JavaSE09:String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder底层源码解析(纯干货)
写在前面
结束了多线程的学习后,常用类的学习立马就安排上了。在学习的过程中,发现源码是很重要的,只知道怎么用却不知道底层是很不好的,而我又太懒。看源码也是零零散散,所以本篇博客旨在鞭策自己多多阅读现阶段基础学习的源码,养成习惯,同时也能达到巩固学习内容的效果
String类解析
初识String
String的介绍


从源码的文档注释中可以看到,String类从JDK1.0就开始有了,相关的类有我们要学习的StringBuffer、StringBuilder,还有Object类的toString方法,另一个类将在io流部分再学习
附:常见注解

再来看看String继承的类,实现的接口,以及它的属性
public final class String
implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence {
/** The value is used for character storage. */
private final char value[];
/** Cache the hash code for the string */
private int hash; // Default to 0
/** use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.0.2 for interoperability */
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6849794470754667710L;
这样,我们可以知道:
1 String是一个final类,代表不可变的字符序列。
2.字符串value[]被final修饰是常量,用双引号引起来表示。它们的值在创建之后不能更改。
3.String对象的字符内容是存储在一个字符数组value[]中的。
什么是不可变字符序列呢?
举个例子
public class StringTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = new String("abc");
String b = a + "def";
System.out.println(a);//abc
System.out.println(b);//abcdef
}
}
运行结果:

我们可以看到,a在被添加"def"后自身并不会发生改变,而a又是引用数据类型。底层是在相当于重新造了个"abcdef",而不是在"abc"的基础上去添加,这就涉及到接下来提及的内存解析了。
String类的内存解析
创建String类对象的常见方式
String str1 = "deserts";//字面量定义
String str2 = new String("deserts");//构造器创建
学习面向对象后我们知道,创建类的对象需要构造器,String也不例外。而第一种以字面量形式对变量进行赋值,在内存中当然也不太一样。在进行内存解析之前,我们先来看看String的几个常用构造器。
无参构造默认创建长度为0的char[]数组
public String() {
this.value = "".value;
}
也可以传入String类对象
public String(String original) {
this.value = original.value;
this.hash = original.hash;
}
也可以传入char[]数组利用Arrays工具类进行复制
public String(char value[]) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOf(value, value.length);
}
传入char[]数组,复制从offset开始count长度的元素给String属性char[]数组,offset、count错误会报异常
public String(char value[], int offset, int count) {
if (offset < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
}
if (count <= 0) {
if (count < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);
}
if (offset <= value.length) {
this.value = "".value;
return;
}
}
// Note: offset or count might be near -1>>>1.
if (offset > value.length - count) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);
}
this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset+count);
}
传入byte[]数组,复制从offset开始count长度的元素给String属性byte[]数组,offset、count错误会报异常(用于解码)
public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length) {
checkBounds(bytes, offset, length);
this.value = StringCoding.decode(bytes, offset, length);
}
了解了几个构造器之后,我们来看看在内存中长什么样
首先来看字面量定义的方式:
String arr1 = "abc";
String arr2 = "abc";
String arr3 = "abc" + "def";
 通过简陋的图我们可以知道,常量池中值相同的内容只会存在一份,即使像str3让两个字符串拼接,也不会改变原有字符串的内容,而用字面量形式定义的String类型变量是直接指向常量池常量的地址的。
通过简陋的图我们可以知道,常量池中值相同的内容只会存在一份,即使像str3让两个字符串拼接,也不会改变原有字符串的内容,而用字面量形式定义的String类型变量是直接指向常量池常量的地址的。
那么,使用构造器创建的呢?
String arr1 = new String("abc");
String arr2 = arr1 + "def";
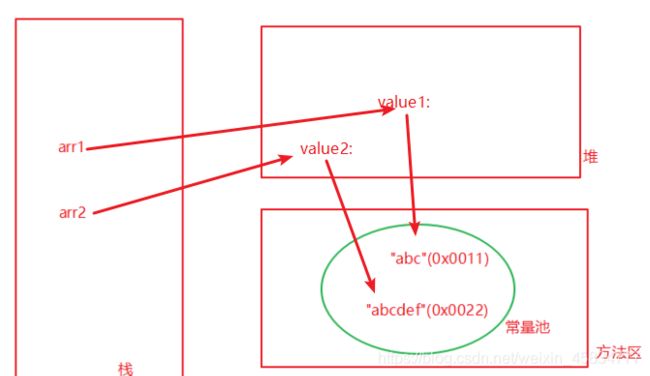 String str1 = new String(“abc”)创建了两个对象。有对象参与拼接,可以理解成在堆中创建了字符数组对象,指向常量池中的字符串常量,而str2指向堆中字符串数组value2,存的value2的地址值。
String str1 = new String(“abc”)创建了两个对象。有对象参与拼接,可以理解成在堆中创建了字符数组对象,指向常量池中的字符串常量,而str2指向堆中字符串数组value2,存的value2的地址值。
做点练习加深一下理解(==比较地址值)
String s1 = "javaEE";
String s2 = "javaEE";
String s3 = new String("javaEE");
String s4 = new String("javaEE");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//true
System.out.println(s1 == s3);//false
System.out.println(s1 == s4);//false
System.out.println(s3 == s4);//false
从源码中学习String类常用方法
int length():返回字符串的长度:
public int length() {
return value.length;
}
boolean isEmpty():判断是否是空字符串:
public boolean isEmpty() {
return value.length == 0;
}
char charAt(int index): 返回某索引处的字符
public char charAt(int index) {
if ((index < 0) || (index >= value.length)) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
return value[index];
}
public int codePointAt(int index):返回索引处字符的Unicode值
public int codePointAt(int index) {
if ((index < 0) || (index >= value.length)) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
return Character.codePointAtImpl(value, index, value.length);
}
void getChars(char dst[], int dstBegin):将该String类型对象的value[]数组复制到dst[]数组,从该数组的dstBegin开始,不提供范围检查
/**
* Copy characters from this string into dst starting at dstBegin.
* This method doesn't perform any range checking.
*/
void getChars(char dst[], int dstBegin) {
System.arraycopy(value, 0, dst, dstBegin, value.length);
}
public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char dst[], int dstBegin) :将该String类型对象的value[]数组【srcBegin,srcEnd)范围的字符串复制到dst[]数组,从dst[]数组的dstBegin开始,范围错误会报异常
/**
* Copies characters from this string into the destination character
* array.
*
* The first character to be copied is at index {@code srcBegin};
* the last character to be copied is at index {@code srcEnd-1}
* (thus the total number of characters to be copied is
* {@code srcEnd-srcBegin}). The characters are copied into the
* subarray of {@code dst} starting at index {@code dstBegin}
* and ending at index:
*
* dstBegin + (srcEnd-srcBegin) - 1
*
*
* @param srcBegin index of the first character in the string
* to copy.
* @param srcEnd index after the last character in the string
* to copy.
* @param dst the destination array.
* @param dstBegin the start offset in the destination array.
* @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException If any of the following
* is true:
* - {@code srcBegin} is negative.
*
- {@code srcBegin} is greater than {@code srcEnd}
*
- {@code srcEnd} is greater than the length of this
* string
*
- {@code dstBegin} is negative
*
- {@code dstBegin+(srcEnd-srcBegin)} is larger than
* {@code dst.length}
*/
public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char dst[], int dstBegin) {
if (srcBegin < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcBegin);
}
if (srcEnd > value.length) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd);
}
if (srcBegin > srcEnd) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd - srcBegin);
}
System.arraycopy(value, srcBegin, dst, dstBegin, srcEnd - srcBegin);
}
public byte[] getBytes():返回字节码数组
public byte[] getBytes() {
return StringCoding.encode(value, 0, value.length);
}
public boolean equals(Object anObject):比较两个String对象内容是否相同
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
int n = value.length;
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean contentEquals(StringBuffer sb) :比较与StringBuffer对象内容是否相等
public boolean contentEquals(StringBuffer sb) {
return contentEquals((CharSequence)sb);
}
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString):忽略大小写比较两个String类对象内容是否相等
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString) {
return (this == anotherString) ? true
: (anotherString != null)
&& (anotherString.value.length == value.length)
&& regionMatches(true, 0, anotherString, 0, value.length);
}
public int compareTo(String anotherString):比较与另一个String类对象的大小(字节码大小),返回差值
public int compareTo(String anotherString) {
int len1 = value.length;
int len2 = anotherString.value.length;
int lim = Math.min(len1, len2);
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int k = 0;
while (k < lim) {
char c1 = v1[k];
char c2 = v2[k];
if (c1 != c2) {
return c1 - c2;
}
k++;
}
return len1 - len2;
}
public int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) :忽略大小写比较与另一个String类对象的大小(字节码大小),返回差值
public int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) {
return CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER.compare(this, str);
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset):测试此字符串从指定索引开始的子字符串是否以指定前缀开始
public boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset) {
char ta[] = value;
int to = toffset;
char pa[] = prefix.value;
int po = 0;
int pc = prefix.value.length;
// Note: toffset might be near -1>>>1.
if ((toffset < 0) || (toffset > value.length - pc)) {
return false;
}
while (--pc >= 0) {
if (ta[to++] != pa[po++]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix):测试此字符串是否以指定的前缀开始,调用上面的方法
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return startsWith(prefix, 0);
}
public boolean endsWith(String suffix):测试此字符串是否以指定的后缀结束
public boolean endsWith(String suffix) {
return startsWith(suffix, value.length - suffix.value.length);
}
public int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) :返回该字符串中从索引位置开始某个字符的下标,找不到返回-1
public int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) {
return indexOf(value, 0, value.length,
str.value, 0, str.value.length, fromIndex);
}
public int indexOf(String str):返回指定子字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引,找不到返回-1
public int indexOf(String str) {
return indexOf(str, 0);
}
public int lastIndexOf(String str):返回指定子字符串在此字符串中最右边出现处的索引。未找到返回-1
public int lastIndexOf(String str) {
return lastIndexOf(str, value.length);
}
public int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) :返回指定子字符串在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引开始反向搜索,未找到返回-1
public int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) {
return lastIndexOf(value, 0, value.length,
str.value, 0, str.value.length, fromIndex);
}
public String substring(int beginIndex):返回一个新的字符串,它是此字符串的从beginIndex开始截取到最后的一个子字符串。
public String substring(int beginIndex) {
if (beginIndex < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);
}
int subLen = value.length - beginIndex;
if (subLen < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(subLen);
}
return (beginIndex == 0) ? this : new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);
}
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex):返回一个新字符串,它是此字符串从beginIndex开始截取到endIndex(不包含)的一个子字符串
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) {
if (beginIndex < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);
}
if (endIndex > value.length) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(endIndex);
}
int subLen = endIndex - beginIndex;
if (subLen < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(subLen);
}
return ((beginIndex == 0) && (endIndex == value.length)) ? this
: new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);
}
public String concat(String str):将指定字符串连接到此字符串的结尾。 等价于用“+”,原理是使用getChars方法建新数组
public String concat(String str) {
int otherLen = str.length();
if (otherLen == 0) {
return this;
}
int len = value.length;
char buf[] = Arrays.copyOf(value, len + otherLen);
str.getChars(buf, len);
return new String(buf, true);
}
public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar):返回一个新的字符串,它是通过用 newChar 替换此字符串中出现的所有 oldChar 得到的。
public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) {
if (oldChar != newChar) {
int len = value.length;
int i = -1;
char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */
while (++i < len) {
if (val[i] == oldChar) {
break;
}
}
if (i < len) {
char buf[] = new char[len];
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
buf[j] = val[j];
}
while (i < len) {
char c = val[i];
buf[i] = (c == oldChar) ? newChar : c;
i++;
}
return new String(buf, true);
}
}
return this;
}
public String trim():返回字符串的副本,忽略前导空白和尾部空白
public String trim() {
int len = value.length;
int st = 0;
char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */
while ((st < len) && (val[st] <= ' ')) {
st++;
}
while ((st < len) && (val[len - 1] <= ' ')) {
len--;
}
return ((st > 0) || (len < value.length)) ? substring(st, len) : this;
}
public boolean matches(String regex):告知此字符串是否匹配给定的正则表达式。
public boolean matches(String regex) {
return Pattern.matches(regex, this);
}
public boolean contains(CharSequence s):当且仅当此字符串包含指定的 char 值序列时,返回 true
public boolean contains(CharSequence s) {
return indexOf(s.toString()) > -1;
}
String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement) : 使 用 给 定 的replacement 替换此字符串匹配给定的正则表达式的第一个子字符串。
public String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement) {
return Pattern.compile(regex).matcher(this).replaceFirst(replacement);
}
String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) : 使 用 给 定 的replacement 替换此字符串所有匹配给定的正则表达式的子字符串。
public String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) {
return Pattern.compile(regex).matcher(this).replaceAll(replacement);
}
String replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement):使用指定的字面值替换序列替换此字符串所有匹配字面值目标序列的子字符串。
public String replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement) {
return Pattern.compile(target.toString(), Pattern.LITERAL).matcher(
this).replaceAll(Matcher.quoteReplacement(replacement.toString()));
}
public static String join(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence… elements) :返回一个String字符串,后面元素间隔delimiter拼接而成,如:String message = String.join("-", “Java”, “is”, “cool”); // message returned is: "Java-is-cool"
public static String join(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence... elements) {
Objects.requireNonNull(delimiter);
Objects.requireNonNull(elements);
// Number of elements not likely worth Arrays.stream overhead.
StringJoiner joiner = new StringJoiner(delimiter);
for (CharSequence cs: elements) {
joiner.add(cs);
}
return joiner.toString();
}
String toLowerCase():使用默认语言环境,将 String 中的所有字符转换为小写
public String toLowerCase() {
return toLowerCase(Locale.getDefault());
}
String toUpperCase():使用默认语言环境,将 String 中的所有字符转换为大写。跟上个方法原理有点复杂,只能等以后再回头看了
public String toUpperCase() {
return toUpperCase(Locale.getDefault());
}
public String toString() :返回整个字符串
public String toString() {
return this;
}
public static String valueOf(char data[]):返回data[]数组转换成的String类型字符串
public static String valueOf(char data[]) {
return new String(data);
}
public static String valueOf(char data[], int offset, int count) :返回data[]数组从offset开始count个字符组成的char[]数组组成的String类型字符串
public static String valueOf(char data[], int offset, int count) {
return new String(data, offset, count);
}
以下是装箱所用方法:
public static String valueOf(boolean b) {
return b ? "true" : "false";
}
public static String valueOf(char c) {
char data[] = {c};
return new String(data, true);
}
public static String valueOf(int i) {
return Integer.toString(i);
}
public static String valueOf(long l) {
return Long.toString(l);
}
public static String valueOf(float f) {
return Float.toString(f);
}
public static String valueOf(double d) {
return Double.toString(d);
}
常用方法汇集:
这些方法底层的写法需要我们了解,这样才能更好的使用,当然,也要多加练习,这样,某些情况下适当运用这些方法会有更好的解决方案。
StringBuffer、StringBuilder
为什么把两个类放在一起学习?
StringBuffer、StringBuilder两个类的方法基本相同,区别在于:StringBuffer线程安全,效率低;StringBuilder线程不安全,但是效率高。
初识StringBuffer、StringBuilder
同样,我们看看两个类的源码注释
StringBuffer


StringBuilder

 可以看到,StringBuffer从JDK1.0就有了,StringBuilder是JDK1.5新增的,它们有个共同点:都继承了各自的Abstract类并实现了两个接口,想要了解这两个类,就得从它们的抽象类开始
可以看到,StringBuffer从JDK1.0就有了,StringBuilder是JDK1.5新增的,它们有个共同点:都继承了各自的Abstract类并实现了两个接口,想要了解这两个类,就得从它们的抽象类开始
AbstractStringBuilder
以AbstractStringBuilder为例,我们来看看它们的抽象类长什么样~
概况
成员属性
/**
* The value is used for character storage.
*/
char[] value;
/**
* The count is the number of characters used.
*/
int count;
value[]数组是用来储存长度,没有用final修饰,说明它是可变的,拼接时不用像String那样重新造个对象,因此拼接效率要远远高于String类
构造器
空参构造器:子类继承使用
/**
* This no-arg constructor is necessary for serialization of subclasses.
*/
AbstractStringBuilder() {
}
带参构造器:创建指定容量的字符串数组
/**
* Creates an AbstractStringBuilder of the specified capacity.
*/
AbstractStringBuilder(int capacity) {
value = new char[capacity];
}
常用方法
StringBuffer、StringBuilder很多方法都是从抽象类继承的,因此我们得了解抽象类的常用方法
重写length()方法,返回实际的长度(返回存储字符的长度)
/**
* Returns the length (character count).
*
* @return the length of the sequence of characters currently
* represented by this object
*/
@Override
public int length() {
return count;
}
** public int capacity():返回存储字符的长度**
/**
* Returns the current capacity. The capacity is the amount of storage
* available for newly inserted characters, beyond which an allocation
* will occur.
*
* @return the current capacity
*/
public int capacity() {
return value.length;
}
public void trimToSize():切除无效部分的长度,比如实际存储了5个字符,而总容量是16,把这五个字符取出来创建新数组再赋给value[]数组
public void trimToSize() {
if (count < value.length) {
value = Arrays.copyOf(value, count);
}
}
public void setLength(int newLength):设置新长度(容量)
public void setLength(int newLength) {
if (newLength < 0)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(newLength);
ensureCapacityInternal(newLength);
if (count < newLength) {
Arrays.fill(value, count, newLength, '\0');
}
count = newLength;
}
public char charAt(int index):返回指定索引位置的字符
@Override
public char charAt(int index) {
if ((index < 0) || (index >= count))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
return value[index];
}
public AbstractStringBuilder append(Object obj):拼接
public AbstractStringBuilder append(Object obj) {
return append(String.valueOf(obj));
}
public AbstractStringBuilder append(String str):拼接String类型字符串并返回
public AbstractStringBuilder append(String str) {
if (str == null)
return appendNull();
int len = str.length();
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
str.getChars(0, len, value, count);
count += len;
return this;
}
// Documentation in subclasses because of synchro difference
public AbstractStringBuilder append(StringBuffer sb) {
if (sb == null)
return appendNull();
int len = sb.length();
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
sb.getChars(0, len, value, count);
count += len;
return this;
}
还有一些相似用法的感兴趣可以看看源码。大多都是重载,传入参数类型可以是:
 这一个比较特殊:
这一个比较特殊:
public AbstractStringBuilder append(boolean b) {
if (b) {
ensureCapacityInternal(count + 4);
value[count++] = 't';
value[count++] = 'r';
value[count++] = 'u';
value[count++] = 'e';
} else {
ensureCapacityInternal(count + 5);
value[count++] = 'f';
value[count++] = 'a';
value[count++] = 'l';
value[count++] = 's';
value[count++] = 'e';
}
return this;
}
public AbstractStringBuilder delete(int start, int end):删除从start开始到end(不包含)索引的字符
public AbstractStringBuilder delete(int start, int end) {
if (start < 0)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (end > count)
end = count;
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException();
int len = end - start;
if (len > 0) {
System.arraycopy(value, start+len, value, start, count-end);
count -= len;
}
return this;
}
public AbstractStringBuilder deleteCharAt(int index):删除指定索引的字符并返回该字符串
public AbstractStringBuilder deleteCharAt(int index) {
if ((index < 0) || (index >= count))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
System.arraycopy(value, index+1, value, index, count-index-1);
count--;
return this;
}
public AbstractStringBuilder replace(int start, int end, String str):用str替换[start,end)位置并返回新字符串
public AbstractStringBuilder replace(int start, int end, String str) {
if (start < 0)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (start > count)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("start > length()");
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("start > end");
if (end > count)
end = count;
int len = str.length();
int newCount = count + len - (end - start);
ensureCapacityInternal(newCount);
System.arraycopy(value, end, value, start + len, count - end);
str.getChars(value, start);
count = newCount;
return this;
}
public String substring(int start):返回从statrt位置开始到结束的子串
public String substring(int start) {
return substring(start, count);
}
** public CharSequence subSequence(int start, int end):左开右闭,返回指定索引子串**
@Override
public CharSequence subSequence(int start, int end) {
return substring(start, end);
}
** public String substring(int start, int end):左开右闭,返回指定索引子串**
public String substring(int start, int end) {
if (start < 0)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (end > count)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(end);
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(end - start);
return new String(value, start, end - start);
}
public AbstractStringBuilder insert(int index, char[] str, int offset, int len):将str数组从offset开始len个字符插入到value[]数组的index后,并返回新数组
public AbstractStringBuilder insert(int index, char[] str, int offset, int len)
{
if ((index < 0) || (index > length()))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
if ((offset < 0) || (len < 0) || (offset > str.length - len))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(
"offset " + offset + ", len " + len + ", str.length "
+ str.length);
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
System.arraycopy(value, index, value, index + len, count - index);
System.arraycopy(str, offset, value, index, len);
count += len;
return this;
}
insert的重载:
public int indexOf(String str) {
return indexOf(str, 0);
}
 public AbstractStringBuilder reverse():把当前字符序列逆转
public AbstractStringBuilder reverse():把当前字符序列逆转
public AbstractStringBuilder reverse() {
boolean hasSurrogates = false;
int n = count - 1;
for (int j = (n-1) >> 1; j >= 0; j--) {
int k = n - j;
char cj = value[j];
char ck = value[k];
value[j] = ck;
value[k] = cj;
if (Character.isSurrogate(cj) ||
Character.isSurrogate(ck)) {
hasSurrogates = true;
}
}
if (hasSurrogates) {
reverseAllValidSurrogatePairs();
}
return this;
}
接下来正式学习StringBuilder
构造器
空参构造默认创建16容量的字符数组
public StringBuilder() {
super(16);
}
带参构造器指定容量
public StringBuilder(int capacity) {
super(capacity);
}
带参构造器传入String字符串,容量为str.length()+16
public StringBuilder(String str) {
super(str.length() + 16);
append(str);
}
带参构造器传入字面量形式字符串,容量为seq.length()+16
public StringBuilder(CharSequence seq) {
this(seq.length() + 16);
append(seq);
}
toString重写
@Override
public String toString() {
// Create a copy, don't share the array
return new String(value, 0, count);
}
StringBuilder的源码只有300多行,很多方法都是重写了AbstractStringBuilder的方法,所以,常用方法的了解可以从上面抽象类的方法学习。StringBuffer的用法也一样,就不多介绍。下面是总结常用方法:
String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder的区别
String是不可变字符序列,适合不需要频繁修改字符串时使用,当需要频繁修改字符序列,最好使用StringBuffer、StringBuilder,StringBuffer线程安全但效率不高,StringBuilder线程不安全但效率高,可视情况灵活使用
三者效率的测试
package com.deserts.stringdemo01;
public class StringTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//初始设置
long startTime = 0L;
long endTime = 0L;
String text = "";
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer("");
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("");
//开始对比
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 20000; i++) {
buffer.append(String.valueOf(i));
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("StringBuffer的执行时间:" + (endTime - startTime));
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 20000; i++) {
builder.append(String.valueOf(i));
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("StringBuilder的执行时间:" + (endTime - startTime));
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 20000; i++) {
text = text + i;
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("String的执行时间:" + (endTime - startTime));
}
}











