234 // 普通整数
1234n // BigInt需要了解BigInt数字操作时的支持情况,以免踩坑
| 操作 | 是否支持 |
|---|---|
| 单目 (+) 运算符 | N |
+、*、-、**、% 运算符 |
Y |
| \ 除法运算符 | 带小数的运算会被取整 |
>>> 无符号右移位操作符 |
N |
| 其他位移操作符 | Y |
| 与 Number 混合运算 | N(必须转换为同类型) |
| Math 对象方法 | N |
| Number 与 BigInt 比较(排序) | Y(宽松相等 ==) |
| Boolean 表现 | 类型 Number 对象 |
| JSON 中使用 | N |
浏览器支持情况
9. 使用Array.prototype.at()简化arr.length
Array.prototype.at()接收一个正整数或者负整数作为参数,表示获取指定位置的成员
参数正数就表示顺数第几个,负数表示倒数第几个,这可以很方便的某个数组末尾的元素
例如
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
// 以前获取最后一位
console.log(arr[arr.length-1]) //5
// 简化后
console.log(arr.at(-1)) // 5
10. 使用哈希前缀#将类字段设为私有
在类中通过哈希前缀#标记的字段都将被私有,子类实例将无法继承
例如
class ClassWithPrivateField {
#privateField;
#privateMethod() {
return 'hello world';
}
constructor() {
this.#privateField = 42;
}
}
const instance = new ClassWithPrivateField()
console.log(instance.privateField); //undefined
console.log(instance.privateMethod); //undefined
可以看到,属性privateField和方法privateMethod都被私有化了,在实例中无法获取到
结语
很多新特性都有很多人在用了,特别是??和?.以及动态引入import(),不知道你都用过哪些?
好了,以上就是本文的相关内容,如有问题欢迎指出~
最后还赠送一份前端大礼包送给大家【加君羊:581286372】帮助大家更好的学习!
![]()