人工智能 | ShowMeAI资讯日报 #2022.06.03
ShowMeAI日报系列全新升级!覆盖AI人工智能 工具&框架 | 项目&代码 | 博文&分享 | 数据&资源 | 研究&论文 等方向。点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
1.工具&框架
![]()
工具库:SynapseML - 基于Apache Spark & SparkML的分布式机器学习库
tags:[机器学习,分布式,Spark,SparkML,SynapseML]
GitHub:http://github.com/microsoft/SynapseML
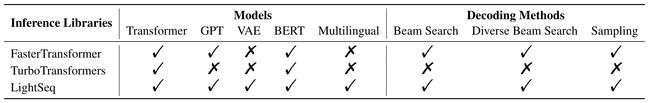
工具库:LightSeq - 序列处理和生成高性能推理库
tags:[序列处理,推理,sequence,BERT,GPT2,Transformer]
支持现代 NLP 模型,如 BERT,GPT2,Transformer 等的高效计算
LightSeq: A High Performance Inference Library for Sequence Processing and Generation’ by Bytedance Inc.
GitHub:http://github.com/bytedance/lightseq
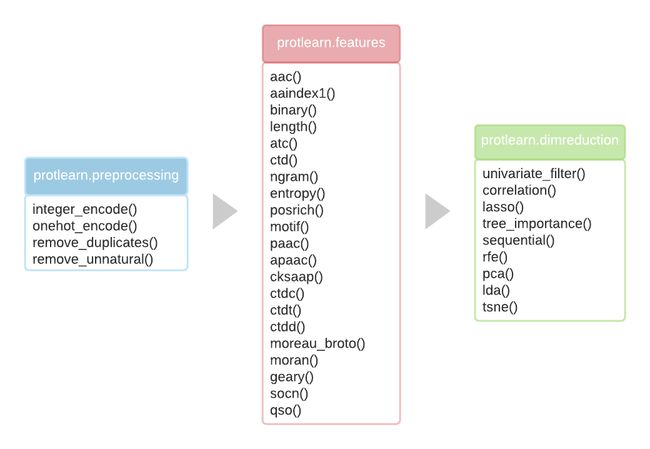
工具库:protlearn - 用于提取蛋白质序列特征的Python包
tags:[蛋白质序列,python,特征提取,序列特征]
‘protlearn - A Python package for extracting protein sequence features’ by Thomas Dorfer
GitHub:http://github.com/tadorfer/protlearn
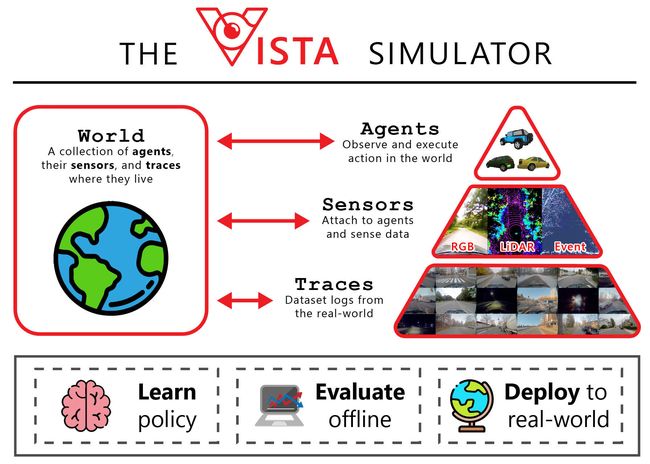
工具库:VISTA Driving Simulator - 数据驱动无人驾驶模拟器
tags:[数据驱动,无人驾驶,模拟器]
‘VISTA Driving Simulator - Data-driven simulation for training and evaluating full-scale autonomous vehicles.’ by vista-simulator
GitHub:http://github.com/vista-simulator/vista
工具库:agi-upscale - 老游戏像素背景图超分辨率工具
tags:[超分辨率,清晰化]
‘agi-upscale - agi pic viewer’ by Robin Ward
GitHub:http://github.com/eviltrout/agi-upscale
工具库:Calcure - 命令行界面的现代版日历,功能丰富,支持日程/代办等
tags:[工具,命令行,日历]
‘Calcure - Modern TUI calendar and task manager with minimal and customizable UI.’ by anufrievroman
GitHub:http://github.com/anufrievroman/calcure
2.项目&代码
![]()
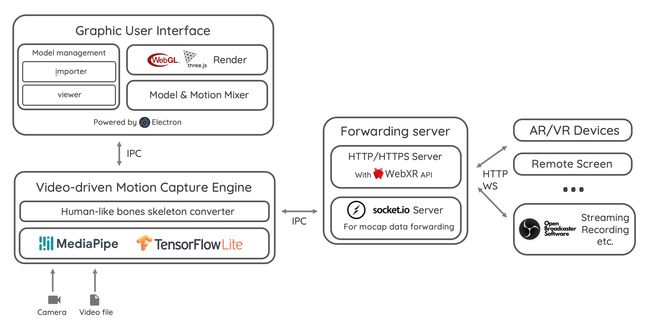
系统:SysMocap - 用于3D虚拟角色动画制作的实时动作捕捉系统
tags:[3D,动作捕捉,动作识别,姿态检测]
‘SysMocap - A real-time motion capture system for 3D virtual character animating.’ by xianfei
GitHub:http://github.com/xianfei/SysMocap
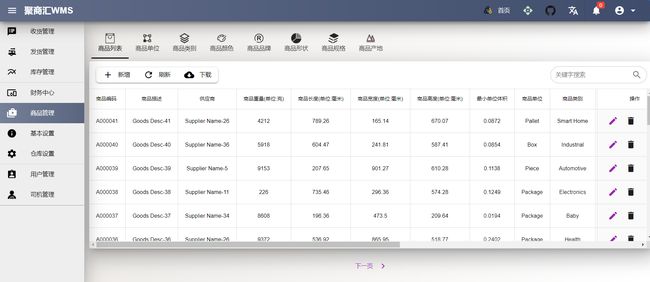
系统:聚商汇WMS仓库管理系统
tags:[管理系统,仓库管理,物流管理]
‘GreaterWMS–Open Source Warehouse Management System’ by GreaterWMS
@项目作者:「完全开源仓储管理软件,遵循Apache License 2.0协议,前后端分离,且完全开源,API使用restful协议,方便二次开发,前端代码使用quasar进行构建,后端使用Python Django3.1,利用API,可以支持多仓,波次发货,合并拣货,Milk-Run等业务模型。」
GitHub:http://github.com/Singosgu/GreaterWMS
3.博文&分享
![]()
免费书籍:深度神经网络应用(Keras)
下载地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2009.05673
书籍源码:《统计学习导论及R语言应用》Python版源码
‘ISL_python - An Introduction to Statistical Learning with Applications in PYTHON’ by Xu, Qiuping (Kim)
GitHub:http://github.com/qx0731/Sharing_ISL_python
书籍源码:《高效Pandas指南》随书代码
‘effective_pandas_book - Errata and code for Effective Pandas: Patterns for Data Manipulation book’ by matt harrison
GitHub:http://github.com/mattharrison/effective_pandas_book
4.数据&资源
![]()
数据集:DroneDeploy NeRF 数据集(“DNF”)
它包含许多由无人机捕获的真实世界场景,包括高分辨率图像、相机姿势(内在和外在)和密集的彩色点云。可用于计算机视觉研究。Dataset by Nicholas Pilkington
GitHub:http://github.com/nickponline/dd-nerf-dataset
资源列表:系统设计资源集
‘system-design-resources - These are the best resources for System Design on the Internet’ by InterviewReady
GitHub:http://github.com/InterviewReady/system-design-resources
资源列表:技术面试准备清单
针对面试过程中容易被问到的数据结构LeetCode题进行归类整理的清单
‘leetcode-curation-topical - Tech interview prep list’ by Fabian Terh
GitHub:http://github.com/fterh/leetcode-curation-topical
5.研究&论文
![]()
可以点击 这里 回复关键字 日报,免费获取整理好的6月论文合辑。
论文:Mip-NeRF: A Multiscale Representation for Anti-Aliasing Neural Radiance Fields
论文标题:Mip-NeRF: A Multiscale Representation for Anti-Aliasing Neural Radiance Fields
论文时间:ICCV 2021
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:图像渲染
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13415
代码实现:https://github.com/google/mipnerf , https://github.com/hjxwhy/mipnerf_pl
论文作者:Jonathan T. Barron, Ben Mildenhall, Matthew Tancik, Peter Hedman, Ricardo Martin-Brualla, Pratul P. Srinivasan
论文简介:Mip-NeRF is also able to match the accuracy of a brute-force supersampled NeRF on our multiscale dataset while being 22x faster./Mip-NeRF 还能够在我们的多尺度数据集上达到强力超采样 NeRF 的准确性,同时速度提高 22 倍。
论文摘要:The rendering procedure used by neural radiance fields (NeRF) samples a scene with a single ray per pixel and may therefore produce renderings that are excessively blurred or aliased when training or testing images observe scene content at different resolutions. The straightforward solution of supersampling by rendering with multiple rays per pixel is impractical for NeRF, because rendering each ray requires querying a multilayer perceptron hundreds of times. Our solution, which we call “mip-NeRF” (a la “mipmap”), extends NeRF to represent the scene at a continuously-valued scale. By efficiently rendering anti-aliased conical frustums instead of rays, mip-NeRF reduces objectionable aliasing artifacts and significantly improves NeRF’s ability to represent fine details, while also being 7% faster than NeRF and half the size. Compared to NeRF, mip-NeRF reduces average error rates by 17% on the dataset presented with NeRF and by 60% on a challenging multiscale variant of that dataset that we present. Mip-NeRF is also able to match the accuracy of a brute-force supersampled NeRF on our multiscale dataset while being 22x faster.
神经辐射场 (NeRF) 使用的渲染过程对每个像素单条射线的场景进行采样,因此在训练或测试图像以不同分辨率观察场景内容时,可能会产生过度模糊或混叠的渲染。对于 NeRF 来说,通过每个像素渲染多条光线来进行超级采样的直接解决方案是不切实际的,因为渲染每条光线需要查询多层感知器数百次。我们的解决方案,我们称之为“mip-NeRF”(a la“mipmap”),扩展了 NeRF 以在连续值的尺度上表示场景。通过有效地渲染抗锯齿圆锥截头体而不是射线,mip-NeRF 减少了令人反感的锯齿伪影,并显着提高了 NeRF 表示精细细节的能力,同时比 NeRF 快 7% 但只有一半的大小。与 NeRF 相比,mip-NeRF 在NeRF提出和使用的数据集上将平均错误率降低了 17%,在我们呈现的该数据集的具有挑战性的多尺度变体上错误率降低了 60%。 Mip-NeRF 还能够在我们的多尺度数据集上达到蛮力超采样 NeRF 的准确性,同时速度提高 22 倍。
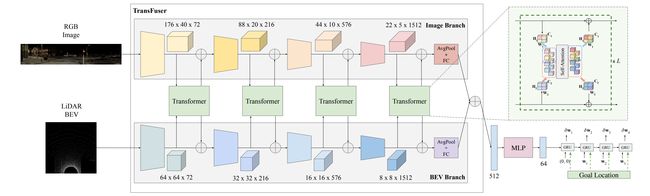
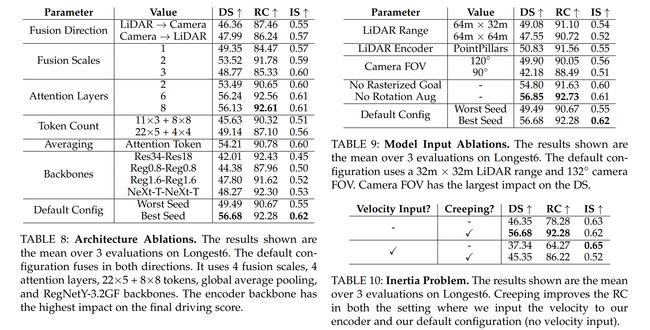
论文:TransFuser: Imitation with Transformer-Based Sensor Fusion for Autonomous Driving
论文标题:TransFuser: Imitation with Transformer-Based Sensor Fusion for Autonomous Driving
论文时间:31 May 2022
所属领域:Computer Vision/计算机视觉
对应任务:Autonomous Driving,Imitation Learning,Motion Forecasting,Object Detection,自动驾驶,模仿学习,运动预测,物体检测
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.15997
代码实现:https://github.com/autonomousvision/transfuser
论文作者:Kashyap Chitta, Aditya Prakash, Bernhard Jaeger, Zehao Yu, Katrin Renz, Andreas Geiger
论文简介:At the time of submission, TransFuser outperforms all prior work on the CARLA leaderboard in terms of driving score by a large margin./在本论文提交时,TransFuser 在驾驶得分方面大大优于 CARLA 排行榜上的所有先前工作。
论文摘要:How should we integrate representations from complementary sensors for autonomous driving? Geometry-based fusion has shown promise for perception (e.g. object detection, motion forecasting). However, in the context of end-to-end driving, we find that imitation learning based on existing sensor fusion methods underperforms in complex driving scenarios with a high density of dynamic agents. Therefore, we propose TransFuser, a mechanism to integrate image and LiDAR representations using self-attention. Our approach uses transformer modules at multiple resolutions to fuse perspective view and bird’s eye view feature maps. We experimentally validate its efficacy on a challenging new benchmark with long routes and dense traffic, as well as the official leaderboard of the CARLA urban driving simulator. At the time of submission, TransFuser outperforms all prior work on the CARLA leaderboard in terms of driving score by a large margin. Compared to geometry-based fusion, TransFuser reduces the average collisions per kilometer by 48%.
我们应该如何整合来自互补传感器的表示以用于自动驾驶?基于几何的融合已显示出感知的前景(例如对象检测、运动预测)。然而,在端到端驾驶的背景下,我们发现基于现有传感器融合方法的模仿学习在具有高密度动态代理的复杂驾驶场景中表现不佳。因此,我们提出了 TransFuser,这是一种使用自注意力集成图像和 LiDAR 表示的机制。我们的方法使用多种分辨率的transformer模块来融合透视图和鸟瞰图特征图。我们在具有挑战性的新基准(具有长路线和密集交通)以及 CARLA 城市驾驶模拟器的官方排行榜上通过实验验证其功效。在提交时,TransFuser 在驾驶分数方面大大优于 CARLA 排行榜上的所有先前工作。与基于几何的融合相比,TransFuser 将每公里的平均碰撞次数减少了 48%。
论文:PYSKL: Towards Good Practices for Skeleton Action Recognition
论文标题:PYSKL: Towards Good Practices for Skeleton Action Recognition
论文时间:19 May 2022
所属领域:Computer Vision/计算机视觉
对应任务:Action Recognition,Skeleton Based Action Recognition,动作识别,基于骨架的动作识别
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.09443
代码实现:https://github.com/kennymckormick/pyskl
论文作者:Haodong Duan, Jiaqi Wang, Kai Chen, Dahua Lin
论文简介:The toolbox supports a wide variety of skeleton action recognition algorithms, including approaches based on GCN and CNN./该工具箱支持多种骨架动作识别算法,包括基于 GCN 和 CNN 的方法。
论文摘要:We present PYSKL: an open-source toolbox for skeleton-based action recognition based on PyTorch. The toolbox supports a wide variety of skeleton action recognition algorithms, including approaches based on GCN and CNN. In contrast to existing open-source skeleton action recognition projects that include only one or two algorithms, PYSKL implements six different algorithms under a unified framework with both the latest and original good practices to ease the comparison of efficacy and efficiency. We also provide an original GCN-based skeleton action recognition model named ST-GCN++, which achieves competitive recognition performance without any complicated attention schemes, serving as a strong baseline. Meanwhile, PYSKL supports the training and testing of nine skeleton-based action recognition benchmarks and achieves state-of-the-art recognition performance on eight of them. To facilitate future research on skeleton action recognition, we also provide a large number of trained models and detailed benchmark results to give some insights. PYSKL is released at https://github.com/kennymckormick/pyskl and is actively maintained. We will update this report when we add new features or benchmarks. The current version corresponds to PYSKL v0.2.
我们提出了 PYSKL:一个基于 PyTorch 的基于骨架的动作识别的开源工具箱。该工具箱支持多种骨架动作识别算法,包括基于 GCN 和 CNN 的方法。现有的开源骨架动作识别项目仅包含一两个算法,我们的工具库PYSKL 在一个统一的框架下实现了六种不同的算法,并结合了最新和原创的良好实践,以方便比较功效和效率。我们还提供了一个原始的基于 GCN 的骨架动作识别模型 ST-GCN++,它在没有任何复杂的注意力方案的情况下实现了有竞争力的识别性能,作为一个强大的基线。同时,PYSKL 支持 9 个基于骨架的动作识别基准的训练和测试,并在其中 8 个上实现了最先进的识别性能。为了便于未来对骨骼动作识别的研究,我们还提供了大量经过训练的模型和详细的基准测试结果,以提供一些灵感思路和便利(给大家)。
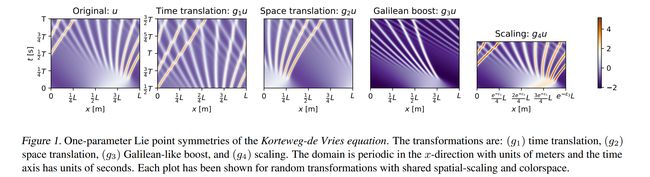
论文:Lie Point Symmetry Data Augmentation for Neural PDE Solvers
论文标题:Lie Point Symmetry Data Augmentation for Neural PDE Solvers
论文时间:15 Feb 2022
所属领域:Methodology
对应任务:Data Augmentation/数据增强
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.07643
代码实现:https://github.com/brandstetter-johannes/lpsda
论文作者:Johannes Brandstetter, Max Welling, Daniel E. Worrall
论文简介:In this paper, we present a method, which can partially alleviate this problem, by improving neural PDE solver sample complexity – Lie point symmetry data augmentation (LPSDA)./在本文中,我们提出了一种方法,可以通过提高神经 PDE 求解器样本复杂性来部分缓解偏微分方程(PDE)中的问题——Lie点对称数据增强 (LPDA)。
论文摘要:Neural networks are increasingly being used to solve partial differential equations (PDEs), replacing slower numerical solvers. However, a critical issue is that neural PDE solvers require high-quality ground truth data, which usually must come from the very solvers they are designed to replace. Thus, we are presented with a proverbial chicken-and-egg problem. In this paper, we present a method, which can partially alleviate this problem, by improving neural PDE solver sample complexity – Lie point symmetry data augmentation (LPSDA). In the context of PDEs, it turns out that we are able to quantitatively derive an exhaustive list of data transformations, based on the Lie point symmetry group of the PDEs in question, something not possible in other application areas. We present this framework and demonstrate how it can easily be deployed to improve neural PDE solver sample complexity by an order of magnitude.
神经网络越来越多地用于求解偏微分方程(PDE),以取代较慢的数值求解器。然而,一个关键问题是神经 PDE 求解器需要高质量的地面实况数据,这些数据通常必须来自它们旨在替代的求解器。因此,我们遇到了一个众所周知的先有鸡还是先有蛋的问题。在本文中,我们提出了一种方法,可以通过提高神经 PDE 求解器样本复杂度来部分缓解这个问题——Lie点对称数据增强 (LPDA)。在偏微分方程的背景下,事实证明,我们能够基于所讨论的偏微分方程的Lie点对称群,定量地推导出详尽的数据变换列表,这在其他应用领域是不可能的。我们展示了这个框架并演示了如何轻松部署它以将神经 PDE 求解器样本的复杂性提高一个数量级。
论文:Augmented Shortcuts for Vision Transformers
论文标题:Augmented Shortcuts for Vision Transformers
论文时间:NeurIPS 2021
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:图像识别,图像分类
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.15941
代码实现:https://github.com/huawei-noah/CV-Backbones/tree/master/augvit_pytorch , https://github.com/mindspore-ai/models/tree/master/research/cv/augvit , https://github.com/kingcong/augvit
论文作者:Yehui Tang, Kai Han, Chang Xu, An Xiao, Yiping Deng, Chao Xu, Yunhe Wang
论文简介:Transformer models have achieved great progress on computer vision tasks recently./Transformer 模型最近在计算机视觉任务上取得了很大进展。
论文摘要:Transformer models have achieved great progress on computer vision tasks recently. The rapid development of vision transformers is mainly contributed by their high representation ability for extracting informative features from input images. However, the mainstream transformer models are designed with deep architectures, and the feature diversity will be continuously reduced as the depth increases, i.e., feature collapse. In this paper, we theoretically analyze the feature collapse phenomenon and study the relationship between shortcuts and feature diversity in these transformer models. Then, we present an augmented shortcut scheme, which inserts additional paths with learnable parameters in parallel on the original shortcuts. To save the computational costs, we further explore an efficient approach that uses the block-circulant projection to implement augmented shortcuts. Extensive experiments conducted on benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, which brings about 1% accuracy increase of the state-of-the-art visual transformers without obviously increasing their parameters and FLOPs.
最近,Transformer 模型在计算机视觉任务上取得了很大进展。视觉transformer的快速发展主要归功于它们从输入图像中提取信息特征的高表示能力。然而,主流的 Transformer 模型都是采用深度架构设计的,随着深度的增加,特征多样性会不断降低,即特征崩溃。在本文中,我们从理论上分析了特征崩溃现象,并研究了这些 Transformer 模型中快捷方式与特征多样性之间的关系。然后,我们提出了一种增强的捷径方案,它在原始捷径上并行插入具有可学习参数的附加路径。为了节省计算成本,我们进一步探索了一种使用块循环投影来实现增强shortcuts方式的有效方法。在基准数据集上进行的大量实验证明了所提出方法的有效性,它使最先进的视觉transformer准确率提高了 1%,而没有明显增加它们的参数和 FLOPs。
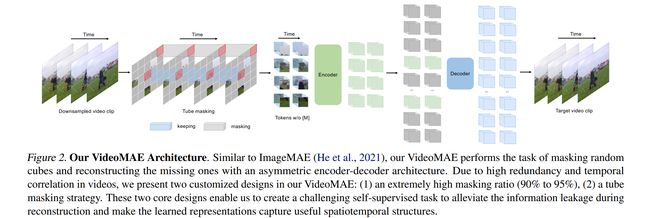
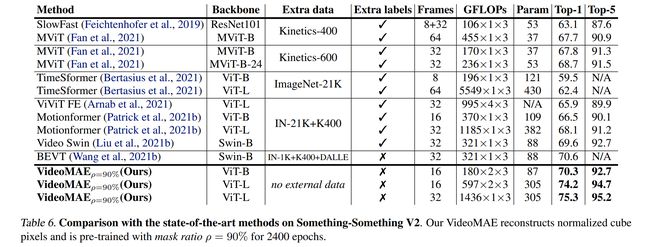
论文:VideoMAE: Masked Autoencoders are Data-Efficient Learners for Self-Supervised Video Pre-Training
论文标题:VideoMAE: Masked Autoencoders are Data-Efficient Learners for Self-Supervised Video Pre-Training
论文时间:23 Mar 2022
所属领域:Computer Vision/计算机视觉
对应任务:Action Classification,Action Recognition,Self-Supervised Action Recognition,Video Reconstruction,Video Understanding,动作分类,动作识别,自监督动作识别,视频重建,视频理解
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.12602
代码实现:https://github.com/MCG-NJU/VideoMAE
论文作者:Zhan Tong, Yibing Song, Jue Wang, LiMin Wang
论文简介:We obtain three important findings on SSVP: (1) An extremely high proportion of masking ratio (i. e., 90% to 95%) still yields favorable performance of VideoMAE./我们在 SSVP 上获得了三个重要发现:(1)极高比例的掩蔽率(即 90% 到 95%)仍然产生了 VideoMAE 的良好性能。
论文摘要:Pre-training video transformers on extra large-scale datasets is generally required to achieve premier performance on relatively small datasets. In this paper, we show that video masked autoencoders (VideoMAE) are data-efficient learners for self-supervised video pre-training (SSVP). We are inspired by the recent ImageMAE and propose customized video tube masking and reconstruction. These simple designs turn out to be effective for overcoming information leakage caused by the temporal correlation during video reconstruction. We obtain three important findings on SSVP: (1) An extremely high proportion of masking ratio (i.e., 90% to 95%) still yields favorable performance of VideoMAE. The temporally redundant video content enables higher masking ratio than that of images. (2) VideoMAE achieves impressive results on very small datasets (i.e., around 3k-4k videos) without using any extra data. This is partially ascribed to the challenging task of video reconstruction to enforce high-level structure learning. (3) VideoMAE shows that data quality is more important than data quantity for SSVP. Domain shift between pre-training and target datasets are important issues in SSVP. Notably, our VideoMAE with the vanilla ViT backbone can achieve 83.9% on Kinects-400, 75.3% on Something-Something V2, 90.8% on UCF101, and 61.1% on HMDB51 without using any extra data. Code will be released at https://github.com/MCG-NJU/VideoMAE .
通常需要在超大规模数据集上预训练视频transformer,以在相对较小的数据集上实现最佳性能。在本文中,我们展示了视频掩码自动编码器 (VideoMAE) 是用于自监督视频预训练 (SSVP) 的数据高效学习器。我们受到最近 ImageMAE 的启发,提出了定制的视频管掩蔽和重建。事实证明,这些简单的设计对于克服视频重建过程中由时间相关性引起的信息泄漏是有效的。我们在 SSVP 上获得了三个重要发现:
(1)极高比例的掩码率(即 90% 到 95%)仍然产生了 VideoMAE 的良好性能。时间冗余的视频内容实现了比图像更高的掩码率。
(2) VideoMAE 在非常小的数据集(即大约 3k-4k 视频)上取得了很好的结果,而无需使用任何额外的数据。这部分归因于视频重建以执行高级结构学习的挑战性任务。
(3) VideoMAE表明,对于SSVP,数据质量比数据量更重要。预训练和目标数据集之间的领域转移是 SSVP 中的重要问题。值得注意的是,我们的带有 vanilla ViT 主干的 VideoMAE 可以在 Kinects-400 上达到 83.9%,在 Something-Something V2 上达到 75.3%,在 UCF101 上达到 90.8%,在 HMDB51 上达到 61.1%,而无需使用任何额外数据。
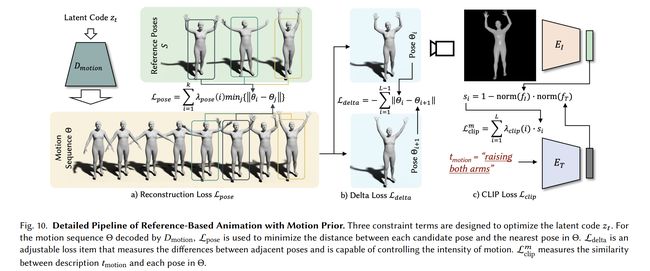
论文:AvatarCLIP: Zero-Shot Text-Driven Generation and Animation of 3D Avatars
论文标题:AvatarCLIP: Zero-Shot Text-Driven Generation and Animation of 3D Avatars
论文时间:17 May 2022
所属领域:Natural Language Processing/自然语言处理
对应任务:Language Modelling,motion synthesis,Texture Synthesis,语言建模,运动合成,纹理合成
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.08535
代码实现:https://github.com/hongfz16/avatarclip
论文作者:Fangzhou Hong, Mingyuan Zhang, Liang Pan, Zhongang Cai, Lei Yang, Ziwei Liu
论文简介:Our key insight is to take advantage of the powerful vision-language model CLIP for supervising neural human generation, in terms of 3D geometry, texture and animation./我们论文的核心想法是利用强大的视觉语言模型 CLIP 在 3D 几何、纹理和动画方面监督人类神经生成。
论文摘要:3D avatar creation plays a crucial role in the digital age. However, the whole production process is prohibitively time-consuming and labor-intensive. To democratize this technology to a larger audience, we propose AvatarCLIP, a zero-shot text-driven framework for 3D avatar generation and animation. Unlike professional software that requires expert knowledge, AvatarCLIP empowers layman users to customize a 3D avatar with the desired shape and texture, and drive the avatar with the described motions using solely natural languages. Our key insight is to take advantage of the powerful vision-language model CLIP for supervising neural human generation, in terms of 3D geometry, texture and animation. Specifically, driven by natural language descriptions, we initialize 3D human geometry generation with a shape VAE network. Based on the generated 3D human shapes, a volume rendering model is utilized to further facilitate geometry sculpting and texture generation. Moreover, by leveraging the priors learned in the motion VAE, a CLIP-guided reference-based motion synthesis method is proposed for the animation of the generated 3D avatar. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments validate the effectiveness and generalizability of AvatarCLIP on a wide range of avatars. Remarkably, AvatarCLIP can generate unseen 3D avatars with novel animations, achieving superior zero-shot capability.
3D 头像创建在数字时代起着至关重要的作用。然而,整个生产过程非常耗时且劳动密集。为了将这项技术普及到更多的受众,我们提出了 AvatarCLIP,这是一个用于 3D 头像生成和动画的零镜头文本驱动框架。与需要专业知识的专业软件不同,AvatarCLIP 使外行用户能够自定义具有所需形状和纹理的 3D 化身,并仅使用自然语言以描述的动作驱动化身。我们的核心思路是利用强大的视觉语言模型 CLIP 在 3D 几何、纹理和动画方面监督人类神经生成。具体来说,在自然语言描述的驱动下,我们使用形状 VAE 网络初始化 3D 人体几何生成。基于生成的 3D 人体形状,使用体积渲染模型进一步促进几何雕刻和纹理生成。此外,通过利用在运动 VAE 中学习的先验,提出了一种 CLIP 引导的基于参考的运动合成方法,用于生成 3D 化身的动画。广泛的定性和定量实验验证了 AvatarCLIP 在广泛的化身上的有效性和普遍性。值得注意的是,AvatarCLIP 可以生成具有新颖动画的看不见的 3D 化身,实现卓越的零样本学习能力。
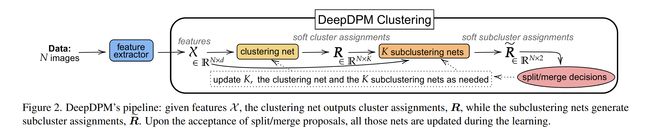
论文:DeepDPM: Deep Clustering With an Unknown Number of Clusters
论文标题:DeepDPM: Deep Clustering With an Unknown Number of Clusters
论文时间:27 Mar 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Deep Clustering,Deep Nonparametric Clustering,Model Selection,Nonparametric Clustering,Unsupervised Image Classification,深度聚类,深度非参数聚类,模型选择,非参数聚类,无监督图像分类
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.14309
代码实现:https://github.com/bgu-cs-vil/deepdpm
论文作者:Meitar Ronen, Shahaf E. Finder, Oren Freifeld
论文简介:Using a split/merge framework, a dynamic architecture that adapts to the changing K, and a novel loss, our proposed method outperforms existing nonparametric methods (both classical and deep ones)./使用拆分/合并框架、适应变化的 K 的动态架构和新颖的损失,我们提出的方法优于现有的非参数方法(包括经典方法和深度方法)。
论文摘要:Deep Learning (DL) has shown great promise in the unsupervised task of clustering. That said, while in classical (i.e., non-deep) clustering the benefits of the nonparametric approach are well known, most deep-clustering methods are parametric: namely, they require a predefined and fixed number of clusters, denoted by K. When K is unknown, however, using model-selection criteria to choose its optimal value might become computationally expensive, especially in DL as the training process would have to be repeated numerous times. In this work, we bridge this gap by introducing an effective deep-clustering method that does not require knowing the value of K as it infers it during the learning. Using a split/merge framework, a dynamic architecture that adapts to the changing K, and a novel loss, our proposed method outperforms existing nonparametric methods (both classical and deep ones). While the very few existing deep nonparametric methods lack scalability, we demonstrate ours by being the first to report the performance of such a method on ImageNet. We also demonstrate the importance of inferring K by showing how methods that fix it deteriorate in performance when their assumed K value gets further from the ground-truth one, especially on imbalanced datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/BGU-CS-VIL/DeepDPM.
深度学习(DL)在无监督的聚类任务中显示出巨大的前景。也就是说,虽然在经典(即非深度)聚类中,非参数方法的好处是众所周知的,但大多数深度聚类方法是参数化的:它们需要预定义且固定数量的聚类数 K ,但K是未知的,使用模型选择标准来选择其最佳值可能会变得计算成本高昂,尤其是在 DL 中,因为必须多次重复训练过程。在这项工作中,我们通过引入一种有效的深度聚类方法来弥补这一差距,该方法不需要知道 K 的值,而是在学习期间推断它。使用拆分/合并框架、适应不断变化的 K 的动态架构和新颖的损失,我们提出的方法优于现有的非参数方法(包括经典方法和深度方法)。虽然极少数现有的深度非参数方法缺乏可扩展性,但我们通过第一个在 ImageNet 上报告此类方法的性能来证明我们的方法。我们还展示了推断 K 的重要性,展示了当假设的 K 值远离真实值时,修复它的方法如何降低性能,尤其是在不平衡的数据集上。我们的代码可在 https://github.com/BGU-CS-VIL/DeepDPM 获得。
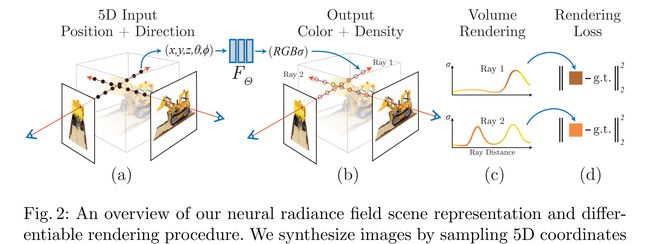
论文:NeRF: Representing Scenes as Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis
论文标题:NeRF: Representing Scenes as Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis
论文时间:ECCV 2020
所属领域:Computer Vision/计算机视觉
对应任务:Neural Rendering,Novel View Synthesis,神经渲染,新颖的视图合成
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.08934
代码实现:https://github.com/bmild/nerf , https://github.com/nvlabs/instant-ngp , https://github.com/facebookresearch/pytorch3d/tree/master/projects/nerf , https://github.com/yenchenlin/nerf-pytorch , https://github.com/keras-team/keras-io/blob/master/examples/vision/nerf.py
论文作者:Ben Mildenhall, Pratul P. Srinivasan, Matthew Tancik, Jonathan T. Barron, Ravi Ramamoorthi, Ren Ng
论文简介:Our algorithm represents a scene using a fully-connected (non-convolutional) deep network, whose input is a single continuous 5D coordinate (spatial location ( x , y , z ) (x, y, z) (x,y,z) and viewing direction ( θ , ϕ ) (\theta, \phi) (θ,ϕ)) and whose output is the volume density and view-dependent emitted radiance at that spatial location./ 我们的算法使用全连接(非卷积)深度网络表示场景,其输入是单个连续 5D 坐标(空间位置 ( x , y , z ) (x, y, z) (x,y,z) 和观察方向 ( θ , p h i ) (\theta, \ phi) (θ, phi)),其输出是该空间位置的体积密度和与视图相关的发射辐射。
论文摘要:We present a method that achieves state-of-the-art results for synthesizing novel views of complex scenes by optimizing an underlying continuous volumetric scene function using a sparse set of input views. Our algorithm represents a scene using a fully-connected (non-convolutional) deep network, whose input is a single continuous 5D coordinate (spatial location ( x , y , z ) (x,y,z) (x,y,z) and viewing direction ( θ , ϕ ) (\theta, \phi) (θ,ϕ)) and whose output is the volume density and view-dependent emitted radiance at that spatial location. We synthesize views by querying 5D coordinates along camera rays and use classic volume rendering techniques to project the output colors and densities into an image. Because volume rendering is naturally differentiable, the only input required to optimize our representation is a set of images with known camera poses. We describe how to effectively optimize neural radiance fields to render photorealistic novel views of scenes with complicated geometry and appearance, and demonstrate results that outperform prior work on neural rendering and view synthesis. View synthesis results are best viewed as videos, so we urge readers to view our supplementary video for convincing comparisons.
我们提出了一种方法,该方法通过使用稀疏输入视图集优化底层连续体积场景函数,实现了合成复杂场景的新视图的最新结果。我们的算法使用全连接(非卷积)深度网络表示场景,其输入是单个连续 5D 坐标(空间位置 ( x , y , z ) (x,y,z) (x,y,z) 和观察方向 ( θ , ϕ ) (\theta,\phi) (θ,ϕ) ),其输出是该空间位置的体积密度和与视图相关的发射辐射。我们通过沿相机光线查询 5D 坐标来合成视图,并使用经典的体积渲染技术将输出颜色和密度投影到图像中。因为体积渲染是自然可微的,所以优化我们的表示所需的唯一输入是一组具有已知相机姿势的图像。我们描述了如何有效地优化神经辐射场以渲染具有复杂几何和外观的场景的逼真的新颖视图,并展示了优于先前神经渲染和视图合成工作的结果。查看合成结果最好以视频形式观看,大家可以查看我们的补充视频里的效果比较。
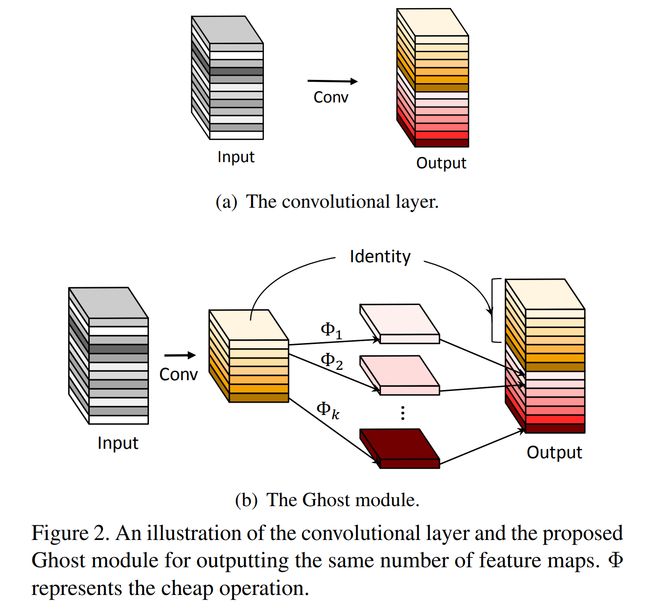
论文:GhostNet: More Features from Cheap Operations
论文标题:GhostNet: More Features from Cheap Operations
论文时间:CVPR 2020
所属领域:Natural Language Processing/自然语言处理
对应任务:Image Classification/图像分类
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.11907
代码实现:https://github.com/huawei-noah/ghostnet , https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models , https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection , https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleClas , https://github.com/osmr/imgclsmob
论文作者:Kai Han, Yunhe Wang, Qi Tian, Jianyuan Guo, Chunjing Xu, Chang Xu
论文简介:Deploying convolutional neural networks (CNNs) on embedded devices is difficult due to the limited memory and computation resources./由于内存和计算资源有限,在嵌入式设备上部署卷积神经网络 (CNN) 很困难。
论文摘要:Deploying convolutional neural networks (CNNs) on embedded devices is difficult due to the limited memory and computation resources. The redundancy in feature maps is an important characteristic of those successful CNNs, but has rarely been investigated in neural architecture design. This paper proposes a novel Ghost module to generate more feature maps from cheap operations. Based on a set of intrinsic feature maps, we apply a series of linear transformations with cheap cost to generate many ghost feature maps that could fully reveal information underlying intrinsic features. The proposed Ghost module can be taken as a plug-and-play component to upgrade existing convolutional neural networks. Ghost bottlenecks are designed to stack Ghost modules, and then the lightweight GhostNet can be easily established. Experiments conducted on benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed Ghost module is an impressive alternative of convolution layers in baseline models, and our GhostNet can achieve higher recognition performance (e.g. 75.7% top-1 accuracy) than MobileNetV3 with similar computational cost on the ImageNet ILSVRC-2012 classification dataset. Code is available at https://github.com/huawei-noah/ghostnet.
由于内存和计算资源有限,在嵌入式设备上部署卷积神经网络 (CNN) 很困难。特征图中的冗余是那些线性的(效果好的)CNN 的一个重要特征,但在神经架构设计中很少被研究。本文提出了一种新颖的 Ghost 模块,可以从简单的操作中生成更多的特征图。基于一组内在特征图,我们应用一系列低(计算)成本的线性变换来生成许多鬼特征图,这些特征图可以充分揭示内在特征的信息。所提出的 Ghost 模块可以作为一个即插即用的组件来升级现有的卷积神经网络。 Ghost 瓶颈旨在堆叠 Ghost 模块,然后可以轻松建立轻量级的 GhostNet。在基准上进行的实验表明,所提出的 Ghost 模块是基线模型中卷积层的一个效果显著的替代方案,我们的 GhostNet 可以在 ImageNet ILSVRC-2012 上以相似的计算成本实现比 MobileNetV3 更高的识别性能(例如 75.7% 的 top-1 准确率)分类数据集。代码在https://github.com/huawei-noah/ghostnet。
我们是 ShowMeAI,致力于传播AI优质内容,分享行业解决方案,用知识加速每一次技术成长!点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
- 作者:韩信子@ShowMeAI
- 历史文章列表
- 专题合辑&电子月刊
- 声明:版权所有,转载请联系平台与作者并注明出处
- 欢迎回复,拜托点赞,留言推荐中有价值的文章、工具或建议,我们都会尽快回复哒~