1.问题
如何判断元素是否在切片中,Golang 并没有提供直接的库函数来判断,最容易想到的实现便是通过遍历来判断。
2.遍历查询
以字符串切片为例,判断字符串切片中是否包含某个字符串。
// InSlice 判断字符串是否在 slice 中。
func InSlice(items []string, item string) bool {
for _, eachItem := range items {
if eachItem == item {
return true
}
}
return false
}
这种实现时间复杂度是 O(n),n 为切片元素个数。
如果切片长度比较短(10以内)或者不是频繁调用,该性能是可以接受的。但是如果切片长度较长且频繁调用,那么这种方法的性能将无法接受,我们可以借助 map 优化一波。
3.map 查询
先将 slice 转为 map,通过查询 map 来快速查看元素是否在 slice 中。
// ConvertStrSlice2Map 将字符串 slice 转为 map[string]struct{}。
func ConvertStrSlice2Map(sl []string) map[string]struct{} {
set := make(map[string]struct{}, len(sl))
for _, v := range sl {
set[v] = struct{}{}
}
return set
}
// InMap 判断字符串是否在 map 中。
func InMap(m map[string]struct{}, s string) bool {
_, ok := m[s]
return ok
}
注意:使用空结构体 struct{} 作为 value 的类型,因为 struct{} 不占用任何内存空间。
fmt.Println(unsafe.Sizeof(bool(false))) // 1
fmt.Println(unsafe.Sizeof(struct{}{})) // 0
虽然将 slice 转为 map 的时间复杂度为 O(n),但是只转换一次可以忽略。查询元素是否在 map 中的时间复杂度为 O(1)。
4.性能对比
我们可以看下在元素数量为 26 的情况下,取中位元素,做个基准测试(benchmark),对比下二者的查询性能。
func BenchmarkInSlice(b *testing.B) {
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
InSlice(sl, "m")
}
}
func BenchmarkInMap(b *testing.B) {
m := ConvertStrSlice2Map(sl)
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
InMap(m, "m")
}
}
执行测试命令输出:
D:\code\gotest\contain>go test -bench=.
goos: windows
goarch: amd64
pkg: main/contain
cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-9700 CPU @ 3.00GHz
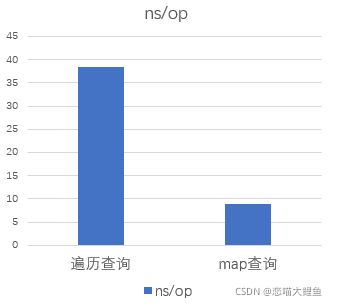
BenchmarkInSlice-8 30564058 38.35 ns/op
BenchmarkInMap-8 134556465 8.846 ns/op
PASS
ok main/contain 3.479s
测试结果中,看到函数后面的 -8 个表示运行时对应的 GOMAXPROCS 的值。接着的一串很大的数字表示运行 for 循环的次数,也就是调用被测试代码的次数,最后的38.35 ns/op表示每次需要花费 38.35 纳秒。
以上是测试时间默认是 1 秒,也就是1秒的时间,如果想让测试运行的时间更长,可以通过 -lunchtime 指定,比如 5 秒。
性能对比:
可以预料到的是随着切片长度增长,性能差距会越来越大。
5.转换通用化
我们可以借助空接口 interface{} 来实现任意类型的切片转换为 map,方便调用方使用。
// ToMapSetStrictE converts a slice or array to map set with error strictly.
// The result of map key type is equal to the element type of input.
func ToMapSetStrictE(i interface{}) (interface{}, error) {
// check param
if i == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("unable to converts %#v of type %T to map[interface{}]struct{}", i, i)
}
t := reflect.TypeOf(i)
kind := t.Kind()
if kind != reflect.Slice && kind != reflect.Array {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("the input %#v of type %T isn't a slice or array", i, i)
}
// execute the convert
v := reflect.ValueOf(i)
mT := reflect.MapOf(t.Elem(), reflect.TypeOf(struct{}{}))
mV := reflect.MakeMapWithSize(mT, v.Len())
for j := 0; j < v.Len(); j++ {
mV.SetMapIndex(v.Index(j), reflect.ValueOf(struct{}{}))
}
return mV.Interface(), nil
}
func main() {
var sl = []string{"a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f", "g", "h", "i", "j", "k", "l", "m", "n", "o", "p", "q", "r", "s", "t", "u", "v", "w", "x", "y", "z"}
m, _ := ToMapSetStrictE(sl)
mSet = m.(map[string]struct{})
if _, ok := m["m"]; ok {
fmt.Println("in")
}
if _, ok := m["mm"]; !ok {
fmt.Println("not in")
}
}
运行输出:
in
not in
上面的转换函数ToMapSetStrictE()已经放到开源 Go 工具库 go-huge-util,可直接通过 go mod 方式 import 使用。
import (
huge "github.com/dablelv/go-huge-util"
)
// 使用 go-huge-util
m, _ := huge.ToMapSetStrictE(sl)
mSet = m.(map[string]struct{})
// 或使用进一步封装的函数,不用再断言
mSet := huge.ToStrMapSetStrict(s)
6.借助开源库 golang-set
上面其实是利用 map 实现了一个 set(元素不重复集合),然后再判断某个 set 中是否存在某个元素。Golang 标准库并没有 set,但是我们可以用 map 来间接实现,就像上面那样子。
如果想使用 set 的完整功能,如初始化、Add、Del、Clear、Contains 等操作,推荐使用 Github 上成熟的开源库 golang-set,描述中说 Docker 用的也是它。库中提供了两种 set 实现,线程安全和非线程安全的 set。
golang-set 提供了五个生成 set 的函数:
// NewSet creates and returns a reference to an empty set. Operations
// on the resulting set are thread-safe.
func NewSet(s ...interface{}) Set {}
// NewSetWith creates and returns a new set with the given elements.
// Operations on the resulting set are thread-safe.
func NewSetWith(elts ...interface{}) Set {}
// NewSetFromSlice creates and returns a reference to a set from an
// existing slice. Operations on the resulting set are thread-safe.
func NewSetFromSlice(s []interface{}) Set {}
// NewThreadUnsafeSet creates and returns a reference to an empty set.
// Operations on the resulting set are not thread-safe.
func NewThreadUnsafeSet() Set {}
// NewThreadUnsafeSetFromSlice creates and returns a reference to a
// set from an existing slice. Operations on the resulting set are
// not thread-safe.
func NewThreadUnsafeSetFromSlice(s []interface{}) Set {}
下面借助 golang-set 来判断切片中是否存在某个元素。
package main
import (
"fmt"
mapset "github.com/deckarep/golang-set"
)
func main() {
var sl = []interface{}{"a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f", "g", "h", "i", "j", "k", "l", "m", "n", "o", "p", "q", "r", "s", "t", "u", "v", "w", "x", "y", "z"}
s := mapset.NewSetFromSlice(sl)
fmt.Println(s.Contains("m")) // true
fmt.Println(s.Contains("mm")) // false
}
7.小结
本文从问题“判断元素是否在切片中”开始讨论,给出相关的实现方式。这个问题可以引申抽象为“如何将 slice 转为元素不重复的 set”,并给出自己的通用转换函数 go-huge-util ToMapSetStrictE()。
当然,网上已经有很多成熟优秀的代码库直接使用,比如 golang-set,感兴趣的同学可以深入了解其用法和实现。
参考文献
- 知乎.Go 小知识之 Go 中如何使用 set
- Golang 基准测试(Benchmark)
到此这篇关于如何用Go判断元素是否在切片中的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Go判断元素在切片内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!