每天都在写Getter、Setter方法,我不耐烦了,于是用了神器MapperStruct,crud效率一下子提高了~
前言
相信绝大多数的业务开发同学,日常的工作都离不开写getter、setter方法。要么是将下游的RPC结果通过getter、setter方法进行获取组装。要么就是将自己系统内部的处理结果通过getter、setter方法处理成前端所需要的VO对象。
public UserInfoVO originalCopyItem(UserDTO userDTO){
UserInfoVO userInfoVO = new UserInfoVO();
userInfoVO.setUserName(userDTO.getName());
userInfoVO.setAge(userDTO.getAge());
userInfoVO.setBirthday(userDTO.getBirthday());
userInfoVO.setIdCard(userDTO.getIdCard());
userInfoVO.setGender(userDTO.getGender());
userInfoVO.setIsMarried(userDTO.getIsMarried());
userInfoVO.setPhoneNumber(userDTO.getPhoneNumber());
userInfoVO.setAddress(userDTO.getAddress());
return userInfoVO;
}
传统的方法一般是采用硬编码,将每个对象的值都逐一设值。当然为了偷懒也会有采用一些BeanUtil简约代码的方式:
public UserInfoVO utilCopyItem(UserDTO userDTO){
UserInfoVO userInfoVO = new UserInfoVO();
//采用反射、内省机制实现拷贝
BeanUtils.copyProperties(userDTO, userInfoVO);
return userInfoVO;
}
但是,像BeanUtils这类通过反射、内省等实现的框架,在速度上会带来比较严重的影响。尤其是对于一些大字段、大对象而言,这个速度的缺陷就会越明显。针对速度这块我还专门进行了测试,对普通的setter方法、BeanUtils的拷贝以及本次需要介绍的mapperStruct进行了一次对比。得到的耗时结果如下所示:(具体的运行代码请见附录)
| 运行次数 | setter方法耗时 | BeanUtils拷贝耗时 | MapperStruct拷贝耗时 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2921528(1) | 3973292(1.36) | 2989942(1.023) |
| 10 | 2362724(1) | 66402953(28.10) | 3348099(1.417) |
| 100 | 2500452(1) | 71741323(28.69) | 2120820(0.848) |
| 1000 | 3187151(1) | 157925125(49.55) | 5456290(1.711) |
| 10000 | 5722147(1) | 300814054(52.57) | 5229080(0.913) |
| 100000 | 19324227(1) | 244625923(12.65) | 12932441(0.669) |
以上单位均为毫微秒。括号内的为当前组件同Setter比较的比值。可以看到BeanUtils的拷贝耗时基本为setter方法的十倍、二十倍以上。而MapperStruct方法拷贝的耗时,则与setter方法相近。由此可见,简单的BeanUtils确实会给服务的性能带来很大的压力。而MapperStruct拷贝则可以很好的解决这个问题。
使用教程
maven依赖
首先要导入mapStruct的maven依赖,这里我们选择最新的版本1.5.0.RC1。
...
<properties>
<org.mapstruct.version>1.5.0.RC1</org.mapstruct.version>
</properties>
...
//mapStruct maven依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct</artifactId>
<version>${org.mapstruct.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
...
//编译的组件需要配置
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source> <!-- depending on your project -->
<target>1.8</target> <!-- depending on your project -->
<annotationProcessorPaths>
<path>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-processor</artifactId>
<version>${org.mapstruct.version}</version>
</path>
<!-- other annotation processors -->
</annotationProcessorPaths>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
在引入maven依赖后,我们首先来定义需要转换的DTO及VO信息,主要包含的信息是名字、年龄、生日、性别等信息。
@Data
public class UserDTO {
private String name;
private int age;
private Date birthday;
//1-男 0-女
private int gender;
private String idCard;
private String phoneNumber;
private String address;
private Boolean isMarried;
}
@Data
public class UserInfoVO {
private String userName;
private int age;
private Date birthday;
//1-男 0-女
private int gender;
private String idCard;
private String phoneNumber;
private String address;
private Boolean isMarried;
}
紧接着需要编写相应的mapper类,以便生成相应的编译类。
@Mapper
public interface InfoConverter {
InfoConverter INSTANT = Mappers.getMapper(InfoConverter.class);
@Mappings({
@Mapping(source = "name", target = "userName")
})
UserInfoVO convert(UserDTO userDto);
}
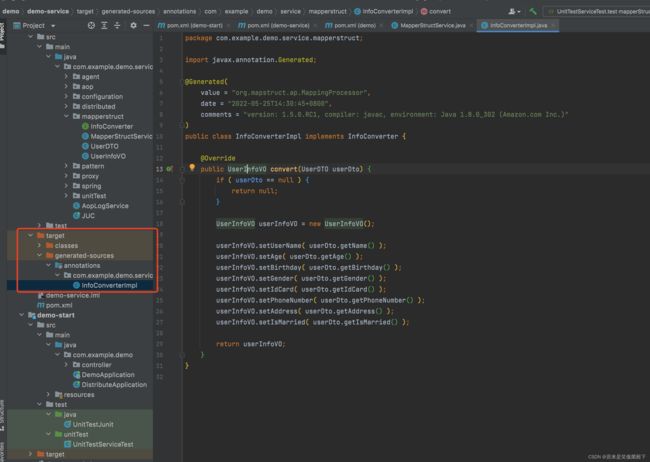
需要注意的是,因为DTO中的name对应的其实是VO中的userName。因此需要在converter中显式声明。在编写完对应的文件之后,需要执行maven的complie命令使得IDE编译生成对应的Impl对象。(自动生成)
到此,mapperStruct的接入就算是完成了~。我们就可以在我们的代码中使用这个拷贝类了。
public UserInfoVO newCopyItem(UserDTO userDTO, int times) {
UserInfoVO userInfoVO = new UserInfoVO();
userInfoVO = InfoConverter.INSTANT.convert(userDTO);
return userInfoVO;
}
怎么样,接入是不是很简单~
FAQ
1、接入项目时,发现并没有生成对应的编译对象class,这个是什么原因?
答:可能的原因有如下几个:
- 忘记编写对应的@Mapper注解,因而没有生成
- 没有配置上述提及的插件maven-compiler-plugin
- 没有执行maven的Compile,IDE没有进行相应编译
2、接入项目后发现,我项目内的Lombok、@Data注解不好使了,这怎么办呢?
由于Lombok本身是对AST进行修改实现的,但是mapStruct在执行的时候并不能检测到Lombok所做的修改,因此需要额外的引入maven依赖lombok-mapstruct-binding。
......
<org.mapstruct.version>1.5.0.RC1org.mapstruct.version>
<lombok-mapstruct-binding.version>0.2.0lombok-mapstruct-binding.version>
<lombok.version>1.18.20lombok.version>
......
......
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstructgroupId>
<artifactId>mapstructartifactId>
<version>${org.mapstruct.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombok-mapstruct-bindingartifactId>
<version>${lombok-mapstruct-binding.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>${lombok.version}version>
dependency>
更详细的,mapperStruct在官网中还提供了一个实现Lombok及mapStruct同时并存的案例
3、更多问题:
欢迎查看MapStruct官网文档,里面对各种问题都有更详细的解释及解答。
实现原理
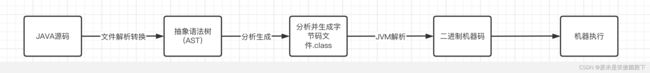
在聊到mapstruct的实现原理之前,我们就需要先回忆一下JAVA代码运行的过程。大致的执行生成的流程如下所示:
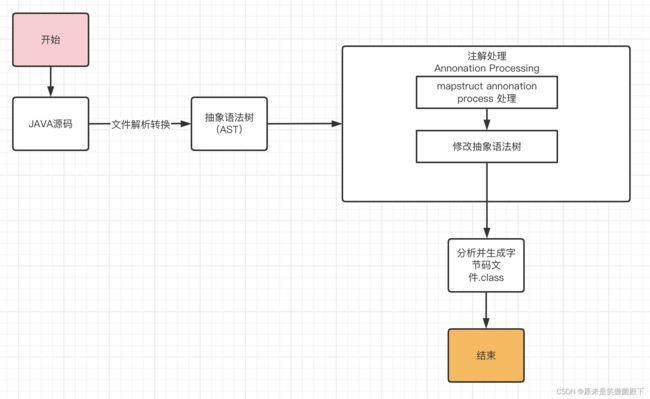
可以直观的看到,如果我们想不通过编码的方式对程序进行修改增强,可以考虑对抽象语法树进行相应的修改。而mapstruct也正是如此做的。具体的执行逻辑如下所示:
为了实现该方法,mapstruct基于JSR 269实现了代码。JSR 269是JDK引进的一种规范。有了它,能够在编译期处理注解,并且读取、修改和添加抽象语法树中的内容。JSR 269使用Annotation Processor在编译期间处理注解,Annotation Processor相当于编译器的一种插件,因此又称为插入式注解处理。想要实现JSR 269,主要有以下几个步骤:
- 继承AbstractProcessor类,并且重写process方法,在process方法中实现自己的注解处理逻辑。
- 在META-INF/services目录下创建javax.annotation.processing.Processor文件注册自己实现的Annotation Processor。
通过实现AbstractProcessor,在程序进行compile的时候,会对相应的AST进行修改。从而达到目的。
public void compile(List<JavaFileObject> sourceFileObjects,
List<String> classnames,
Iterable<? extends Processor> processors)
{
if (processors != null && processors.iterator().hasNext())
explicitAnnotationProcessingRequested = true;
// as a JavaCompiler can only be used once, throw an exception if
// it has been used before.
if (hasBeenUsed)
throw new AssertionError("attempt to reuse JavaCompiler");
hasBeenUsed = true;
// forcibly set the equivalent of -Xlint:-options, so that no further
// warnings about command line options are generated from this point on
options.put(XLINT_CUSTOM.text + "-" + LintCategory.OPTIONS.option, "true");
options.remove(XLINT_CUSTOM.text + LintCategory.OPTIONS.option);
start_msec = now();
try {
initProcessAnnotations(processors);
//此处会调用到mapStruct中的processor类的方法.
delegateCompiler =
processAnnotations(
enterTrees(stopIfError(CompileState.PARSE, parseFiles(sourceFileObjects))),
classnames);
delegateCompiler.compile2();
delegateCompiler.close();
elapsed_msec = delegateCompiler.elapsed_msec;
} catch (Abort ex) {
if (devVerbose)
ex.printStackTrace(System.err);
} finally {
if (procEnvImpl != null)
procEnvImpl.close();
}
}
关键代码,在mapstruct-processor包中,有个对应的类MappingProcessor继承了AbstractProcessor,并实现其process方法。通过对AST进行相应的代码增强,从而实现对最终编译的对象进行修改的方法。
@SupportedAnnotationTypes({"org.mapstruct.Mapper"})
@SupportedOptions({"mapstruct.suppressGeneratorTimestamp", "mapstruct.suppressGeneratorVersionInfoComment", "mapstruct.unmappedTargetPolicy", "mapstruct.unmappedSourcePolicy", "mapstruct.defaultComponentModel", "mapstruct.defaultInjectionStrategy", "mapstruct.disableBuilders", "mapstruct.verbose"})
public class MappingProcessor extends AbstractProcessor {
public boolean process(Set<? extends TypeElement> annotations, RoundEnvironment roundEnvironment) {
if (!roundEnvironment.processingOver()) {
RoundContext roundContext = new RoundContext(this.annotationProcessorContext);
Set<TypeElement> deferredMappers = this.getAndResetDeferredMappers();
this.processMapperElements(deferredMappers, roundContext);
Set<TypeElement> mappers = this.getMappers(annotations, roundEnvironment);
this.processMapperElements(mappers, roundContext);
} else if (!this.deferredMappers.isEmpty()) {
Iterator var8 = this.deferredMappers.iterator();
while(var8.hasNext()) {
MappingProcessor.DeferredMapper deferredMapper = (MappingProcessor.DeferredMapper)var8.next();
TypeElement deferredMapperElement = deferredMapper.deferredMapperElement;
Element erroneousElement = deferredMapper.erroneousElement;
String erroneousElementName;
if (erroneousElement instanceof QualifiedNameable) {
erroneousElementName = ((QualifiedNameable)erroneousElement).getQualifiedName().toString();
} else {
erroneousElementName = erroneousElement != null ? erroneousElement.getSimpleName().toString() : null;
}
deferredMapperElement = this.annotationProcessorContext.getElementUtils().getTypeElement(deferredMapperElement.getQualifiedName());
this.processingEnv.getMessager().printMessage(Kind.ERROR, "No implementation was created for " + deferredMapperElement.getSimpleName() + " due to having a problem in the erroneous element " + erroneousElementName + ". Hint: this often means that some other annotation processor was supposed to process the erroneous element. You can also enable MapStruct verbose mode by setting -Amapstruct.verbose=true as a compilation argument.", deferredMapperElement);
}
}
return false;
}
}
如何断点调试:
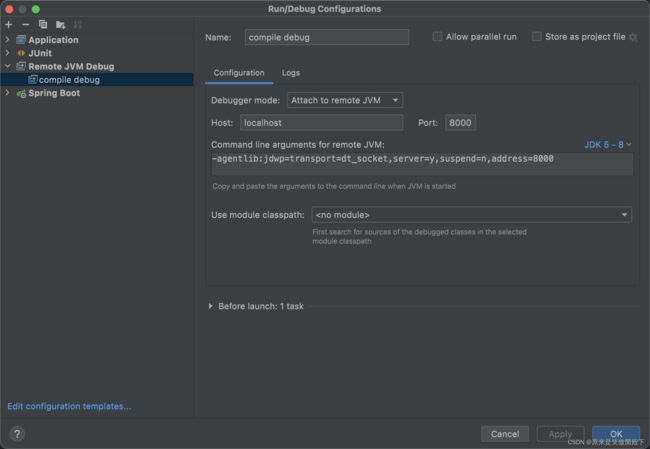
因为这个注解处理器是在解析->编译的过程完成,跟普通的jar包调试不太一样,maven框架为我们提供了调试入口,需要借助maven才能实现debug。所以需要在编译过程打开debug才可调试。
- 在项目的pom文件所在目录执行mvnDebug compile
- 接着用idea打开项目,添加一个remote,端口为8000
- 打上断点,debug 运行remote即可调试。
附录
测试代码如下,采用Spock框架 + JAVA代码 实现。Spock框架作为当前最火热的测试框架,你值得学习一下。Spock框架初体验:更优雅地写好你的单元测试
// @Resource
@Shared
MapperStructService mapperStructService
def setupSpec() {
mapperStructService = new MapperStructService()
}
@Unroll
def "test mapperStructTest times = #times"() {
given: "初始化数据"
UserDTO dto = new UserDTO(name: "笑傲菌", age: 20, idCard: "1234",
phoneNumber: "18211932334", address: "北京天安门", gender: 1,
birthday: new Date(), isMarried: false)
when: "调用方法"
// 传统的getter、setter拷贝
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
UserInfoVO oldRes = mapperStructService.originalCopyItem(dto, times)
Duration originalWasteTime = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
// 采用工具实现反射类的拷贝
long startTime1 = System.nanoTime();
UserInfoVO utilRes = mapperStructService.utilCopyItem(dto, times)
Duration utilWasteTime = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime1);
long startTime2 = System.nanoTime();
UserInfoVO mapStructRes = mapperStructService.newCopyItem(dto, times)
Duration mapStructWasteTime = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime2);
then: "校验数据"
println("times = "+ times)
println("原始拷贝的消耗时间为: " + originalWasteTime.getNano())
println("BeanUtils拷贝的消耗时间为: " + utilWasteTime.getNano())
println("mapStruct拷贝的消耗时间为: " + mapStructWasteTime.getNano())
println()
where: "比较不同次数调用的耗时"
times || ignore
1 || null
10 || null
100 || null
1000 || null
}
测试的Service如下所示:
public class MapperStructService {
public UserInfoVO newCopyItem(UserDTO userDTO, int times) {
UserInfoVO userInfoVO = new UserInfoVO();
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
userInfoVO = InfoConverter.INSTANT.convert(userDTO);
}
return userInfoVO;
}
public UserInfoVO originalCopyItem(UserDTO userDTO, int times) {
UserInfoVO userInfoVO = new UserInfoVO();
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
userInfoVO.setUserName(userDTO.getName());
userInfoVO.setAge(userDTO.getAge());
userInfoVO.setBirthday(userDTO.getBirthday());
userInfoVO.setIdCard(userDTO.getIdCard());
userInfoVO.setGender(userDTO.getGender());
userInfoVO.setIsMarried(userDTO.getIsMarried());
userInfoVO.setPhoneNumber(userDTO.getPhoneNumber());
userInfoVO.setAddress(userDTO.getAddress());
}
return userInfoVO;
}
public UserInfoVO utilCopyItem(UserDTO userDTO, int times) {
UserInfoVO userInfoVO = new UserInfoVO();
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
BeanUtils.copyProperties(userDTO, userInfoVO);
}
return userInfoVO;
}
}
参考文献
踩坑BeanUtils.copy**()导致的业务处理速度过慢
mapstruct原理解析
MapStruct官网
Mapstruct源码解析- 框架实现原理