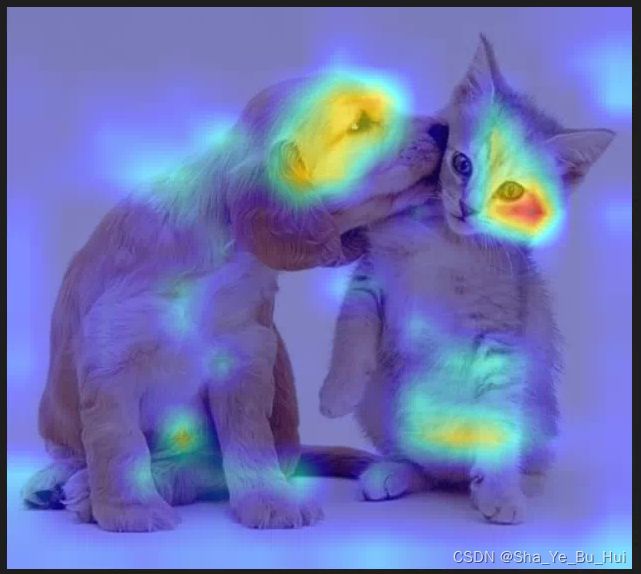
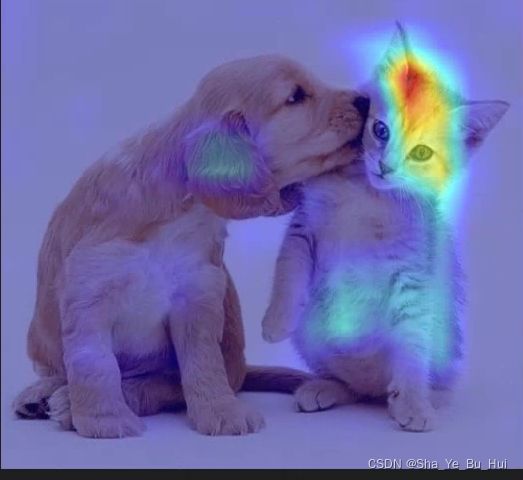
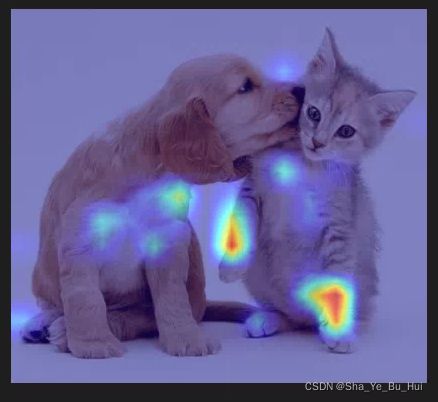
分类使用Pytorch实现Grad-CAM并绘制热力图
import os
import numpy as np
import torch
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from torchvision import models
from torchvision import transforms
import cv2
# from utils import GradCAM, show_cam_on_image, center_crop_img
activations = []
gradients = []
handles = []
def save_activation( module, input, output):
activation = output
activations.append(activation.cpu().detach())
def save_gradient(module, grad_input, grad_output):
grad = grad_output[0]
global gradients
gradients = [grad.cpu().detach()] + gradients
def get_loss(output, target_category): # 这是为了batch size != 1的情况准备的
loss = 0
for i in range(len(target_category)):
loss = loss + output[i, target_category[i]]
return loss
def scale_cam_image(cam, target_size=None):
result = []
for img in cam:
img = img - np.min(img)
img = img / (1e-7 + np.max(img))
if target_size is not None:
img = cv2.resize(img, target_size)
result.append(img)
result = np.float32(result)
return result
def aggregate_multi_layers( cam_per_target_layer):
cam_per_target_layer = np.concatenate(cam_per_target_layer, axis=1)
cam_per_target_layer = np.maximum(cam_per_target_layer, 0)
result = np.mean(cam_per_target_layer, axis=1)
return scale_cam_image(result)
def show_cam_on_image(img: np.ndarray,
mask: np.ndarray,
use_rgb: bool = False,
colormap: int = cv2.COLORMAP_JET) -> np.ndarray:
""" This function overlays the cam mask on the image as an heatmap.
By default the heatmap is in BGR format.
:param img: The base image in RGB or BGR format.
:param mask: The cam mask.
:param use_rgb: Whether to use an RGB or BGR heatmap, this should be set to True if 'img' is in RGB format.
:param colormap: The OpenCV colormap to be used.
:returns: The default image with the cam overlay.
"""
heatmap = cv2.applyColorMap(np.uint8(255 * mask), colormap)
if use_rgb:
heatmap = cv2.cvtColor(heatmap, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
heatmap = np.float32(heatmap) / 255
if np.max(img) > 1:
raise Exception(
"The input image should np.float32 in the range [0, 1]")
cam = heatmap + img
cam = cam / np.max(cam)
return np.uint8(255 * cam)
def main():
model = models.mobilenet_v3_large(pretrained=True)
# 获取最分类层之前的
target_layers = [model.features[-1]]
data_transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])
img_path = "/data/ZA/medicine/remote_sensing_image/code/tensorboard/dog.jpg"
assert os.path.exists(img_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(img_path)
img = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
img = np.array(img, dtype=np.uint8)
# img = cv2.reszie()
print(img.shape)
# [C, H, W]
img_tensor = data_transform(img)
# expand batch dimension
# [C, H, W] -> [N, C, H, W]
input_tensor = torch.unsqueeze(img_tensor, dim=0)
# target_category = 3
target_category = 254 # pug, pug-dog
for target_layer in target_layers:
handles.append(
target_layer.register_forward_hook(
save_activation
)
)
# Backward compatibility with older pytorch versions:
if hasattr(target_layer, 'register_full_backward_hook'):
handles.append(
target_layer.register_full_backward_hook(
save_gradient))
else:
handles.append(
target_layer.register_backward_hook(
save_gradient))
print(handles[0]) # 在这 现在只是一个hook的状态 所以我们所以现在来看 没有进行反向传播的时候好像什么用都没有
print(activations) # 这时候里面什么参数都没有
# forward
model.eval()
output = model(input_tensor)
# # 正向传播得到网络输出logits(未经过softmax)
target_category = [target_category] * input_tensor.size(0) # 将结果格式话
model.zero_grad() # 梯度归零
loss = get_loss(output,target_category) # 计算损失
loss.backward(retain_graph=True) # 反向传播
# print(handles) 这个时候就有了参数了
activations_list = [a.cpu().data.numpy()
for a in activations]
grads_list = [g.cpu().data.numpy()
for g in gradients]
target_size = input_tensor.size(-1), input_tensor.size(-2)
cam_per_target_layer = []
for layer_activations,layer_grads in zip(activations_list,grads_list):
weights = np.mean(layer_grads, axis=(2, 3), keepdims=True) # 使用均值作为权重
# print(weights)
weighted_activations = weights * layer_activations # 对应相乘在相加
cam = weighted_activations.sum(axis=1)
cam[cam < 0] = 0 # relu
scaled = scale_cam_image(cam, target_size)
cam_per_target_layer.append(scaled[:, None, :])
grayscale_cam = aggregate_multi_layers(cam_per_target_layer) # 将多层进行合并
grayscale_cam = grayscale_cam[0]
visualization = show_cam_on_image(img.astype(dtype=np.float32) / 255.,
grayscale_cam,
use_rgb=True)
plt.imsave("./cam.png",visualization)
# cam = GradCAM(model=model, target_layers=target_layers, use_cuda=False)
# target_category = 281 # tabby, tabby cat
# target_category = 254 # pug, pug-dog
# grayscale_cam = cam(input_tensor=input_tensor, target_category=target_category)
# grayscale_cam = grayscale_cam[0, :]
# visualization = show_cam_on_image(img.astype(dtype=np.float32) / 255.,
# grayscale_cam,
# use_rgb=True)
# plt.imsave("./cam.png",visualization)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
具体实现和细节部分 可以参考b站大神https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1e3411j7x7?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0的视频 我也就是按照他的方法来实现的
其次就是我发现的一点小问题就是感觉没有eval 要好一点
请大知道的大佬教导一下