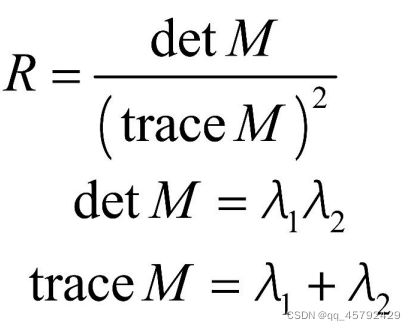计算机视觉(二):局部图像描述子
计算机视觉二:局部图像描述子
- 一、序
-
- 1、角点(corner points)
- 2. 如何判断是否是好的角点检测算法
- 二、Harris角点检测器
-
- 1、基本思想
- 2、数学表达
- 3、角点计算流程
- 4、算法实现
-
- 4.1 角点响应函数
- 4.2 筛选角点
- 4.3 显示角点
- 4.4 结果显示
- 5. 寻找对应点
-
- 5.1 兴趣点描述子
-
- 5.1.1 获取图像像素块,并使用归一化的互相关矩阵进行比较
- 结果显示
- 三、SIFT算法
-
- 1、产生
- 2、了解
-
- 2.1 兴趣点
- 2.2 描述子
- 2.3 检测兴趣点
- 2.4 匹配描述子
- 四、匹配地理标记图像
-
- 1、下载地理标记图像
- 2、使用局部描述子匹配
- 3、可视化连接的图像
一、序
局部图像描述子主要是为了寻找图像间的对应点和对应区域。以下内容将出现两种用于图像匹配的局部描述子算法。
特征匹配的基本流程:
- 根据特定准则,提取图像中的特征点
- 提取特征点周围的图像块,构造特征描述符
- 通过特征描述符对比,实现特征匹配
特征点必须具有不变性
特征可以分为以下几类:
- 角点:Harris算子,SUSAN算子。FSAT算子
- 梯度特征点:SIFT、SURF、GLOH、ASIFT、PSIFT算子
- 边缘特征(线性):Canny算子、Marr算子
- 纹理特征:灰度共生矩阵,小波Gabor算子
- 快速特征匹配的基本策略:以图像中稳定角点的领域训练特征分类器,为输入图像的特征分类
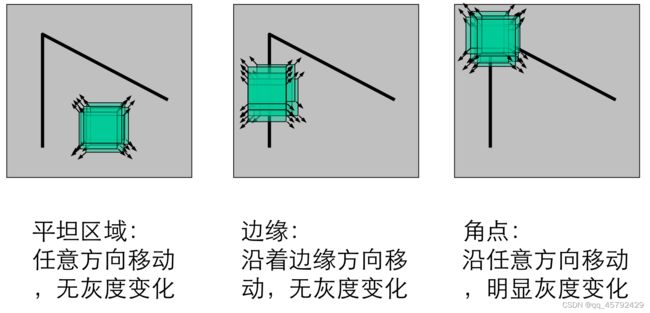
1、角点(corner points)
局部窗口沿各方向移动,均产生明显变化的点
图像局部曲率突变的点
经典的角点检测算法
Harris角点检测
CSS角点检测
2. 如何判断是否是好的角点检测算法
- 检测出图像中“真实的”角点
- 准确的定位性能
- 很高的稳定性
- 具有对噪声的鲁棒性
- 具有较高的计算效率
二、Harris角点检测器
1、基本思想
从图像局部的小窗口观察图像特征,利用角点定义判断,如下图
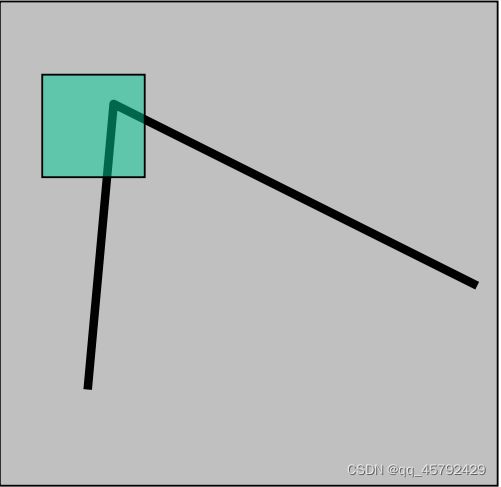
如果在平坦区域:那么超任意方向移动,都无灰度变化
如果在边缘处移动:沿着边缘方向移动,无灰度变化
在角点处:沿任意方向移动,有明显的灰度变化
2、数学表达
将图像窗口平移==[u,v]产生灰度变化E(u,v)==
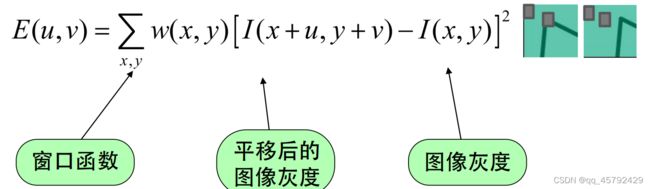
我们可以利用泰勒展开来获得上图式子中的E和I
窗口函数的两种表示:

对于局部微小的移动量[u,v],我们可以获得以下近似值
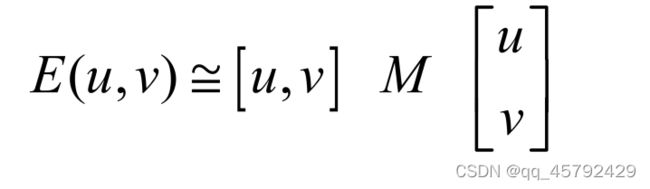
M是由图像的导数求得的2X2的矩阵。
所以窗口移动导致的图像变化量其实就是对对称矩阵M的特征值分析,通过两个特征值的大小我们可以对图像点进行分类:
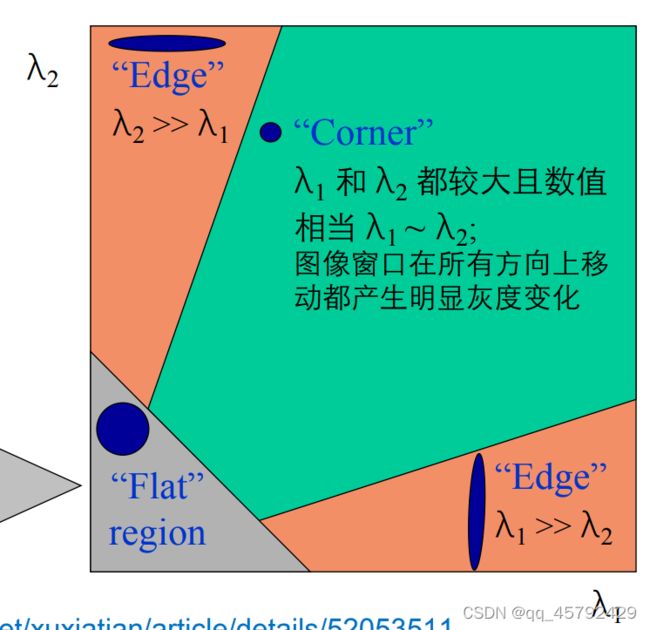
当两个特征值都很小时,图像窗口在所有方向上移动都无明显灰度变化
我们可以定义一个角点响应函数R:
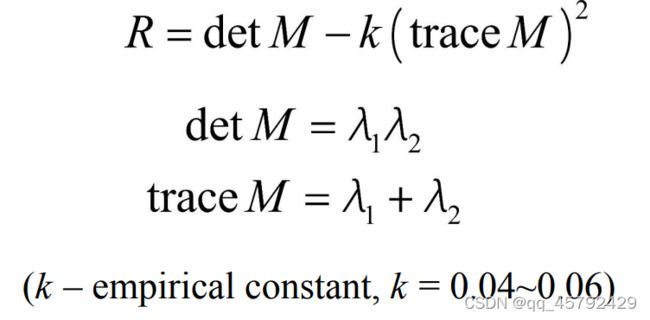
我们将上面的区域划分换一种划分方式,则为:
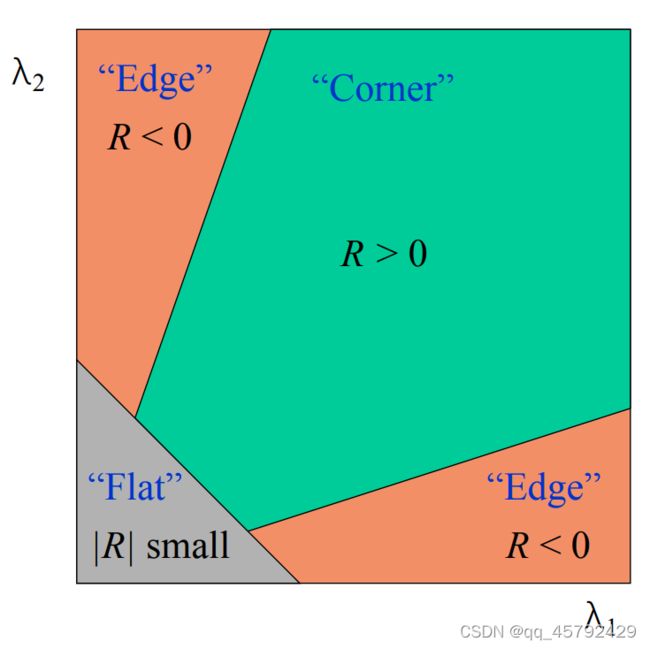
我们可以看到:
在角点时:R为大叔之正数
在边缘点时:R为大数值负数
在平坦区时:R为小数值
3、角点计算流程
- 对角点响应函数R进行阈值处理
R>threshold - 提取R的局部极大值
4、算法实现
4.1 角点响应函数
from scipy.ndimage import filters
def compute_harris_response(im,sigma=3):
""" Compute the Harris corner detector response function
for each pixel in a graylevel image. """
imx = zeros(im.shape)
filters.gaussian_filter(im, (sigma,sigma), (0,1), imx)
imy = zeros(im.shape)
filters.gaussian_filter(im, (sigma,sigma), (1,0), imy)
Wxx = filters.gaussian_filter(imx*imx,sigma)
Wxy = filters.gaussian_filter(imx*imy,sigma)
Wyy = filters.gaussian_filter(imy*imy,sigma)
Wdet = Wxx*Wyy - Wxy**2
Wtr = Wxx + Wyy
return Wdet / (Wtr*Wtr)
4.2 筛选角点
def get_harris_points(harrisim,min_dist=10,threshold=0.1):
# find top corner candidates above a threshold
corner_threshold = harrisim.max() * threshold
harrisim_t = (harrisim > corner_threshold) * 1
# get coordinates of candidates
coords = array(harrisim_t.nonzero()).T
# ...and their values
candidate_values = [harrisim[c[0],c[1]] for c in coords]
# sort candidates
index = argsort(candidate_values)
# store allowed point locations in array
allowed_locations = zeros(harrisim.shape)
allowed_locations[min_dist:-min_dist,min_dist:-min_dist] = 1
# select the best points taking min_distance into account
filtered_coords = []
for i in index:
if allowed_locations[coords[i,0],coords[i,1]] == 1:
filtered_coords.append(coords[i])
allowed_locations[(coords[i,0]-min_dist):(coords[i,0]+min_dist),
(coords[i,1]-min_dist):(coords[i,1]+min_dist)] = 0
return filtered_coords
4.3 显示角点
def plot_harris_points(image,filtered_coords):
figure()
gray()
imshow(image)
plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords],
[p[0] for p in filtered_coords],'*')
axis('off')
show()
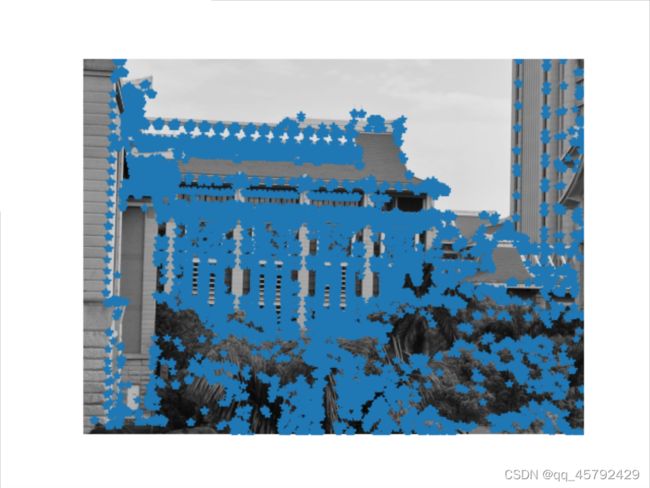
4.4 结果显示
5. 寻找对应点
5.1 兴趣点描述子
分配给兴趣点的一个向量,描述该点附近的图像的表观信息。描述子约到,寻找到的对应点越好。描述子通常是由周围图像像素块的灰度值,以及用于比较归一互相关矩阵构成的。
5.1.1 获取图像像素块,并使用归一化的互相关矩阵进行比较
def get_descriptors(image,filtered_coords,wid=5):
desc = []
for coords in filtered_coords:
patch = image[coords[0]-wid:coords[0]+wid+1,
coords[1]-wid:coords[1]+wid+1].flatten()
desc.append(patch)
return desc
def match(desc1,desc2,threshold=0.5):
n = len(desc1[0])
# pair-wise distances
d = -ones((len(desc1),len(desc2)))
for i in range(len(desc1)):
for j in range(len(desc2)):
d1 = (desc1[i] - mean(desc1[i])) / std(desc1[i])
d2 = (desc2[j] - mean(desc2[j])) / std(desc2[j])
ncc_value = sum(d1 * d2) / (n-1)
if ncc_value > threshold:
d[i,j] = ncc_value
ndx = argsort(-d)
matchscores = ndx[:,0]
return matchscores
def match_twosided(desc1,desc2,threshold=0.5):
matches_12 = match(desc1,desc2,threshold)
matches_21 = match(desc2,desc1,threshold)
ndx_12 = where(matches_12 >= 0)[0]
# remove matches that are not symmetric
for n in ndx_12:
if matches_21[matches_12[n]] != n:
matches_12[n] = -1
return matches_12
匹配点可视化
def appendimages(im1,im2):
# select the image with the fewest rows and fill in enough empty rows
rows1 = im1.shape[0]
rows2 = im2.shape[0]
if rows1 < rows2:
im1 = concatenate((im1,zeros((rows2-rows1,im1.shape[1]))),axis=0)
elif rows1 > rows2:
im2 = concatenate((im2,zeros((rows1-rows2,im2.shape[1]))),axis=0)
# if none of these cases they are equal, no filling needed.
return concatenate((im1,im2), axis=1)
def plot_matches(im1,im2,locs1,locs2,matchscores,show_below=True):
im3 = appendimages(im1,im2)
if show_below:
im3 = vstack((im3,im3))
imshow(im3)
cols1 = im1.shape[1]
for i,m in enumerate(matchscores):
if m>0:
plot([locs1[i][1],locs2[m][1]+cols1],[locs1[i][0],locs2[m][0]],'c')
axis('off')
结果显示
三、SIFT算法
1、产生
David G.Lowe教授总结了基于特征不变技术的检测方法,在图像尺度空间基础上,提出对图像缩放、旋转保存不变性的图像局部特征描述算子–SIFT,即尺度不变特征变换。
SIFT算法可以解决以下问题:
- 目标的旋转、缩放、平移
- 图像仿射/投影变换
- 弱光照影响
- 部分目标遮挡
- 杂物场景
- 噪声
2、了解
实质可以归为在不同尺度空间商查找特征点(关键点)的问题
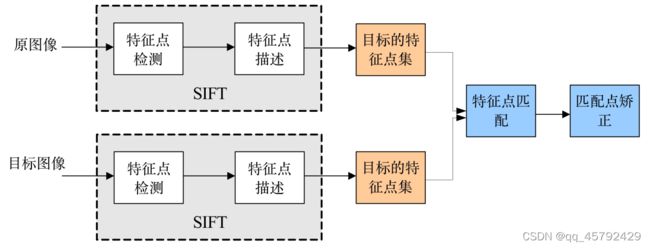
流程如下:
- 提取关键点
- 对关键点附加详细信息(局部特征),即描述符
- 通过特征点(附带上特征向量的关键点)的两两比较找出相互匹配的若干对特征点,建立对应关系
SIFT要查找的点是一些十分突出的点,不会因光照、尺度、旋转等因素的改变而消失 ,比如:角点、边缘点、暗区域的点以及亮区域的暗点。也就是说SIFT希望选出在尺度、旋转、亮度都具有不变性的点
主要思想是通过对原始图像进行尺度变换,获得图像多尺度下的空间表示。从而实现边缘、角点检测和不同分辨率上的特征提取,以满足特征点的尺度不变性。尺度越大图像越模糊。

2.1 兴趣点
DoG高斯差分金字塔:对应DOG算子,需构建DOG金字塔
通过高斯差分图像看出图像上的像素值变化情况。如果没有变化,也就没有特征。特征必须是变化尽可能多的点。DOG图像描绘的是目标轮廓。

DOG的局部极值点:特征点是由DOG空间得局部极值点组成的。每一个像素点要和它所有的相邻点比较,看其是否比它的图像域和尺度域的相邻点大或者小。
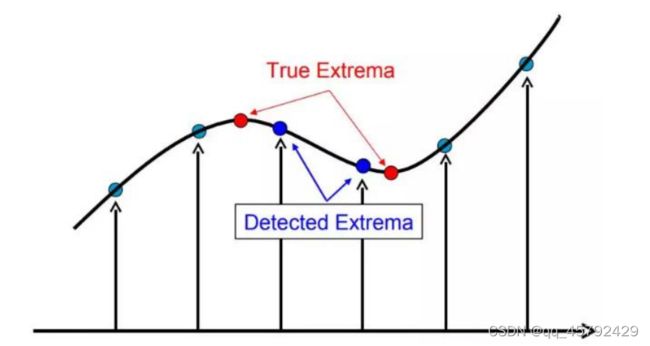
中间的监测点和它同尺度的8个相邻点和上下相邻尺度对应的9×2个点共26个点比较,以确保在尺度空间和二维图像空间都检测到极值点。
去除边缘响应DOG函数在图像边缘有较强的边缘响应。DOG函数的峰值点在边缘方向有较大的主曲率,在垂直边缘的方向有较小的主曲率。主曲率可以通过计算在该点位置尺度的2×2的Hessian矩阵得到。
2.2 描述子
为了实现旋转不变性,基于每个点周围图像梯度的方向和大小。SIFT描述子又引入参考方向。SIFT描述子使用主方向描述参考方向。
2.3 检测兴趣点
使用开源工具包VLFeat提供的二进制文件来计算图像的SIFT特征。代码如下:
def process_image(imagename,resultname,params="--edge-thresh 10 --peak-thresh 5"):
if imagename[-3:] != 'pgm':
# create a pgm file
im = Image.open(imagename).convert('L')
im.save('tmp.pgm')
imagename = 'tmp.pgm'
cmmd = str("sift "+imagename+" --output="+resultname+
" "+params)
os.system(cmmd)
print ('processed', imagename, 'to', resultname)
#读取特征数值到数值
def read_features_from_file(filename):
f = loadtxt(filename)
return f[:,:4],f[:,4:]
#输出结构保存到特征图片
def write_features_to_file(filename,locs,desc):
savetxt(filename,hstack((locs,desc)))
#可视化
def plot_features(im,locs,circle=False):
def draw_circle(c,r):
t = arange(0,1.01,.01)*2*pi
x = r*cos(t) + c[0]
y = r*sin(t) + c[1]
plot(x,y,'b',linewidth=2)
imshow(im)
if circle:
for p in locs:
draw_circle(p[:2],p[2])
else:
plot(locs[:,0],locs[:,1],'ob')
axis('off')
结果显示:
待续。。。
2.4 匹配描述子
一图像中的特征匹配到另一幅图像的特征,使用两个特征距离和两个最匹配特征距离的比率。相对于图像的其他特征,该准则保证能够找到足够相似的唯一特征。能够降低错误的匹配数。
代码:
def match(desc1,desc2):
desc1 = array([d/linalg.norm(d) for d in desc1])
desc2 = array([d/linalg.norm(d) for d in desc2])
dist_ratio = 0.6
desc1_size = desc1.shape
matchscores = zeros((desc1_size[0]),'int')
desc2t = desc2.T # precompute matrix transpose
for i in range(desc1_size[0]):
dotprods = dot(desc1[i,:],desc2t) # vector of dot products
dotprods = 0.9999*dotprods
# inverse cosine and sort, return index for features in second image
indx = argsort(arccos(dotprods))
# check if nearest neighbor has angle less than dist_ratio times 2nd
if arccos(dotprods)[indx[0]] < dist_ratio * arccos(dotprods)[indx[1]]:
matchscores[i] = int(indx[0])
return matchscores
该函数使用描述子向量间的家教作为距离度量。但是我们需要将描述子向量归一化到单位长度。因为匹配是单向的,所以我们可以先计算第二幅图兴趣点描述子向量的装置矩阵。
为了增加匹配的稳健性,我们可以再反过来执行一次该步骤,从第二幅图象中的特征向第一幅图像中的特征匹配。最后,我们保留同时满足这两种匹配准则的对应。代码如下:
def match_twosided(desc1,desc2):
matches_12 = match(desc1,desc2)
matches_21 = match(desc2,desc1)
ndx_12 = matches_12.nonzero()[0]
# remove matches that are not symmetric
for n in ndx_12:
if matches_21[int(matches_12[n])] != n:
matches_12[n] = 0
return matches_12
结果显示:
待续。。。
四、匹配地理标记图像
1、下载地理标记图像
从Panoramio下载图像,其提供了一个API接口
import os
import urllib, urlparse
import json
# query for images
url = 'http://www.panoramio.com/map/get_panoramas.php?order=popularity&set=public&from=0&to=20&minx=-77.037564&miny=38.896662&maxx=-77.035564&maxy=38.898662&size=medium'
c = urllib.urlopen(url)
# get the urls of individual images from JSON
j = json.loads(c.read())
imurls = []
for im in j['photos']:
imurls.append(im['photo_file_url'])
# download images
for url in imurls:
image = urllib.URLopener()
image.retrieve(url, os.path.basename(urlparse.urlparse(url).path))
print 'downloading:', url
2、使用局部描述子匹配
对图像进行SIFT特征处理后,将特征保存,使用下列代码进行逐个匹配
3、可视化连接的图像
使用pydot工具包进行可视化连接。
创建一个图,图表示深度为2的树,具有5个分支,将分支添加到分支节点上
当匹配的数目高于一个阈值,使用边来连接相应的图像节点。
from pylab import *
from numpy import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.tools import imtools
import pydot
download_path = "panoimages" # set this to the path where you downloaded the panoramio images
path = "/FULLPATH/panoimages/" # path to save thumbnails (pydot needs the full system path)
# list of downloaded filenames
imlist = imtools.get_imlist(download_path)
nbr_images = len(imlist)
# extract features
featlist = [imname[:-3]+'sift' for imname in imlist]
for i,imname in enumerate(imlist):
sift.process_image(imname, featlist[i])
matchscores = zeros((nbr_images,nbr_images))
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i,nbr_images): # only compute upper triangle
print 'comparing ', imlist[i], imlist[j]
l1,d1 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
l2,d2 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[j])
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1,d2)
nbr_matches = sum(matches > 0)
print 'number of matches = ', nbr_matches
matchscores[i,j] = nbr_matches
# copy values
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i+1,nbr_images): # no need to copy diagonal
matchscores[j,i] = matchscores[i,j]
threshold = 2 # min number of matches needed to create link
g = pydot.Dot(graph_type='graph') # don't want the default directed graph
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i+1,nbr_images):
if matchscores[i,j] > threshold:
# first image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[i])
im.thumbnail((100,100))
filename = path+str(i)+'.png'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(i),fontcolor='transparent',shape='rectangle',image=filename))
# second image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[j])
im.thumbnail((100,100))
filename = path+str(j)+'.png'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(j),fontcolor='transparent',shape='rectangle',image=filename))
g.add_edge(pydot.Edge(str(i),str(j)))
g.write_png('whitehouse.png')