有看过我之前发表过的C#相关文章分享和阅读过我代码的朋友们可能会在我的代码里面经常看到各种各样的λ表达式动态拼接,C#的λ表达式树是一个好东西,也是别的语言学不来的,熟悉掌握λ表达式就能够实现各种场景的个性化操作,如动态拼接查询条件、排序方式等,也能够实现替代反射的高性能操作,比如我们常用到的IQueryable和IEnumerable,每个扩展方法就全是λ表达式树。
本文给大家分享C#使用表达式树(LambdaExpression)动态更新类的属性值的相关知识,在某些业务中会遇到需要同步两个类的属性值的情况,而且有些字段是要过滤掉的。如果手动赋值则需要写很多重复的代码:
public class Teacher
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Age { get; set; }
}
public class Student
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Age { get; set; }
}
///
/// 比如需要把teacher的某些属性值赋给student,而id不需要赋值
///
///
///
public static void SetProperty(Student student, Teacher teacher)
{
if (student.Name != teacher.Name)
{
student.Name = teacher.Name;
}
if (student.Age != teacher.Age)
{
student.Age = teacher.Age;
}
}
使用反射的话性能考虑,尝试写一个扩展方法使用lambda表达式树去构建一个方法
public static class ObjectExtensions
{
///
/// 缓存表达式
///
///
{
private static Action func { get; set; }
public static TSource Set(TSource source, TTarget target, params string[] properties)
{
if (func == null)
{
var sourceType = typeof(TSource);
var targetType = typeof(TTarget);
BindingFlags bindingFlags = BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Public;
if (properties.Length == 0)
{
//get all properties
if (sourceType == targetType)
{
//如果是相同类型则获取所有属性
properties = sourceType.GetProperties(bindingFlags).Select(x => x.Name)
.ToArray();
}
else
{
//如果没有传指定的属性则默认获取同名属性
List propertyInfos = new List();
foreach (var property in sourceType.GetProperties(bindingFlags))
{//不同类型指定同名且类型相同的属性
var targetProperty = targetType.GetProperty(property.Name, bindingFlags);
if (targetProperty != null && targetProperty.PropertyType == property.PropertyType)
{
propertyInfos.Add(property);
}
}
properties = propertyInfos.Select(x => x.Name).ToArray();
}
}
//定义lambda 3个参数
var s = Expression.Parameter(typeof(TSource), "s");
var t = Expression.Parameter(typeof(TTarget), "t");
var ps = Expression.Parameter(typeof(string[]), "ps");
//获取泛型扩展方法Contains
var methodInfo = typeof(Enumerable).GetMethods().FirstOrDefault(e => e.Name == "Contains" && e.GetParameters().Length == 2);
if (methodInfo == null)
{
// properties.Contains()
throw new NullReferenceException(nameof(methodInfo));
}
MethodInfo genericMethod = methodInfo.MakeGenericMethod(typeof(String));//创建泛型方法
List bs = new List();
foreach (string field in properties)
{
//获取两个类型里面的属性
var sourceField = Expression.Property(s, field);
var targetField = Expression.Property(t, field);
//创建一个条件表达式
var notEqual = Expression.NotEqual(sourceField, targetField);//sourceField!=targetField
var method = Expression.Call(null, genericMethod, ps, Expression.Constant(field));//ps.Contains(f);
//构建赋值语句
var ifTrue = Expression.Assign(sourceField, targetField);
//拼接表达式 sourceField!=targetField&&ps.Contains(f)
var condition = Expression.And(notEqual, Expression.IsTrue(method));
//判断是否相同,如果不相同则赋值
var expression = Expression.IfThen(condition, ifTrue);
bs.Add(Expression.Block(expression));
}
var lambda = Expression.Lambda>(Expression.Block(bs), s, t, ps);
func = lambda.Compile();
}
func.Invoke(source, target, properties);
return source;
}
}
///
/// 通过目标类更新源类同名属性值
///
/// 待更新的数据类型
/// 目标数据类型
/// 源数据
/// 目标数据
/// 要变更的属性名称
/// 返回源数据,更新后的
public static TSource SetProperties(this TSource source, TTarget target, params string[] properties)
{
return MapperAccessor.Set(source, target, properties);
}
}
编写测试方法
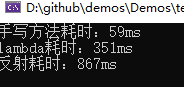
////// 比如需要把teacher的某些属性值赋给student,而id不需要赋值 /// /// /// public static void SetProperty(Student student, Teacher teacher) { if (student.Name != teacher.Name) { student.Name = teacher.Name; } if (student.Age != teacher.Age) { student.Age = teacher.Age; } } public static void SetProperty2(Student student, Teacher teacher, params string[] properties) { var sourceType = student.GetType(); var targetType = teacher.GetType(); foreach (var property in properties) { var aP = sourceType.GetProperty(property); var bP = targetType.GetProperty(property); var apValue = aP.GetValue(student); var bpValue = bP.GetValue(teacher); if (apValue != bpValue) { aP.SetValue(student, bpValue); } } } static (List, List ) CreateData(int length) { var rd = new Random(); (List , List ) ret; ret.Item1 = new List (); ret.Item2 = new List (); for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { Student student = new Student() { Id = Guid.NewGuid(), Name = Guid.NewGuid().ToString("N"), Age = rd.Next(1, 100) }; ret.Item1.Add(student); Teacher teacher = new Teacher() { Id = Guid.NewGuid(), Name = Guid.NewGuid().ToString("N"), Age = rd.Next(1, 100) }; ret.Item2.Add(teacher); } return ret; } static void Main(string[] args) { var length = 1000000; var data = CreateData(length); Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); sw.Start(); for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { SetProperty(data.Item1[i], data.Item2[i]); } sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine($"手写方法耗时:{sw.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms"); data.Item1.Clear(); data.Item2.Clear(); var data2 = CreateData(length); sw.Restart(); for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { data2.Item1[i].SetProperties(data2.Item2[i], nameof(Student.Age), nameof(Student.Name)); } data2.Item1.Clear(); data2.Item2.Clear(); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine($"lambda耗时:{sw.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms"); var data3 = CreateData(length); sw.Restart(); for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { SetProperty2(data3.Item1[i], data3.Item2[i], nameof(Student.Age), nameof(Student.Name)); } sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine($"反射耗时:{sw.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms"); data3.Item1.Clear(); data3.Item2.Clear(); Console.ReadKey(); }
可以看到性能和手写方法之间的差距,如果要求比较高还是手写方法,如果字段多的话写起来是很痛苦的事。但是日常用这个足够了,而且是扩展方法,通用性很强。
到此这篇关于C#使用表达式树(LambdaExpression)动态更新类的属性值的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C#表达式树类的属性值内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!