Python DOTA与PASCAL VOC格式标签数据的相互转化
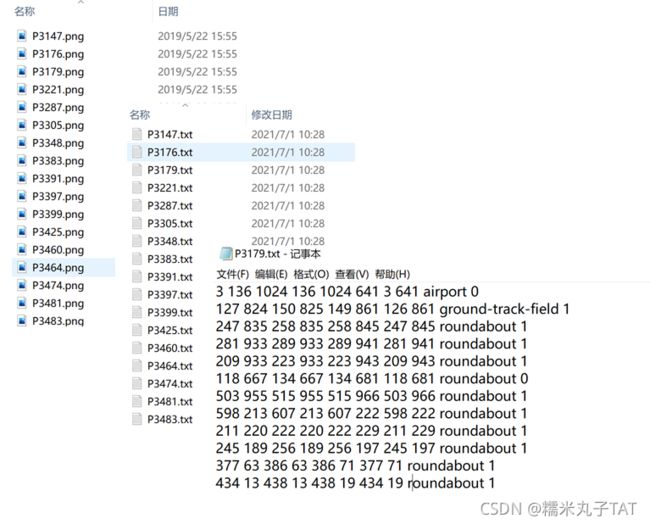
DOTA数据集是遥感影像目标检测的常用标准数据集,其标签文件以txt的形式存储,一个txt对应一张样本影像,txt中的每一行对应影像中的一个目标,每个目标的外围边界框表示为【 x1 y1 x2 y2 x3 y3 x4 y4 label difficult 】,具体如下所示:
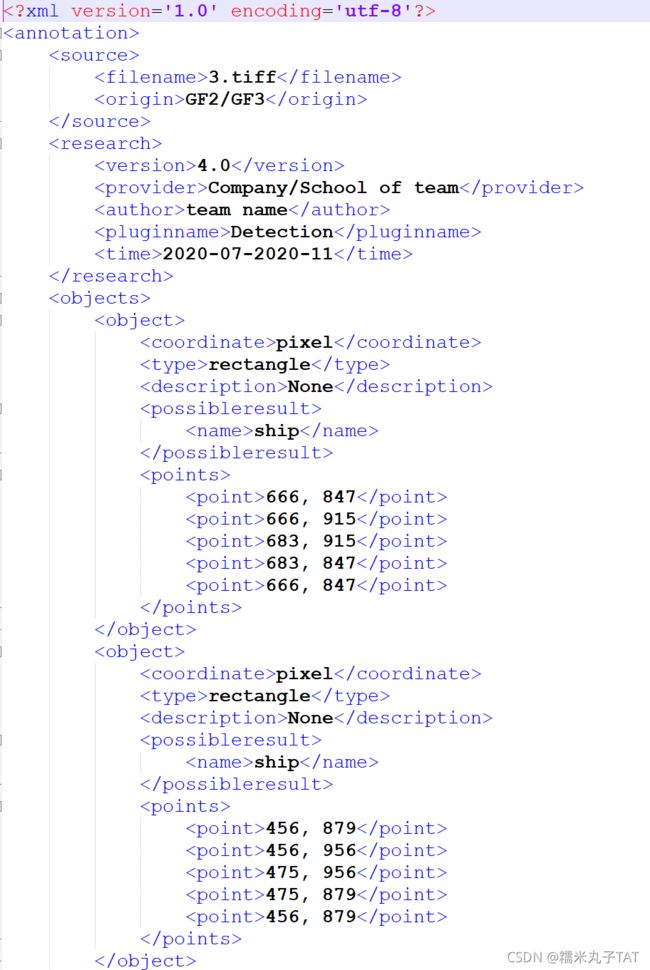
PASCAL VOC也是目标检测、图像分割任务中常用的基准数据之一,其样本标签以xml的文件形式存储,每个xml对应一张样本影像,object的边界框信息由顶点坐标值【xmin ymin xmax ymax】表示,具体如下所示:
有时候,我们同时想用倾斜框和矩形框模型对目标进行检测,就可以将标记的DOTA格式的倾斜框坐标转化为PASCAL VOC格式的矩形框坐标,转化方式如下所示:
import os
from xml.dom.minidom import Document
from xml.dom.minidom import parse
import xml.dom.minidom
import numpy as np
import csv
import cv2
import string
def poly2rect(box_list):
box_list = np.array(box_list)
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(box_list)
xmin = x - w / 2.0
ymin = y - h / 2.0
xmax = x + w / 2.0
ymax = y + h / 2.0
return xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax
def WriterXMLFiles(filename, path, box_list, label_list, w, h, d):
# dict_box[filename]=json_dict[filename]
doc = xml.dom.minidom.Document()
root = doc.createElement('annotation')
doc.appendChild(root)
foldername = doc.createElement("folder")
foldername.appendChild(doc.createTextNode("JPEGImages"))
root.appendChild(foldername)
nodeFilename = doc.createElement('filename')
nodeFilename.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(filename))
root.appendChild(nodeFilename)
pathname = doc.createElement("path")
pathname.appendChild(doc.createTextNode("xxxx"))
root.appendChild(pathname)
sourcename = doc.createElement("source")
databasename = doc.createElement("database")
databasename.appendChild(doc.createTextNode("The VOC2007 Database"))
sourcename.appendChild(databasename)
annotationname = doc.createElement("annotation")
annotationname.appendChild(doc.createTextNode("PASCAL VOC2007"))
sourcename.appendChild(annotationname)
imagename = doc.createElement("image")
imagename.appendChild(doc.createTextNode("flickr"))
sourcename.appendChild(imagename)
flickridname = doc.createElement("flickrid")
flickridname.appendChild(doc.createTextNode("0"))
sourcename.appendChild(flickridname)
root.appendChild(sourcename)
nodesize = doc.createElement('size')
nodewidth = doc.createElement('width')
nodewidth.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(w)))
nodesize.appendChild(nodewidth)
nodeheight = doc.createElement('height')
nodeheight.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(h)))
nodesize.appendChild(nodeheight)
nodedepth = doc.createElement('depth')
nodedepth.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(d)))
nodesize.appendChild(nodedepth)
root.appendChild(nodesize)
segname = doc.createElement("segmented")
segname.appendChild(doc.createTextNode("0"))
root.appendChild(segname)
for (box, label) in zip(box_list, label_list):
nodeobject = doc.createElement('object')
nodename = doc.createElement('name')
nodename.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(label)))
nodeobject.appendChild(nodename)
nodebndbox = doc.createElement('bndbox')
nodex1 = doc.createElement('xmin')
nodex1.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(box[0])))
nodebndbox.appendChild(nodex1)
nodey1 = doc.createElement('ymin')
nodey1.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(box[1])))
nodebndbox.appendChild(nodey1)
nodex2 = doc.createElement('xmax')
nodex2.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(box[2])))
nodebndbox.appendChild(nodex2)
nodey2 = doc.createElement('ymax')
nodey2.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(box[3])))
nodebndbox.appendChild(nodey2)
nodeobject.appendChild(nodebndbox)
root.appendChild(nodeobject)
fp = open(path + filename, 'w')
doc.writexml(fp, indent='\n')
fp.close()
def load_annoataion(p):
'''
load annotation from the text file
:param p:
:return:
'''
text_rects = []
text_tags = []
if not os.path.exists(p):
return np.array(text_rects, dtype=np.float32)
with open(p, 'r') as f:
for line in f.readlines():
x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4, label = line.split(' ')[0:9]
text_poly = np.array(([x1, y1], [x2, y2], [x3, y3], [x4, y4])).astype(int)
# xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = poly2rect(text_poly)
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(text_poly) #x,y为左上点坐标
xmin = x
ymin = y
xmax = x + w
ymax = y + h
text_rects.append([xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax])
text_tags.append(label)
return np.array(text_rects, dtype=np.int32), np.array(text_tags, dtype=np.str)
if __name__ == "__main__":
txt_path = './txt_labels/'
xml_path = './xml_labels/'
img_path = './images/'
txts = os.listdir(txt_path)
for count, t in enumerate(txts):
boxes, labels = load_annoataion(os.path.join(txt_path, t))
xml_name = t.replace('.txt', '.xml')
img_name = t.replace('.txt', '.png')
print(img_name)
img = cv2.imread(os.path.join(img_path, img_name))
h, w, d = img.shape
WriterXMLFiles(xml_name, xml_path, boxes, labels, w, h, d)同理,也可以将xml格式的标签文件转化为DOTA的txt格式(以AIR-SARship数据集的标签为例):
import os
import os.path
from xml.dom.minidom import parse
def xml2txt(xml_path, txt_path):
filenames = os.listdir(xml_path)
for filename in filenames:
if '.xml' in filename:
file_data = ''
xml_file = os.path.join(xml_path, filename)
dom = parse(xml_file)
root = dom.documentElement
# 根据文件的树状结构,一级级找到point点所在的位置即可
for obj in root.getElementsByTagName('object'):
line = ['0'] * 9
name = obj.getElementsByTagName('name')[0].childNodes[0].data
x1, y1 = obj.getElementsByTagName('point')[0].childNodes[0].data.split(',')
x2, y2 = obj.getElementsByTagName('point')[1].childNodes[0].data.split(',')
x3, y3 = obj.getElementsByTagName('point')[2].childNodes[0].data.split(',')
x4, y4 = obj.getElementsByTagName('point')[3].childNodes[0].data.split(',')
line = x1 + y1 + ' ' + x2 + y2 + ' ' + x3 + y3 + ' ' + x4 + y4 + ' ' + name + '\n'
file_data += line
with open(txt_path + filename.replace('.xml', '.txt'), 'w') as fw:
print('filename: ', filename)
print('file_data: ', file_data)
fw.write(file_data)
if __name__ == "__main__":
xml_path = './AIR-SARShip-2.0-xml/'
# xml_path = './test_xml/'
txt_path = './AIR-SARShip-2.0-txt/'
xml2txt(xml_path, txt_path)