Mybaties-plus 分页使用
1.简介:
查询分页分为物理分页和逻辑分页。
1)逻辑分页: 一次性查出所有数据,然后在内存中筛选需要的数据。
缺点:大数据量时容易造成内存溢出,因为是一次性查出每次返回需要的所有数据时效性低不推荐使用。
2)物理分页: 通过sql 的limit 去控制数据的偏移量每次只查出需要的数据效率高,推荐使用。
2.mybaties-plus 分页
mybaties-plus 默认的分页插件为逻辑分页不推荐使用所以需要扩展分页插件。
2.1 导入mybaties-plus 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.2</version>
</dependency>
2.2 配置mybaties-plus 分页插件
@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true)
@Configuration
public class MybatisPlusConfig
{
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor()
{
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
// 分页插件
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(paginationInnerInterceptor());
return interceptor;
}
/**
* 分页插件,自动识别数据库类型 https://baomidou.com/guide/interceptor-pagination.html
*/
public PaginationInnerInterceptor paginationInnerInterceptor()
{
PaginationInnerInterceptor paginationInnerInterceptor = new PaginationInnerInterceptor();
// 设置数据库类型为mysql
paginationInnerInterceptor.setDbType(DbType.MYSQL);
// 设置最大单页限制数量,默认 500 条,-1 不受限制
paginationInnerInterceptor.setMaxLimit(-1L);
return paginationInnerInterceptor;
}
}
2.3 分页查询实操
2.31)使用mybaties-plus 自动生成方法分页
使用service原生的page方法,推荐在controller层的请求参数继承一个基类,基类包含分页信息。
基类
@Data
public class BaseRequest {
private long current = 1;
private long size = 50;
public Page toMybatisPage() {
return new Page(current, size);
}
}
请求参数类
@Data
public class DeptRequest extends BaseRequest {
private Long id;
private String name;
}
controller
@RequestMapping("/listByPage")
public ResponseUtil listByPage(DeptRequest deptRequest){
Page page = deptService.page(deptRequest.toMybatisPage());
return ResponseUtil.ok(page.getRecords());
}
请求参数:
执行sql:
分页插件每次会先查询 count,如果count为0则不会执行查询否则执行对应的分页查询。

结果:
{
"code": 200,
"msg": null,
"data": [
{
"createBy": null,
"createTime": "2022-06-15",
"updateTime": "2022-06-15",
"deptId": 2,
"parentId": 0,
"name": "程序",
"orderNum": 1,
"departmentLeader": "lisi"
}
]
}
2.32)自定义sql分页查询
后续直接在单元测试演示
1)xml定义sql
在方法第一个参数传入IPage,方法返回值也为IPage,这两个IPage是一个对象。
mapper:
IPage<Dept>listMyPage(IPage<Dept>page);
xml:
<select id="listMyPage" resultType="Dept">
select * from t_dept
</select>
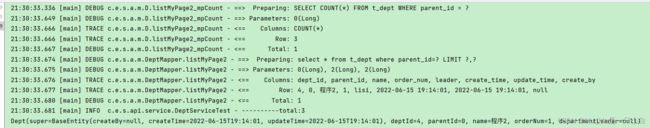
测试
@Test
void testListByPage(){
IPage<Dept> deptIPage = deptMapper.listMyPage(new Page<>(2, 2));
log.info("----------total:{}",deptIPage.getTotal());
deptIPage.getRecords().forEach(System.out::println);
}
2)xml 自定义sql并含有参数
mapper:
IPage<Dept>listMyPage2(IPage<Dept>page,@Param("dept")Dept dept);
xml:
<select id="listMyPage2" parameterType="Dept" resultType="Dept">
select * from t_dept where parent_id=#{dept.parentId}
</select>
测试:
@Test
void testListByPage2(){
IPage<Dept> deptIPage = deptMapper.listMyPage2(new Page<>(2, 2),new Dept().setParentId(0L));
log.info("----------total:{}",deptIPage.getTotal());
deptIPage.getRecords().forEach(System.out::println);
}
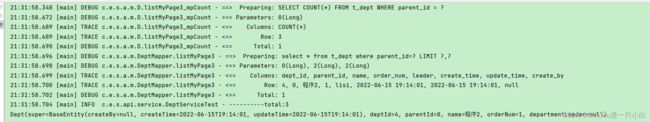
3)mapper 里面 @select 带参数分页查询
mapper:
@Select("select * from t_dept where parent_id=#{dept.parentId}")
IPage<Dept>listMyPage3(IPage<Dept>page,@Param("dept") Dept dept);
测试:
@Test
void testListByPage3(){
IPage<Dept> deptIPage = deptMapper.listMyPage3(new Page<>(2, 2),new Dept().setParentId(0L));
log.info("----------total:{}",deptIPage.getTotal());
deptIPage.getRecords().forEach(System.out::println);
}
执行sql和结果:
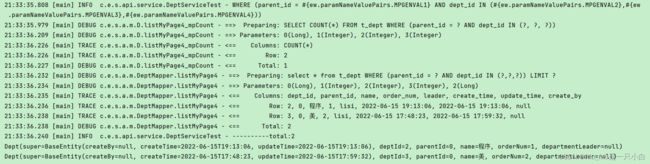
4)mapper 里面 @select 带Wrapper参数分页查询
mapper:
@Select("select * from t_dept ${ew.customSqlSegment} ")
IPage<Dept>listMyPage4(IPage<Dept>page,@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<Dept> deptWrapper);
测试:
@Test
void testListByPage4(){
LambdaQueryWrapper<Dept> wrapper = Wrappers.<Dept>lambdaQuery().eq(Dept::getParentId, 0L);
wrapper = wrapper.in(Dept::getDeptId, Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));
log.info(wrapper.getCustomSqlSegment());
IPage<Dept> deptIPage = deptMapper.listMyPage4(new Page<>(1, 2),wrapper);
log.info("----------total:{}",deptIPage.getTotal());
deptIPage.getRecords().forEach(System.out::println);
}
执行sql和结果:
以上就是在mybaties-plus的几种分页查询方式。