二叉树链式结构及实现(前序、中序、后序遍历、层序遍历、分治算法、递归、数据结构、C语言)
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、二叉树的链式结构
- 二、二叉树的遍历
-
- (一)、前中后序遍历的基本概念
- (二)、前中后序遍历的实现
-
- 1、二叉树的前序遍历
- 2、二叉树的中序遍历
- 3、二叉树的后序遍历
- (三)、其他相关的函数接口
-
- 1、求所有结点的数量
- 2、求叶子结点的数量
- 3、求第K层的结点个数
- 4、求二叉树的深度
- 5、二叉树查找值为x的结点
- 6、二叉树的销毁 - 后序遍历
- (四)、层序遍历
-
- 1、void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
- 2、Queue.h
- 3、Queue.c
- 4、test.c
- 5、判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树(*)
前言
- 本篇博客主要介绍二叉树链式结构以及相关接口函数的实现,内容包括前中后序的遍历,运用分治的思路去编写相关函数
- 重点:分治算法的思想、二叉树的前序遍历
- 代码:C语言
一、二叉树的链式结构
二叉树的链式存储结构是指,用链表来表示一棵二叉树,即用链来指示元素的逻辑关系。 通常的方法是
链表中每个结点由三个域组成,数据域和左右指针域,左右指针分别用来给出该结点左孩子和右孩子所
在的链结点的存储地址 。链式结构又分为二叉链和三叉链,当前我们学习中一般都是二叉链,后面课程
学到高阶数据结构如红黑树等会用到三叉链。
- 说明:在学习二叉树的基本操作前,需先要创建一棵二叉树,然后才能学习其相关的基本操作。由于现在大家对二叉树结构掌握还不够深入,为了降低大家学习成本,此处手动快速创建一棵简单的二叉树,快速进入二叉树操作学习,等二叉树结构了解的差不多时,我们反过头再来研究二叉树真正的创建方式。代码如下:
typedef int BTDateType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
BTDateType date;
}BTNode;
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDateType x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
assert(node);
node->date = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left = node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
return node1;
}
- 看二叉树基本操作前,再回顾下二叉树的概念,二叉树是:
- 空树
- 非空:根节点,根节点的左子树、根节点的右子树组成的。
- 从概念中可以看出,二叉树定义是递归式的,因此后序基本操作中基本都是按照该概念实现的。
二、二叉树的遍历
(一)、前中后序遍历的基本概念
学习二叉树结构,最简单的方式就是遍历。所谓二叉树遍历(Traversal)是按照某种特定的规则,依次对二叉树中的节点进行相应的操作,并且每个节点只操作一次。访问结点所做的操作依赖于具体的应用问题。 遍历是二叉树上最重要的运算之一,也是二叉树上进行其它运算的基础。
按照规则,二叉树的遍历有:前序/中序/后序的递归结构遍历:
- 前序遍历(Preorder Traversal 亦称先序遍历)——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之前。
- 中序遍历(Inorder Traversal)——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之中(间)。
- 后序遍历(Postorder Traversal)——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之后。
由于被访问的结点必是某子树的根,所以N(Node)、L(Left subtree)和R(Right subtree)又可解释为根、根的左子树和根的右子树。NLR、LNR和LRN分别又称为先根遍历、中根遍历和后根遍历。
前中后序遍历的函数接口如下:
// 二叉树前序遍历
void PreOrder(BTNode* root);
// 二叉树中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* root);
// 二叉树后序遍历
void PostOrder(BTNode* root);
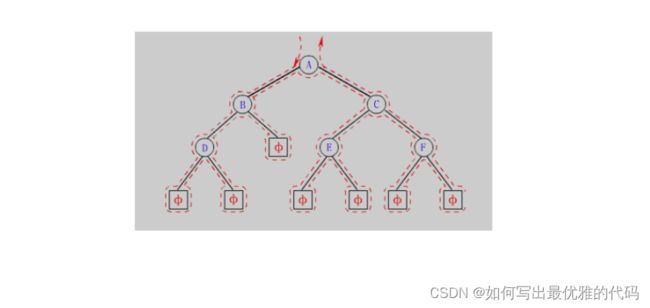
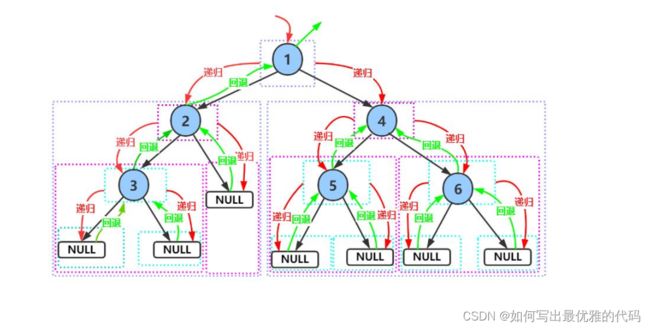
下面主要分析前序递归遍历,中序与后序图解类似,这里就不过多赘述。
- 前序、中序、后序遍历均是深度优先遍历,但前序遍历效率更佳、更优
(二)、前中后序遍历的实现
1、二叉树的前序遍历
void PreOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("# ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->date);
PreOrder(root->left);
PreOrder(root->right);
}
2、二叉树的中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("# ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->date);
InOrder(root->right);
}
3、二叉树的后序遍历
void PosOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("# ");
return;
}
PosOrder(root->left);
PosOrder(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->date);
}
(三)、其他相关的函数接口
运用分治和二叉树的前中后序遍历,还有以下几个相关的函数接口:
//用分治思想 - 求所有结点的数量
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
//求叶子结点的数量 - 分治
int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
//求第K层的结点个数 K >= 1
int TreeKLevel(BTNode* root, int k)
//求二叉树的深度
int TreeDepth(BTNode* root)
//二叉树查找值为x的结点
BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDateType x)
1、求所有结点的数量
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 :
TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
2、求叶子结点的数量
int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return 1;
return TreeLeafSize(root->left) + TreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
3、求第K层的结点个数
int TreeKLevel(BTNode* root, int k)
{
assert(k >= 1);
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (k == 1)
return 1;
return TreeKLevel(root->left, k - 1) + TreeKLevel(root->right, k - 1);
}
4、求二叉树的深度
int TreeDepth(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int leftDepth = TreeDepth(root->left);
int rightDepth = TreeDepth(root->right);
return leftDepth > rightDepth ? leftDepth + 1 : rightDepth + 1;
}
5、二叉树查找值为x的结点
BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDateType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->date == x)
return root;
BTNode* ret1 = TreeFind(root->left, x);
if (ret1)
return ret1;
BTNode* ret2 = TreeFind(root->right, x);
if (ret2)
return ret2;
return NULL;
}
6、二叉树的销毁 - 后序遍历
void TreeDestroy(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
TreeDestroy(root->left);
TreeDestroy(root->right);
free(root);
}
(四)、层序遍历
// 层序遍历
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root);
1、void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
// 层序遍历
//队列的数据应该存结点的指针
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
{
//进队列
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
//出对头的数据
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
printf("%d ", front->date);
QueuePop(&q);//释放的是队列的结点,而不是树的结点
//每一层从左至右,依次入队
if (front->left)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (front->right)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
printf("\n");
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
2、Queue.h
#pragma once
#include 3、Queue.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#pragma warning(disable:6031)
#include "Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = NULL;
pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDateType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->date = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
if (pq->head->next == NULL)//只剩下一个结点
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else//多个结点
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
}
QDateType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->date;
}
QDateType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail->date;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
int size = 0;
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
size++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}
4、test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#pragma warning(disable:6031)
#include "Heap.h"
#include "Queue.h"
typedef int BTDateType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
BTDateType date;
}BTNode;
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDateType x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
assert(node);
node->date = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left = node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
return node1;
}
// 层序遍历
//队列的数据应该存结点的指针
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
{
//进队列
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
//出对头的数据
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
printf("%d ", front->date);
QueuePop(&q);
//每一层从左至右,依次入队
if (front->left)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (front->right)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
printf("\n");
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
LevelOrder(root);
return 0;
}
5、判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树(*)
bool TreeComplelte(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
{
//进队列
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
//取对头的数据
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
//每一层从左至右,依次入队
if (front)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
else
{
//遇到空以后则跳出层序遍历
break;
}
}
//1. 如果后面全是空,则是完全二叉树
//1. 如果后面还有非空空,则不是完全二叉树
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
//取对头的数据
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front)
{
QueueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}
学习记录:
- 本篇博客整理于2022.7.7
- 请多多指教