- HarmonyNext实战:基于ArkTS的高性能图像处理应用开发
应用开发
引言在HarmonyNext生态系统中,图像处理是一个重要且具有挑战性的领域。本文将深入探讨如何利用ArkTS语言开发一个高性能的图像处理应用,重点介绍图像卷积、边缘检测等核心算法的实现。我们将从理论基础出发,逐步构建一个完整的图像处理应用,并通过优化技巧提升性能。图像处理基础1.1图像表示在数字图像处理中,图像通常被表示为一个二维矩阵,每个元素代表一个像素的灰度值或颜色值。在HarmonyNex
- HarmonyNext实战:基于ArkTS的高性能图像处理应用开发
harmonyos-next
HarmonyNext实战:基于ArkTS的高性能图像处理应用开发引言在HarmonyNext生态系统中,图像处理是一个重要且具有挑战性的领域。本文将深入探讨如何利用ArkTS语言开发一个高性能的图像处理应用,重点介绍图像卷积、边缘检测等核心算法的实现。我们将从理论基础出发,逐步构建一个完整的图像处理应用,并通过优化技巧提升性能。1.图像处理基础1.1图像表示在数字图像处理中,图像通常被表示为一个
- 图像处理与机器视觉
Be_auto
图像处理计算机视觉
1.图像处理与机器视觉的概念图像处理(ImageProcessing)是对图像进行分析、增强、变换等操作以改善图像质量或提取有用信息的过程。它通常涉及数字图像处理技术,包括滤波、边缘检测、图像分割、特征提取等。图像处理的目标可以是增强图像的视觉效果,或者使图像更适合于某种特定的机器分析。详细解释图文处理,就像是给照片和文档“化妆”和“打扮”一样。它可不是简单的涂抹或者穿衣搭配,而是需要掌握一系列“
- 常用图像增强算法原理及 OpenCV C++ 实现
埃菲尔铁塔_CV算法
opencv计算机视觉人工智能c++算法机器学习
一、引言图像增强是数字图像处理中的一个重要分支,其目的是改善图像的视觉效果,突出图像中的重要信息,或者将图像转换为更适合人或机器分析处理的形式。在实际应用中,图像增强技术广泛应用于医学影像、遥感图像、安防监控等领域。本文将详细介绍常用的图像增强算法原理,并给出基于OpenCVC++库的实现代码。二、图像增强算法分类图像增强算法可以分为空间域增强和频域增强两大类。空间域增强是直接对图像的像素值进行操
- (图像梯度处理、图像边缘化检测、图像轮廓查找和绘制、透视变换、举例轮廓的外接边界框)
GWY_uu
计算机视觉人工智能图像处理
梯度处理的Sobel算子函数功能:Sobel算子是一种用于边缘检测的梯度计算方法,它通过计算图像在水平方向和垂直方向上的梯度来增强边缘信息。参数:src:输入图像。ddepth:输出图像的深度,通常选择为CV_16S以避免溢出。dx和dy:分别指定是否对x轴或y轴求导数,0表示不求导,1表示求一阶导数。ksize(可选):使用的Sobel核大小,默认为3。返回值:经过Sobel算子处理后的图像,通
- 彻底理解数字图像处理中的卷积-以Sobel算子为例
守得云开现月明
图像处理图像处理
链接:原文出处作者:FreeBlues概述卷积在信号处理领域有极其广泛的应用,也有严格的物理和数学定义.本文只讨论卷积在数字图像处理中的应用.在数字图像处理中,有一种基本的处理方法:线性滤波.待处理的平面数字图像可被看做一个大矩阵,图像的每个像素对应着矩阵的每个元素,假设我们平面的分辨率是1024*768,那么对应的大矩阵的行数=1024,列数=768.用于滤波的是一个滤波器小矩阵(也叫卷积核),
- OpenCV-Python实战(4)——OpenCV常见图像处理技术_opencv图像处理实战简答
2401_84281648
程序员opencvpython图像处理
OpenCV-Python实战(4)——OpenCV常见图像处理技术0.前言1.拆分与合并通道2.图像的几何变换2.1缩放图像2.2平移图像2.3旋转图像2.4图像的仿射变换2.5图像的透视变换2.6裁剪图像3.图像滤波如何自学黑客&网络安全黑客零基础入门学习路线&规划初级黑客1、网络安全理论知识(2天)①了解行业相关背景,前景,确定发展方向。②学习网络安全相关法律法规。③网络安全运营的概念。④等
- C语言图像处理技术:从基础到高级应用
南城游子
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:C语言在图像处理领域拥有丰富的应用,涉及计算机视觉和数字信号处理。本课程深入探讨C语言进行图像处理的各项核心技术,包括像素操作、色彩模型理解、滤波算法、色彩空间转换、边缘检测、以及图像变换等。通过详细解析,学习者将掌握如何使用C语言和OpenCV库来实现高效的图像处理,并能够解决实际问题。1.像素操作与图像基本组成数字图像处理是现代计算机视觉和图像理解的基础,
- 利用 OpenCV 进行棋盘检测与透视变换
萧鼎
python基础到进阶教程opencv人工智能计算机视觉
利用OpenCV进行棋盘检测与透视变换1.引言在计算机视觉领域,棋盘检测与透视变换是一个常见的任务,广泛应用于摄像机标定、文档扫描、增强现实(AR)等场景。本篇文章将详细介绍如何使用OpenCV进行棋盘检测,并通过透视变换将棋盘区域转换为一个标准的矩形图像。我们将基于一段Python代码进行分析,代码的主要任务包括:读取图像并进行预处理(灰度转换、自适应直方图均衡化、去噪)检测边缘并提取棋盘区域计
- 基于图像处理的裂缝宽度检测系统-matlab
人工智能专属驿站
计算机视觉图像处理人工智能
图像处理技术广泛地应用于桥梁、房屋、道路等工程施工中出现的表面裂缝,利用数字图像处理技术来测量结构物表面裂缝宽度是一种无损检测方法.基于图像处理的裂缝宽度检测系统需采用的图像处理算法有:(1)读取裂缝图像;(2)图像转化为灰度图像;(3)图像的增强;(4)平滑滤波;(5)阈值分割;(6)形态学去噪;(7)边缘检测(Canny算子);(8)边缘坐标点的提取;结果见:源程序见:基于图像处理的裂缝宽度检
- LabVIEW图像水印系统
LabVIEW开发
LabVIEW开发案例计算机视觉LabVIEW开发案例
图像水印技术在数字图像处理中起着重要作用,它能够保护图像的版权、确保图像的完整性,并提供额外的信息嵌入。本项目旨在利用LabVIEW开发一个图像水印系统,实现图像水印的嵌入和提取功能,为数字图像处理提供便捷的工具。一、项目背景随着数字图像的广泛应用,图像的版权保护和信息嵌入变得尤为重要。传统的图像水印技术已经无法满足快速、高效的需求,因此需要开发一种基于LabVIEW的图像水印系统,以解决这一问题
- 用skimage学习数字图像处理(003):Skimage各模块初探(中)
Jason 2008
学习scikit-learn图像处理python计算机视觉人工智能
本节将简要介绍skimage扩展库,重点介绍各个模块的功能,大家可以将其作为一个手册来查询。这是中篇,主要介绍几个算法类的子库,包括:metrics(评价指标)、transform(几何变换)、exposure(点变换)、filter(滤波)、restoration(复原)、morphology(形态学)等模块,这些内容对应图像处理领域中的底层技术。本篇文档约8000字。目录2.3算法类模块2.3
- 音视频开发成长之路与音视频知识点总结
Linux服务器开发
音视频开发webrtcffmpeg音视频开发流媒体服务器开发webrtcFFmpeg嵌入式音视频开发
音视频涉及语音信号处理、数字图像处理、信息论、封装格式、编解码、流媒体协议、网络传输、渲染、算法等。在现实生活中,音视频发挥着越来越重要的作用,如视频会议、直播、短视频、播放器、语音聊天等。所以从事音视频开发是一件有意义的事情,机遇和挑战并存。本文将从:音视频开发基础、音视频高级成长、音视频工作方向、音视频开源库、音视频相关书籍,配套的学习资源等几个方面来进行介绍。那么我们该如何系统的学习音视频开
- python 图像特征提取_python实现LBP方法提取图像纹理特征实现分类的步骤
weixin_39969060
python图像特征提取
题目描述这篇博文是数字图像处理的大作业.题目描述:给定40张不同风格的纹理图片,大小为512*512,要求将每张图片分为大小相同的9块,利用其中的5块作为训练集,剩余的4块作为测试集,构建适当的模型实现图片的分类.图片如下图所示:分析:由于数据集太小,所以神经网络模型并不适合此类的图像处理.就需要寻找方法提取图像的纹理信息.本文采用LBP的方法提取图像的纹理信息,然后转化成直方图作为图像的特征,然
- 《OpenCV》——图像透视转换
Kai HVZ
opencv人工智能计算机视觉
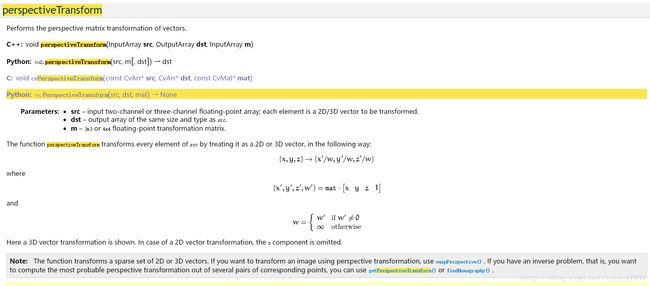
图像透视转换简介在OpenCV里,图像透视转换属于重要的几何变换,也被叫做投影变换。下面从原理、实现步骤、相关函数和应用场景几个方面为你详细介绍。原理实现步骤选取对应点:要在源图像和目标图像上分别找出至少四个对应的点。这些对应点不能共线,因为它们是计算透视变换矩阵的关键依据。计算透视变换矩阵:利用OpenCV的cv2.getPerspectiveTransform函数,依据前面选取的对应点来计算透
- [特殊字符]【计算机视觉必杀技】三行代码实现文档智能校正(附完整代码)
我的青春不太冷
计算机视觉人工智能科技学习Pythonopencv
文章目录基于四点透视变换的文档图像校正技术1.实现效果2.技术原理2.1透视变换数学模型2.2算法流程3.核心代码解析3.1.1坐标点排序3.1.2透视变换矩阵4.实验结果分析4.1中间过程可视化4.2性能指标5.应用场景5.1纸质文档电子化5.2车牌识别预处理5.3AR场景平面检测5.4工业视觉中的平面定位6.总实现代码7.结论基于四点透视变换的文档图像校正技术在计算机视觉领域,图像几何变换是实
- OpenCV中的图像处理函数详解
Luzem0319
opencv图像处理人工智能
在OpenCV中,图像处理函数是实现图像处理和计算机视觉任务的基础。下面将详细介绍六个重要的图像处理函数:二值化函数、自适应二值化函数、腐蚀函数、膨胀函数、仿射变换函数和透视变换函数。一、二值化函数功能二值化函数(cv2.threshold())用于将灰度图像转换为二值图像。二值图像中,每个像素只有两种可能的值(通常是0和255),分别代表黑色和白色。参数src:输入图像,应为灰度图像。thres
- OpenCV中的边缘检测和轮廓处理
Luzem0319
opencv人工智能计算机视觉
在图像处理和计算机视觉任务中,边缘检测和轮廓处理是非常重要的步骤。OpenCV库提供了多种函数来实现这些功能,包括Sobel算子、Laplacian算子、Canny算子、findContours函数、drawContours函数以及透视变换函数等。本文将详细介绍这些函数的功能、参数、返回值和应用。1.Sobel算子函数功能:Sobel算子用于计算图像灰度的近似梯度,梯度越大越有可能是边缘。参数:s
- 什么是ISP?
一袋米扛几楼98
cameratunningISPCameraTuning相机c++
ISP(Imagesignalprocessor)图像信号处理,用于处理图像信号传感器(sensor)输出的图像信号。广义的ISP:ISP通过一系列数字图像处理算法完成对数字图像的效果处理。主要包括坏点校正、去噪、强光抑制、背光补偿、色彩增强、镜头阴影校正等处理。ISP的控制结构上图所示,lens将光信号投射到sensor的感光区域后,sensor经过光电转换,将bayer格式的原始图像送给ISP
- 数字图像处理——matlab实现 图像灰度等级化(2个等级,4个等级,8个等级,16个等级,32个等级,64个等级,128个等级的灰度图)
miilue
实验报告图像处理MATLAB图像处理灰度等级化RGB转灰度代码实现
图像灰度等级化相关知识读者可以自行百度,本篇文章只放matlab的实现代码。在做这个实验时,在网上没有找到好用的代码,自己后来试了一些他人的方法,最后修改完善得到了该篇文章的代码,希望有所帮助。My=imread('E:\informt\lesson\数字图像处理与安全\图像集\Fruit.bmp');%读取图像MyGrayPic=rgb2gray(My);%灰度图像等级化holdon;figur
- c++介绍与入门基础(详细总结)
X_Pqk
c++开发语言
操作系统以及大型系统软件开发服务器端开发游戏开发嵌入式和物联网领域数字图像处理人工智能分布式应用C++关键字命名空间实际工程应用中:命名空间的作用:命名空间需求展示命名空间定义命名空间使用C++输入&输出c++的《helloworld》输入&输出说明:输入&输出展示std命名空间的使用惯例缺省参数缺省参数概念缺省参数分类函数重载函数重载概念C++支持函数重载的原理–名字修饰(nameManglin
- Kotlin Bytedeco OpenCV 图像图像49 仿射变换 图像裁剪
深色風信子
kotlinopencv仿射变换图像裁剪bytedecojavacpp
KotlinBytedecoOpenCV图像图像49仿射变换图像裁剪1添加依赖2测试代码3测试结果在OpenCV中,仿射变换(AffineTransformation)和透视变换(PerspectiveTransformation)是两种常用的图像几何变换方法。变换方法适用场景仿射变换简单的几何变换(平移、旋转、缩放、剪切)。透视变换改变图像视角和模拟3D投影效果。变换方法解释特点应用场景实现方法
- Kotlin Bytedeco OpenCV 图像图像55 图像透视变换
深色風信子
kotlinopencv透视变换bytedeco
KotlinBytedecoOpenCV图像图像53图像透视变换1添加依赖2测试代码3测试结果1添加依赖4.0.0com.xuKotlinOpenCV1.02.0.0UTF-8official1.8mavenCentralhttps://repo1.maven.org/maven2/cn.hutoolhutool-all5.8.29org.apache.commonscommons-compres
- MATLAB语言的计算机基础
疯狂小小小码农
包罗万象golang开发语言后端
MATLAB语言的计算机基础引言在当今信息技术飞速发展的时代,编程能力已成为当代人士必备的一项基本技能。MATLAB(矩阵实验室)作为一种高级编程语言和环境,广泛应用于数据分析、算法开发、模型创建、数字图像处理和计算机视觉等多个领域。MATLAB以其强大的矩阵运算和可视化能力,成为了科研人员和工程师的重要工具,尤其在数学、物理、工程等学科中,它的应用不可或缺。本文将从MATLAB的基本概念、环境搭
- 数字图像处理(一系列对图像进行处理、分析和改进的技术)
编程日记✧
智能医疗计算机视觉图像处理人工智能
数字图像处理是指对图像进行一系列的数学和算法处理,以增强、分析或理解图像的内容。这些处理包括从基础的像素操作到复杂的高维变换和机器学习模型。1.图像降噪在图像获取和传输过程中,往往会引入噪声。降噪技术用于减少这些噪声,同时尽量保持图像的细节。常见方法有:均值滤波:将像素邻域内的像素值取平均值,从而平滑图像。这种方法简单但可能会模糊边缘。高斯滤波:使用高斯函数为权重对像素进行加权平均,可以更好地平滑
- 基于语言的三种图像简单去噪算法:高效C++实现
m0_57781768
C语言(C++)算法研究和解读算法c++计算机视觉
基于语言的三种图像简单去噪算法:高效C++实现图像处理在现代计算机视觉中占有重要地位,而去噪处理则是图像处理的重要环节之一。本文将介绍三种基于语言的简单图像去噪算法,并提供详细的C++实现。我们将重点介绍均值滤波、中值滤波和高斯滤波三种方法,并探讨它们在图像去噪中的应用和效果。引言在数字图像处理中,噪声是不可避免的。它可能是由传感器噪声、传输错误或压缩伪影引起的。去噪的目的是在保留图像重要特征的同
- 24.7.27学习笔记
kkkkk021106
学习笔记
(按照老师发的学习计划走)先学习数字图像处理:1.单色图像0-255黑到白2.彩色图像:红绿蓝三元组的二维矩阵0-255像元(Pixel,图像元素的简称)是数字图像中最小的单元,代表图像中的一个点。每个像元都有一个特定的颜色和亮度值,组合在一起形成完整的图像。以下是关于像元的一些关键点:定义:像元是构成数字图像的基本单元。每个像元通常由多个颜色通道(如红色、绿色和蓝色)组成每个像元的颜色通常用数字
- 数字图像处理 - 形态学腐蚀
HelloZEX
数字图像处理C++图像处理opencv形态学处理
一、理论与概念讲解——从现象到本质1.1形态学概述形态学(morphology)一词通常表示生物学的一个分支,该分支主要研究动植物的形态和结构。而我们图像处理中指的形态学,往往表示的是数学形态学。下面一起来了解数学形态学的概念。数学形态学(Mathematicalmorphology)是一门建立在格论和拓扑学基础之上的图像分析学科,是数学形态学图像处理的基本理论。其基本的运算包括:二值腐蚀和膨胀、
- matlab计算正交变换,图像的正交变换matlab.pdf
大Victor
matlab计算正交变换
图像的正交变换matlab《数字图像处理》课程实验报告实验名:图像的正交变换实验1院系:自动化测试与控制系班级:1201132姓名:李丹阳学号:1120110113哈尔滨工业大学电气工程及自动化学院光电信息工程2015年12月13日一、实验原理二、实验内容三、实验结果与分析1、傅立叶变换A)绘制一个二值图像矩阵,并将其傅立叶函数可视化。(傅里叶变换A)的实验结果B)利用傅立叶变换分析两幅图像的相关
- 【教程】详解相机模型与坐标转换
小锋学长生活大爆炸
数码相机
转载请注明出处:小锋学长生活大爆炸[xfxuezhang.cn]由于复制过来,如果有格式问题,推荐大家直接去我原网站上查看:相机模型与坐标转换-生活大爆炸目录经纬度坐标系转地球直角坐标系大地直角坐标系转经纬度坐标系地理坐标系转大地直角坐标机体坐标系转地理坐标系相机坐标系转机体坐标系图像坐标系转像素坐标系相机坐标系转图像坐标系世界坐标系转相机坐标系世界坐标系转像素坐标系透视变换下的坐标转换坐标系系统
- 矩阵求逆(JAVA)利用伴随矩阵
qiuwanchi
利用伴随矩阵求逆矩阵
package gaodai.matrix;
import gaodai.determinant.DeterminantCalculation;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 矩阵求逆(利用伴随矩阵)
* @author 邱万迟
- 单例(Singleton)模式
aoyouzi
单例模式Singleton
3.1 概述 如果要保证系统里一个类最多只能存在一个实例时,我们就需要单例模式。这种情况在我们应用中经常碰到,例如缓存池,数据库连接池,线程池,一些应用服务实例等。在多线程环境中,为了保证实例的唯一性其实并不简单,这章将和读者一起探讨如何实现单例模式。 3.2
- [开源与自主研发]就算可以轻易获得外部技术支持,自己也必须研发
comsci
开源
现在国内有大量的信息技术产品,都是通过盗版,免费下载,开源,附送等方式从国外的开发者那里获得的。。。。。。
虽然这种情况带来了国内信息产业的短暂繁荣,也促进了电子商务和互联网产业的快速发展,但是实际上,我们应该清醒的看到,这些产业的核心力量是被国外的
- 页面有两个frame,怎样点击一个的链接改变另一个的内容
Array_06
UIXHTML
<a src="地址" targets="这里写你要操作的Frame的名字" />搜索
然后你点击连接以后你的新页面就会显示在你设置的Frame名字的框那里
targerts="",就是你要填写目标的显示页面位置
=====================
例如:
<frame src=&
- Struts2实现单个/多个文件上传和下载
oloz
文件上传struts
struts2单文件上传:
步骤01:jsp页面
<!--在进行文件上传时,表单提交方式一定要是post的方式,因为文件上传时二进制文件可能会很大,还有就是enctype属性,这个属性一定要写成multipart/form-data,不然就会以二进制文本上传到服务器端-->
<form action="fileUplo
- 推荐10个在线logo设计网站
362217990
logo
在线设计Logo网站。
1、http://flickr.nosv.org(这个太简单)
2、http://www.logomaker.com/?source=1.5770.1
3、http://www.simwebsol.com/ImageTool
4、http://www.logogenerator.com/logo.php?nal=1&tpl_catlist[]=2
5、ht
- jsp上传文件
香水浓
jspfileupload
1. jsp上传
Notice:
1. form表单 method 属性必须设置为 POST 方法 ,不能使用 GET 方法
2. form表单 enctype 属性需要设置为 multipart/form-data
3. form表单 action 属性需要设置为提交到后台处理文件上传的jsp文件地址或者servlet地址。例如 uploadFile.jsp 程序文件用来处理上传的文
- 我的架构经验系列文章 - 前端架构
agevs
JavaScriptWeb框架UIjQuer
框架层面:近几年前端发展很快,前端之所以叫前端因为前端是已经可以独立成为一种职业了,js也不再是十年前的玩具了,以前富客户端RIA的应用可能会用flash/flex或是silverlight,现在可以使用js来完成大部分的功能,因此js作为一门前端的支撑语言也不仅仅是进行的简单的编码,越来越多框架性的东西出现了。越来越多的开发模式转变为后端只是吐json的数据源,而前端做所有UI的事情。MVCMV
- android ksoap2 中把XML(DataSet) 当做参数传递
aijuans
android
我的android app中需要发送webservice ,于是我使用了 ksop2 进行发送,在测试过程中不是很顺利,不能正常工作.我的web service 请求格式如下
[html]
view plain
copy
<Envelope xmlns="http://schemas.
- 使用Spring进行统一日志管理 + 统一异常管理
baalwolf
spring
统一日志和异常管理配置好后,SSH项目中,代码以往散落的log.info() 和 try..catch..finally 再也不见踪影!
统一日志异常实现类:
[java]
view plain
copy
package com.pilelot.web.util;
impor
- Android SDK 国内镜像
BigBird2012
android sdk
一、镜像地址:
1、东软信息学院的 Android SDK 镜像,比配置代理下载快多了。
配置地址, http://mirrors.neusoft.edu.cn/configurations.we#android
2、北京化工大学的:
IPV4:ubuntu.buct.edu.cn
IPV4:ubuntu.buct.cn
IPV6:ubuntu.buct6.edu.cn
- HTML无害化和Sanitize模块
bijian1013
JavaScriptAngularJSLinkySanitize
一.ng-bind-html、ng-bind-html-unsafe
AngularJS非常注重安全方面的问题,它会尽一切可能把大多数攻击手段最小化。其中一个攻击手段是向你的web页面里注入不安全的HTML,然后利用它触发跨站攻击或者注入攻击。
考虑这样一个例子,假设我们有一个变量存
- [Maven学习笔记二]Maven命令
bit1129
maven
mvn compile
compile编译命令将src/main/java和src/main/resources中的代码和配置文件编译到target/classes中,不会对src/test/java中的测试类进行编译
MVN编译使用
maven-resources-plugin:2.6:resources
maven-compiler-plugin:2.5.1:compile
&nbs
- 【Java命令二】jhat
bit1129
Java命令
jhat用于分析使用jmap dump的文件,,可以将堆中的对象以html的形式显示出来,包括对象的数量,大小等等,并支持对象查询语言。 jhat默认开启监听端口7000的HTTP服务,jhat是Java Heap Analysis Tool的缩写
1. 用法:
[hadoop@hadoop bin]$ jhat -help
Usage: jhat [-stack <bool&g
- JBoss 5.1.0 GA:Error installing to Instantiated: name=AttachmentStore state=Desc
ronin47
进到类似目录 server/default/conf/bootstrap,打开文件 profile.xml找到: Xml代码<bean
name="AttachmentStore"
class="org.jboss.system.server.profileservice.repository.AbstractAtta
- 写给初学者的6条网页设计安全配色指南
brotherlamp
UIui自学ui视频ui教程ui资料
网页设计中最基本的原则之一是,不管你花多长时间创造一个华丽的设计,其最终的角色都是这场秀中真正的明星——内容的衬托
我仍然清楚地记得我最早的一次美术课,那时我还是一个小小的、对凡事都充满渴望的孩子,我摆放出一大堆漂亮的彩色颜料。我仍然记得当我第一次看到原色与另一种颜色混合变成第二种颜色时的那种兴奋,并且我想,既然两种颜色能创造出一种全新的美丽色彩,那所有颜色
- 有一个数组,每次从中间随机取一个,然后放回去,当所有的元素都被取过,返回总共的取的次数。写一个函数实现。复杂度是什么。
bylijinnan
java算法面试
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
/**
* http://weibo.com/1915548291/z7HtOF4sx
* #面试题#有一个数组,每次从中间随机取一个,然后放回去,当所有的元素都被取过,返回总共的取的次数。
* 写一个函数实现。复杂度是什么
- struts2获得request、session、application方式
chiangfai
application
1、与Servlet API解耦的访问方式。
a.Struts2对HttpServletRequest、HttpSession、ServletContext进行了封装,构造了三个Map对象来替代这三种对象要获取这三个Map对象,使用ActionContext类。
----->
package pro.action;
import java.util.Map;
imp
- 改变python的默认语言设置
chenchao051
python
import sys
sys.getdefaultencoding()
可以测试出默认语言,要改变的话,需要在python lib的site-packages文件夹下新建:
sitecustomize.py, 这个文件比较特殊,会在python启动时来加载,所以就可以在里面写上:
import sys
sys.setdefaultencoding('utf-8')
&n
- mysql导入数据load data infile用法
daizj
mysql导入数据
我们常常导入数据!mysql有一个高效导入方法,那就是load data infile 下面来看案例说明
基本语法:
load data [low_priority] [local] infile 'file_name txt' [replace | ignore]
into table tbl_name
[fields
[terminated by't']
[OPTI
- phpexcel导入excel表到数据库简单入门示例
dcj3sjt126com
PHPExcel
跟导出相对应的,同一个数据表,也是将phpexcel类放在class目录下,将Excel表格中的内容读取出来放到数据库中
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
set_time_limit(0);
?>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type"
- 22岁到72岁的男人对女人的要求
dcj3sjt126com
22岁男人对女人的要求是:一,美丽,二,性感,三,有份具品味的职业,四,极有耐性,善解人意,五,该聪明的时候聪明,六,作小鸟依人状时尽量自然,七,怎样穿都好看,八,懂得适当地撒娇,九,虽作惊喜反应,但看起来自然,十,上了床就是个无条件荡妇。 32岁的男人对女人的要求,略作修定,是:一,入得厨房,进得睡房,二,不必服侍皇太后,三,不介意浪漫蜡烛配盒饭,四,听多过说,五,不再傻笑,六,懂得独
- Spring和HIbernate对DDM设计的支持
e200702084
DAO设计模式springHibernate领域模型
A:数据访问对象
DAO和资源库在领域驱动设计中都很重要。DAO是关系型数据库和应用之间的契约。它封装了Web应用中的数据库CRUD操作细节。另一方面,资源库是一个独立的抽象,它与DAO进行交互,并提供到领域模型的“业务接口”。
资源库使用领域的通用语言,处理所有必要的DAO,并使用领域理解的语言提供对领域模型的数据访问服务。
- NoSql 数据库的特性比较
geeksun
NoSQL
Redis 是一个开源的使用ANSI C语言编写、支持网络、可基于内存亦可持久化的日志型、Key-Value数据库,并提供多种语言的API。目前由VMware主持开发工作。
1. 数据模型
作为Key-value型数据库,Redis也提供了键(Key)和值(Value)的映射关系。除了常规的数值或字符串,Redis的键值还可以是以下形式之一:
Lists (列表)
Sets
- 使用 Nginx Upload Module 实现上传文件功能
hongtoushizi
nginx
转载自: http://www.tuicool.com/wx/aUrAzm
普通网站在实现文件上传功能的时候,一般是使用Python,Java等后端程序实现,比较麻烦。Nginx有一个Upload模块,可以非常简单的实现文件上传功能。此模块的原理是先把用户上传的文件保存到临时文件,然后在交由后台页面处理,并且把文件的原名,上传后的名称,文件类型,文件大小set到页面。下
- spring-boot-web-ui及thymeleaf基本使用
jishiweili
springthymeleaf
视图控制层代码demo如下:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/")
public class MessageController {
private final MessageRepository messageRepository;
@Autowired
public MessageController(Mes
- 数据源架构模式之活动记录
home198979
PHP架构活动记录数据映射
hello!架构
一、概念
活动记录(Active Record):一个对象,它包装数据库表或视图中某一行,封装数据库访问,并在这些数据上增加了领域逻辑。
对象既有数据又有行为。活动记录使用直截了当的方法,把数据访问逻辑置于领域对象中。
二、实现简单活动记录
活动记录在php许多框架中都有应用,如cakephp。
<?php
/**
* 行数据入口类
*
- Linux Shell脚本之自动修改IP
pda158
linuxcentosDebian脚本
作为一名
Linux SA,日常运维中很多地方都会用到脚本,而服务器的ip一般采用静态ip或者MAC绑定,当然后者比较操作起来相对繁琐,而前者我们可以设置主机名、ip信息、网关等配置。修改成特定的主机名在维护和管理方面也比较方便。如下脚本用途为:修改ip和主机名等相关信息,可以根据实际需求修改,举一反三!
#!/bin/sh
#auto Change ip netmask ga
- 开发环境搭建
独浮云
eclipsejdktomcat
最近在开发过程中,经常出现MyEclipse内存溢出等错误,需要重启的情况,好麻烦。对于一般的JAVA+TOMCAT项目开发,其实没有必要使用重量级的MyEclipse,使用eclipse就足够了。尤其是开发机器硬件配置一般的人。
&n
- 操作日期和时间的工具类
vipbooks
工具类
大家好啊,好久没有来这里发文章了,今天来逛逛,分享一篇刚写不久的操作日期和时间的工具类,希望对大家有所帮助。
/*
* @(#)DataFormatUtils.java 2010-10-10
*
* Copyright 2010 BianJing,All rights reserved.
*/
package test;
impor