使用ArcGis+Python(GDAL)制作语义分割遥感数据集
遥感数据集制作ArcGis+Python
- 一、选择裁剪合适的影像区域
- 二、创建标签shp文件,目视解译勾画标签区域
- 三、标签shp修改属性并转换为tif文件
- 四、使用python滑动裁剪图像及标签
- 五、数据增强
- 六、训练集(图像,标签)和验证集(图像,标签)
制作遥感数据集首先要有遥感影像数据。影像数据种类、来源很多,这里以GF-2的影像数据为例,制作用于 语义分割的数据集。直接获取的遥感影像需要进行预处理,进行大气校正、辐射定标等,这里不再介绍。这里使用预处理过后的GF-2影像(多光谱)进行数据集制作。
一、选择裁剪合适的影像区域
一景影像的数据非常大,我们所要使用的区域可能仅仅是一小部分,多余部分反而对数据集造成影像,而且影像尺寸过大,制作标签非常耗时耗力。因此要选择并裁剪所需要的区域。
选取技巧及原则:
1、选取矩形区域(利于滑动裁剪)
2、选择所要区分地物影像特征较强、对比明显的区域
3、类间差距大,类内差距小
1.1 打开ArcMap,加载影像。注意,实际上是4通道。制作的标签为RGB三通道,后面实际导出了三通道的影像。
1.2 新建shpfie文件,注意设置坐标系与影像一致。!!!
1.3画出所要选择的区域,尽量是矩形
1.4 使用裁剪工具裁剪
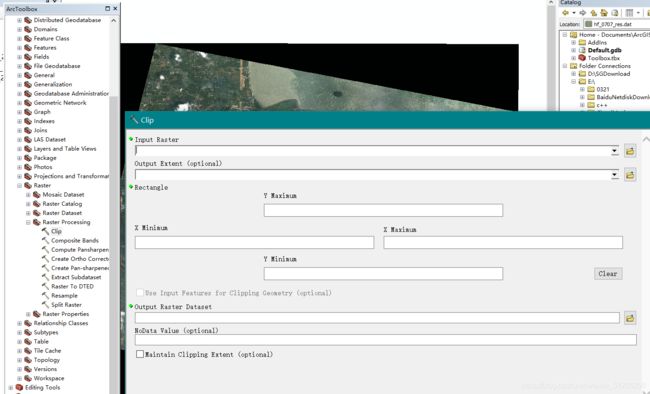

可使用data export导出三通道tif。
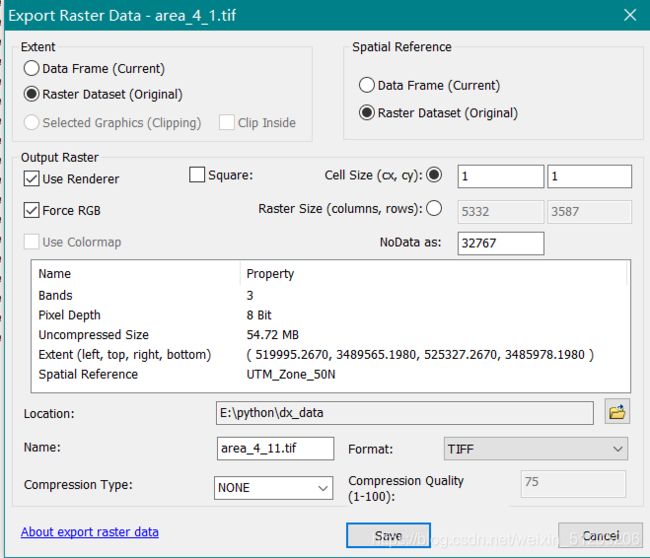
结果:原始影像area_4_1.tif就做好了,(5332,3587,3)
二、创建标签shp文件,目视解译勾画标签区域
影像数据是tif,我们需要的标签数据也应是tif,但是要先通过矢量文件勾画标签区域,再转化为栅格数据。
2.1创建shp面文件,注意,设置坐标系与原始影像一致!!
2.2目视解译勾画区域,需要结合地物在遥感影像上的特点。结合色调(全色影像)、颜色(彩色影像)、阴影*、形状、纹理、大小等特征进行判断。

三、标签shp修改属性并转换为tif文件
3.1 我们制作好标签shp后,修改它的属性id字段为255(0-255,RGB)。

3.2 转换为tif文件,注意:一定要设置像元大小与原始图像一致!!
否则有精度丢失!!

3.3 使用reclassify工具将生成tif文件的背景Nodata修改为0(0-255)
结果:标签文件lable_4.tif
注意检查影像与标签的尺寸大小是否相同,必须相同才能进行下一步。

四、使用python滑动裁剪图像及标签
上述获得的影像数据和标签数据尺寸是几千几千,对于模型来说过大,这里使用python+gdal库自动裁剪为256256(或其他尺寸,2的n次方)的图像,并按一定命名方式存储(1,2,3。。。命名)
同时对影像数据和标签数据裁剪。
代码:
import os
import gdal
import numpy as np
# 读取tif数据集
def readTif(fileName):
dataset = gdal.Open(fileName)
if dataset == None:
print(fileName + "文件无法打开")
return dataset
# 保存tif文件函数
def writeTiff(im_data, im_geotrans, im_proj, path):
if 'int8' in im_data.dtype.name:
datatype = gdal.GDT_Byte
elif 'int16' in im_data.dtype.name:
datatype = gdal.GDT_UInt16
else:
datatype = gdal.GDT_Float32
if len(im_data.shape) == 3:
im_bands, im_height, im_width = im_data.shape
elif len(im_data.shape) == 2:
im_data = np.array([im_data])
im_bands, im_height, im_width = im_data.shape
# 创建文件
driver = gdal.GetDriverByName("GTiff")
dataset = driver.Create(path, int(im_width), int(im_height), int(im_bands), datatype)
if (dataset != None):
dataset.SetGeoTransform(im_geotrans) # 写入仿射变换参数
dataset.SetProjection(im_proj) # 写入投影
for i in range(im_bands):
dataset.GetRasterBand(i + 1).WriteArray(im_data[i])
del dataset
'''
滑动窗口裁剪函数
TifPath 影像路径
SavePath 裁剪后保存目录
CropSize 裁剪尺寸
RepetitionRate 重复率
'''
def TifCrop(TifPath, SavePath, CropSize, RepetitionRate):
dataset_img = readTif(TifPath)
width = dataset_img.RasterXSize
height = dataset_img.RasterYSize
proj = dataset_img.GetProjection()
geotrans = dataset_img.GetGeoTransform()
img = dataset_img.ReadAsArray(0, 0, width, height) # 获取数据
# 获取当前文件夹的文件个数len,并以len+1命名即将裁剪得到的图像
new_name = len(os.listdir(SavePath))
# 裁剪图片,重复率为RepetitionRate
for i in range(int((height - CropSize * RepetitionRate) / (CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)))):
for j in range(int((width - CropSize * RepetitionRate) / (CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)))):
# 如果图像是单波段
if (len(img.shape) == 2):
cropped = img[
int(i * CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)): int(i * CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)) + CropSize,
int(j * CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)): int(j * CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)) + CropSize]
# 如果图像是多波段
else:
cropped = img[:,
int(i * CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)): int(i * CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)) + CropSize,
int(j * CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)): int(j * CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)) + CropSize]
# 写图像
writeTiff(cropped, geotrans, proj, SavePath + "/%d.tif" % new_name)
# 文件名 + 1
new_name = new_name + 1
# 向前裁剪最后一列
for i in range(int((height - CropSize * RepetitionRate) / (CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)))):
if (len(img.shape) == 2):
cropped = img[int(i * CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)): int(i * CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)) + CropSize,
(width - CropSize): width]
else:
cropped = img[:,
int(i * CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)): int(i * CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)) + CropSize,
(width - CropSize): width]
# 写图像
writeTiff(cropped, geotrans, proj, SavePath + "/%d.tif" % new_name)
new_name = new_name + 1
# 向前裁剪最后一行
for j in range(int((width - CropSize * RepetitionRate) / (CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)))):
if (len(img.shape) == 2):
cropped = img[(height - CropSize): height,
int(j * CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)): int(j * CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)) + CropSize]
else:
cropped = img[:,
(height - CropSize): height,
int(j * CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)): int(j * CropSize * (1 - RepetitionRate)) + CropSize]
writeTiff(cropped, geotrans, proj, SavePath + "/%d.tif" % new_name)
# 文件名 + 1
new_name = new_name + 1
# 裁剪右下角
if (len(img.shape) == 2):
cropped = img[(height - CropSize): height,
(width - CropSize): width]
else:
cropped = img[:,
(height - CropSize): height,
(width - CropSize): width]
writeTiff(cropped, geotrans, proj, SavePath + "/%d.tif" % new_name)
new_name = new_name + 1
#训练集和验证集都要裁剪
#裁剪出 图像 特征。拿到 影像数据增强中进行数据增强
# 将影像1裁剪为重复率为0.1的256×256的数据集
#图像
TifCrop(r"E:\python\dx_data\area_3.tif",
r"E:\python\dx_data\train\image1", 256, 0.1)
#标签
# TifCrop(r"E:\python\dx_data\lable.tif",
# r"E:\python\dx_data\train\lable1", 256, 0.1)
#标签裁剪不正确????标签255问题????
#可能是无背景的原因
#已解决
#见笔记
五、数据增强
数据增强是根据上述获得的裁剪后的256*256的影像和标签进行图像变换,实现数据集增多。
代码:
import gdal
import numpy as np
import os
import cv2
# 读取tif数据集
def readTif(fileName, xoff=0, yoff=0, data_width=0, data_height=0):
dataset = gdal.Open(fileName)
if dataset == None:
print(fileName + "文件无法打开")
# 栅格矩阵的列数
width = dataset.RasterXSize
# 栅格矩阵的行数
height = dataset.RasterYSize
# 波段数
bands = dataset.RasterCount
# 获取数据
if (data_width == 0 and data_height == 0):
data_width = width
data_height = height
data = dataset.ReadAsArray(xoff, yoff, data_width, data_height)
# 获取仿射矩阵信息
geotrans = dataset.GetGeoTransform()
# 获取投影信息
proj = dataset.GetProjection()
return width, height, bands, data, geotrans, proj
# 保存tif文件函数
def writeTiff(im_data, im_geotrans, im_proj, path):
if 'int8' in im_data.dtype.name:
datatype = gdal.GDT_Byte
elif 'int16' in im_data.dtype.name:
datatype = gdal.GDT_UInt16
else:
datatype = gdal.GDT_Float32
if len(im_data.shape) == 3:
im_bands, im_height, im_width = im_data.shape
elif len(im_data.shape) == 2:
im_data = np.array([im_data])
im_bands, im_height, im_width = im_data.shape
# 创建文件
driver = gdal.GetDriverByName("GTiff")
dataset = driver.Create(path, int(im_width), int(im_height), int(im_bands), datatype)
if (dataset != None):
dataset.SetGeoTransform(im_geotrans) # 写入仿射变换参数
dataset.SetProjection(im_proj) # 写入投影
for i in range(im_bands):
dataset.GetRasterBand(i + 1).WriteArray(im_data[i])
del dataset
#训练集的数据及标签
train_image_path = r"E:\python\dx_data\train\image1"
train_label_path = r"E:\python\dx_data\train\lable1"
# 进行几何变换数据增强
imageList = os.listdir(train_image_path)
labelList = os.listdir(train_label_path)
tran_num = len(imageList) + 1
for i in range(len(imageList)):
# 图像
img_file = train_image_path + "\\" + imageList[i]
im_width, im_height, im_bands, im_data, im_geotrans, im_proj = readTif(img_file)
# 标签
label_file = train_label_path + "\\" + labelList[i]
label = cv2.imread(label_file)
# 图像水平翻转
im_data_hor = np.flip(im_data, axis=2)
hor_path = train_image_path + "\\" + str(tran_num) + imageList[i][-4:]
writeTiff(im_data_hor, im_geotrans, im_proj, hor_path)
# 标签水平翻转
Hor = cv2.flip(label, 1)
hor_path = train_label_path + "\\" + str(tran_num) + labelList[i][-4:]
cv2.imwrite(hor_path, Hor)
tran_num += 1
# 图像垂直翻转
im_data_vec = np.flip(im_data, axis=1)
vec_path = train_image_path + "\\" + str(tran_num) + imageList[i][-4:]
writeTiff(im_data_vec, im_geotrans, im_proj, vec_path)
# 标签垂直翻转
Vec = cv2.flip(label, 0)
vec_path = train_label_path + "\\" + str(tran_num) + labelList[i][-4:]
cv2.imwrite(vec_path, Vec)
tran_num += 1
# 图像对角镜像
im_data_dia = np.flip(im_data_vec, axis=2)
dia_path = train_image_path + "\\" + str(tran_num) + imageList[i][-4:]
writeTiff(im_data_dia, im_geotrans, im_proj, dia_path)
# 标签对角镜像
Dia = cv2.flip(label, -1)
dia_path = train_label_path + "\\" + str(tran_num) + labelList[i][-4:]
cv2.imwrite(dia_path, Dia)
tran_num += 1
获得的数据将继续按顺序使用数字命名在相同文件夹下
六、训练集(图像,标签)和验证集(图像,标签)
结果上述步骤,获得众多影像数据和标签数据。

这里需要手动分割出验证集,新建文件夹存放,按一定比例分割。
注意:影像要与标签一一对应,即名称相同!
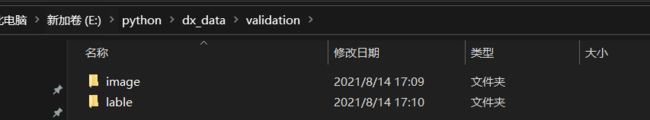
这样就制作好了一份遥感数据集用于语义分割,包括训练集(影像,标签)和验证集(影像,标签)
可在模型训练过程中不断调整数据集。
