2 TensorFlow入门笔记之建造神经网络并将结果可视化
————————————————————————————————————
写在开头:此文参照莫烦python教程(墙裂推荐!!!)
————————————————————————————————————
TensorFlow之建造第一个神经网络
1 定义添加层
import tensorflow as tf
def add_layer(inputs,in_size,out_size,activation_function=None):
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size,out_size]))#用随机数来初始化Weights,这比全部为0要好,int_size行,out_size列
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,out_size])+0.1) #1行,out_size列,均为0.1
Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs,Weights) + biases #预测出来但还没激活的值
if activation_function is None: #如果没有激活函数,则返回预测原值
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b) #否则,返回预测值激活之后的值
return outputs2 建立神经网络结构
import numpy as np
#生成数据
x_data = np.linspace(-1,1,300)[:,np.newaxis] #有300行,即一个特性,300个对象
noise = np.random.normal(0,0.05,x_data.shape) #加入噪音,用期望为0、方差为0.05的正态分布的随机数来建立
y_data = np.square(x_data)-0.5 + noise
#将输入数据和输出数据定义为placeholder
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1]) #1为属性数,None为随意数都行
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1])
#第一层layer,即输入层,这里只有一个神经元
#第二层layer,即隐藏层,这里定义10个神经元
#第三层layer,这里为输出层,这里有一个神经元
#下面增加第二层,即这里的隐藏层
l1 = add_layer(xs,1,10,activation_function=tf.nn.relu)
#下面定义输出层
prediction = add_layer(l1,10,1,activation_function=None)
#计算损失
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys -prediction),reduction_indices=[1]))#求和之后求平均
#训练
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss) #学习效率为0.1,学习效率一般小于1
#初始所有变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
for i in range(1000):
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={xs:x_data,ys:y_data})
if i % 50 == 0:
print(sess.run(loss,feed_dict={xs:x_data,ys:y_data})) #打印误差,如果误差不断减小,则模型有不断学习0.32276458
0.012201915
0.0066840313
0.0057683536
0.0053448635
0.0050948677
0.004914441
0.004781631
0.0046798103
0.0046042935
0.004543632
0.0044809543
0.0044029644
0.0042897784
0.004155126
0.004016761
0.0038873414
0.003766319
0.0036393174
0.0035409257
由上面结果可知,误差是越来越小的。这说明,这个网络是在不断学习的
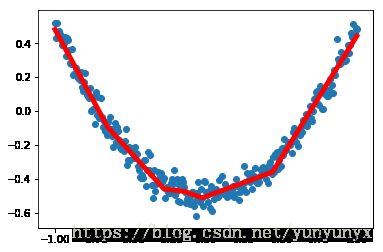
3 结果可视化
#在上面的for之前加入一些绘图的代码,如下:
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #结果可视化所用
#加入绘图代码,先打印x_data和y_data
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
ax.scatter(x_data,y_data)
plt.ion() #使show()后不会暂停程序
#plt.show()
for i in range(1000):
#训练
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={xs:x_data,ys:y_data})
if i % 50 == 0:
#print(sess.run(loss,feed_dict={xs:x_data,ys:y_data})) #打印误差,如果误差不断减小,则模型有不断学习
try:
ax.lines.remove(lines[0])
except Exception:
pass
prediction_value = sess.run(prediction,feed_dict={xs:x_data}) #计算预测值
lines = ax.plot(x_data,prediction_value,'r-',lw = 5) #绘制预测值的曲线,红色,线框为5
#ax.lines.remove(lines[0]) #抹除掉第一个线段
plt.pause(1) #暂停1秒这里应该是有一条红色的线在不断拟合这些蓝点的。这里只显示了最后一条红色的线
4 加速神经网络
- SGD:把数据分块,每次使用批量数据。虽然损失了一点精度,但速度大大加快了
- Mmomentum:在更新W权值时加速。公式如下:
m = b1*m - learning rate * dx;
W += m - AdaGrad:在更新W权值时加速。公式如下:
v += pow(dx,2)
W += -Learning rate * dx /sqrt(v) - RMSProp:在更新W权值时加速。公式如下:
v = b1*v + (1-b1)*pow(dx,2)
W += -Learning rate * dx/sqrt(v) - Adam:在更新W权值时加速。公式如下:(又快又好)
m = b1*m +(1-b1)*dx
v = b2*v + (1-b2)*pow(dx,2)
W += -Learning tate *m/sqrt(v)
5 Optimizer优化器
TensorFlow有很多优化器,可以去tensorflow的官网查询
#这里列出几种优化器:
tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer #初级常用
tf.train.AdadeltaOptimizer
tf.train.AdagradOptimizer
tf.train.MomentumOptimizer #常用
tf.train.AdamOptimizer #常用
tf.train.FtrlOptimizer
tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer #常用6 网络可视化工具:tensorboard
利用Tensorboard,可以很好的画出我们的网络结构。下面以上面的例子为例,实践一下。
#把上面的代码copy下来先
import tensorflow as tf
def add_layer(inputs,in_size,out_size,activation_function=None):
with tf.name_scope('layer'): #加入名字
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size,out_size]))#用随机数来初始化Weights,这比全部为0要好,int_size行,out_size列
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,out_size])+0.1) #1行,out_size列,均为0.1
with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'):
Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs,Weights) + biases #预测出来但还没激活的值
if activation_function is None: #如果没有激活函数,则返回预测原值
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b) #否则,返回预测值激活之后的值
return outputs
import numpy as np
x_data = np.linspace(-1,1,300)[:,np.newaxis]
noise = np.random.normal(0,0.05,x_data.shape)
y_data = np.square(x_data)-0.5 + noise
with tf.name_scope('input'):
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1],name='x_input') #加入名字name
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1],name='y_input')
#第一层layer,即输入层,这里只有一个神经元
#第二层layer,即隐藏层,这里定义10个神经元
#第三层layer,这里为输出层,这里有一个神经元
#下面增加第二层,即这里的隐藏层
l1 = add_layer(xs,1,10,activation_function=tf.nn.relu)
#下面定义输出层
prediction = add_layer(l1,10,1,activation_function=None)
#计算损失
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys -prediction),reduction_indices=[1]),name='mean')
#训练
with tf.name_scope('train'):
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)
sess = tf.Session()
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("desktop",sess.graph)
#初始所有变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)这样桌面便出现了events.out。但我在win10下无法打开。
*点击[这儿:TensorFlow]发现更多关于TensorFlow的文章*