数据结构与算法python语言实现 Michael T.Goodrich- Chapter3&Chapter4课后习题
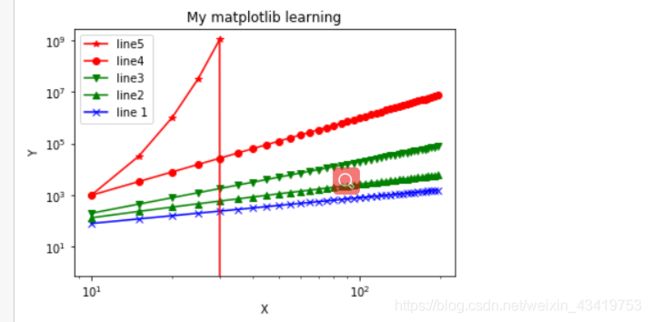
R3.1以log为坐标画出函数4n、4nlogn、2n3、n3、2n四个图形
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math
a = plt.subplot(1,1,1)
x = np.arange(10,200,5)
y2 =[4*m*math.log(m,2)for m in x]
#这里b表示blue,g表示green,r表示red,-表示连接线,--表示虚线链接
a1 = a.plot(x, 8*x, 'bx-', label = 'line 1')
a2 = a.plot(x, y2, 'g^-', label = 'line2')
a3 = a.plot(x, 2*x**2, 'gv-', label = 'line3')
a4 = a.plot(x, x**3, 'ro-', label = 'line4')
a5 = a.plot(x, 2**x, 'p
*-', label = 'line5')
#标记图的题目,x和y轴
plt.title("My matplotlib learning")
plt.xlabel("X")
plt.ylabel("Y")
#显示图例
handles, labels = a.get_legend_handles_labels()
a.legend(handles[::-1], labels[::-1])
#转换成对数坐标
plt.semilogx(2)
plt.semilogy(2)
plt.show()
R-4.1 递归算法找出序列最大值,并给出算法的时间和空间复杂度
def sum_recursive(list):
if len(list)==1:
return list[0]
return list[0] if list[0]>sum_recursive(list[1:]) else sum_recursive(list[1:])
sum_recursive([1,38,2,90])
90
算法时间复杂度O[n],空间复杂度O[n]
R-4.6计算第n个调和数
def harmonic_number(n):
if n == 1:
return 1
else:
return 1/n + harmonic_number(n-1)
harmonic_number(4)
2.083333333333333
R-4.7 将一串数字转换成整数
#R-4.7
INT_MIN = -2147483648
INT_MAX = 2147483647
def convert(s):
"""
:type str: str
:rtype: int
"""
if len(s) is 0:
return 0
c = s[0]
if c in ' ':
# greedily eat space
return self.convert(s[1:])
depth = 0
def incrementDepth():
# in languages with a ++ operator this is unnecessary
# because a++ evaluates to a (and increments a)
nonlocal depth
depth += 1
return 0
def inner(s):
nonlocal depth
if len(s) is 0:
return 0
c = s[0]
if c not in "0123456789":
return 0
# this is the magic; we need to evaluate depth AFTER
# recursing and BEFORE incrementing it
return inner(s[1:]) + 10**(depth) * (ord(c) - 48) + incrementDepth()
# non greedily eat other leading chars
if c in "-":
return max(-1 * inner(s[1:]), INT_MIN)
if c in "+":
return min(inner(s[1:]), INT_MAX)
return min(max(inner(s), INT_MIN), INT_MAX)
s = '12123'
convert(s)
12123
C-4.9用简短的递归python函数,在不使用循环的条件下查找一个序列的最小值和最大值
def getMaxMin(nums,low,high):
if low>= high:
return nums[low],nums[high]
mid = (low+high)//2
leftmax,leftmin=getMaxMin(nums,low,mid)
rightmax,rightmin=getMaxMin(nums,mid+1,high)
if leftmax<rightmax:
leftmax=rightmax
if leftmin>rightmin:
leftmin=rightmin
return [leftmax,leftmin]
nums = [10,223,18,890,23,12,142]
low =0
high = len(nums)-1
getMaxMin(nums,low,high)(nums,low,high)
输出:(890,10)
C-4.10 用递归算法计算以2为底的n的对数的整数部分
def log2(a,n = 0):
if a >=1:
if a >= 1 and a< 2:
return n
return log2(a/2,n+1)
else:
if a>= 1/2 and a<1:
return n-1
return log2(a*2,n-1)
log2(5)
2
c.14汉诺塔问题
def move(n,a,b,c):
if n == 1:
print(a,"--->",c)
else:
move(n-1,a,c,b)
print(a,"--->",c)
move(n-1,b,a,c)
move(4,'a','b','c')
a ---> b
a ---> c
b ---> c
a ---> b
c ---> a
c ---> b
a ---> b
a ---> c
b ---> c
b ---> a
c ---> a
b ---> c
a ---> b
a ---> c
b ---> c
C-4.16输出字符串的逆序以及判断是否是一个回文
def reverse(s,start,stop):
if start < stop -1:
s[start],s[stop-1] = s[stop-1],s[start]
reverse(s,start+1,stop-1)
return ''.join(s)
s = 'asdguasdga'
s = list(s)
start = 0
stop = len(s)
print(reverse(s,start,stop))
s == reverse(s,start,stop)
'agdsaugdsa'
False
C-4.19输出序列偶数值在奇数值前面
def chapter4_func19(arr,start,stop):
if stop -start <1:
return arr
if stop - start >= 1:
if arr[start] %2 ==0 and arr[stop] %2 ==0:
return chapter4_func19(arr,start+1,stop)
if arr[start] %2 == 1 and arr[stop] %2 == 1:
return chapter4_func19(arr,start,stop-1)
if arr[start] %2 == 1 and arr[stop]%2 ==0:
arr[start],arr[stop] = arr[stop],arr[start]
return chapter4_func19(arr,start+1,stop-1)
if arr[start] %2 == 0 and arr[stop] %2 == 1:
return chapter4_func19(arr,start +1 ,stop -1)
arr = [1,2,32,5,24,23,423]
start = 0
stop = len(arr) -1
chapter4_func19(arr,start,stop)
[24, 2, 32, 5, 1, 23, 423]
c-4.21用递归算法找到序列S 中总和为k的两个整数,找到输出True、否则False
def chapter4_func21(arr,start,stop,k):
if stop- start <1:
return arr[start] + arr[stop] == k
if stop -start >= 1:
if arr[stop] + arr[start] == k:
return True
if arr[start] + arr[stop] > k:
return chapter4_func21(arr,start,stop-1,k)
if arr[start] + arr[stop] <k:
return chapter4_func21(arr,start+1,stop,k)
arr = [1,3,5,6,7,120,123]
start = 0
stop = len(arr) -1
k = 178
chapter4_func21(arr,start,stop,k)
False