手把手带你Yolov5 (v6.1)添加注意力机制(二)(在C3模块中加入注意力机制)
之前在《手把手带你Yolov5 (v6.1)添加注意力机制(并附上30多种顶会Attention原理图)》文章中已经介绍过了如何在主干网络里添加单独的注意力层,今天这篇将会介绍如何在C3模块里面加入注意力层。
文章目录
-
- 1.添加方式介绍
- 1.1 C3SE
- 1.2 C3CA
- 1.3 C3CBAM
- 1.4 C3ECA
1.添加方式介绍
1.1 C3SE
第一步;要把注意力结构代码放到common.py文件中,以C3SE举例,将这段代码粘贴到common.py文件中
class SEBottleneck(nn.Module):
# Standard bottleneck
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5, ratio=16): # ch_in, ch_out, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, 3, 1, g=g)
self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
# self.se=SE(c1,c2,ratio)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.l1 = nn.Linear(c1, c1 // ratio, bias=False)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.l2 = nn.Linear(c1 // ratio, c1, bias=False)
self.sig = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
y = self.avgpool(x1).view(b, c)
y = self.l1(y)
y = self.relu(y)
y = self.l2(y)
y = self.sig(y)
y = y.view(b, c, 1, 1)
out = x1 * y.expand_as(x1)
# out=self.se(x1)*x1
return x + out if self.add else out
class C3SE(C3):
# C3 module with SEBottleneck()
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__(c1, c2, n, shortcut, g, e)
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(SEBottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut) for _ in range(n)))
第二步;找到yolo.py文件里的parse_model函数,将类名加入进去

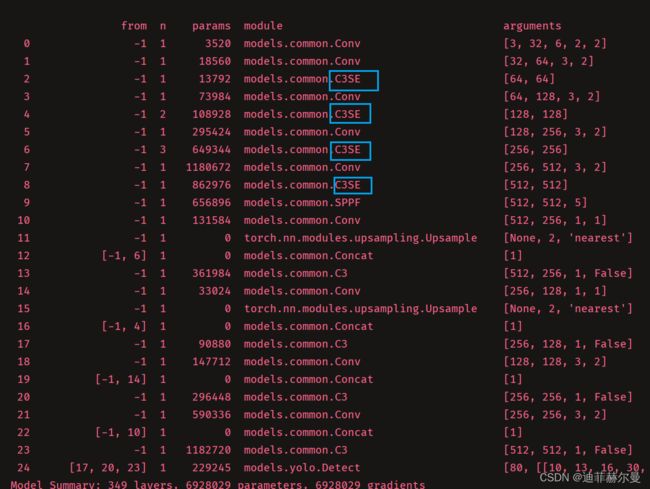
第三步;修改配置文件(我这里拿yolov5s.yaml举例子),将C3层替换为我们新引入的C3SE层
yolov5s_C3SE.yaml
# YOLOv5 by Ultralytics, GPL-3.0 license
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.50 # layer channel multiple
anchors:
- [10,13, 16,30, 33,23] # P3/8
- [30,61, 62,45, 59,119] # P4/16
- [116,90, 156,198, 373,326] # P5/32
# YOLOv5 v6.0 backbone
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 6, 2, 2]], # 0-P1/2
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, C3SE, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 6, C3SE, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, C3SE, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 3, C3SE, [1024]],
[-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]], # 9
]
# YOLOv5 v6.0 head
head:
[[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 13
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, C3, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large)
[[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]
1.2 C3CA
class CABottleneck(nn.Module):
# Standard bottleneck
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5, ratio=32): # ch_in, ch_out, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, 3, 1, g=g)
self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
# self.ca=CoordAtt(c1,c2,ratio)
self.pool_h = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((None, 1))
self.pool_w = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, None))
mip = max(8, c1 // ratio)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(c1, mip, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(mip)
self.act = h_swish()
self.conv_h = nn.Conv2d(mip, c2, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv_w = nn.Conv2d(mip, c2, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
def forward(self, x):
x1=self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
n, c, h, w = x.size()
# c*1*W
x_h = self.pool_h(x1)
# c*H*1
# C*1*h
x_w = self.pool_w(x1).permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
y = torch.cat([x_h, x_w], dim=2)
# C*1*(h+w)
y = self.conv1(y)
y = self.bn1(y)
y = self.act(y)
x_h, x_w = torch.split(y, [h, w], dim=2)
x_w = x_w.permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
a_h = self.conv_h(x_h).sigmoid()
a_w = self.conv_w(x_w).sigmoid()
out = x1 * a_w * a_h
# out=self.ca(x1)*x1
return x + out if self.add else out
class C3CA(C3):
# C3 module with CABottleneck()
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__(c1, c2, n, shortcut, g, e)
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(CABottleneck(c_, c_,shortcut) for _ in range(n)))
1.3 C3CBAM
class CBAMBottleneck(nn.Module):
# Standard bottleneck
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5,ratio=16,kernel_size=7): # ch_in, ch_out, shortcut, groups, expansion
super(CBAMBottleneck,self).__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, 3, 1, g=g)
self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
self.channel_attention = ChannelAttention(c2, ratio)
self.spatial_attention = SpatialAttention(kernel_size)
#self.cbam=CBAM(c1,c2,ratio,kernel_size)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
out = self.channel_attention(x1) * x1
# print('outchannels:{}'.format(out.shape))
out = self.spatial_attention(out) * out
return x + out if self.add else out
class C3CBAM(C3):
# C3 module with CBAMBottleneck()
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__(c1, c2, n, shortcut, g, e)
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(CBAMBottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut) for _ in range(n)))
1.4 C3ECA
class ECABottleneck(nn.Module):
# Standard bottleneck
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5, ratio=16, k_size=3): # ch_in, ch_out, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, 3, 1, g=g)
self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
# self.eca=ECA(c1,c2)
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.conv = nn.Conv1d(1, 1, kernel_size=k_size, padding=(k_size - 1) // 2, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
# out=self.eca(x1)*x1
y = self.avg_pool(x1)
y = self.conv(y.squeeze(-1).transpose(-1, -2)).transpose(-1, -2).unsqueeze(-1)
y = self.sigmoid(y)
out = x1 * y.expand_as(x1)
return x + out if self.add else out
class C3ECA(C3):
# C3 module with ECABottleneck()
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__(c1, c2, n, shortcut, g, e)
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(ECABottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut) for _ in range(n)))
本人更多Yolov5(v6.1)实战内容导航
1.手把手带你调参Yolo v5 (v6.1)(一)
2.手把手带你调参Yolo v5 (v6.1)(二)
3.手把手带你Yolov5 (v6.1)添加注意力机制(并附上30多种顶会Attention原理图)
4.Yolov5如何更换激活函数?
5.如何快速使用自己的数据集训练Yolov5模型
6.连夜看了30多篇改进YOLO的中文核心期刊 我似乎发现了一个能发论文的规律