5.基于深度学习的轴承故障诊断--连续小波变换cwt
该专栏将较为详细的介绍如何利用深度学习进行故障诊断方面的学术研究,主要以轴承为例,包括深度学习常用框架Tensorflow的搭建以及使用,并会记录完整搭建过程,并以卷积神经网络与循环神经网络为例进行代码编写和实际运行,相信经过本次学习,你能够入门开始着手研究。
完成该专栏的学习,你将会收获以下知识:
1.Anaconda的安装以及使用,深度学习框架Tensorflow2的安装以及使用
2.学会如何利用卷积神经网络与循环神经网络进行轴承故障诊断-以凯斯西楚大学轴承数据集为例
3.学会一些常用调参技巧
4.入门利用深度学习进行故障诊断的学术研究
说明:
1.专栏所涉及代码会全部公开在本人的github上,欢迎交流以及star。
https://github.com/boating-in-autumn-rain?tab=repositories
2.该专栏涉及数据集以及相关安装包在公众号《秋雨行舟》回复轴承即可领取。
3.对于该项目有疑问的可以公众号留言,看到了就会回复。
4.该专栏对应的视频可在B站搜索《秋雨行舟》进行观看学习。
利用连续小波变换进行信号时域到时频域的转换。
# 博客:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38918049/article/details/124948664?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
# github:https://github.com/boating-in-autumn-rain?tab=repositories
# 微信公众号:秋雨行舟
# B站:秋雨行舟
#
# 该项目涉及数据集以及相关安装包在公众号《秋雨行舟》回复轴承即可领取。
# 对于该项目有疑问的可以在上述四个平台中留言,看到了就会回复。
# 该项目对应的视频可在B站搜索《秋雨行舟》进行观看学习。
# 欢迎交流学习,共同进步
import pywt
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sign import preprocess
path = r'../sign/data/0HP'
x_train, y_train, x_valid, y_valid, x_test, y_test = preprocess.prepro(
d_path=path,
length=784,
number=30,
normal=True,
rate=[0.6, 0.2, 0.2],
enc=False, enc_step=28)
for i in range(52, len(x_train)):
N = 784
fs = 12000
t = np.linspace(0, 784 / fs, N, endpoint=False)
wavename = 'cmor3-3'
totalscal = 256
fc = pywt.central_frequency(wavename)
cparam = 2 * fc * totalscal
scales = cparam / np.arange(totalscal, 1, -1)
[cwtmatr, frequencies] = pywt.cwt(x_train[i], scales, wavename, 1.0 / fs)
plt.contourf(t, frequencies, abs(cwtmatr))
plt.axis('off')
plt.gcf().set_size_inches(784 / 100, 784 / 100)
plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_locator(plt.NullLocator())
plt.gca().yaxis.set_major_locator(plt.NullLocator())
plt.subplots_adjust(top=1, bottom=0, right=1, left=0, hspace=0, wspace=0)
plt.margins(0, 0)
x = r'./cwt_picture/train/' + str(i) + '-' + str(y_train[i]) + '.jpg'
plt.savefig(x)利用连续小波变换之后的时频图进行深度学习模型训练以及分类实验。
读取图片代码:
# 博客:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38918049/article/details/124948664?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
# github:https://github.com/boating-in-autumn-rain?tab=repositories
# 微信公众号:秋雨行舟
# B站:秋雨行舟
#
# 该项目涉及数据集以及相关安装包在公众号《秋雨行舟》回复轴承即可领取。
# 对于该项目有疑问的可以在上述四个平台中留言,看到了就会回复。
# 该项目对应的视频可在B站搜索《秋雨行舟》进行观看学习。
# 欢迎交流学习,共同进步
import numpy as np
import os
from PIL import Image
def read_directory(directory_name,height,width,normal):
file_list=os.listdir(directory_name)
file_list.sort(key=lambda x: int(x.split('-')[0]))
img = []
label0=[]
for each_file in file_list:
img0 = Image.open(directory_name + '/'+each_file)
img0 = img0.convert('L')
gray = img0.resize((height,width))
img.append(np.array(gray).astype(np.float))
label0.append(float(each_file.split('.')[0][-1]))
if normal:
data = np.array(img)/255.0#归一化
else:
data = np.array(img)
data=data.reshape(-1,1,height,width)
label=np.array(label0)
return data,label
分类实验代码:
# 博客:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38918049/article/details/124948664?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
# github:https://github.com/boating-in-autumn-rain?tab=repositories
# 微信公众号:秋雨行舟
# B站:秋雨行舟
#
# 该项目涉及数据集以及相关安装包在公众号《秋雨行舟》回复轴承即可领取。
# 对于该项目有疑问的可以在上述四个平台中留言,看到了就会回复。
# 该项目对应的视频可在B站搜索《秋雨行舟》进行观看学习。
# 欢迎交流学习,共同进步
from cwt.read_picture import read_directory
from tensorflow import keras
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow.keras as keras
import tensorflow.keras.layers as layers
from tensorflow_core.python.keras import layers
import random
from datetime import datetime
import numpy as np
num_classes = 10
height = 52
width = 52
# 小波时频图---2D-CNN输入
x_train, y_train = read_directory(r'cwt_picture\train', height, width, normal=1)
x_valid, y_valid = read_directory(r'cwt_picture\valid', height, width, normal=1)
x_test, y_test = read_directory(r'cwt_picture\test', height, width, normal=1)
x_train = np.squeeze(x_train)
x_valid = np.squeeze(x_valid)
x_test = np.squeeze(x_test)
x_train = np.expand_dims(x_train, axis=3)
x_valid = np.expand_dims(x_valid, axis=3)
x_test = np.expand_dims(x_test, axis=3)
y_train = [int(i) for i in y_train]
y_valid = [int(i) for i in y_valid]
y_test = [int(i) for i in y_test]
x_train = np.array(x_train)
y_train = np.array(y_train)
x_valid = np.array(x_valid)
y_valid = np.array(y_valid)
x_test = np.array(x_test)
y_test = np.array(y_test)
print(x_train.shape)
print(x_test.shape)
print(y_train[:5])
print("---------------------------------")
print(y_train.shape)
print(y_test.shape)
print("x_train的最大值和最小值:", x_train.max(), x_train.min())
print("x_test的最大值和最小值:", x_test.max(), x_test.min())
index = [i for i in range(len(y_train))]
random.shuffle(index)
x_train = np.array(x_train)[index]
y_train = np.array(y_train)[index]
index = [i for i in range(len(y_valid))]
random.shuffle(index)
x_valid = np.array(x_valid)[index]
y_valid = np.array(y_valid)[index]
index2 = [i for i in range(len(y_test))]
random.shuffle(index2)
x_test = np.array(x_test)[index2]
y_test = np.array(y_test)[index2]
class CustomModelCheckpoint(keras.callbacks.Callback):
def __init__(self, model, path):
self.model = model
self.path = path
self.best_loss = np.inf
def on_epoch_end(self, epoch, logs=None):
val_loss = logs['val_loss']
if val_loss < self.best_loss:
print("\nValidation loss decreased from {} to {}, saving model".format(self.best_loss, val_loss))
self.model.save_weights(self.path, overwrite=True)
self.best_loss = val_loss
def mymodel():
inputs = keras.Input(shape=(x_train.shape[1], x_train.shape[2], x_train.shape[3]))
h1 = layers.Conv2D(filters=8, kernel_size=(3, 3), strides=(1,1), padding='same', activation='relu')(inputs)
h1 = layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2, 2), padding='same')(h1)
h1 = layers.Conv2D(filters=16, kernel_size=(3,3), strides=(1,1), padding='same', activation='relu')(h1)
h1 = layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2), padding='same')(h1)
h1 = layers.Flatten()(h1)
h1 = layers.Dense(32, activation='relu')(h1)
h1 = layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')(h1)
deep_model = keras.Model(inputs, h1, name="cnn")
return deep_model
model = mymodel()
model.summary()
startdate = datetime.utcnow() # 获取当前时间
# 编译模型
model.compile(
optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(),
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
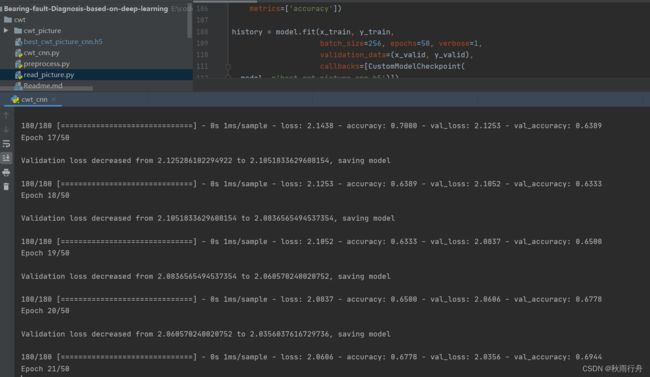
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train,
batch_size=256, epochs=50, verbose=1,
validation_data=(x_valid, y_valid),
callbacks=[CustomModelCheckpoint(
model, r'best_cwt_picture_cnn.h5')])
#加载模型
model.load_weights(filepath='best_cwt_picture_cnn.h5')
# 编译模型
model.compile(loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(), metrics=['accuracy'])
# 评估模型
scores = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=1)
print('%s: %.2f%%' % (model.metrics_names[1], scores[1] * 100))
y_predict = model.predict(x_test)
y_pred_int = np.argmax(y_predict, axis=1)
# print(y_pred_int[0:5])
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred_int, digits=4))
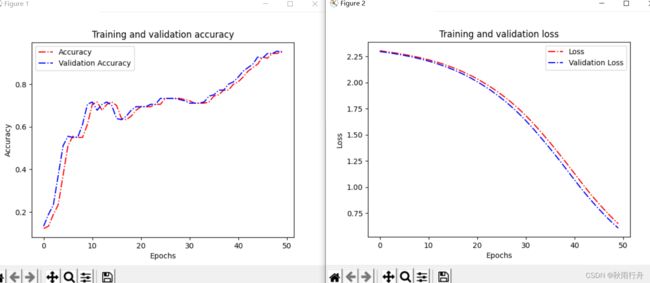
def acc_line():
# 绘制acc和loss曲线
acc = history.history['accuracy']
val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs = range(len(acc)) # Get number of epochs
# 画accuracy曲线
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'r', linestyle='-.')
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', linestyle='dashdot')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel("Accuracy")
plt.legend(["Accuracy", "Validation Accuracy"])
plt.figure()
# 画loss曲线
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'r', linestyle='-.')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'b', linestyle='dashdot')
plt.title('Training and validation loss')
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.legend(["Loss", "Validation Loss"])
plt.show()
acc_line()
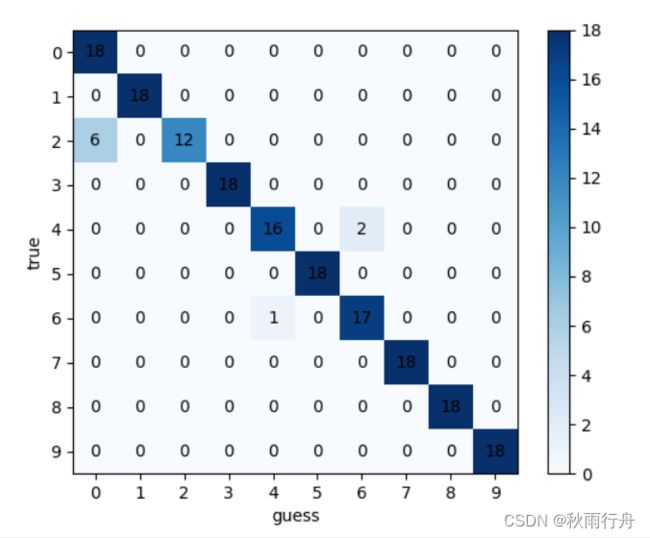
# 绘制混淆矩阵
def confusion():
y_pred_gailv = model.predict(x_test, verbose=1)
y_pred_int = np.argmax(y_pred_gailv, axis=1)
print(len(y_pred_int))
con_mat = confusion_matrix(y_test.astype(str), y_pred_int.astype(str))
print(con_mat)
classes = list(set(y_train))
classes.sort()
plt.imshow(con_mat, cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
indices = range(len(con_mat))
plt.xticks(indices, classes)
plt.yticks(indices, classes)
plt.colorbar()
plt.xlabel('guess')
plt.ylabel('true')
for first_index in range(len(con_mat)):
for second_index in range(len(con_mat[first_index])):
plt.text(first_index, second_index, con_mat[second_index][first_index], va='center', ha='center')
plt.show()
confusion()
实验结果展示:
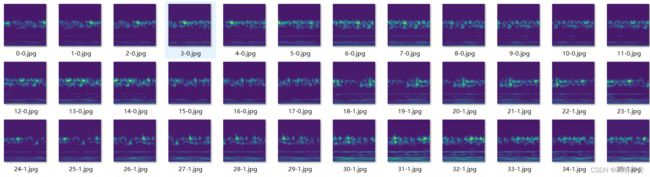
连续小波变换后的时频图像:
前面的数字代表张数,后面代表标签。
利用连续小波变换进行分类实验:
训练过程:
混淆矩阵:
最后,如有疑问欢迎交流,共同进步。