redis 是使用 C 语言编写的,但是 C 语言是没有字典这个数据结构的,因此 C 语言自己使用结构体来自定义一个字典结构
typedef struct redisDb
src\server.h 中的 redis 数据库 数据结构
/* Redis database representation. There are multiple databases identified
* by integers from 0 (the default database) up to the max configured
* database. The database number is the 'id' field in the structure. */
typedef struct redisDb {
dict *dict; /* The keyspace for this DB */
dict *expires; /* Timeout of keys with a timeout set */
dict *blocking_keys; /* Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP)*/
dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */
dict *watched_keys; /* WATCHED keys for MULTI/EXEC CAS */
int id; /* Database ID */
long long avg_ttl; /* Average TTL, just for stats */
unsigned long expires_cursor; /* Cursor of the active expire cycle. */
list *defrag_later; /* List of key names to attempt to defrag one by one, gradually. */
} redisDb;redisDb 存放了 redis 数据库底层的数据结构:
- dict
字典类型
- expires
过期时间
- blocking_keys
客户端等待数据的键 (BLPOP)
- ready_keys
收到PUSH的键被阻塞
- watched_keys
监控 MULTI/EXEC CAS 的键,例如事务的时候就会使用到
- id
数据库的 id, 0 – 15
- avg_ttl
统计平均的 ttl
- expires_cursor
记录过期周期
- defrag_later
存放 key 的列表
typedef struct dict
src\dict.h 字典的数据结构
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type;
void *privdata;
dictht ht[2];
long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */
int16_t pauserehash; /* If >0 rehashing is paused (<0 indicates coding error) */
} dict;dict 存放字典的数据结构
- type
字典的类型
- privdata
私有数据
- ht
hash 表, 一个旧表,一个新表,是有当 hash 表扩容的时候,新表才会被使用到,也就是 ht[1]
typedef struct dictType
typedef struct dictType {
uint64_t (*hashFunction)(const void *key);
void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);
void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);
int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);
void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);
void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);
int (*expandAllowed)(size_t moreMem, double usedRatio);
} dictType;dictType 定义了多个函数指针,便于后续进行方法的实现和调用
例如 keyCompare 函数指针,他是一个指针,指向的是一个函数,这个函数有 3 个参数,和 1 个返回值:
3 个参数
- privdata
具体的数据
- key1
key1 这个键具体的值
- key2
key2 这个键具体的值
这个指针 keyCompare 指向的函数作用是比较两个 key 的大小
typedef struct dictht
/* This is our hash table structure. Every dictionary has two of this as we
* implement incremental rehashing, for the old to the new table. */
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table;
unsigned long size;
unsigned long sizemask;
unsigned long used;
} dictht;dictht 存放的是 hash 表使用到的数据结构
- table
实际的 key-value 键值对
- size
hashtable 的容量
- sizemask
等于 size -1
- used
hashtable 元素的个数
typedef struct dictEntry
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key;
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;dictEntry 为键值对的实际数据结构
- key
key 值,实际上是一个 sds 类型的
- v
value 值,是一个联合体
- next
dictEntry 指针,指向下一个数据,主要是解决 hash 冲突的
例如上一篇我们介绍到的 hash,如下图中,key 就是 1,v 就是 (k3,v3) ,next 指向的就是 (k2,v2),一般默认情况 next 指向 NULL
上述联合体 v ,里面第 1 个元素是, void *val;
实际上这个元素才是指向真正的值,这个元素是一个指针,实际的数据结构是这个样子的
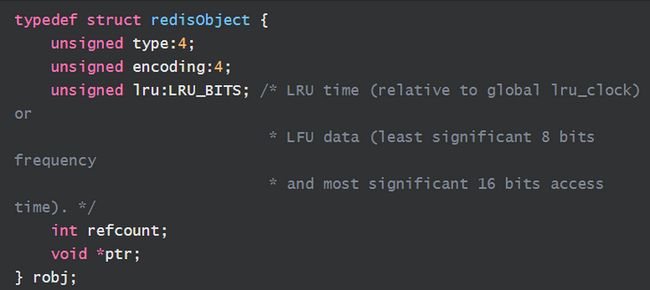
typedef struct redisObject {
unsigned type:4;
unsigned encoding:4;
unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or
* LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency
* and most significant 16 bits access time). */
int refcount;
void *ptr;
} robj;- type
类型,占 4 个 bit ,是用来约束客户端 api 的,例如 string 类型,embstr,hash,zset 等等
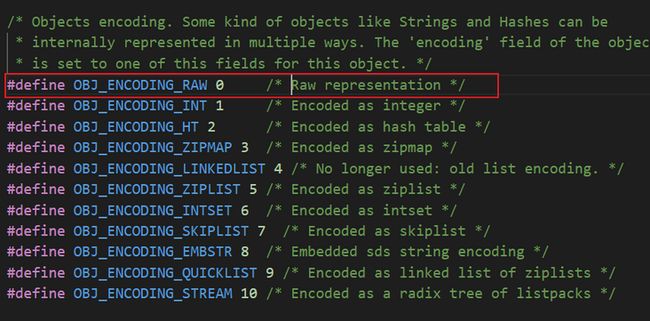
- encoding
编码类型,占 4 个bit ,使用到的数字有 0 - 10,分别表示不同的数据类型
- lru
lru 占 24 个bit ,3 个字节 , 内存淘汰算法
- refcount
引用计数 , int 类型,占 4 个字节
- ptr
实际的数据指针 , 64 位操作系统中, ptr 占 8个字节
bitmap 的小案例
设置一个 bitmap 的 key,作用为标记 11 号的在线用户
127.0.0.1:6379> SETBIT login:9:11 25 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> SETBIT login:9:11 26 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> SETBIT login:9:11 27 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> BITCOUNT login:9:11
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> strlen login:9:11
(integer) 4- BITCOUNT key [start end]
通过 BITCOUNT 可以看出 11 号在线人数 3 个人,login:9:11 占用字节数位 4 字节
127.0.0.1:6379> SETBIT login:9:12 26 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> SETBIT login:9:12 25 0
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> SETBIT login:9:12 27 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> STRLEN login:9:12
(integer) 4通过 BITCOUNT 可以看出 12 号在线人数 2 个人,login:9:12 占用字节数位 4 字节
下面我们将取 login:9:11 和 login:9:12 的 与操作,来计算 11 号 和 12 号两天来都在线的人数
127.0.0.1:6379> BITOP and login:and login:9:11 login:9:12
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> BITCOUNT login:and
(integer) 2- BITOP operation destkey key [key ...]
根据上述结果我们可以看出,11 号 和 12 号两天来都在线的人数为 2 人,验证 ok
我们再来看看11 号 和 12 号任意一天在线的人数
127.0.0.1:6379> BITOP or login:or login:9:11 login:9:12
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> BITCOUNT login:or
(integer) 3根据上述结果我们可以看出,11 号 和 12 号任意一天在线的人数为 3 人,验证 ok
127.0.0.1:6379> type login:or
string
127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT encoding login:or
"raw"
127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT encoding login:9:12
"raw"
127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT encoding login:and
"raw"咱们来看看上述用到的 key ,在 redis 里面实际是什么数据类型吧,
- OBJECT encoding [arguments [arguments ...]]
可以看出上述都是 “raw” 类型, 也就是 redis 的 sds 类型
缓存行
咱们再来看一个小例子,redis 中设置一个字符串 key
127.0.0.1:6379> set name xiaoming
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT encoding name
"embstr"我们可以看出 name 的类型是 “embstr”,那么 “embstr” 底层是如何实现的呢?“embstr” 有能承载多少个字节的数据呢?
上述我们有说到 redis 里面存放键值对的地方在 dictEntry 结构体中,dictEntry 结构体中的val 指针指向的是一个 redisObject 结构体,是这样的
我们在一个 64 位的机器中,CPU 在内存中读取数据的是通过读取缓存行的方式来实现的
一个缓存行有 64 字节
一个 redisObject 结构体占 16 字节
那么就还剩 48 字节 可以使用,那么使用 redis 里面 哪一个 sds 数据结构来存放数据数据呢?
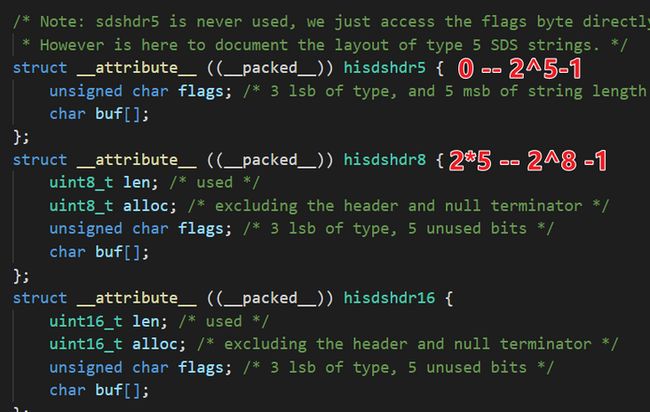
使用 hisdshdr8 类型,hisdshdr8 类型 sds 的前 3 个元素占用 3 个字节,那么剩下的 buf 存放数据就可以存放 45个字节(64 - 16 - 3)的数据了
如果你这么认为了,那么就有点粗心哦,因为 redis 为了兼容 C 语言的标准,会在字符串的后面加上 1 个 ‘\0’ ,他是占一个字节的因此最终 “embstr” 实际能存放的字节数是:
44 字节
来回顾上一篇文章,可以看出
当数据占用空间在 0 - - 2^5-1 , 使用 hisdshdr5 数据类型
2^5 – 2^8-1 的占用空间的时候,使用 hisdshdr8 数据类型
小小的实践
我们在 redis 中设置一个 test 的值为一个 44字节 的内容,查看这个 key 的类型,是 embstr
127.0.0.1:6379> set test 99999999991111111111222222222233333333334444
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT encoding test
"embstr"
127.0.0.1:6379> STRLEN test
(integer) 44再来设置 test2 为 大于 44 字节的内容,再查看他的内容是 raw
127.0.0.1:6379> set test2 999999999911111111112222222222333333333344449
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT encoding test2
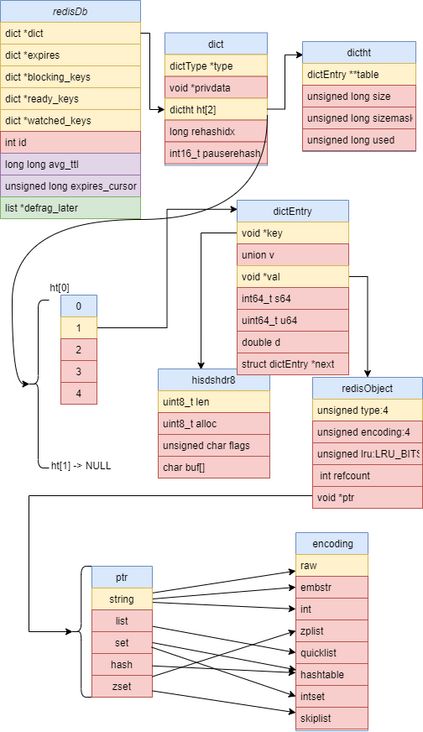
"raw"最后送上一张上述数据结构的关系图
参考资料:
- redis_doc
- reids 源码 reids-6.2.5 Redis 6.2.5 is the latest stable version.
欢-迎点赞,关注,收藏
朋友们,你的支持和鼓励,是我坚持分享,提高质量的动力
好了,本次就到这里
技术是开放的,我们的心态,更应是开放的。拥抱变化,向阳而生,努力向前行。
我是小魔童哪吒,欢迎点赞关注收藏,下次见~