JSON
参考链接:
http://www.w3school.com.cn/json/index.asp
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data-interchange format. It is easy for humans to read and write. It is easy for machines to parse and generate. It is based on a subset of the JavaScript Programming Language, Standard ECMA-262 3rd Edition - December 1999. JSON is a text format that is completely language independent but uses conventions that are familiar to programmers of the C-family of languages, including C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, Perl, Python, and many others. These properties make JSON an ideal data-interchange language.
JSON is built on two structures:
- A collection of name/value pairs. In various languages, this is realized as an object, record, struct, dictionary, hash table, keyed list, or associative array.
- An ordered list of values. In most languages, this is realized as an array, vector, list, or sequence.
These are universal data structures. Virtually all modern programming languages support them in one form or another. It makes sense that a data format that is interchangeable with programming languages also be based on these structures.
In JSON, they take on these forms:
An object is an unordered set of name/value pairs. An object begins with { (left brace) and ends with } (right brace). Each name is followed by : (colon) and the name/value pairs are separated by , (comma).
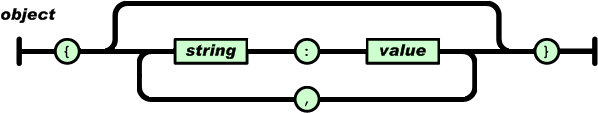
An array is an ordered collection of values. An array begins with [ (left bracket) and ends with ] (right bracket). Values are separated by , (comma).
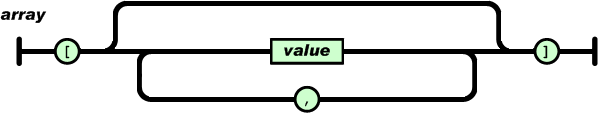
A value can be a string in double quotes, or a number, or true or false or null, or an object or an array. These structures can be nested.
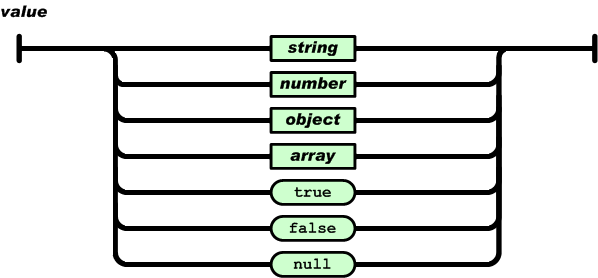
A string is a sequence of zero or more Unicode characters, wrapped in double quotes, using backslash escapes. A character is represented as a single character string. A string is very much like a C or Java string.
A number is very much like a C or Java number, except that the octal and hexadecimal formats are not used.
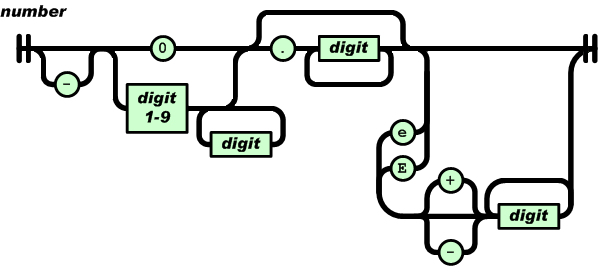
Whitespace can be inserted between any pair of tokens. Excepting a few encoding details, that completely describes the language.
-------------------------------------------------------------我是分隔符--------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------我是分隔符--------------------------------------------------------------------------
JSON介绍
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。 易于人阅读和编写。同时也易于机器解析和生成。 它基于JavaScript Programming Language, Standard ECMA-262 3rd Edition - December 1999的一个子集。 JSON采用完全独立于语言的文本格式,但是也使用了类似于C语言家族的习惯(包括C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, Perl, Python等)。 这些特性使JSON成为理想的数据交换语言。
JSON建构于两种结构:
- “名称/值”对的集合(A collection of name/value pairs)。不同的语言中,它被理解为对象(object),纪录(record),结构(struct),字典(dictionary),哈希表(hash table),有键列表(keyed list),或者关联数组 (associative array)。
- 值的有序列表(An ordered list of values)。在大部分语言中,它被理解为数组(array)。
这些都是常见的数据结构。事实上大部分现代计算机语言都以某种形式支持它们。这使得一种数据格式在同样基于这些结构的编程语言之间交换成为可能。
JSON具有以下这些形式:
对象是一个无序的“‘名称/值’对”集合。一个对象以“{”(左括号)开始,“}”(右括号)结束。每个“名称”后跟一个“:”(冒号);“‘名称/值’ 对”之间使用“,”(逗号)分隔。

数组是值(value)的有序集合。一个数组以“[”(左中括号)开始,“]”(右中括号)结束。值之间使用“,”(逗号)分隔。

值(value)可以是双引号括起来的字符串(string)、数值(number)、true、false、 null、对象(object)或者数组(array)。这些结构可以嵌套。

字符串(string)是由双引号包围的任意数量Unicode字符的集合,使用反斜线转义。一个字符(character)即一个单独的字符串(character string)。
字符串(string)与C或者Java的字符串非常相似。

数值(number)也与C或者Java的数值非常相似。除去未曾使用的八进制与十六进制格式。除去一些编码细节。

空白可以加入到任何符号之间。 以下描述了完整的语言。