Python 带电粒子在复合场中的动力学仿真
高中物理具有抽象性特点,由于高中生的抽象思维发展还未完全,在学习过程中难免存在一定的问题和困惑,若不能及时解决存在的这一矛盾,则对今后物理学习产生不利影响。
实践的认识的唯一来源。
但是,由于条件和技术限制,不可能每一个问题都通过做实验的方式解决。
那我们就可以结合发达的信息技术,通过软件模拟现实情况,暂时替代实验。
程序设计
运用Python编程并导入NumPy库
代码缩略图
完整代码
import turtle as t # 海龟画图库
import numpy as np
import time # 时间库,用来放缩模拟速率
step_xy = 50 # 坐标单位长度(像素)
E0, Arg_E0, slot_E0 = 50, 0.5 * np.pi, 4 # 电场的场强,方向,所在象限
B0, Dir_B0, slot_B0 = 0.01, -1, 1 # 磁场的场强,方向,所在象限
x, y = 0, 100 # 质点初始坐标
loc1 = np.array([x, y]) # 初始的数组形式,方便调用numpy计算
class Environment:
"""
画环境
"""
def __init__(self):
self.xlim = int(400)
self.ylim = int(300)
pass
def draw_cs(self):
"""
画坐标系
:return: 无返回值
"""
# 设置画笔
t.speed(10)
t.pensize(2)
# 画x轴
t.penup()
t.goto(-self.xlim - 30, 0) # 画出头
t.pendown()
t.goto(self.xlim, 0)
# 画x轴的箭头
t.penup()
t.goto(self.xlim - 5, 5)
t.pendown()
t.goto(self.xlim, 0)
t.goto(self.xlim - 5, -5)
# 画x轴的点
for i in range(-self.xlim, self.xlim, step_xy):
# 画点
t.penup()
t.goto(i, 10)
t.pendown()
t.goto(i, 0)
# 画字
# t.penup()
# if i == 0: # 对0的处理
# t.goto(i - 10, - (step_xy - 50))
# t.write(i, align='center')
# else:
# t.goto(i, -(step_xy - 25))
# t.write(i, align='center')
# t.pendown()
# 画x轴的X
t.penup()
t.goto(self.xlim * 0.96, -self.xlim * 0.1) # x的相对位置
t.pendown()
t.write('x', font=("Arial", 16))
# 画y轴
t.penup()
t.goto(0, -self.ylim - 30)
t.pendown()
t.goto(0, self.ylim)
# 画y轴的箭头
t.penup()
t.goto(-5, self.ylim - 5)
t.pendown()
t.goto(0, self.ylim)
t.goto(5, self.ylim - 5)
# 画y轴的点
for i in range(-self.ylim, self.ylim, step_xy):
# 画点
t.penup()
t.goto(10, i)
t.pendown()
t.goto(0, i)
# # 画字
# t.penup()
# if i == 0: # 对0的处理
# pass
# else:
# t.goto(- (step_xy - 25), i - 5)
# t.write(i, align='center')
# t.pendown()
# 画y轴的y
t.penup()
t.goto(-self.ylim * 0.1, self.ylim * 0.93) # y的相对位置
t.pendown()
t.write('y', font=("Arial", 16))
# 恢复初始位置
t.penup()
t.goto(0, 0)
t.pendown()
t.pensize(1)
pass
def electric_field(self, E, Arg_E, slot_E):
"""
画电场
:param E: 电场强度
:param Arg_E: 电场方向向量辐角
:param slot_E: 电场所在象限
:return: 无返回值
"""
t.speed(speed=None)
t.delay(delay=None)
t.tracer(n=10, delay=None)
t.pensize(1)
list_start = (0, 50, -50, -50, 50)
x_start = list_start[slot_E]
sign = (0, 1, 1, -1, -1)
signy = sign[slot_E]
if Arg_E == 0.5 * np.pi: # 90d
t.pendown()
for i in range(x_start, x_start // abs(x_start) * self.xlim, x_start // abs(x_start) * step_xy):
t.penup()
t.goto(i, signy * self.ylim)
t.pendown()
t.goto(i, 0)
# 画箭头
t.penup()
t.goto(i - 5, signy * self.ylim - 5)
t.pendown()
t.goto(i, signy * self.ylim)
t.goto(i + 5, signy * self.ylim - 5)
t.penup()
elif Arg_E == np.pi:
t.pendown()
for i in range(x_start, x_start // abs(x_start) * self.ylim, x_start // abs(x_start) * step_xy):
t.penup()
t.goto(signy * self.xlim, i)
t.pendown()
t.goto(0, i)
# 画箭头
t.penup()
t.goto(signy * self.xlim + 5, i + 5)
t.pendown()
t.goto(signy * self.xlim, i)
t.goto(signy * self.xlim + 5, i - 5)
t.penup()
elif Arg_E == 1.5 * np.pi:
t.pendown()
for i in range(x_start, x_start // abs(x_start) * self.xlim, x_start // abs(x_start) * step_xy):
t.penup()
t.goto(i, signy * self.ylim)
t.pendown()
t.goto(i, 0)
# 画箭头
t.penup()
t.goto(i + 5, signy * self.ylim + 5)
t.pendown()
t.goto(i, signy * self.ylim)
t.goto(i - 5, signy * self.ylim + 5)
t.penup()
elif Arg_E == 0:
t.pendown()
for i in range(x_start, x_start // abs(x_start) * self.ylim, x_start // abs(x_start) * step_xy):
t.penup()
t.goto(signy * self.xlim, i)
t.pendown()
t.goto(0, i)
# 画箭头
t.penup()
t.goto(signy * self.xlim - 5, i - 5)
t.pendown()
t.goto(signy * self.xlim, i)
t.goto(signy * self.xlim - 5, i + 5)
t.penup()
else: # y = tan a * (x - b)
print('不支持方向')
pass
t.goto(x_start // abs(x_start) * self.xlim // 2, self.ylim * 1.1) # y的相对位置
t.pendown()
t.write('E = ', font=("Arial", 16))
t.penup()
t.goto(x_start // abs(x_start) * self.xlim // 2 + 40, self.ylim * 1.1)
t.write(str(E), font=("Arial", 16))
t.goto(x_start // abs(x_start) * self.xlim // 2 + 80, self.ylim * 1.1)
t.write('V/m', font=("Arial", 16))
t.goto(0, 0)
t.pendown()
pass
def magnetic_field(self, B, Dir_B, slot_B):
"""
画磁场
:param B: 磁感应强度
:param Dir_B: 磁场方向,1为向外,-1为向内
:param slot_B: 磁场所在象限
:return: 无返回值
"""
t.penup()
x_start = [0, 0.5 * step_xy, -self.xlim + 0.5 * step_xy, -self.xlim + 0.5 * step_xy, 0.5 * step_xy]
y_start = [0, 0.5 * step_xy, 0.5 * step_xy, -self.ylim + 0.5 * step_xy, -self.ylim + 0.5 * step_xy]
startx = int(x_start[slot_B])
starty = int(y_start[slot_B])
# 画磁场
if Dir_B == 1:
for i in range(startx, startx + self.xlim, step_xy):
for j in range(starty, starty + self.ylim, step_xy):
t.goto(i, j)
t.pensize(3)
t.pendown()
t.goto(i + 2, j)
t.penup()
pass
t.goto(0, 0)
pass
elif Dir_B == -1:
size = 3
for i in range(startx, startx + self.xlim, step_xy):
for j in range(starty, starty + self.ylim, step_xy):
t.goto(i, j)
t.pensize(size - 1)
t.penup()
t.goto(i + size, j + size)
t.pendown()
t.goto(i - size, j - size)
t.penup()
t.goto(i - size, j + size)
t.pendown()
t.goto(i + size, j - size)
t.penup()
t.goto(0, 0)
pass
else:
print('错误')
pass
# 画文字
t.goto(startx // abs(startx) * self.xlim // 2, self.ylim * 1.1 - 20)
t.write('B = ', font=("Arial", 16))
t.penup()
t.goto(startx // abs(startx) * self.xlim // 2 + 40, self.ylim * 1.1 - 20)
t.write(str(B), font=("Arial", 16))
t.goto(startx // abs(startx) * self.xlim // 2 + 80, self.ylim * 1.1 - 20)
t.write('T', font=("Arial", 16))
t.goto(0, 0)
t.penup()
pass
@staticmethod
def Judge(x, y):
slot = None
if y > 0:
if x > 0:
slot = 1
elif x < 0:
slot = 2
else:
pass
elif y < 0:
if x > 0:
slot = 4
elif x < 0:
slot = 3
else:
pass
else:
pass
# print(slot)
return slot
pass
class MassPoint:
"""
质点
"""
mass = 0.001 # 质量(kg)
q = 0.2 # 电荷量(C)带正负
v = 100 # m/s
Angle_v = -0.3 * np.pi # rad
V = np.array([v * np.cos(Angle_v), v * np.sin(Angle_v)]) # 速度向量,大小(m/s)
specific_charge = q / mass # 比荷
slot_now = Environment().Judge(x, y)
pass
class Move:
@staticmethod
def ElectricFieldForce(slot):
if slot == slot_E0:
qE = MassPoint.q * E0
F_electric = np.array([qE * np.cos(Arg_E0), qE * np.sin(Arg_E0)])
else:
F_electric = 0
return F_electric
pass
@staticmethod
def LorentzForce(v1, Angle_v, slot):
if slot == slot_B0:
Bqv = B0 * MassPoint.q * v1 # 标量
F_lorentz = np.array([Bqv * np.cos(Angle_v - Dir_B0 * np.pi / 2),
Bqv * np.sin(Angle_v - Dir_B0 * np.pi / 2)])
else:
F_lorentz = 0
return F_lorentz
pass
@staticmethod
def Gravity():
g = 0 # 重力加速度(m/s)
G = np.array([0, -MassPoint.mass * g])
return G
pass
@staticmethod
def Painter(T):
X = np.array([0, 0])
x1, y1 = x, y
loc = np.array([x1, y1])
slot = Environment.Judge(x1, y1)
F = Move.LorentzForce(MassPoint.v, MassPoint.Angle_v, slot) + Move.ElectricFieldForce(slot) + Move.Gravity()
a = F / MassPoint.mass
V = MassPoint.V
t.tracer(n=1, delay=None)
t.goto(x1, y1)
t.pendown()
while True:
slot = Environment.Judge(loc[0], loc[1])
v = np.linalg.norm(V)
print(v)
if V[1] > 0:
Angle_v = np.arccos(V[0] / v)
elif V[1] < 0:
Angle_v = -np.arccos(V[0] / v)
else:
if V[0] > 0:
Angle_v = 0
elif V[0] < 0:
Angle_v = np.pi
else:
Angle_v = None
slot = Environment.Judge(loc[0], loc[1])
F = Move.LorentzForce(v, Angle_v, slot) + Move.ElectricFieldForce(slot) + Move.Gravity()
a = F / MassPoint.mass
V = V + a * [T]
X = X + V * [T]
loc = loc + X
t.goto(loc[0], loc[1])
print(X)
if __name__ == '__main__':
Environment().draw_cs()
Environment().electric_field(E0, Arg_E0, slot_E0)
Environment().magnetic_field(B0, Dir_B0, slot_B0)
t.tracer(n=1, delay=None)
t.penup()
t.goto(x, y)
Move().Painter(0.005)
t.mainloop()
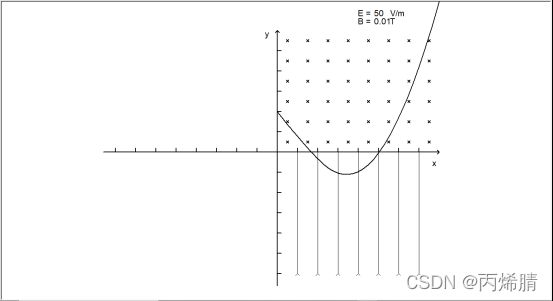
运行效果
问题和BUG
轨迹总是左偏,电场线在部分象限画的有问题