【王道Java】网络编程实战详解二
文章目录
- 一,前言
- 二,通信协议
- 三,TCP实时通信
-
- 3.1,demo02.java服务端
-
- 3.1.2 使用管道流
- 3.2,demo01.java用户端
- 3.3,效果图
- 四,进阶版
- 七,附源码
- 六,后言
一,前言
上篇文章,记录了Java万物皆对象的ip和端口的讲解记录。
下面该记录一下:
二,通信协议
协议就是一个约定呗,大家用一个约定的协议可以相互通信。
TCP/IP协议簇:
- TCP 用来用户传输的协议 (打电话)
特点:稳定,三次握手,4次挥手。(去百度哈) - UDP 就是一个用户数据包协议 (发短信)
DDOS攻击:洪水攻击。
区别:TCP需要先连接,UDP不需要连接就能发送。
三,TCP实时通信
实现思路:
用户端:
1,需要先连接到服务端:使用Socket
2,发送消息
服务端:
1,建立服务的端口信息:ServerSocket
2,等待用户连接。
3,接受用户的消息。
开始写代码:
demo01.java为用户端。
demo02.java为服务端。
3.1,demo02.java服务端
ServerSocket类:在服务器上开一个端口,等待访问。如下:
ServerSocket ServerSocket= new ServerSocket(3245);
Socket类代表一个客户端套接字。等待客户端的消息,如下:
Socket socket = ServerSocket.accept();
InputStream类标志那些从不同数据起源产生输入的类。读取客户端的消息,如下:
is = socket.getInputStream();
3.1.2 使用管道流
ByteArrayOutputStream 对byte类型数据进行写入的类 相当于一个中间缓冲层,将类写入到文件等其他outputStream。它是对字节进行操作,属于内存操作流。
ByteArrayOutputStream baos =new ByteArrayOutputStream();
遍历读取:
byte类型
byte[] buffer =new byte[1024];
int len1;
while((len1=is.read(buffer))!=-1){
baos.write(buffer,0,len1);
}
输出如下:
System.out.println(baos.toString());
3.2,demo01.java用户端
要知道服务器的地址。
使用之前的InetAddress类:
InetAddress serverIP=InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
int port=3245;
Socket类客户端套接字。如下代码:
创建一个socket链接
Socket socket= new Socket(serverIP,port);
发送消息 IO流。
OutputStream类:文件输出流
OutputStream os =socket.getOutputStream();
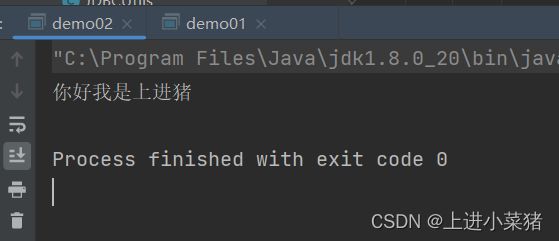
os.write("你好我是上进猪".getBytes());
基础版的完事了。我们运行看一下。
3.3,效果图
四,进阶版
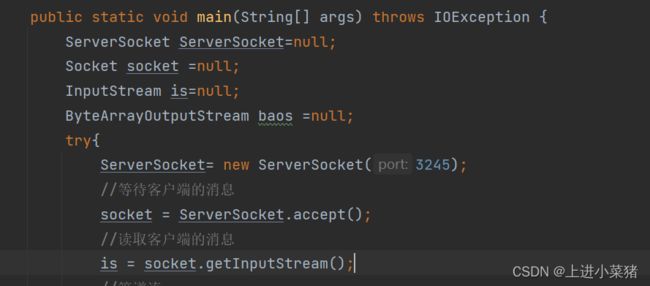
改作用域,写异常处理,及时关闭资源。
ServerSocket ServerSocket=null;
Socket socket =null;
InputStream is=null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos =null;
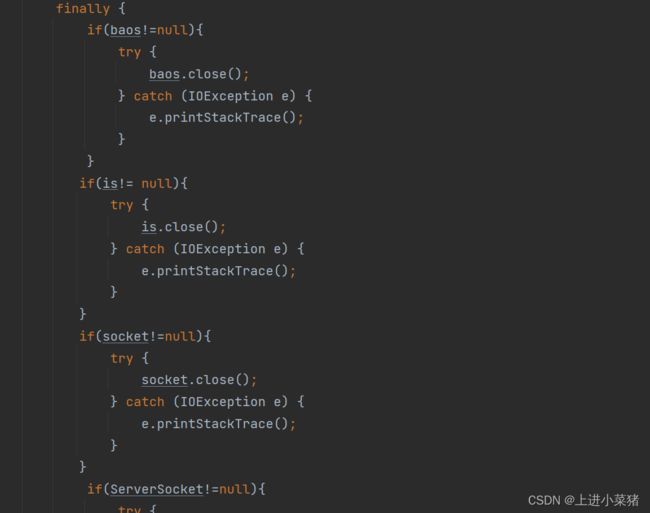
管道关闭,一节一节的关闭,注意顺序。
规则,谁先接,谁先断开。
七,附源码
demo01.java用户端 源码:
package tcp02;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
//客户端
public class demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket= null;
OutputStream os =null;
//1.要知道服务器的地址
try{
InetAddress serverIP=InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
int port=3245;
//2.创建一个socket链接
socket=new Socket(serverIP,port);
//3.发送消息 IO流
os =socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("你好我是上进猪".getBytes());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(os!=null)
{
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(socket!=null)
{
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
demo02.java服务端源码:
package tcp02;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
//服务端
public class demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket ServerSocket=null;
Socket socket =null;
InputStream is=null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos =null;
try{
ServerSocket= new ServerSocket(3245);
//等待客户端的消息
socket = ServerSocket.accept();
//读取客户端的消息
is = socket.getInputStream();
//管道流
baos =new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer =new byte[1024];
int len1;
while((len1=is.read(buffer))!=-1){
baos.write(buffer,0,len1);
//String msg= new String(buffer,0,len1);
//System.out.println(msg);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
if(baos!=null){
try {
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(is!= null){
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(socket!=null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(ServerSocket!=null){
try {
ServerSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}