如何转换为YOLO txt格式
YOLO训练的label bbox格式是txt文档,如果是PASCAL VOC XML格式的文档或者其他类型文档,需要另外转换格式。
YOLO格式要求
YOLO txt文档格式,它是由class id,归一化后的center_x,center_y中心坐标以及归一化后的w,h组成,如下图所示:
<class_id> <center_x> <center_y> <w> <h>
如果 x m i n 、 x m a x 、 y m i n 、 y m a x x_{min}、x_{max}、y_{min}、y_{max} xmin、xmax、ymin、ymax分别表示标注框的x轴方向的最小最大值和y轴方向的最小最大值,则计算公式如下:

WIDER FACE label转换
接下来介绍WIDER FACE数据集的label格式,是由图片位置路径,边框的数量以及边框的属性组成,其中边框的属性有:x1, y1, w, h, blur, expression, illumination, invalid, occlusion, pose
数据集所在地址:http://shuoyang1213.me/WIDERFACE/
- x1, y1 是指BBox的左上角坐标,w, h是指BBox的宽高
- blur 是指照片的模糊程度: 0清晰、1一般、2严重
- expression 是指照片的表情: 0正常、1夸张
- illumination 是指照片的曝光程度: 0正常、1极度
- invalid 是指照片是否无效: 0否、1是
- occlusion 是指照片是否有被遮挡: 0无、1部分、2大量
- pose 是指照片的姿势: 0正常,1非典型
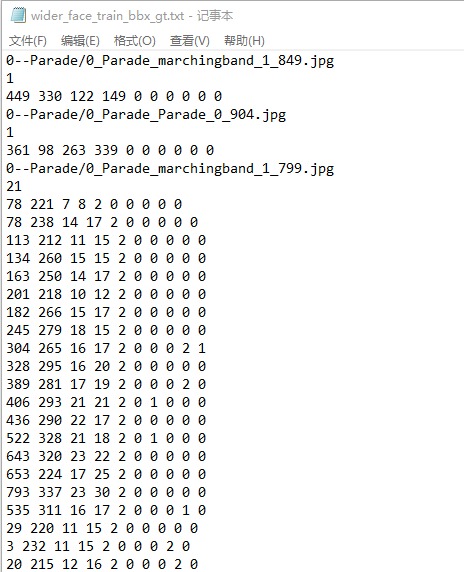
W I D E R F A C E 数 据 集 的 l a b e l 格 式 WIDER FACE 数据集的 label 格式 WIDERFACE数据集的label格式
了解格式后就可以做转换啦~~或是也可以直接使用以下我提供的代码,我的目录格式如下。其中 cfg 是自己创建的文件夹,用来放生成的 train.txt, val.txt (会写入所有的训练集路径)。而 wider_face_split, WIDER_train, WIDER_val 则是 WIDER FACE 数据集的训练集、验证集、label。

因為我的数据集类别只有一个,所以第80行 f.write(‘0 %s %s %s %s\n’ % (x, y, w, h)) 的第一个参数是0
import os
import shutil
import cv2
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1./size[0]
dh = 1./size[1]
x = (box[0] + box[1])/2.0
y = (box[2] + box[3])/2.0
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x*dw
w = w*dw
y = y*dh
h = h*dh
return (x,y,w,h)
def run_convert(data_file, wider_train, yolo_path, file_info_name, write_txt):
now_path = os.getcwd()
data_counter = 0
with open(data_file, 'r') as f:
print("read file...")
data = f.readlines()
for data_line in data:
data_line = data_line.strip()
data_info = data_line.split('/')
# the image name
if len(data_info) == 2:
label_0_counter = 1
data_info_path = os.path.join(data_info[0], data_info[1])
data_path = os.path.join(wider_train, data_info_path)
# copy image to yolo path and rename
shutil.copyfile(data_path, yolo_path + str(data_counter) + '.jpg')
image = cv2.imread(data_path)
image_size = [image.shape[1],image.shape[0]]
# image --> rename
with open(file_info_name, 'a') as f:
line_txt = [data_info_path, ' --> ', yolo_path + str(data_counter) + '.jpg', '\n']
f.writelines(line_txt)
with open(write_txt, 'a') as f:
path = os.path.join(now_path, yolo_path)
line_txt = [path + str(data_counter) + '.jpg', '\n']
f.writelines(line_txt)
data_counter += 1
label_list = []
# process other info
sub_count = 1
continue
# the count of bndBox
if sub_count == 1:
sub_count += 1
continue
# bndBox info
print("process ", label_0_counter, " bndBox info...")
if sub_count >= 2:
label_0_counter += 1
info_list = data_line.split(' ')
# print("WIDER FACE(x1, y1, w, h): ", info_list[0], info_list[1], info_list[2], info_list[3])
xmin = int(info_list[0])
xmax = int(info_list[0])+int(info_list[2])
ymin = int(info_list[1])
ymax = int(info_list[1])+int(info_list[3])
box = [xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax]
x, y, w, h = convert(image_size,box)
# print("YOLO txt(x, y, w, h): ", x, y, w, h)
with open(yolo_path + str(data_counter-1) + '.txt', 'a+') as f:
f.write('0 %s %s %s %s\n' % (x, y, w, h))
print('the file is processed')
wider_train = "WIDER_train/images"
yolo_path = "yolo_train/"
data_file = "wider_face_split/wider_face_train_bbx_gt.txt"
file_info_name = 'file_info_train.txt'
write_txt = 'cfg/train.txt'
# wider_train = "WIDER_val/images"
# yolo_path = "yolo_val/"
# data_file = "wider_face_split/wider_face_val_bbx_gt.txt"
# file_info_name = 'file_info_val.txt'
# write_txt = 'cfg/val.txt'
if not os.path.exists(yolo_path):
os.mkdir(yolo_path)
else:
lsdir = os.listdir(yolo_path)
for name in lsdir:
if name.endswith('.txt') or name.endswith('.jpg'):
os.remove(os.path.join(yolo_path, name))
if os.path.exists(file_info_name):
file=open(file_info_name, 'w')
if os.path.exists(write_txt):
file=open(write_txt, 'w')
run_convert(data_file, wider_train, yolo_path, file_info_name, write_txt)
转换好的格式会放在 yolo_train, yolo_val 文件夹里,所有 train, validate 的图片路径 txt文档则会放在cfg文件夹里(train.txt, val.txt)。转换完就可以开始训练了。
PASCAL VOC XML转换
以下就是 VOC xml 的格式, 里的 是指照片的 width, height, depth, 是检测目标信息: 类别 name,BBox的xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax,也就是指 BBox 的 x, y 坐标的最小与最大值。
<annotation>
<folder>VOC2012folder>
<filename>2007_000027.jpgfilename>
<source>
<database>The VOC2007 Databasedatabase>
<annotation>PASCAL VOC2007annotation>
<image>flickrimage>
source>
<size>
<width>486width>
<height>500height>
<depth>3depth>
size>
<segmented>0segmented>
<object>
<name>personname>
<pose>Unspecifiedpose>
<truncated>0truncated>
<difficult>0difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>174xmin>
<ymin>101ymin>
<xmax>349xmax>
<ymax>351ymax>
bndbox>
<part>
<name>headname>
<bndbox>
<xmin>169xmin>
<ymin>104ymin>
<xmax>209xmax>
<ymax>146ymax>
bndbox>
part>
<part>
<name>handname>
<bndbox>
<xmin>278xmin>
<ymin>210ymin>
<xmax>297xmax>
<ymax>233ymax>
bndbox>
part>
<part>
<name>footname>
<bndbox>
<xmin>273xmin>
<ymin>333ymin>
<xmax>297xmax>
<ymax>354ymax>
bndbox>
part>
<part>
<name>footname>
<bndbox>
<xmin>319xmin>
<ymin>307ymin>
<xmax>340xmax>
<ymax>326ymax>
bndbox>
part>
object>
annotation>
接着就可以使用以下代码来转换:
要将第57行 all_classes设定为要预测的类别:
import os
import shutil
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
def run_convert(all_classes, train_img, train_annotation, yolo_path, write_txt):
now_path = os.getcwd()
data_counter = 0
for data_file in os.listdir(train_annotation):
try:
with open(os.path.join(train_annotation, data_file), 'r') as f:
print("read file...")
soup = BeautifulSoup(f.read(), 'xml')
img_name = soup.select_one('filename').text
for size in soup.select('size'):
img_w = int(size.select_one('width').text)
img_h = int(size.select_one('height').text)
img_info = []
for obj in soup.select('object'):
xmin = int(obj.select_one('xmin').text)
xmax = int(obj.select_one('xmax').text)
ymin = int(obj.select_one('ymin').text)
ymax = int(obj.select_one('ymax').text)
objclass = all_classes.get(obj.select_one('name').text)
x = (xmin + (xmax-xmin)/2) * 1.0 / img_w
y = (ymin + (ymax-ymin)/2) * 1.0 / img_h
w = (xmax-xmin) * 1.0 / img_w
h = (ymax-ymin) * 1.0 / img_h
img_info.append(' '.join([str(objclass), str(x),str(y),str(w),str(h)]))
# copy image to yolo path and rename
img_path = os.path.join(train_img, img_name)
img_format = img_name.split('.')[1] # jpg or png
shutil.copyfile(img_path, yolo_path + str(data_counter) + '.' + img_format)
# create yolo bndbox txt
with open(yolo_path + str(data_counter) + '.txt', 'a+') as f:
f.write('\n'.join(img_info))
# create train or val txt
with open(write_txt, 'a') as f:
path = os.path.join(now_path, yolo_path)
line_txt = [path + str(data_counter) + '.' + img_format, '\n']
f.writelines(line_txt)
data_counter += 1
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print('the file is processed')
all_classes = {'class_2': 2, 'class_1': 1, 'class_0': 0}
train_img = "train/image"
train_annotation = "train/annotation"
yolo_path = "yolo_train/"
write_txt = 'cfg/train.txt'
if not os.path.exists(yolo_path):
os.mkdir(yolo_path)
else:
lsdir = os.listdir(yolo_path)
for name in lsdir:
if name.endswith('.txt') or name.endswith('.jpg') or name.endswith('.png'):
os.remove(os.path.join(yolo_path, name))
cfg_file = write_txt.split('/')[0]
if not os.path.exists(cfg_file):
os.mkdir(cfg_file)
if os.path.exists(write_txt):
file=open(write_txt, 'w')
run_convert(all_classes, train_img, train_annotation, yolo_path, write_txt)
转换好的格式会放在yolo_train, yolo_val文件夹里,所有 train, validate 的图片路径txt文档会放在cfg文件夹里(train.txt, val.txt)。
labelme转YOLO格式
我的labelme是自己改过的,如果报 label_file.imageWidth错误,请自己读一下图片的宽高。用法:直接改一下dirpath,dstpath路径即可,dirpath里面可以有子文件夹,最后dstpath里面的标定内容是从0开始顺序编号的文件。
import os
import io
from io import BytesIO
import uuid
import PIL.Image
import codecs
import threadpool
import numpy as np
import cv2
import base64
from math import radians,fabs,sin,cos
from labelme.label_file import *
from labelme import utils
import shutil
dirpath = r'xxxxx'
dst_path_dir = r'xxxxx'
files = [os.path.join(y, file) for y, z, x in os.walk(dirpath)
for file in x if os.path.splitext(file)[1] == '.json']
if not os.path.exists(dst_path_dir):
os.makedirs(dst_path_dir)
index_files = []
for i in range(len(files)):
index_files.append([i, files[i]])
def ThreadFun_c1(file):
index = file[0]
file = file[1]
print(file)
txtname = os.path.join(dst_path_dir, '{}.txt'.format(index))
label_file = LabelFile()
label_file.load(file)
shutil.copy(file.replace('.json','.jpg'), txtname.replace('.txt','.jpg'))
with codecs.open(txtname,'w','GBK') as f:
for shape in label_file.shapes:
x1 = shape['points'][0][0]/label_file.imageWidth
y1 = shape['points'][0][1]/label_file.imageHeight
x2 = shape['points'][1][0]/label_file.imageWidth
y2 = shape['points'][1][1]/label_file.imageHeight
f.write('{} {} {} {} {}\n'.format(shape['label'],(x1+x2)/2,(y1+y2)/2,abs(x1-x2),abs(y1-y2)))
# 定义了一个线程池,最多创建8个线程
pool = threadpool.ThreadPool(16)
# 创建要开启多线程的函数,以及函数相关参数和回调函数,其中回调数可以不写,default是none
requests = threadpool.makeRequests(ThreadFun_c1, index_files)
# 将所有要运行多线程的请求扔进线程池
[pool.putRequest(req) for req in requests]
# 所有的线程完成工作后退出
pool.wait()
'''
检查标注文件对不对
'''
for file in index_files:
index = file[0]
file = file[1]
txtname = os.path.join(dst_path_dir, '{}.txt'.format(index))
imgfile = txtname.replace('.txt','.jpg')
img = cv2.imread(imgfile)
h, w= img.shape[:2]
with codecs.open(txtname,'r','GBK') as f:
liness = f.readlines()
for line in liness:
lines = line.strip('\n').split(' ')
for i in range(1,5):
lines[i] = float(lines[i])
x1 = (lines[1] - lines[3] /2) * w
x2 = (lines[1] + lines[3]/2)*w
y1 = (lines[2] - lines[4]/2)*h
y2 = (lines[2] + lines[4]/2)*h
x1 = int(x1)
x2 = int(x2)
y1 = int(y1)
y2 = int(y2)
if lines[0] == '0':
color = (0,255,0)
else:
color = (0,0,255)
cv2.rectangle(img,(x1,y1),(x2,y2),color)
cv2.imshow('1',img)
cv2.waitKey()
参考目录
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_16952303/article/details/114702534
https://medium.com/ching-i/%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E8%BD%89%E6%8F%9B%E7%82%BAyolo-txt%E6%A0%BC%E5%BC%8F-f1d193736e5c
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40622955/article/details/115733954