尚硅谷java入门bilibili(290p-303p)2022.3.13
290p 多态性练习:几何图形
* 定义三个类,父类GeometricObject代表几何形状,子类Circle代表圆形,MyRectangle代表矩形
public class GeometricObject{//几何图形
protected String color;
protected double weight;
public String getColor(){
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color){
this.color=color;
}
public double getWeight(){
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(double weight){
this.weight=weight;
}
public GeometricObject(String color,double weight){
super();
this.color=color;
this.weight=weight;
}
public double findArea(){
return 0.0;
}
}public class Circle extends GeometricObject{
private double radius;
public Circle(String color,double weight){
super(color,weight);
this.radius=radius;
}
public double getRadius(){
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius){
this.radius=radius;
}
public double findArea(){
return 3.14*radius*radius;
}
}public class MyRectangle extends GeometricObject{
private double width;
private double weight;
public MyRectangle(double width,double height,String color,double weight){
super(color,weight);
this.width=width;
this.weight=weight;
}
public double getWidth(){
return width;
}
public void setWidth(double width){
this.width=width;
}
public double getHeight(){
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double height){
this.height=height;
}
public double findArea(){
return width*height;
}
}定义一个测试类GeometricTest,编写equalsArea方法测试两个对象的面积是否相等
(注意方法的参数类型,利用动态绑定技术),
* 编写displayGeometricObject方法显示对象的面积
(注意方法的参数类型,利用动态绑定技术)。
public class GeometricTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
GeometricTest test=new GeometricTest();
Circle c1=new Circle(2.3,"white",1.0);
test.displayGeometricObject(c1);
Circle c2=new Circle(3.3,"white",1.0);
test.displayGeometricObject(c2);
boolean isEquals=test.equalsArea(c1,c2);
System.out.prinln("c1和c2的面积是否相等:"+isEquals);
MyRectangle rect=new MyRectangle(2.1,3.4,"red",2.0);
test.displayGeometricObject(rect);
}
public void displayGeometircObject(GeometricObject o){//GeometricObject o=new Circle(...) 多态
System.out.println("面积为:"+o.findArea());
}
//测试两个对象的面积是否相等
public boolean equalsArea(GeometricObject o1,GeometricObject o2){
return o1.findArea()==o2.findArea();
}
}291 多态性练习:重写方法
/* 考查多态的笔试题目:
* 面试题:多态是编译时行为还是运行时行为?如何证明?
*
* 拓展问题
*/
public class InterviewTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Base base = new Sub();
base.add(1, 2, 3);
// Sub s = (Sub)base;
// s.add(1,2,3);
}
}
class Base {
public void add(int a, int... arr) {
System.out.println("base");
}
}
class Sub extends Base {
public void add(int a, int[] arr) {
System.out.println("sub_1");
}
// public void add(int a, int b, int c) {
// System.out.println("sub_2");
// }
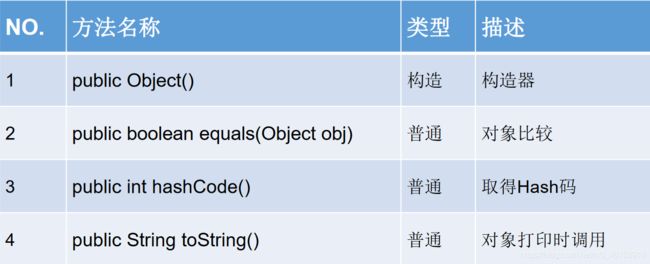
}292 Object类结构的剖析
java.lang.Object类
1.Objcet类是所有Java类的根父类
2.如果在类的声明中未使用extends关键字指明其父类,则默认父类为java.lang.Object类
3.Object类中的功能(属性,方法)都具有通用性
属性:无
方法:equals()/toString()/getClass()/hashCode()/clone()/finalize()/wait(),notify(),notifyAll()
4.Object类只声明了一个空参的构造器
面试题
final,finally,fianlize的区别
public class ObjectTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
Order order=new Order();
System.out.println(order.getClass().getSuperclass());
}
}
class Order{
}293 ==运算符的回顾
面试题:==和equals()的区别
一,回顾==的使用:
==:运算符
1.可以使用在基本数据类型变量和引用数据类型变量中
2.如果比较的是基本数据类型变量,比较两个变量保存的数据是否相等(不一定类型要相同)
如果比较的是引用数据类型变量,比较两个对象的地址值是否相同,即两个引用是否指向同一个对象实体
补充:==符号使用时,必须保证符号左右两边的变量类型一致
public class EqualsTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
//基本数据类型
int i=10;
int j=10;
double d=10.0;
System.out.println(i==j);//true
System.out.println(i==d);//true
char c=10;
System.out.println(i==c);//true
char c1='A';
char c2=65;
System.out.println(c1==c2);//true
//引用类型
Customer cust1=new Customer("Tom",21);
Customer cust2=new Customer("Tom",21);
System.out.println(cust1==cust2);//false
String str1=new String("atguigu");
String str2=new String("atguigu");
System.out.println(str1==str2);//false
System.out.println(cust1.equals(cust2));//false
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));//true
}
}public class Customer{
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name=name;
}
public int getAge(){
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age){
this.age=age;
}
public Customer(){
super();
}
public Customer(String name,int age){
super();
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
}294 equals()的使用
1.是一个方法,而非运算符
2,只能适用于引用数据类型
3.Object类中equals()的定义:
public boolean equals(Object obj){
return(this==obj);
}
说明:Object类中定义的equals()和==的作用是相同的:比较两个对象的地址值是否相同,即两个引用是否指向同一个对象实体
4,像String,Date,File,包装类等都重写了Object类中的equals()方法。重写以后比较的不是两个引用的地址是否相同,而是比较两个对象的“实体内容”是否相同
295 重写equals()
5.通常情况下,我们自定义类如果使用equals()的话,也通常是比较两个对象的实体内容是否相同,那么,我们就需要对Object类中的equals()进行重写
重写的原则:比较两个对象的实体内容(即:name和age)是否相同
public class Customer {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Customer() {
super();
}
public Customer(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//重写的原则:比较两个对象的实体内容(即:name和age)是否相同
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(this==obj){
return true;
}
if(obj instanceof Customer){
Customer cust=(Customer)obj;
//比较两个对象的每个属性是否都相同
if(this.age==cust.age&&this.name.equals(cust.name)){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
}
}296 ==与equals()
对称性:如果x.equals(y)返回是“true”,那么y.equals(x)也应该返回是“true”。
自反性:x.equals(x)必须返回是“true”。
传递性:如果x.equals(y)返回是“true”,而且y.equals(z)返回是“true”,那么z.equals(x)也应该返回是“true”。
一致性:如果x.equals(y)返回是“true”,只要x和y内容一直不变,不管你重复x.equals(y)多少次,返回都是“true”。
任何情况下,x.equals(null),永远返回是“false”;x.equals(和x不同类型的对象)永远返回是“false”。
int it = 65;
float fl= 65.0f;
System.out.println("65和65.0f是否相等?" + (it == fl)); //true
char ch1 = 'A';
char ch2 = 12;
System.out.println("65和'A'是否相等?" + (it == ch1));//true
System.out.println("12和ch2是否相等?" + (12 == ch2));//true
String str1 = new String("hello");
String str2 = new String("hello");
System.out.println("str1和str2是否相等?"+ (str1 == str2));//false
System.out.println("str1是否equals str2?"+(str1.equals(str2)));//true
System.out.println("hello" == new java.util.Date()); //编译不通过
297 equals()练习1:代码实现
编写Order类,有int型的orderId,String型的orderName,
* 相应的getter()和setter()方法,两个参数的构造器,重写父类的equals()方法:public booleanequals(Object obj),
* 并判断测试类中创建的两个对象是否相等。
public class OrderTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
Order order1=new Order(1001,"AA");
Order order2=new Order(1001,"BB");
System.out.println(order1.equals(order2));
Order order3=new Order(1001,"BB");
System.out.println(order2.equals(order3));
}
}
class Order{
private int orderId;
private String orderName;
public int getOrderId(){
return orderId;
}
public void setOrderId(int orderId){
this.orderId=orderId;
}
public String getOrderName(){
return orderName;
}
public void setOrderName(String orderName){
this.orderName=orderName;
}
public Order(int orderId,String orderName){
super();
this.orderId=orderId;
this.orderName=orderName;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(this==obj){
return true;
}
if(obj instanceof Order){
Order order=(Order)obj;
return this.orderId==order.orderId&&
this.orderName.equals(order.orderName);
}
return false;
}
}298 equals()练习2:代码实现
public class MyDateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyDate m1= new MyDate(14, 3, 1976);
MyDate m2= new MyDate(14, 3, 1976);
if(m1== m2) {
System.out.println("m1==m2");
} else{
System.out.println("m1!=m2"); // m1 != m2
}
if(m1.equals(m2)) {
System.out.println("m1 is equal to m2");// m1 is equal to m2
} else{
System.out.println("m1 is not equal to m2");
}
}
}
class Mydate{
private int day;
private int month;
private int year;
public MyDate(int day,int month,int year){
super();
this.day=day;
this.month=month;
this.year=year;
public int getDay(){
return day;
}
public void setDay(int day){
this.day=day;
}
public int getMonth(){
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month){
this.month=month;
}
public int getYear(){
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year){
this.year=year;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(this==obj){
return true;
}
if(obj instanceof MyDate){
MyDate mydate=(MyDate)obj;
return this.day==myDate.day&&this.month==myDate.month&&this.year==myDate.year;
}
return false;
}
}
}299 toString()的使用
1.当我们输出一个对象的引用时,实际上就是调用当前对象的toString()
2.Object类中toString()的定义
public String toString() {
* return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode()); * }
3.像String,Date,File,包装类等都重写了Object类中的toString()方法
使得在调用对象的toString()时,返回实体内容信息
4.自定义类也可以重写toString()方法,当调用此方法时,返回对象的实体内容
public class ToStringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer cust1 = new Customer("Tom" ,21);
System.out.println(cust1.toString()); //github4.Customer@15db9742
System.out.println(cust1); //github4.Customer@15db9742 ---> Customer[name = Tom,age = 21]
String str = new String("MM");
System.out.println(str);
Date date = new Date(45362348664663L);
System.out.println(date.toString()); //Wed Jun 24 12:24:24 CST 3407
}
}
300 综合练习
public class GeometricObject{
protected String color;
protected double weight;
public GeometricObject(){
super();
this.color="white";
this.weight=1.0;
}
public GeometricObject(String color,double weight){
super();
this.color=color;
this.weight=weight;
}
public String getColor(){
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color){
this.color=color;
}
public double getWeight(){
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(double weight){
this.weight=weight;
}
}public class Circle extends GeometricObject{
private double radius;
public Circle(){
super();
radius=1.0;
}
public Circle(double radius){
super();
this.radius=radius;
}
public Circle(double radius,String color,double weight){
super(color,weight);
this.radius=radius;
}
public double getRadius(){
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius){
this.radius=radius;
}
public double findArea(){
return 3.14*radius*radius;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(this==obj){
return true;
}
if(obj instanceof Circle){
Circle c=(Circle)obj;
return this.radius==c.radius;
}
return false;
}
public String toString(){
return "Circle[radius="+radius+"]";
}
}public class CircleTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
Circle circle1=new Circle(2.3);
Circle circle2=new Circle(2.3,"white",2.0);
System.out.println("颜色是否相等"+circle1.getColor().equals(circle2.getColor()));
System.out.println("半径是否相等"+circle1.equals(circle2));301 单元测试方法的使用
java中的JUnit单元测试
*
* 步骤:
* 1.选中当前项目工程 --》 右键:build path --》 add libraries --》 JUnit 4 --》 下一步
* 2.创建一个Java类进行单元测试。
* 此时的Java类要求:①此类是公共的 ②此类提供一个公共的无参构造器
* 3.此类中声明单元测试方法。
* 此时的单元测试方法:方法的权限是public,没有返回值,没有形参。
*
* 4.此单元测试方法上需要声明注解:@Test并在单元测试类中调用:import org.junit.Test;
* 5.声明好单元测试方法以后,就可以在方法体内测试代码。
* 6.写好代码后,左键双击单元测试方法名:右键 --》 run as --》 JUnit Test
*
* 说明:如果执行结果无错误,则显示是一个绿色进度条,反之,错误即为红色进度条。
import org.junit.Test;
public class JUnitTest{
int num=10;
@Test
public void testEquals(){
String s1="MM";
String s2="MM";
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
//ClassCastException
//Object obj=new String("GG");
//Date date=(Date)obj;
System.out.println(num);
show();
}
public void show(){
num=20;
System.out.println("show()....");
}
@Test
public void testToString(){
String s2="MM";
System.out.println(s2.toString());
}
}302 包装类的理解
wrapper
包装类的使用
* 1.java提供了8种基本数据类型对应的包装类,使得基本数据类型的变量具有类的特征
* 基本数据类型 包装类
* byte Byte
* short Short
* int Integer
* long Long
* float Float
* double Double
* boolean Boolean
* char Character
* 注意:其中Byte、Short、Integer、Long、Float、Double的父类是:Number
303 基本数据类型转换为包装类
包装类的使用:
1.java提供了8种基本数据类型对应的包装类,使得基本数据类型的变量具有类的特征
2.掌握的:基本数据类型,包装类,String三者之间的相互转换
import org.junit.Test;
public class WrapperTest{
//基本数据类型--->包装类:调用包装类的构造器
@Test
public void test1(){
int num1=10;
Integer in1=new Integer(num1);
System.out.println(in1.toString());
Integer in2=new Integer("123");
System.out.println(in2.toString());
}
}