Yolov5-v6.0模型详解
Yolov5-v6.0模型详解
先看看yaml文件:可以知道6.0模型主要构成为conv、bottlenet、cs3、sppf、detect层
yaml文件如下:
# YOLOv5 v6.0 backbone
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[[-1, 1, Conv, [64[l1] , 6[l2] , 2[l3] , 2[l4] ]], # 0-P1/2
# 来自上层,含瓶颈层数,本层类型,【输出通道,核大小,滑动,?分组】
#含瓶颈层数只对c3有效,其他层均为1
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3[l5] , C3, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 6, C3, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, C3, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 3, C3, [1024]],
[-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]], # 9
]
# YOLOv5 v6.0 head
head:
[[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 13
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, C3, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large)
[[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect[l6] , [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]
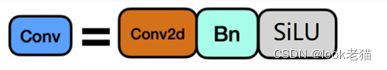
以下根据图示看源码---------------------------------------------------------
class Conv(nn.Module):
# Standard convolution
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, k, s, autopad(k, p), groups=g, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)
self.act = nn.SiLU() if act is True else (act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity())
def forward(self, x):
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
def forward_fuse(self, x):
return self.act(self.conv(x))
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
# Standard bottleneck
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels 可以增加通道数,扩充网络宽度
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, 3, 1, g=g) #核是3
self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
def forward(self, x):
return x + self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) if self.add else self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
class C3(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck with 3 convolutions
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels 可以扩充网络宽度
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv3 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1) # act=FReLU(c2) concat后conv输入通道要是2 * c_,
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(Bottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut, g, e=1.0) for _ in range(n)))
#通道数不会变化都是c_
# self.m = nn.Sequential(*[CrossConv(c_, c_, 3, 1, g, 1.0, shortcut) for _ in range(n)])
def forward(self, x):
return self.cv3(torch.cat((self.m(self.cv1(x)), self.cv2(x)), dim=1))
sppf图示:
class SPPF(nn.Module): # SPPF 输入通道c1,输出通道c2,大小不变
# Spatial Pyramid Pooling - Fast (SPPF) layer for YOLOv5 by Glenn Jocher
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=5): # equivalent to SPP(k=(5, 9, 13))
super().__init__()
c_ = c1 // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1) #核1,滑动1
self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * 4, c2, 1, 1) #
self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=k, stride=1, padding=k // 2) #最大池化,滑动1,此处大小不变
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter('ignore') # suppress torch 1.9.0 max_pool2d() warning
y1 = self.m(x)
y2 = self.m(y1)
return self.cv2(torch.cat([x, y1, y2, self.m(y2)], 1))
detect层是最后一层:
如果是训练时,
(1)3个head,经过conv,
(2)每层原来数据为4维:[batch,anchor*(class+5),h,w] 经过处理后变为5维:
[batch,anchor,h,w,class+5]
见下面绿色代码
如果是预测,3个head预测结果经过(1)(2)
(3)conv后sigmoid变为0~1,然后转化到格子空间。
(4)3个头的数据转化为(batch, _ ,85)然后cat在一起
#-----------------detct源码-------------------------------------------------------
class Detect(nn.Module):#如果是训练,输出3个张量,如果是预测输出【【batch,_,类+5】
stride = None # strides computed during build
onnx_dynamic = False # ONNX export parameter
def __init__(self, nc=80, anchors=(), ch=(), inplace=True): # detection layer
#ch=()应该是3个头的通道数
super().__init__()
self.nc = nc # number of classes
self.no = nc + 5 # number of outputs per anchor
self.nl = len(anchors) # number of detection layers
self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2 # number of anchors,一般为3
self.grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init grid
self.anchor_grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init anchor grid
self.register_buffer('anchors', torch.tensor(anchors).float().view(self.nl, -1, 2))
# shape(nl,na,2)
self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, self.no * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv
#ch 输入的3个头输出的通道【128,256,512】
self.inplace = inplace # use in-place ops (e.g. slice assignment)
def forward(self, x):
z = [] # inference output
for i in range(self.nl): #3个头分别处理 nl是 检测层的数量3
x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # conv
bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85)
x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
#4维转为5维 x(bs,3,20,20,85)
if not self.training: # inference,如果不是训练,把数据处理成(batch,_,85)
if self.onnx_dynamic or self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4]:
self.grid[i], self.anchor_grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny, i)
y = x[i].sigmoid() #0~1化
#下面把预测映射到格子空间尺度。预测使用下面结果 y
if self.inplace:
y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
else: # for YOLOv5 on AWS Inferentia https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/2953
xy = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
y = torch.cat((xy, wh, y[..., 4:]), -1)
z.append(y.view(bs, -1, self.no))
return x if self.training else (torch.cat(z, 1), x)
#如果是训练直接返回x(3个头),是预测把3个头的数据转化为(batch, _ ,85)然后cat在一起
[l1]输出通道
[l2]核大小
[l3]滑动步长
[l4]可能是分组
[l5]C3中残差模块个数
其他层都为1
[l6]3层预测结果0~1,转为真实的结果输出