【Android实战】保存QQ账号与密码
大家好,我是汤姆凯特。
写在前面:今天用保存QQ账号和密码的实战演练,带大家掌握Android存储中最基本的文件存储方式
文件存储是Android中最基本的一种数据存储方式,它与Java中的文件存储类似,都是通过I/O流形式把数据直接存储到文件中,下面我们一起来看一下如何用Android实现文件存储功能吧!
文章目录
-
- 1.UI界面
-
- 1)垂直线性布局为整体框架
- 2)头像获取
- 3)子线性布局编辑框和密码框
- 4)登录button按钮
- 2.构建工具类
-
- 1)将数据存入文件
- 2)从文件中读取数据
- 3.编写界面交互代码
-
- 1)读取文件
- 2)按钮监听事件
- 3)保存登录信息
- 4.运行程序
- 5.查看文件所处位置
1.UI界面
1)垂直线性布局为整体框架
2)头像获取
3)子线性布局编辑框和密码框
4)登录button按钮
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#E6E6E6"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="10dp">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="70dp"
android:layout_height="70dp"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_marginTop="30dp"
android:src="@drawable/head" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:background="@android:color/white"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="账号:"
android:textColor="#000"
android:textSize="20sp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_account"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dp"
android:background="@null"
android:padding="10dp" />
LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:background="@android:color/white"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_password"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="密码:"
android:textColor="#000"
android:textSize="20sp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_password"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dp"
android:background="@null"
android:inputType="textPassword"
android:padding="10dp" />
LinearLayout>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_login"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="25dp"
android:background="#3C8DC4"
android:text="登录"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
android:textSize="20sp" />
LinearLayout>
2.构建工具类
1)将数据存入文件
Android开发中,内部存储使用的是Context提供的openFileOutput()方法这个方法能够返回进行写操作的FileOutputStream对象,示例如下:
FileOutputStream fos = openFileOutput(String name, int mode);
其中参数name表示文件名,mode表示文件的操作模式,也就是读写文件的方式。mode的取值有4种,具体如下:
MODE_PRIVATE:该文件只能被当前程序读写MODE_APPEND:该文件的内容可以追加MODE_WORLD_READABLE:该文件的内容可以被其他程序读MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE:该文件的内容可以被其他程序写
存储数据时,使用FileOutputStream对象将数据存储到文件中,创建了一个saveUserInfo()方法,用于将QQ账号和密码保存到data.txt文件中。
//保存QQ账号和登录密码到data.txt文件中
public static boolean saveUserInfo(Context context, String account, String
password) {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
//获取文件的输出流对象fos
fos = context.openFileOutput("data.txt",
Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
//将数据转换为字节码的形式写入data.txt文件中
fos.write((account + ":" + password).getBytes());
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}finally {
try {
if(fos != null){
fos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2)从文件中读取数据
使用Context提供的openFileOutput()方法这个方法能够返回进行写操作的FileInputStream对象,示例如下:
FileInputStream fos = openFileInput(String name);
创建了一个getUserInfo()方法,用于从data.txt文件中获取QQ账号和密码。
需要注意的是,这里的存储和获取都是需要用字节码的形式,所以存取完再改为String类型。
//从data.txt文件中获取存储的QQ账号和密码
public static Map<String, String> getUserInfo(Context context) {
String content = "";
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
//获取文件的输入流对象fis
fis = context.openFileInput("data.txt");
//将输入流对象中的数据转换为字节码的形式
byte[] buffer = new byte[fis.available()];
fis.read(buffer);//通过read()方法读取字节码中的数据
content = new String(buffer); //将获取的字节码转换为字符串
Map<String, String> userMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
String[] infos = content.split(":");//将字符串以“:”分隔后形成一个数组的形式
userMap.put("account", infos[0]); //将数组中的第一个数据放入userMap集合中
userMap.put("password", infos[1]); //将数组中的第二个数据放入userMap集合中
return userMap;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}finally {
try {
if(fis != null){
fis.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3.编写界面交互代码
1)读取文件
通过工具类FileSaveQQ中的getUserInfo()方法获取QQ账号和密码信息
Map<String, String> userInfo = FileSaveQQ.getUserInfo(this);
if (userInfo != null) {
et_account.setText(userInfo.get("account")); //将获取的账号显示到界面上
et_password.setText(userInfo.get("password")); //将获取的密码显示到界面上
}
2)按钮监听事件
创建一个initView()方法,用于初始化界面控件。再对onClick()方法重写,添加点击登录事件后的响应。
private EditText et_account; //账号输入框
private EditText et_password; //密码输入框
private Button btn_login; //登录按钮
private void initView() {
et_account = findViewById(R.id.et_account);
et_password = findViewById(R.id.et_password);
btn_login = findViewById(R.id.btn_login);
//设置按钮的点击监听事件
btn_login.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.btn_login:
//当点击登录按钮时,获取界面上输入的QQ账号和密码
String account = et_account.getText().toString().trim();
String password = et_password.getText().toString();
//检验输入的账号和密码是否为空
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(account)) {
Toast.makeText(this, "请输入QQ账号", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return;
}
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(password)) {
Toast.makeText(this, "请输入密码", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return;
}
Toast.makeText(this, "登录成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
}
}
3)保存登录信息
调用工具类FileSaveQQ中的saveUserInfo()方法将登录信息保存到本地文件中。
boolean isSaveSuccess = FileSaveQQ.saveUserInfo(this, account,password);
if (isSaveSuccess) {
Toast.makeText(this, "保存成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} else {
Toast.makeText(this, "保存失败", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
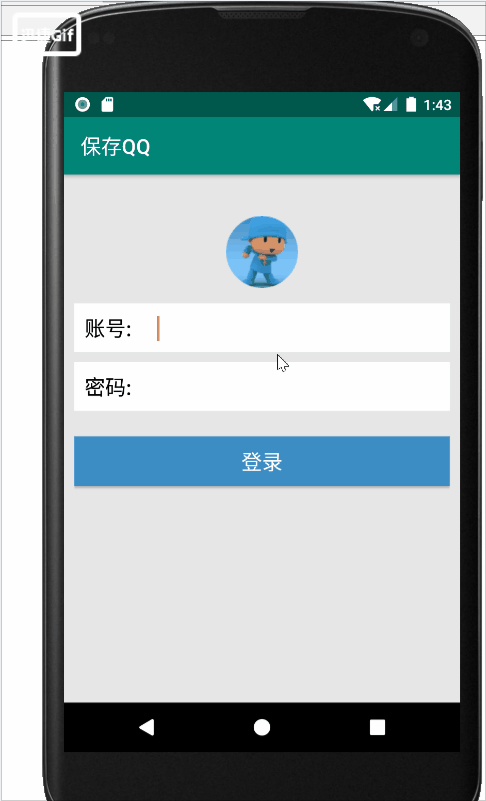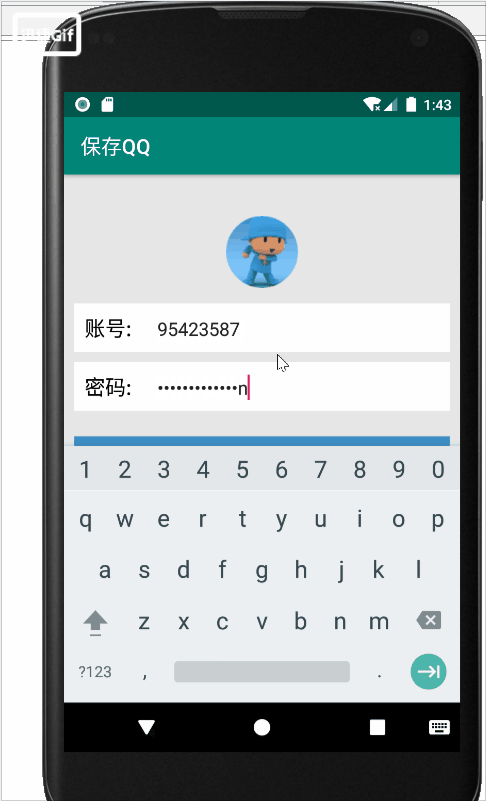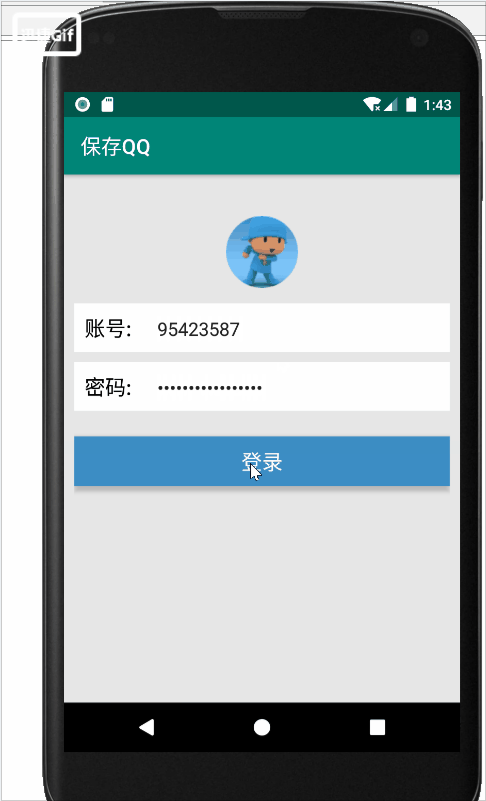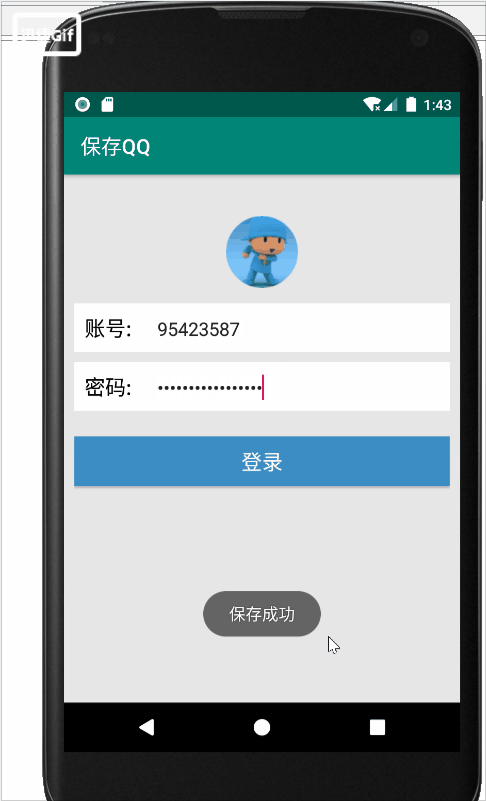
4.运行程序
在界面中输入账号和密码,点击“登录”按钮,会弹出“登录成功”与”保存成功“的提示信息
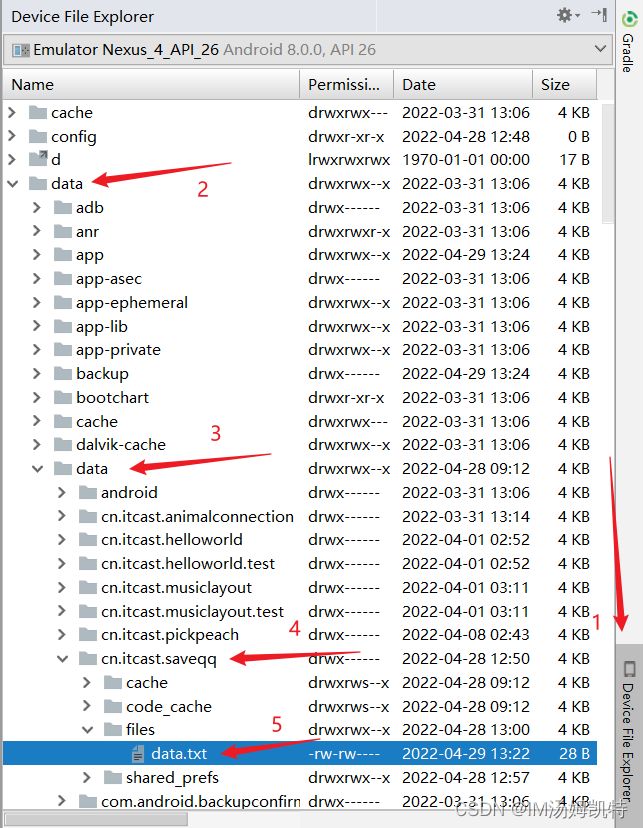
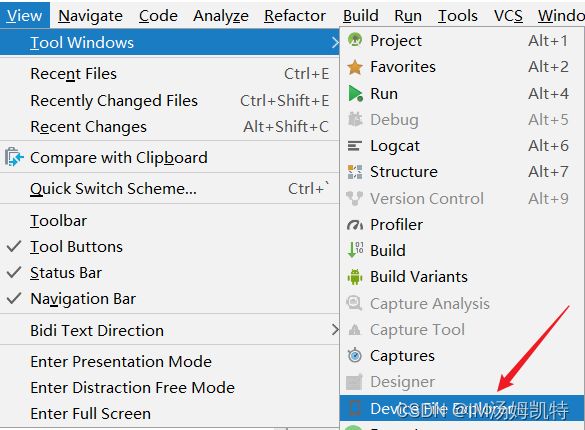
5.查看文件所处位置
1)View——Tool Windows ——Device
2)右侧的Device File Explorer ——data ——data ——项目包名——files