java讲座总结报告_20175313 张黎仙《Java综合讲座》第十三周课堂测试总结
一、JAVA中两大类型
基本类型(byte、short、int->(Integer)、long、float、double)
类 类型
两者优缺点:使用基本类型效率高,但是类类型里面可以有一些属性、方法
二、基本类型与类类型的相互转化
例如:
int 与Integer类相互转化
public int intValue() Integer 转化成int
public static Integer valueOf(String s)throwsNumberFormatExcepton
int转化成Integer
其他类型与之相似
三、int与Integer之间的区别
代码验证1:int i1=1;
int i2=2;
System.out.println(i1==i2);//结果为true
代码验证2:Integer i1=Integer.valueOf(1);
Integer i2=Integer.valueOf(1);
System.out.println(i1==i2);//结果为true
代码验证3:Integer i1=Integer.new(1);
Integer i2=Integer.new(1);
System.out.println(i1==i2);//结果为false
代码验证4:Integer i1 =100;
Integer i2 =100;
if (i1 == i2){
System.out.println("i1 == i2");
} else {
System.out.println("i1 != i2");
}
//输出i1==i2;
代码验证5:Integer i1 =200;
Integer i2 =200;
if (i1 == i2){
System.out.println("i1 == i2");
} else {
System.out.println("i1 != i2");
}
//输出i1!=i2;
部分运行结果截图:
理解情况:
由于Integer变量实际上是对一个Integer对象的引用,所以两个通过new生成的Integer变量永远是不相等的。(因为引用不相同)
Integer变量和int变量比较时,只要两个变量的值是相等的,则结果为true。
原因:因为包装类Integer和基本数据类型int比较时,java会自动拆包装为int,然后进行比较,实际上就变为两个int变量的比较。
例如:Integet i1=100; 默认为Integer i1=Integer.valueOf(100)。
对于两个非new生成的Integer对象,进行比较时,如果两个变量的值在区间-128到127之间,则比较结果为true,如果两个变量的值不在此区间,则比较结果为false
因为Integer有个默认范围-128-127。
但你也可以通过如下指令修改范围:java -Djava.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high=300;//将范围改为-128-300
四、String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder三者之间的区别
代码验证1:
String s1="hello"
String s2="hello"
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//输出结果为true
代码验证2:
String s1="hello";
String s2=s1;
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//输出结果为true
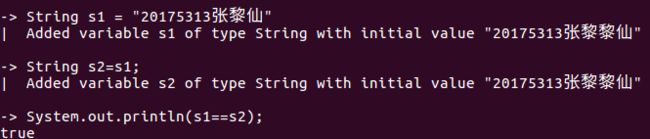
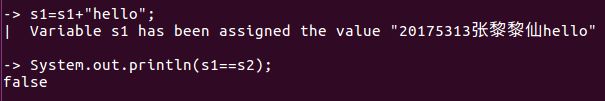
代码验证3:
String s1=new String("hello");
String s2=s1;
s1=s1+"world";
System.out.printlns(s1==s2);//输出结果为false
代码验证4:
StringBuilder s1=new StringBuilder("hello");
StringBuilder s2=s1;
s1=s1,append("hello");
System.out.printlns(s1==s2);//输出结果为true
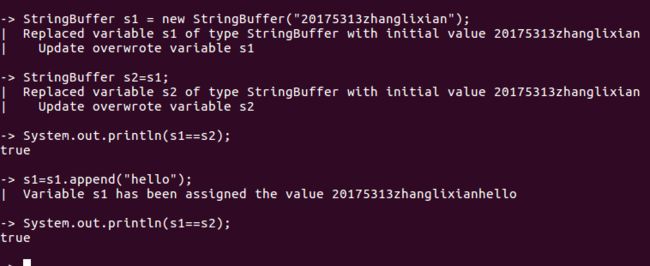
代码验证5:
StringBuffer s1=new StringBuffer("hello");
StringBufferr s2=s1;
s1=s1,append("hello");
System.out.printlns(s1==s2);//输出结果为true
部分运行结果截图:
理解情况:
String为字符串常量,而StringBuilder和StringBuffer均为字符串变量,即String对象一旦创建之后该对象是不可更改的,但后两者的对象是变量,是可以更改的。(String后面一旦加上一个字符串就重新new)
StringBuilder类与StringBuffer类使用 append方法往后加字符串时不改变引用
StringBuilder:适用于单线程下在字符缓冲区进行大量操作的情况
StringBuffer:适用多线程下在字符缓冲区进行大量操作的情况,效率低
五、ArrayList类、Vector类、LinkedList类三者之间的区别
ArrayList类,动态,数组随机访问,访问任何一个元素所用的时间都是一致的 查找快
Vector类,多线程,并发时使用Vector
LinkedList链表,查找慢,插入删除快
代码验证:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.lang.Integer;
import java.util.Vector;
public class TestList {
public static List list = CreatList.creatList();
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (args[0].equals("0")) {
ArrayListTest();
}
if (args[0].equals("1")) {
VectorTest();
}
if (args[0].equals("2")) {
LinkListTest();
}
}
public static void ArrayListTest() {
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList(list);
int index3 = arrayList.indexOf(Integer.valueOf(35));
System.out.println(index3);
}
public static void VectorTest() {
Vector vector = new Vector(list);
int index3 = vector.indexOf(Integer.valueOf(35));
System.out.println(index3);
}
public static void LinkListTest() {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList(list);
int index3 = linkedList.indexOf(35);
System.out.println(index3);
}
}
运行结果截图:
六、HashMap、HashTable、TreeMap三者之间的区别
HashMap具有很快的访问速度。HashMap不支持线程的同步,即任一时刻可以有多个线程同时写HashMap,可能会导致数据的不一致。
Hashtable与HashMap类似,不同的是:它支持线程的同步,即任一时刻只有一个线程能写Hashtable,然而,这也导致了Hashtable在写入时会比较慢。
TreeMap能够把它保存的记录根据键排序,默认是按升序排序,也可以指定排序的比较器。当用Iteraor遍历TreeMap时,得到的记录是排过序的。
代码验证:
代码1:
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
public class HashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map1= new java.util.HashMap();
map1.put("20175313","张黎仙");
map1.put("20175314","薛勐");
map1.put("20175312","陶光远");
map1.put("20175316","盛茂淞");
map1.put("20175311","胡济栋");
map1.put("20175315","陈煜扬");
long start1=System.currentTimeMillis();
Iterator> it1 = map1.entrySet().iterator();
while (it1.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry e = it1.next();
System.out.println("Key: " + e.getKey() + "; Value: " + e.getValue());
}
}
}
代码2:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class HashTable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map= new Hashtable();
map.put("20175313","张黎仙");
map.put("20175314","薛勐");
map.put("20175312","陶光远");
map.put("20175316","盛茂淞");
map.put("20175311","胡济栋");
map.put("20175315","陈煜扬");
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
Iterator> it = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry e = it.next();
System.out.println("Key: " + e.getKey() + "; Value: " + e.getValue());
}
}
}
代码3:
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
public class TreeMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map2= new java.util.TreeMap();
map2.put("20175313","张黎仙");
map2.put("20175314","薛勐");
map2.put("20175312","陶光远");
map2.put("20175316","盛茂淞");
map2.put("20175311","胡济栋");
map2.put("20175315","陈煜扬");
long start2=System.currentTimeMillis();
Iterator> it2 = map2.entrySet().iterator();
while (it2.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry e = it2.next();
System.out.println("Key: " + e.getKey() + "; Value: " + e.getValue());
}
}
}
运行结果截图: