【刷题日记】笔试经典编程题目(六)
大家好,我是白晨,一个不是很能熬夜,但是也想日更的人✈。如果喜欢这篇文章,点个赞,关注一下白晨吧!你的支持就是我最大的动力!
文章目录
- 前言
- 笔试经典编程题目(六)
-
- 1.分解因数
- 2.美国节日
- 3.淘宝网店
- 4.斐波那契凤尾
- 5.剪花布条
- 6.客似云来
- 7.收件人列表
- 8.养兔子
- 9.年会抽奖
- 10.抄送列表
- 11.Rational Arithmetic
- 12.Pre-Post
- 后记
前言
虽然还有很多课,但是也不能忘了写编程题呀。
白晨总结了大厂笔试时所出的经典题目,本周题型包括动态规划,条件控制,数学归纳,算法等,其中数据结构和条件控制题目难度比上周有很大增长。这次的题目平均难度比以前的题都难,特别是最后还出现了英文题目,如果一时间没有想到,不用怀疑自己,试着看完解析再试试。
都是很有代表性的经典题目,适合大家复习和积累经验。
这里是第六周,大家可以自己先试着自己挑战一下,再来看解析哟!
笔试经典编程题目(六)
1.分解因数
原题链接:分解因数
算法思想:
- 这道题的意思就是求一个数的全部的因子,所以我们可以直接使用求质数的方法进行求解。
代码实现:
#include 2.美国节日
原题链接:美国节日
这道题虽然看着平平无奇,但是实现起来是相当复杂。我这里提供两种思路:
- 如果知道蔡勒公式,用蔡勒公式可以简化代码。
- 如果不知道,将2000年当作参考,按照日期加减以及年与年的天数关系求解(麻烦死)。
算法思想:
- 首先,来介绍一下蔡勒公式:
蔡勒(Zeller)公式,是一个计算星期的公式,随便给一个日期,就能用这个公式推算出是星期几。
- D = [ c / 4 ] − 2 c + y + [ y / 4 ] + [ 13 ( m + 1 ) / 5 ] + d − 1 D=[c/4]−2c+y+[y/4]+[13(m+1)/5]+d−1 D=[c/4]−2c+y+[y/4]+[13(m+1)/5]+d−1
- W = D % 7 W=D \% 7 W=D%7
其中:
- W W W 是星期数。注意: W W W为0时,这一天是周日。
- c c c 是世纪数减一,也就是年份的前两位。
- y y y 是年份的后两位。
- m m m 是月份。 m m m 的取值范围是 3 至 14,所以某年的 1、2 月要看作上一年的 13、14月,比如 2019 年的 1 月 1 日要看作 2018 年的 13 月 1 日来计算。
- d d d 是日数。
- [ ] [] [] 是取整运算。
- % \% % 是求余运算。
- 通过蔡勒公式,我们可以得知任意一天的日期,结合题目都是
第x月的第y个星期n这种形式。所以,我们可以先计算出第x月的1号是星期几。 - 以每个月1号的星期数作为参考,求得题目要求的日期。
- 具体实现细节见代码实现:
代码实现:
#include 3.淘宝网店
原题链接:淘宝网店
算法思想:
- 这道题的思路其实并不是很难,本质上就是算两个日期之间间隔的天数,但是这道题中每一天的权重不再都是1了,而是根据月份不同而不同,素月的每一天天权重为1,其他月的每一天权重为2。
- 我们用
逐步逼近的策略,让起始日期不断逼近结束日期,随着起始日期的逼近,总收益也不断随着起始日期的增加而增加,直到最后起始日期等于结束日期。 - 注意:结束日期也在营业,不能忘记最后加上结束日期的收益。
- 这里描述的可能比较抽象,但是代码还是比较好懂的,这道题主要考的就是对于边界的控制,以及思路的实现,实现细节见代码。
代码实现:
#include 4.斐波那契凤尾
原题链接:斐波那契凤尾
算法思想:
- 这道题不能直接计算斐波那契数列,因为在计算到几百位的时候会超过整形最大的存储范围。所以,我们只用存储后6位即可。
- 特别注意:当
n > 24时,斐波那契数会大于等于6位,输出时,必须输出6位。 - eg. 1000001 % 1000000 = 1 1000001 \% 1000000 = 1 1000001%1000000=1 ,存储了1,但是其实原数的后六位是: 000001 000001 000001 ,所以要进行补位。
代码实现:
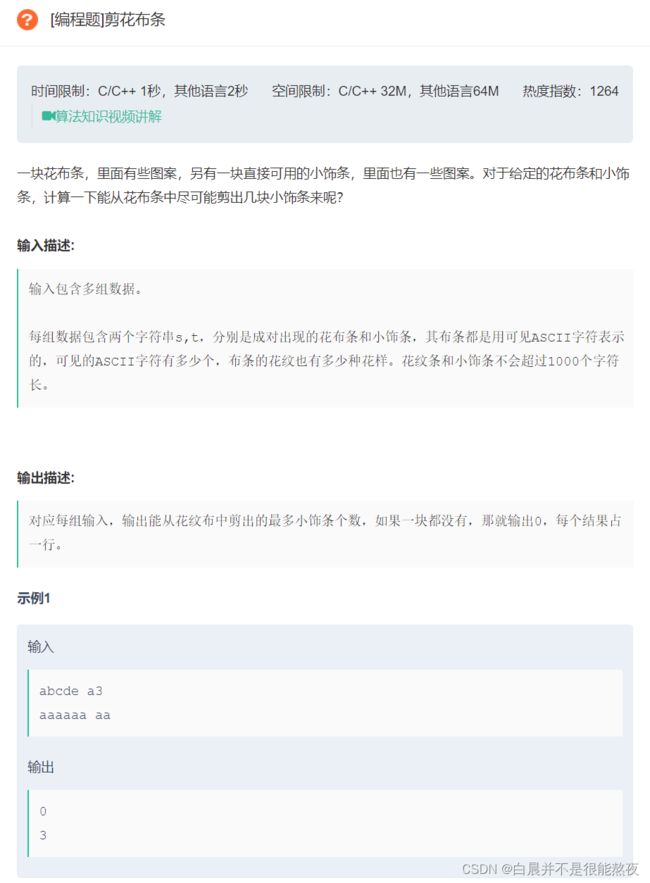
#include 5.剪花布条
原题链接:剪花布条
- 法一:strstr
算法思想:
- 使用
strstr函数进行搜索,将返回的字符指针 + 短串(待匹配串)的长度,也就是下一个搜索的位置。 - 如果上面得到的位置小于长串(匹配串),继续进行搜索,每搜索成功一次
cnt++。 - 直到搜索完匹配串或者找不到待匹配串结束搜索。
代码实现:
#include
- 法二:BF算法
算法思想:
BF算法,即暴力(Brute Force)算法,是普通的模式匹配算法,BF算法的思想就是将目标串S的第一个字符与模式串T的第一个字符进行匹配,若相等,则继续比较S的第二个字符和 T的第二个字符;若不相等,则比较S的第二个字符和T的第一个字符,依次比较下去,直到得出最后的匹配结果。BF算法是一种蛮力算法。
- BF算法C语言详细代码实现:
# define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include 代码实现:
#include
- 法三:KMP算法
算法思想:
- 以下实现就是KMP算法,如果没有接触过KMP算法就可以忽略了,感兴趣的可以看看。
代码实现:
#include 6.客似云来
原题链接:客似云来
算法思想:
- 本题就是斐波那契数列的变种,直接求数列即可。
代码实现:
#include 7.收件人列表
原题链接:收件人列表
算法思想:
- 这个题没有思想上的难度,具体实现细节见下面代码:
代码实现:
#include 8.养兔子
原题链接:养兔子
算法思想:
- 这个题其实就是一道找规律+动态规划的题目,我们可以现写出前7天月兔子的变化情况。
| 时间/月份 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 兔子数量 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 13 | 21 |
- 观察图表,我们可以得到这样一个动态转移方程: f ( x ) = f ( x − 1 ) + f ( x − 2 ) f(x) = f(x-1)+f(x-2) f(x)=f(x−1)+f(x−2) 。
- 这就是斐波那契数列的变式题。
代码实现:
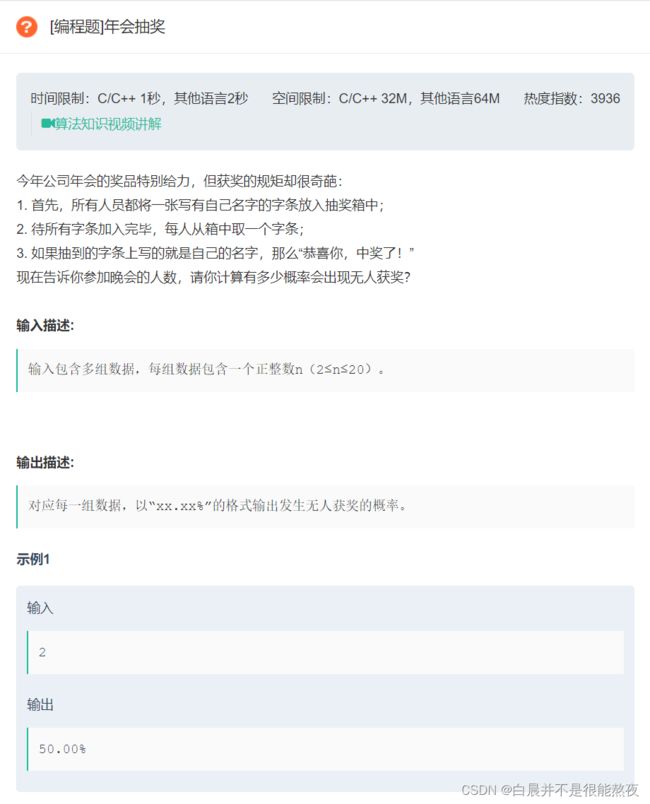
#include 9.年会抽奖
原题链接:年会抽奖
算法思想:
-
这是一道考验排列组合的题目,这里我们可以使用元素法:
无人获奖的概率 = 无人获奖的全部情况数 / 抽奖的所有情况数。 -
设一共有
n个人参与抽奖。 -
抽 奖 的 所 有 情 况 数 = A n n 抽奖的所有情况数 = A_n^n 抽奖的所有情况数=Ann ,也就是排列数。
-
n个人中无人获奖的情况数我们设为
f(n),可以分为以下情况讨论:- 前提条件:
m的名字没有被m拿到,其他n - 1个人都有可能拿到,即有n - 1种情况。 - 假设
k拿到了m的名字,那么对于k的名字有两种情况:
- 前提条件:
-
case1 :是
k的名字被m拿到了,也就是m、k互相拿到了对方的名字,那么对于其他n - 2个人互相拿错又是一个子问题f(n - 2)。 -
case2 :是
k的名字没有被m拿到,这时要保证在除了k的n - 1个人中m不能拿到k的名字,其他人也不能拿到自己的名字,则剩下的问题是子问题f(n - 1)。(此时,在n - 1个人中,相当于m的名字变成了k,而规定自己不能拿自己的名字,所以问题又变成了f(n - 1)。) -
因此可得递推公式 f ( n ) = ( n − 1 ) ∗ ( f ( n − 1 ) + f ( n − 2 ) ) f(n) = (n - 1) * (f(n - 1) + f(n - 2)) f(n)=(n−1)∗(f(n−1)+f(n−2))。
-
易得,
f(1) = 0, f(2) = 1。 -
所以 P = f ( n ) / A n n P = f(n) / A_n^n P=f(n)/Ann 。
代码实现:
- 递归:
#include - 迭代:
#include 10.抄送列表
原题链接:抄送列表
- 法一:逐个遍历,控制条件切割
算法思想:
- 思想上没有难度,主要是实现上的细节,具体细节见代码:
代码实现:
#include
- 法二:查找切割
算法思想:
-
上一个思路思想较难理解而且代码较长,下面我们换个好理解的思路:
-
遇到
"直接找下一个"的位置,将""中的子串切割下来,就是一个名字。 -
不然,就找下一个
,的位置,将两个,间的子串切割,也是一个名字。
-
代码实现:
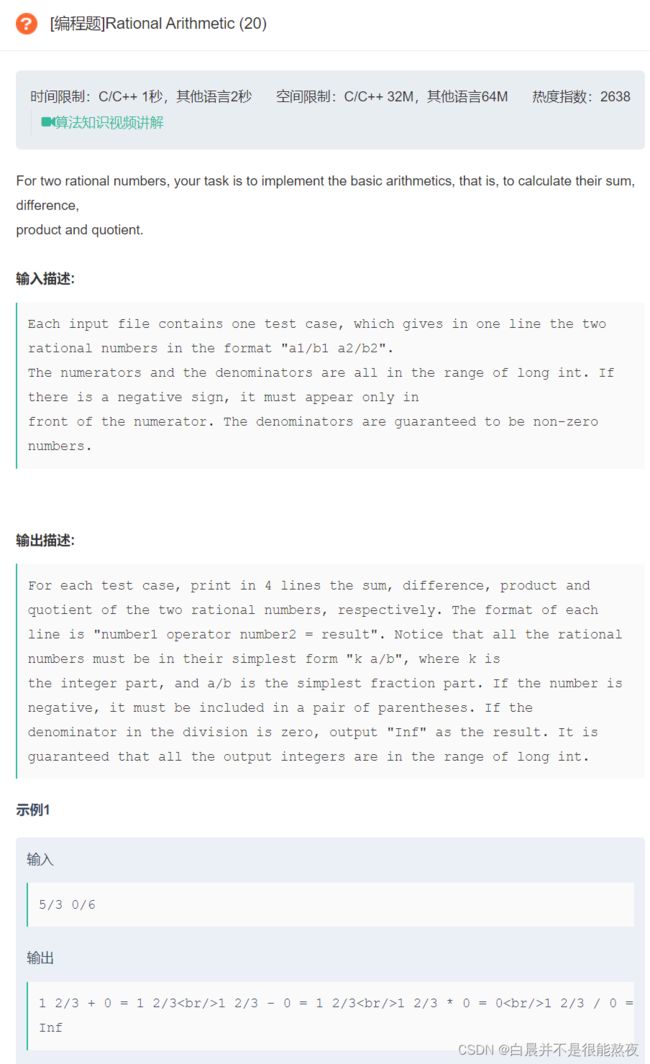
#include 11.Rational Arithmetic
原题链接:Rational Arithmetic
算法思想:
- 这个题目的意思就是要实现分数之间的加减乘除,但是有几点要求:
- 题目给的数如果为假分数,那么输出时要按照带分数输出。eg. 5 3 − − > 1 2 3 \frac{5}{3} --> 1 \frac{2}{3} 35−−>132,转化为题目要求输出格式就是
3/5 --> 1 2/3。 - 所有输出的分数必须为最简形式。eg.
8/6 --> 1 1/3。 - 负数必须带括号。eg.
-7/6 --> (-1 1/6)。 - 如果除数等于0,那么结果输出
Inf。eg.3/4 / 0 = Inf。
- 题目给的数如果为假分数,那么输出时要按照带分数输出。eg. 5 3 − − > 1 2 3 \frac{5}{3} --> 1 \frac{2}{3} 35−−>132,转化为题目要求输出格式就是
- 这道题我的方法是创建一个类,来实现上述功能,具体实现比较复杂,应该是本系列的题目中最复杂的一个了。
- 具体实现细节见代码。
代码实现:
#include 12.Pre-Post
原题链接:Pre-Post
原题链接:Pre-Post
这道题对于数据结构要求能力比较高,第一次做没有思路很正常。但是其实只要理解了思路,这道题还算比较好实现(比上一道题好实现)。
算法思想:
- 众所周知,二叉树只有给出
中序遍历序列 + 前序遍历序列/后序遍历序列才能确定唯一一棵二叉树,但是这道题目就是不给你中序遍历,而只给你前序遍历序列 + 后序遍历序列,并且更变态的一点是,题目要求这棵树是一棵多叉树。输入分叉数 前序遍历序列 后序遍历序列,求满足所给前序遍历序列和后序遍历序列的多叉树所有可能的构型数。 - 首先,我们得了解为什么
中序遍历序列 + 前序遍历序列/后序遍历序列可以唯一构成一棵二叉树
前序遍历 ---- 头节点 左子树 右子树
后序遍历 ---- 左子树 右子树 头节点
中序遍历 ---- 左子树 头节点 右子树观察上面的遍历顺序,我们发现只有中序遍历的左右子树是在头节点的两侧的,而前序和后序都是头节点在一侧,左右子树在另一侧。
- 所以,我们可以在前序遍历序列中找到头节点(就是序列中第一个元素,如果是后序序列,则是最后一个元素)。
- 找到头节点后,再在中序序列中找到这个元素,左右两边就是左右子树。
- 确定左子树元素个数
n后,在前序序列中,头节点后n个元素就是左子树的前序序列,同理可得到右子树的前序序列。- 这样,就得到了左右子树的前序序列和中序序列,再重复1,2,3过程,就可以得到一棵二叉树。
- 所以,中序序列起着划分二叉树左右子树的作用,现在没有中序序列(当然,多叉树没有中序序列),就得依靠前序序列和后序序列的划分子树以及位置。
- 那么前序序列和后序序列如何划分子树呢?
前序遍历 ---- 头节点 左子树 右子树
后序遍历 ---- 左子树 右子树 头节点一定要记住上面的遍历顺序,这很关键!
我们用一道例题来讲解:
输入:13
abejkjkeba
- 总结一下:
- 前序序列确定根,到后序序列中找根元素,确定此根元素子树的所有结点(也可以说确定这棵子树的长度)。
- 通过子树的排列组合确定树的可能构型。
#include 后记
本次题目难度有提升很多,这次题目主要集中在数据结构和条件控制这两个面试最爱考的题目,比较考验大家的逻辑思维以及代码实现能力,相信大家做完会有所收获。
这个是一个新的系列——《笔试经典编程题目》,隶属于【刷题日记】系列,白晨开这个系列的目的是向大家分享经典的笔试编程题,以便于大家参考,查漏补缺以及提高代码能力。如果你喜欢这个系列的话,不如关注白晨,更快看到更新呀。
本文是笔试经典编程题目的第六篇,如果喜欢这个系列的话,不如订阅【刷题日记】系列专栏,更快看到更新哟
如果解析有不对之处还请指正,我会尽快修改,多谢大家的包容。
如果大家喜欢这个系列,还请大家多多支持啦!
如果这篇文章有帮到你,还请给我一个大拇指 和小星星 ⭐️支持一下白晨吧!喜欢白晨【刷题日记】系列的话,不如关注白晨,以便看到最新更新哟!!!
我是不太能熬夜的白晨,我们下篇文章见。