从0到1学vue3
根据B站尚硅谷学的,这里做个人记录
一.认识vue3
1.了解相关信息
- vue3支持vue2的大多数特性
- 更好的支持Typescript
2.性能提升
- 打包大小减少41%
- 初次渲染快55%,更新渲染快133%
- 内存减少54%
- 使用Proxy代替defineProperty实现数据响应式
- 重写虚拟DOM的实现和Tree-Shaking
3.新增特性
- Composition(组合)API
- setup
ref和reactive
computed和watch
新的生命周期函数
provide和inject
…
- 新组件
Fragment - 文档碎片
Teleport - 瞬移组件的位置
Suspense - 异步加载组件的loading界面
- 其他API更新
全局API的修改
将原来的全局API转移到应用对象
模板语法变化
二.两种方式创建vue3项目
1.使用 vue-cli 创建
## 安装或者升级
npm install -g @vue/cli
## 保证 vue cli 版本在 4.5.0 以上
vue --version
## 创建项目
vue create 项目名
Please pick a preset - 选择 Manually select features,第二个没有ts,所以自己配置
Check the features needed for your project - 选择上 TypeScript ,特别注意点空格是选择,点回车是下一步
Choose a version of Vue.js that you want to start the project with - 选择 3.x (Preview)
剩下的
Use class-style component syntax - 直接回车
Use Babel alongside TypeScript - 直接回车
Pick a linter / formatter config - 直接回车
Use history mode for router? - 直接回车
Pick a linter / formatter config - 直接回车
Pick additional lint features - 直接回车
Where do you prefer placing config for Babel, ESLint, etc.? - 直接回车
Save this as a preset for future projects? - 直接回车
2. 使用 vite 创建
vite 是一个由原生 ESM 驱动的 Web 开发构建工具。在开发环境下基于浏览器原生 ES imports 开发,
它做到了本地快速开发启动, 在生产环境下基于 Rollup 打包。
快速的冷启动,不需要等待打包操作;
即时的热模块更新,替换性能和模块数量的解耦让更新飞起;
真正的按需编译,不再等待整个应用编译完成,这是一个巨大的改变。
npm init vite-app 项目名
cd 项目名
npm install
npm run dev
没下载的会问你是否要下,那肯定要的
三.vue3部分源码分析
1.脚手架版
my-project\src\main.ts
app.vue
<template>
<!-- vue2中的HTML模板中必须要有一对跟标签,vue3组件的HTML模板中可以没有根标签 -->
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png" />
<!-- 使用子组件 -->
<HelloWorld msg="Welcome to Your Vue.js + TypeScript App" />
</template>
<script lang="ts">
// 这里可以使用ts的代码
// defineComponent函数,目的是定义一个组件,内部可以传入一个配置对象
import { defineComponent } from "vue";
// 引入一个子级组件
import HelloWorld from "./components/HelloWorld.vue";
// 暴露出去一个定义好的组件
export default defineComponent({
// 当前组件的名字是APP
name: "App",
// 注册组件
components: {
// 注册一个子级组件
HelloWorld,
},
});
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
四.Composition API(常用部分)
组合API文档: https://composition-api.vuejs.org/zh/api.html
1.setup
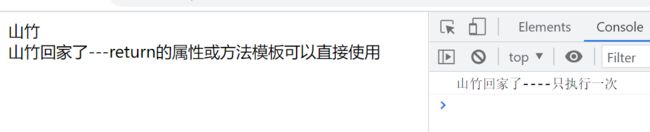
新的option, 所有的组合API函数都在此使用, 只在初始化时执行一次
函数如果返回对象, 对象中的属性或方法, 模板中可以直接使用
尝试在APP.vue中随便测试一下
//my-project\src\App.vue
<template>
<div>山竹</div>
<div>{{ str }}</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
setup() {
console.log("山竹回家了----只执行一次");
const str = "山竹回家了---return的属性或方法模板可以直接使用";
return {
str,
};
},
});
</script>
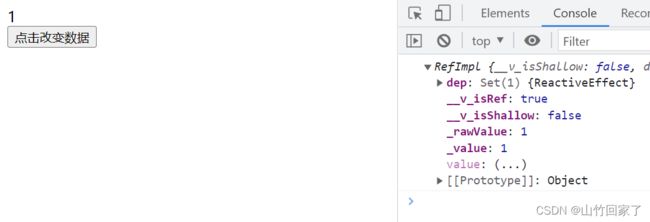
2.ref
作用: 定义一个数据的响应式
语法: const xxx = ref(initValue):
创建一个包含响应式数据的引用(reference)对象
js中操作数据: xxx.value
模板中操作数据: 不需要.value
一般用来定义一个基本类型的响应式数据
//my-project\src\App.vue
<template>
<div>{{ count }}</div>
<button @click="updateCount">点击改变数据</button>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
// 引入ref
import { defineComponent, ref } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
// vue2形式
// data() {
// return { count: 0 };
// },
// methods: {
// updateCount() {
// this.count++;
// },
// },
// vue3形式
setup() {
const count = ref(0);
function updateCount() {
count.value++;
console.log(count, 99); //是个对象
}
return {
count,
updateCount,
};
},
});
</script>
3.reactive
作用: 定义多个数据的响应式
const proxy = reactive(obj): 接收一个普通对象然后返回该普通对象的响应式代理器对象
响应式转换是“深层的”:会影响对象内部所有嵌套的属性
内部基于 ES6 的 Proxy 实现,通过代理对象操作源对象内部数据都是响应式的
<template>
<div>{{ user.name }}</div>
<div>{{ user.age }}</div>
<div>{{ user.hubby }}</div>
<button @click="update">点击改变数据</button>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
// 引入ref
import { defineComponent, reactive } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
setup() {
const obj = {
name: "山竹",
age: 18,
hubby: {
name: "杀生丸",
age: 999,
},
};
// 将复杂的数据变成响应式的数据
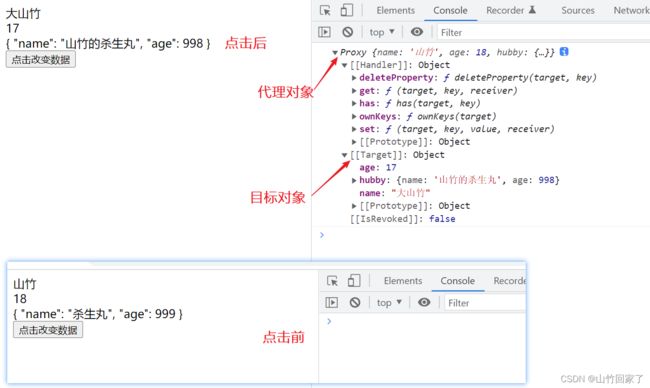
// 返回的是一个Proxy的代理对象,被代理的目标对象就是obj对象
const user = reactive(obj);
function update() {
// user现在是代理对象,obj是目标对象
console.log(user);
user.name = "大山竹";
user.age--;
user.hubby.name = "山竹的杀生丸";
user.hubby.age--;
// 直接使用目标对象的方式来更新目标对象中的成员的值不可行,只能使用代理对象的方式来更新
// obj.name="000"//错误示范
}
return { user, update };
},
});
</script>
4.操作代理数据影响界面更新渲染
<template>
<div>{{ user.name }}</div>
<div>{{ user.age }}</div>
<div>{{ user.hubby }}</div>
<div>{{ user.gender }}</div>
<button @click="update">点击改变数据</button>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, reactive } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
setup() {
const obj: any = {
name: "山竹",
age: 18,
hubby: {
name: "杀生丸",
age: 999,
},
};
const user = reactive(obj);
function update() {
console.log(user);
// user--->代理对象,obj---->目标对象
// 1.user对象或者obj对象添加一个新的属性,哪一种方式会影响界面更新
// obj.gender = "男";//界面没更新,target目标对象打印变化
// user.gender = "男"; //界面更新,target目标对象打印变化
// 2.user对象或obj对象中删除一个已经存在的属性,哪一种方式会影响界面的更新
// delete obj.age;//界面没更新,target目标对象打印变化
delete user.age; //界面更新,target目标对象打印变化
// 总结:如果操作代理对象,目标对象中的数据也会随之变化,同时如果想要在操作数据时,接年也跟着重新更新渲染,name也是操作代理对象
}
return { user, update };
},
});
</script>
5.vue3响应式数据原理
vue2响应式原理
核心:
对象: 通过defineProperty对对象的已有属性值的读取和修改进行劫持(监视/拦截)
数组: 通过重写数组更新数组一系列更新元素的方法来实现元素修改的劫持
Object.defineProperty(data, 'count', {
get () {},
set () {}
})
问题
对象直接新添加的属性或删除已有属性, 界面不会自动更新
直接通过下标替换元素或更新length, 界面不会自动更新 arr[1] = {}
Vue3的响应式
核心:
通过Proxy(代理):拦截对data任意属性的任意(13种)操作, 包括属性值的读写, 属性的添加, 属性的删除等…
通过 Reflect(反射): 动态对被代理对象的相应属性进行特定的操作
文档:
proxy
Reflect
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Proxy 与 Reflect</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const user = {
name: "John",
age: 12
};
/*
proxyUser是代理对象, user是被代理对象
后面所有的操作都是通过代理对象来操作被代理对象内部属性
参数1:user--->target目标对象
参数2:handler--->处理器对象,用来监视数据,及数据的操作
*/
const proxyUser = new Proxy(user, {
get(target, prop) {
console.log('劫持get()', prop)
return Reflect.get(target, prop)
},
set(target, prop, val) {
console.log('劫持set()', prop, val)
return Reflect.set(target, prop, val); // (2)
},
deleteProperty (target, prop) {
console.log('劫持delete属性', prop)
return Reflect.deleteProperty(target, prop)
}
});
// 读取属性值
console.log(proxyUser===user)
console.log(proxyUser.name, proxyUser.age)
// 设置属性值
proxyUser.name = 'bob'
proxyUser.age = 13
console.log(user)
// 添加属性
proxyUser.sex = '男'
console.log(user)
// 删除属性
delete proxyUser.sex
console.log(user)
</script>
</body>
</html>
6.setup细节
- setup执行的时机
在beforeCreate之前执行(一次), 此时组件对象还没有创建
this是undefined, 不能通过this来访问data/computed/methods / props
其实所有的composition API相关回调函数中也都不可以
Vue3中setup执行时机与注意点
- setup的返回值
一般都返回一个对象: 为模板提供数据, 也就是模板中可以直接使用此对象中的所有属性/方法
返回对象中的属性会与data函数返回对象的属性合并成为组件对象的属性
返回对象中的方法会与methods中的方法合并成功组件对象的方法
如果有重名, setup优先
注意:
一般不要混合使用: methods中可以访问setup提供的属性和方法, 但在setup方法中不能访问data和methods
setup不能是一个async函数: 因为返回值不再是return的对象, 而是promise, 模板看不到return对象中的属性数据
- setup的参数
setup(props, context) / setup(props, {attrs, slots, emit})
props: 包含props配置声明且传入了的所有属性的对象
attrs: 包含没有在props配置中声明的属性的对象, 代理对象,相当于this.$attrs
slots: 包含所有传入的插槽内容的对象, 相当于this.$slots
emit: 用来分发自定义事件的函数, 相当于this.$emit
准备父子组件
//父组件
<template>
<h2>父组件</h2>
<div>{{ msg }}</div>
<Child :msg="msg" msg2="msg2" @update="update" />
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, ref } from "vue";
import Child from "./components/Child.vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
components: { Child },
setup() {
const msg = ref("父组件传给子组件的值");
function update(data: string) {
msg.value += data;
}
return { msg, update };
},
});
</script>
//子组件
<template>
<h2>子组件</h2>
<div>{{ msg }}</div>
<button @click="clickUate">更新</button>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "AppChlid",
props: ["msg"],
setup(props, context) {
// 1.props参数是一个对象,里面有父级组件向子组件传递的数据,
// 并且是在子级组件中使用props接收到的所有的属性,包含props配置声明且传入了的所有属性的对象
//2.context参数,是一个对象,里面有
// attrs对象(获取当前组件标签上的所有的属性的对象,但是该属性是在props中没有声明接收的对象)
// emit方法(分发事件)
// slots对象(插槽)
console.log(props, context);
console.log(context.attrs.msg2); //msg2
function clickUate() {
context.emit("update", "++");
}
return { clickUate };
},
});
</script>
7.reactive和ref的细节
ref也可以传入对象吗?
- vue3的composition API中2个最重要的响应式API(reactive,ref)
- ref用来处理基本类型数据,reactive用来处理对象(递归深度响应式)
- 如果用ref对象/数组,内部会自动将对象/数组转为reactive的代理对象
- ref内部:通过value属性添加getter/setter来实现对数据的劫持
- reactive内部:通过使用Proxy来实现对对象内部所有数据的劫持,并通过Reflect操作对象内部数据
- ref的数据操作:在js中要.value,在模板中不需要(内部解析模板时会自动添加.value)
<template>
<div>1.{{one}}</div>
<div>2.{{two}}</div>
<div>3.{{three}}</div>
<button @click="update">更新</button>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import {
defineComponent,
ref,
reactive
} from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
setup() {
const one = ref(1)
const two = reactive({
name: '山竹',
child: {
name: '小山竹'
}
})
const three = ref({
name: '杀生丸',
child: {
wife: '小玲'
}
})
function update() {
one.value++
two.child.name += '++'
three.value.child.wife += '++'
}
return {
one,
two,
three,
update
};
},
});
</script>
8. 计算属性与监视
<template>
<fieldset>
<legend>姓名操作</legend>
姓氏: <input type="text" v-model="user.firstName" /><br />
名字: <input type="text" v-model="user.lastName" />
</fieldset>
<fieldset>
<legend>姓名操作</legend>
姓名1: <input type="text" v-model="fullName1" /><br />
姓名2: <input type="text" v-model="fullName2" /><br />
姓名3: <input type="text" v-model="fullName3" />
</fieldset>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import {
defineComponent,
ref,
reactive,
computed,
watch,
watchEffect
} from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
setup() {
const user = reactive({
firstName: '山',
lastName: '竹'
})
// vue3中计算属性
// 第一个姓名:如果传入回调,表示的是get
const fullName1 = computed(() => {
return `${user.firstName}_${user.lastName}`
})
console.log(fullName1) //是ref类型
// 第二个姓名:有getter与setter的计算属性
const fullName2 = computed({
get() {
return `${user.firstName}_${user.lastName}`
},
set(value: string) {
user.firstName = value.split('_')[0]
user.lastName = value.split('_')[1]
}
})
// watch第三个姓名
const fullName3 = ref('')
// watchEffect: 监视所有回调中使用的数据,加载时触发
// watchEffect(() => {
// fullName3.value = `${user.firstName}_${user.lastName}`
// })
watch(user, () => {
fullName3.value = `${user.firstName}_${user.lastName}`
}, {
immediate: true, // 是否初始化立即执行一次, 默认是false
deep: true // 是否是深度监视, 默认是false
})
// watch一个数据:默认在数据发生改变时执行回调
watch(fullName3, value => {
user.firstName = value.split('_')[0]
user.lastName = value.split('_')[1]
})
/*
watch多个数据:
使用数组来指定
如果是ref对象, 直接指定
如果是reactive对象中的属性, 必须通过函数来指定
*/
watch([() => user.firstName, () => user.lastName, fullName3], values => {
console.log('监视多个数据', values)
})
return {
user,
fullName1,
fullName2,
fullName3
};
},
});
</script>
9.生命周期
- beforeCreate -> 使用 setup()
- created -> 使用 setup()
- beforeMount -> onBeforeMount
- mounted -> onMounted
- beforeUpdate -> onBeforeUpdate
- updated -> onUpdated
- beforeDestroy -> onBeforeUnmount
- destroyed -> onUnmounted
- errorCaptured -> onErrorCaptured
1.vue3中已经没有destroyed 和beforeDestroy 了
2.vue3也可以用vue2的生命周期,vue3生命周期比vue2快
10.自定义hook函数
- 使用vue3的组合API封装的可复用的功能函数
- 自定义hook的按作用类似于vue2中的mixin技术
- 自定义hook的优势:很清楚复用功能代码的来源,更清楚易懂
需求 1: 收集用户鼠标点击的页面坐标
//src\hooks\useMousePosition.ts
import { ref, onMounted, onUnmounted } from 'vue'
export default function useMousePosition() {
// 初始化坐标数据
const x = ref(-1)
const y = ref(-1)
// 用于收集点击事件坐标的函数
const updatePosition = (e: MouseEvent) => {
x.value = e.pageX
y.value = e.pageY
}
onMounted(() => {
document.addEventListener('click', updatePosition)
})
onUnmounted(() => {
document.removeEventListener('click',updatePosition)
})
return { x, y }
}
//src\App.vue
<template>
<span>x:{{x}}</span>
<span>y:{{y}}</span>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import {
defineComponent
} from "vue";
import useMousePosition from './hooks/useMousePosition'
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
setup() {
const {
x,
y
} = useMousePosition()
return {
x,
y
};
},
});
</script>
需求 2: 封装发 ajax 请求的 hook 函数
hooks/useRequest.ts
import { ref } from 'vue'
import axios from 'axios'
/*
使用axios发送异步ajax请求
*/
export default function useUrlLoader<T>(url: string) {
const result = ref<T | null>(null)
const loading = ref(true)
const errorMsg = ref(null)
axios
.get(url)
.then(response => {
loading.value = false
result.value = response.data
})
.catch(e => {
loading.value = false
errorMsg.value = e.message || '未知错误'
})
return {
loading,
result,
errorMsg
}
}
<template>
<div class="about">
<h2 v-if="loading">LOADING...</h2>
<h2 v-else-if="errorMsg">{{ errorMsg }}</h2>
<!-- <ul v-else>
<li>id: {{result.id}}</li>
<li>name: {{result.name}}</li>
<li>distance: {{result.distance}}</li>
</ul> -->
<ul v-for="p in result" :key="p.id">
<li>id: {{ p.id }}</li>
<li>title: {{ p.title }}</li>
<li>price: {{ p.price }}</li>
</ul>
<!-- <img v-if="result" :src="result[0].url" alt=""> -->
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { watch } from 'vue'
import useRequest from './hooks/useRequest'
// 地址数据接口
interface AddressResult {
id: number
name: string
distance: string
}
// 产品数据接口
interface ProductResult {
id: string
title: string
price: number
}
export default {
setup() {
// const {loading, result, errorMsg} = useRequest('/data/address.json')
const { loading, result, errorMsg } = useRequest<ProductResult[]>('/data/products.json')
watch(result, () => {
if (result.value) {
console.log(result.value.length) // 有提示
}
})
return {
loading,
result,
errorMsg
}
}
}
</script>
11.toRefs
- 把一个响应式对象转换成普通对象,该普通对象的每个 property 都是一个 ref
- 应用: 当从合成函数返回响应式对象时,toRefs 非常有用,这样消费组件就可以在不丢失响应式的情况下对返回的对象进行分解使用
- 问题: reactive 对象取出的所有属性值都是非响应式的
- 解决: 利用 toRefs 可以将一个响应式 reactive 对象的所有原始属性转换为响应式的 ref 属性
<template>
<span>name:{{name}}</span>
<span>age:{{age}}</span>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import {
defineComponent,
reactive,
toRefs
} from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
setup() {
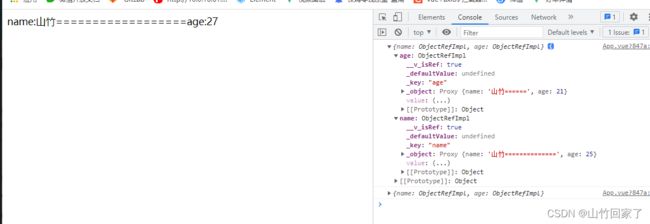
const user = reactive({
name: '山竹',
age: 18
})
//如果注释掉这个与user1,并打开user,是不会有响应
const user1=toRefs(user)
console.log(user1)//是ref
setInterval(() => {
user.name += '=='
user.age++
}, 1000)
return {
// ...user,
...user1
}
}
});
</script>
12.ref获取元素
ref获取元素: 利用ref函数获取组件中的标签元素
功能需求: 让输入框自动获取焦点
<template>
<input type="text" ref="input">
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import {
defineComponent,
onMounted,
ref
} from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
setup() {
//走到这步页面还没加载,还是null,等加载后就是html元素
const input = ref < HTMLElement | null > (null)
onMounted(() => {
input.value && input.value.focus()
})
return {
input
}
}
});
</script>
五、Composition API(其它部分)
1.shallowReactive 与 shallowRef
- shallowReactive : 只处理了对象内最外层属性的响应式(也就是浅响应式)
- shallowRef: 只处理了 value 的响应式, 不进行对象的 reactive 处理
- 什么时候用浅响应式呢?
- 一般情况下使用 ref 和 reactive 即可
- 如果有一个对象数据, 结构比较深, 但变化时只是外层属性变化 ===> shallowReactive
- 如果有一个对象数据, 后面会产生新的对象来替换 ===> shallowRef
<template>
<h2>App</h2>
<h3>m1: {{ m1 }}</h3>
<h3>m2: {{ m2 }}</h3>
<h3>m3: {{ m3 }}</h3>
<h3>m4: {{ m4 }}</h3>
<button @click="update">更新</button>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { reactive, ref, shallowReactive, shallowRef } from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
const m1 = reactive({ a: 1, b: { c: 2 } })
const m2 = shallowReactive({ a: 1, b: { c: 2 } })
const m3 = ref({ a: 1, b: { c: 2 } })
const m4 = shallowRef({ a: 1, b: { c: 2 } })
const update = () => {
// m1.b.c += 1
// m2.b.c += 1
// m3.value.a += 1
m4.value.a += 1
}
return {
m1,
m2,
m3,
m4,
update
}
}
}
</script>
2. readonly 与 shallowReadonly
readonly:
- 深度只读数据
- 获取一个对象 (响应式或纯对象) 或 ref 并返回原始代理的只读代理。
- 只读代理是深层的:访问的任何嵌套 property 也是只读的。
shallowReadonly
- 浅只读数据
- 创建一个代理,使其自身的 property 为只读,但不执行嵌套对象的深度只读转换
应用场景:
- 在某些特定情况下, 我们可能不希望对数据进行更新的操作, 那就可以包装生成一个只读代理对象来读取数据, 而不能修改或删除
<template>
<h3>{{user}}</h3>
<button @click="update">更新</button>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import {
reactive,
defineComponent,
readonly,
shallowReadonly
} from 'vue'
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
const user = reactive({
a: 'name',
b: {
c: 'age'
}
})
const user1 = readonly(user)
const user2 = shallowReadonly(user)
const update = () => {
// user1.a += '---' // error
// user1.b.c += '---' // error
// user2.a+='---' //error
user2.b.c+='---'
}
return {
user,
update
}
}
})
</script>
3.toRaw 与 markRaw
toRaw
- 返回由 reactive 或 readonly 方法转换成响应式代理的普通对象。
- 这是一个还原方法,可用于临时读取,访问不会被代理/跟踪,写入时也不会触发界面更新。
markRaw
- 标记一个对象,使其永远不会转换为代理。返回对象本身
应用场景:
- 有些值不应被设置为响应式的,例如复杂的第三方类实例或 Vue 组件对象。
- 当渲染具有不可变数据源的大列表时,跳过代理转换可以提高性能。
<template>
<h3>{{user}}</h3>
<button @click="update">更新</button>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import {
reactive,
defineComponent,
toRaw,
markRaw,
} from 'vue'
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
const user = reactive < any > ({
a: 'name',
b: {
c: 'age'
}
})
const update = () => {
// const user1 = toRaw(user)
// user1.a += '=='
// console.log('我变了')
const likes = ['吃饭', '睡觉']
user.likes = markRaw(likes)
setInterval(() => {
user.likes[0] += '----'
console.log('变了')
}, 1000)
}
return {
user,
update
}
}
})
</script>
4.toRef
- 为源响应式对象上的某个属性创建一个 ref 对象, 二者内部操作的是同一个数据值, 更新时二者是同步的
- 区别 ref: 拷贝了一份新的数据值单独操作, 更新时相互不影响
- 应用: 当要将 某个 prop 的 ref 传递给复合函数时,toRef 很有用
<template>
<h2>父组件</h2>
<div>{{ user }}</div>
<div>{{ age }}</div>
<div>{{ money }}</div>
<br />
<button @click="update">更新按钮</button>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, reactive, toRef, ref } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
setup() {
const user = reactive({
age: 18,
money: 10000,
});
const age = toRef(user, "age");
console.log(age); //是ref类型
const money = ref(user.money);
console.log(money); //是ref类型
const update = function () {
// 这两个会互相影响
// age.value++;
// user.age++;
money.value++; //这个是属于拷贝的,不会影响user
};
return {
user,
age,
money,
update,
};
},
});
</script>
5.customRef
创建一个自定义的 ref,并对其依赖项跟踪和更新触发进行显式控制
它需要一个工厂函数,该函数接收 track 和 trigger 函数作为参数,并且应该返回一个带有 get 和 set 的对象。
需求: 使用 customRef 实现 debounce(防抖) 的示例
<template>
<input type="text" v-model="keyWord" />
<h4>{{ keyWord }}</h4>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, reactive, toRef, ref, customRef } from "vue";
// 自定义hook防抖函数
//value传入的数据,将来数据的类型不确定,所以用泛型,delay代表防抖间隔时间
function useDebouncedRef<T>(value: T, delay = 200) {
let timeout: number;
// 返回ref对象,所以需要用到customRef,如果直接返回{}那就是普通对象;
// customRef可以有回调,并且返回一个带有 get 和 set 的对象
return customRef((track, trigger) => {
return {
// 返回数据
get() {
// 告诉vue追踪数据,找到数据并返回
track();
return value;
},
// 设置数据
set(newValue: T) {
// 清除定时器
clearTimeout(timeout);
// 开启定时器
timeout = setTimeout(() => {
value = newValue;
// 告诉vue更新界面
trigger();
}, delay);
},
};
});
}
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
setup() {
const keyWord = useDebouncedRef("abc", 500);
return {
keyWord,
};
},
});
</script>
6.provide 与 inject
provide和inject提供依赖注入,功能类似 2.x 的provide/inject
实现跨层级组件(祖孙)间通信
效果
//src\App.vue
<template>
<h4>父组件</h4>
<h4>{{ color }}</h4>
<button @click="color = 'yellow'">黄色</button>
<button @click="color = 'green'">绿色</button>
<button @click="color = 'blue'">蓝色</button>
<Son />
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, provide, ref } from "vue";
import Son from "./components/Son.vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
components: {
Son,
},
setup() {
const color = ref("red");
provide("color", color);
return {
color,
};
},
});
</script>
//src\components\Son.vue
<template>
<h2>子组件</h2>
<Grandson />
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent } from "vue";
import Grandson from "./Grandson.vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "Son",
components: {
Grandson,
},
setup() {
return {};
},
});
</script>
//src\components\Grandson.vue
<template>
<h2 :style="{ color }">孙组件</h2>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, inject } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "Grandson",
setup() {
const color = inject("color");
return {
color,
};
},
});
</script>
7.响应式数据的判断
isRef: 检查一个值是否为一个 ref 对象
isReactive: 检查一个对象是否是由 reactive 创建的响应式代理
isReadonly: 检查一个对象是否是由 readonly 创建的只读代理
isProxy: 检查一个对象是否是由 reactive 或者 readonly 方法创建的代理
六、其他新组件与API
1.Fragment(片断)
在Vue2中: 组件必须有一个根标签
在Vue3中: 组件可以没有根标签, 内部会将多个标签包含在一个Fragment虚拟元素中
好处: 减少标签层级, 减小内存占用
<template>
<h2>aaaa</h2>
<h2>aaaa</h2>
</template>
2.Teleport(瞬移)
Teleport 提供了一种干净的方法, 让组件的html在父组件界面外的特定标签(很可能是body)下插入显示
//src\App.vue
<template>
<h4>父组件</h4>
<Child />
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent } from "vue";
import Child from "./components/Child.vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
components: { Child },
setup() {
return {};
},
});
</script>
//src\components\Child.vue
<template>
<h4>子组件</h4>
<button @click="showModal = true">显示对话框</button>
<teleport to="body">
<div v-if="showModal">
<p>我是对话框</p>
<button @click="showModal = false">关闭对话框</button>
</div>
</teleport>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, ref } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "Child",
setup() {
const showModal = ref(false);
return { showModal };
},
});
</script>
3.uspense(不确定的)
它们允许我们的应用程序在等待异步组件时渲染一些后备内容,可以让我们创建一个平滑的用户体验
人话:在等异步组件加载时空白的那段时间做些操作
<template>
<h4>父组件</h4>
<Suspense>
<template #default>
<Child />
</template>
<template v-slot:fallback>
<h1>LOADING...</h1>
</template>
</Suspense>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent } from "vue";
import Child from "./components/Child.vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "App",
components: { Child },
setup() {
return {};
},
});
</script>
<template>
<h4>子组件</h4>
<h4>{{ msg }}</h4>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent } from "vue";
export default defineComponent({
name: "C_hild",
setup() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve({ msg: "aaa" });
}, 2000);
});
},
});
</script>