pytorch快手上手——从读取数据到ncnn部署
目录
1. 读取数据集
1.1 torch2yaml
1. 2定义一个dataset类
2. 训练模型
3. 图片分类预测
3.1 python中图片预测
3.2 使用ncnn进行图片分类预测
3.2.1 编译和配置ncnn
3.2.2 pytorch模型转ncnn模型
3.2.2 使用ncnn进行预测
4. 代码链接
5. 参考链接
1. 读取数据集
pytorch默认的数据存放格式如下图所示,使用torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder函数可以直接生成数据和标签,ImageFolder内部使用PIL进行数据读取,在python中使用没有问题,但部署时一般都是采用opencv读取图片的,容易造成数据的不统一,故在python中可以直接使用opencv读取图片代码如下:
1.1 torch2yaml
根据图片存储生成存放图片路径和标签的yaml文件,详细代码如下:
import os
import yaml
# class与label对应关系
class2label = {"bird": 0, "boat": 1, "cake": 2, "jellyfish": 3, "king_crab": 4}
# 生成图片路径
def gen_imgdir(dir="train"):
txt = []
for classdir in os.listdir("./mini_imagenet/" + dir):
for imgdir in os.listdir("./mini_imagenet/" + dir + "/" + classdir):
txt.append("./mini_imagenet/" + dir + "/" + classdir + "/" + imgdir)
with open(dir + '.yaml', "w", encoding="utf-8") as f1:
yaml.dump(txt, f1)
# 生成图片标签
def gen_label(dir="train"):
txt = []
with open(dir + ".yaml", "r") as f2:
con = f2.read()
C = yaml.load(con, Loader=yaml.FullLoader)
for i in C:
label = i.split("/")[3]
txt.append(class2label[label])
with open(dir + '_label.yaml', "w", encoding="utf-8") as f2:
yaml.dump(txt, f2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 生成图片路径和标签
# for i in {"train", "test", "val"}:
# dir = i
# gen_imgdir(dir)
# gen_label(dir)
# 下面代码在生成images文件夹下的yaml文件时使用
# txt = []
# for classdir in os.listdir("./images"):
# txt.append("./images" "/" + classdir)
# with open("./images/predict" + '.yaml', "w", encoding="utf-8") as f1:
# yaml.dump(txt, f1)
# txt = []
# with open("./images/predict" + '.yaml', "r") as f2:
# con = f2.read()
# C = yaml.load(con, Loader=yaml.FullLoader)
# for i in C:
# label = i.split("/")[3]
# txt.append(class2label[label])
# with open("./images/predict" + '_label.yaml', "w", encoding="utf-8") as f2:
# yaml.dump(txt, f2)
pass
1. 2定义一个dataset类
有了上面的yaml文件,就可以随手写一个dataset类读取和加载数据
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
import os
import cv2
import warnings
import numpy as np
import torch
import yaml
import albumentations as A
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
# -------------------------------------------------定义数据类---------------------------------------------------
class mydataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self,
trans=True,
mode="train",
img_size=(224, 224)):
# -------------------------------------------初始化数据&标签-----------------------------------------------------
super().__init__()
self.img_size = img_size
self.trans = trans
with open(mode + '.yaml', "r") as f1:
content = f1.read()
self.dir = yaml.load(content, Loader=yaml.FullLoader)
with open(mode + '_label.yaml', "r") as f2:
content = f2.read()
self.label = yaml.load(content, Loader=yaml.FullLoader)
# ----------------------------------------------------获取数据---------------------------------------------------
def __getitem__(self, idx):
imgsdir = self.dir[idx]
img = cv2.imread(imgsdir)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# --------------------------------------------数据增强----------------------------------------------------
if self.trans:
img = self.img_aug(img)
# ---------------------------------------------生成数据-----------------------------------------------------
img = cv2.resize(img, self.img_size)
img = img.transpose(2, 0, 1).astype('float32')
label = np.array(self.label[idx])
return torch.tensor(img), torch.tensor(label.astype('int64'))
# ----------------------------------------------------获取数据量-------------------------------------------------
def __len__(self):
return len(self.dir)
# -----------------------------------------------------数据增强--------------------------------------------------
def img_aug(self, img):
return A.normalize(img=img, mean=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406), std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225))
# -----------------------------------------------------图像显示--------------------------------------------------
def show_normalize(self, idx):
for i in idx:
imgsdir = self.dir[i]
img = cv2.imread(imgsdir)
cv2.imshow('origin_img', img)
cv2.moveWindow('origin_img', 0, 0)
if self.trans:
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = self.img_aug(img)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
img = cv2.resize(img, self.img_size)
cv2.imshow('normalized_img', img)
cv2.moveWindow('normalized_img', 720, 0)
cv2.waitKey(5000)
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = mydataset(trans=True, mode="train")
a.show_normalize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
2. 训练模型
可以加载数据后,我们就可以训练模型了
import os
import json
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
from tqdm import tqdm
from torchsummary import summary
from mobilenet_v3 import mobilenet_v3_small, mobilenet_v3_large
from torchvision.models import shufflenet_v2_x0_5
from mydataset import mydataset
def train():
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print("using {} device.".format(device))
batch_size = 16
epochs = 50
train_dataset = mydataset(trans=True,
mode="train",)
train_num = len(train_dataset)
validate_dataset = mydataset(trans=True,
mode="val",)
val_num = len(validate_dataset)
# 定义数据读取方式
nw = min([os.cpu_count(), batch_size if batch_size > 1 else 0, 8]) # number of workers
print('Using {} dataloader workers every process'.format(nw))
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True,
num_workers=nw, persistent_workers=True)
validate_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(validate_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False,
num_workers=nw, persistent_workers=True)
print("using {} images for training, {} images for validation.".format(train_num,
val_num))
net = shufflenet_v2_x0_5()
# net = mobilenet_v3_small(num_classes=10)
# net = mobilenet_v3_large(num_classes=10)
# net.load_state_dict(torch.load("./model/mobilenet_v3.pth"))
# net.load_state_dict(torch.load("./model/mobilenet_v3_large.pth"))
summary(net, (3, 224, 224), batch_size=1, device="cpu")
net.to(device)
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
params = [p for p in net.parameters() if p.requires_grad]
optimizer = optim.Adam(params, lr=0.0001)
best_acc = 0.0
save_path = './model/shufflenet.pth'
# save_path = './model/mobilenet_v3_large.pth'
train_steps = len(train_loader)
for epoch in range(epochs):
# train
net.train()
running_loss = 0.0
train_bar = tqdm(train_loader)
for step, data in enumerate(train_bar):
images, labels = data
optimizer.zero_grad()
logits = net(images.to(device))
# labels = labels.float()
loss = loss_function(logits, labels.to(device))
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
train_bar.desc = "train epoch[{}/{}] loss:{:.3f}".format(epoch + 1, epochs, loss)
net.eval()
acc = 0.0 # accumulate accurate number / epoch
with torch.no_grad():
val_bar = tqdm(validate_loader)
for val_data in val_bar:
val_images, val_labels = val_data
outputs = net(val_images.to(device))
predict_y = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)[1]
acc += torch.eq(predict_y, val_labels.to(device)).sum().item()
val_bar.desc = "valid epoch[{}/{}]".format(epoch + 1, epochs)
val_accurate = acc / val_num
print('[epoch %d] train_loss: %.3f val_accuracy: %.3f' %
(epoch + 1, running_loss / train_steps, val_accurate))
if val_accurate >= best_acc:
best_acc = val_accurate
torch.save(net.state_dict(), save_path)
print('Finished Training')
if __name__ == '__main__':
train()
3. 图片分类预测
3.1 python中图片预测
拿到训练后的模型后,对图片进行分类预测,精度不高,仅作展示,使用测试集进行预测精度为73%,使用随机选择的15张图片进行预测,精度仅53%,可以通过数据增强、调参等方式提高精度。
import torch
from mydataset import mydataset
from torchvision.models import shufflenet_v2_x0_5
from tqdm import tqdm
import cv2
batch_size = 1
epochs = 50
device = torch.device("cpu" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
class2label = {"bird": 0, "boat": 1, "cake": 2, "jellyfish": 3, "king_crab": 4}
def predict():
model = shufflenet_v2_x0_5(num_classes=5).to(device)
model_weight_path = "./model/shufflenet.pth"
try:
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_weight_path, map_location=device))
print("successed")
except:
print("failed to load model")
print("using {} device.".format(device))
test_dataset = mydataset(trans=True,
mode="./images/predict")
# test_dataset = mydataset(trans=True,
# mode="test")
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False,
num_workers=1)
test_num = len(test_dataset)
model.eval()
test_bar = tqdm(test_loader)
acc = 0.0
with torch.no_grad():
for test_data in test_bar:
test_images, test_labels = test_data
test_images_y = torch.squeeze(test_images).permute(1, 2, 0).numpy()
outputs = model(test_images.to(device))
outputs = torch.squeeze(outputs)
outputs = torch.softmax(outputs, dim=0)
predict = torch.max(outputs, dim=0)[1]
predict_y = predict.numpy()
test_labels_y = test_labels.numpy()
classname = list(class2label.keys())[list(class2label.values()).index(predict_y)]
real_classname = list(class2label.keys())[list(class2label.values()).index(test_labels_y)]
print(f"真实类别为: {real_classname}, 预测类别为: {classname}, 预测概率为: {outputs.numpy()[predict_y]:.3}, "
f"第一个点像数值为: {test_images_y[0, 0, :]}")
# cv2.imshow("test", test_images_y)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
acc += torch.eq(predict, test_labels.to(device)).sum().item()
test_accurate = acc / test_num
print(f"test_accurate = {test_accurate:.3}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
predict()
3.2 使用ncnn进行图片分类预测
3.2.1 编译和配置ncnn
首先是编译ncnn,参考链接如下:
windows下:【ncnn系列一】Win10 + protobuf3.4.0 + NCNN + VS2017 + OpenCV3.4.2 编译和测试_scut_lrr的博客-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42448226/article/details/104951934
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42448226/article/details/104951934
Linux下:
Ubuntu下编译ncnn_努力的老周的博客-CSDN博客_ubuntu编译ncnn![]() https://blog.csdn.net/justidle/article/details/104948080编译好后配置环境,windows下使用vs studio,配置如下:
https://blog.csdn.net/justidle/article/details/104948080编译好后配置环境,windows下使用vs studio,配置如下:
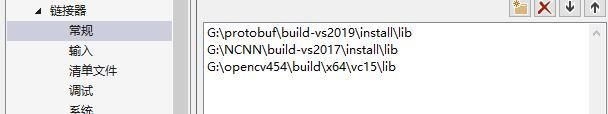
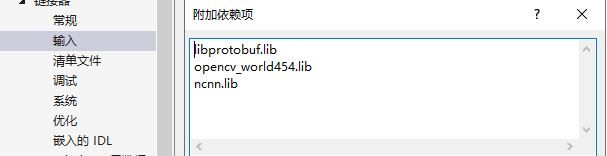
windows下:
Linux下:
写一个Cmakelist配置文件,参考链接如下:
【yolox】——5分钟用ncnn测试yolox_农夫山泉2号的博客-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/u011622208/article/details/119173446
https://blog.csdn.net/u011622208/article/details/119173446
3.2.2 pytorch模型转ncnn模型
首先生成onnx模型,代码如下:
import numpy as np
import torch
import onnxruntime
from torchvision.models import shufflenet_v2_x0_5
device = torch.device("cuda")
# ---------------- --------------------------------tensor2numpy-----------------------------------------------
def to_numpy(tensor):
return tensor.detach().cpu().numpy() if tensor.requires_grad else tensor.cpu().numpy()
def main():
# ------------------------------------------------定义模型--------------------------------------------------
x = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224, device='cuda')
model = shufflenet_v2_x0_5().to(device)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load("./model/shufflenet.pth"))
# ------------------------------------------------导出模型--------------------------------------------------
torch.onnx.export(model, # model
x, # input
"./model/shufflenet.onnx", # saved_model,
export_params=True,
opset_version=11,
input_names=["input"],
output_names=["output"])
# dynamic_axes={'input': {'0': 'batch_size'},
# 'output': {'0': 'batch_size'}})
# ------------------------------------------------精度对比--------------------------------------------------
model.eval()
out = model(x)
ort_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession("./model/shufflenet.onnx")
ort_inputs = {ort_session.get_inputs()[0].name: to_numpy(x)}
ort_outs = ort_session.run(None, ort_inputs)
np.testing.assert_allclose(to_numpy(out), ort_outs[0], rtol=1e-3, atol=1e-5)
print(out)
print(ort_outs)
print("Excepted model has been test with ONNXRuntime, and the result looks good!")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
然后使用onnx模型生成ncnn模型
1. 在pytorch终端简化模型
python3 -m onnxsim model.onnx new_model.onnx
2. 在编译好的ncnn文件中找到onnx2ncnn/onnx2ncnn.exe生成ncnn模型
./onnx2ncnn new_model.onnx new_model.param new_model.bin
3.2.2 使用ncnn进行预测
在ncnn源码自带的案例中随便找一个分类模型,如shufflenetv2.cpp
导入自己的模型,注意路径,在自己的主cpp文件路径下创建model文件夹,并将model.param和model.bin放入
mobilenet_v3.load_param("./model/model.param");
mobilenet_v3.load_model("./model/model.bin");
数据处理,如自己的dataset保持一致
const char* imagepath = argv[1];
cv::Mat m = cv::imread(imagepath);
cv::resize(m, m, cv::Size(224, 224));
cv::cvtColor(m, m, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB);
ncnn::Mat in = ncnn::Mat::from_pixels(bgr.data, ncnn::Mat::PIXEL_RGB, bgr.cols, bgr.rows);
const float mean_vals[3] = { 0.485f, 0.456f, 0.406f };
const float std_vals[3] = { 1 / 0.229f, 1 / 0.224f, 1 / 0.225f };
const float norm_vals[3] = { 1 / 255.f, 1 / 255.f, 1 / 255.f };
in.substract_mean_normalize(0, norm_vals);
in.substract_mean_normalize(mean_vals, std_vals);
模型的输入与输出,"input"和"output"与前面导出onnx模型时候的输入输出保持一致
ex.input("input", in);
ncnn::Mat out;
ex.extract("output", out);
稍作修改后,如下:
// Tencent is pleased to support the open source community by making ncnn available.
//
// Copyright (C) 2018 THL A29 Limited, a Tencent company. All rights reserved.
//
// Licensed under the BSD 3-Clause License (the "License"); you may not use this file except
// in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// https://opensource.org/licenses/BSD-3-Clause
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed
// under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR
// CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
// specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
#include "net.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using std::vector;
using std::string;
using std::endl;
using std::cout;
static const vector classes{ "bird", "boat", "cake", "jellyfish", "king_crab"};
static int detect_mobilenet_v3(const cv::Mat& bgr, std::vector& cls_scores)
{
ncnn::Net mobilenet_v3;
mobilenet_v3.opt.use_int8_inference = true;
mobilenet_v3.load_param("./model/model.param");
mobilenet_v3.load_model("./model/model.bin");
ncnn::Mat in = ncnn::Mat::from_pixels(bgr.data, ncnn::Mat::PIXEL_RGB, bgr.cols, bgr.rows);
const float mean_vals[3] = { 0.485f, 0.456f, 0.406f };
const float std_vals[3] = { 1 / 0.229f, 1 / 0.224f, 1 / 0.225f };
const float norm_vals[3] = { 1 / 255.f, 1 / 255.f, 1 / 255.f };
in.substract_mean_normalize(0, norm_vals);
in.substract_mean_normalize(mean_vals, std_vals);
const float* ptr1 = in.channel(0);
const float* ptr2 = in.channel(1);
const float* ptr3 = in.channel(2);
cout << ptr1[0] << " "<< ptr2[0] << " " << ptr3[0] << endl;
ncnn::Extractor ex = mobilenet_v3.create_extractor();
ex.input("input", in);
ncnn::Mat out;
ex.extract("output", out);
//manually call softmax on the fc output
//convert result into probability
//skip if your model already has softmax operation
{
ncnn::Layer* softmax = ncnn::create_layer("Softmax");
ncnn::ParamDict pd;
softmax->load_param(pd);
softmax->forward_inplace(out, mobilenet_v3.opt);
delete softmax;
}
out = out.reshape(out.w * out.h * out.c);
cls_scores.resize(out.w);
for (int j = 0; j < out.w; j++)
{
cls_scores[j] = out[j];
}
return 0;
}
static int print_topk(const std::vector& cls_scores, int topk)
{
// partial sort topk with index
int size = cls_scores.size();
std::vector > vec;
vec.resize(size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
vec[i] = std::make_pair(cls_scores[i], i);
}
std::partial_sort(vec.begin(), vec.begin() + topk, vec.end(),
std::greater >());
// print topk and score
for (int i = 0; i < topk; i++)
{
float score = vec[i].first;
int index = vec[i].second;
cout.precision(3);
cout << classes[index] << " = " << score << endl;
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
if (argc != 2)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s [imagepath]\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
const char* imagepath = argv[1];
cv::Mat m = cv::imread(imagepath);
cv::resize(m, m, cv::Size(224, 224));
cv::cvtColor(m, m, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB);
cout << m.ptr(0)[0]<< endl;
if (m.empty())
{
fprintf(stderr, "cv::imread %s failed\n", imagepath);
return -1;
}
std::vector cls_scores;
detect_mobilenet_v3(m, cls_scores);
print_topk(cls_scores, 3);
return 0;
}
生成可执行文件后测试:
1. 将mode文件夹和存放测试图片的文件夹放在对应的exe文件同级目录
2. 打开shell,输入./quantification.exe images/13.jpg进行预测
ncnn预测结果
python预测结果
![]()
第一个点的像素值误差在千分之5以内,问题不大,由于有softmax层,预测概率也有一定的误差,但不会影响预测结果。
4. 代码链接
Model-Compression/Quantification at main · liuweixue001/Model-Compression (github.com)
5. 参考链接
1. https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn