1、Spring Boot支持的缓存组件
在Spring Boot中,数据的缓存管理存储依赖于Spring框架中cache相关的org.springframework.cache.Cache和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager缓存管理器接口。
如果程序中没有定义类型为CacheManager的Bean组件或者是名为cacheResolver的CacheResolver缓存解析器,Spring Boot将尝试选择并启用以下缓存组件(按照指定的顺序):
(1)Generic
(2)JCache (JSR-107) (EhCache 3、Hazelcast、Infinispan等)
(3)EhCache 2.x
(4)Hazelcast
(5)Infinispan
(6)Couchbase
(7)Redis
(8)Caffeine
(9)Simple
上面按照Spring Boot缓存组件的加载顺序,列举了支持的9种缓存组件,在项目中添加某个缓存管理组件(例如Redis)后,Spring Boot项目会选择并启用对应的缓存管理器。如果项目中同时添加了多个缓存组件,且没有指定缓存管理器或者缓存解析器(CacheManager或者cacheResolver),那么Spring Boot会按照上述顺序在添加的多个缓存中优先启用指定的缓存组件进行缓存管理。
刚刚讲解的Spring Boot默认缓存管理中,没有添加任何缓存管理组件能实现缓存管理。这是因为开启缓存管理后,Spring Boot会按照上述列表顺序查找有效的缓存组件进行缓存管理,如果没有任何缓存组件,会默认使用最后一个Simple缓存组件进行管理。Simple缓存组件是Spring Boot默认的缓存管理组件,它默认使用内存中的ConcurrentMap进行缓存存储,所以在没有添加任何第三方缓存组件的情况下,可以实现内存中的缓存管理,但是我们不推荐使用这种缓存管理方式
2、基于注解的Redis缓存实现
在Spring Boot默认缓存管理的基础上引入Redis缓存组件,使用基于注解的方式讲解Spring Boot整合Redis缓存的具体实现
(1)添加Spring Data Redis依赖启动器。在pom.xml文件中添加Spring Data Redis依赖启动器
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-data-redis
当我们添加进redis相关的启动器之后, SpringBoot会使用RedisCacheConfigratioin 当做生效的自动配置类进行缓存相关的自动装配,容器中使用的缓存管理器是RedisCacheManager , 这个缓存管理器创建的Cache为 RedisCache , 进而操控redis进行数据的缓存
(2)Redis服务连接配置
# Redis服务地址
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
# Redis服务器连接端口
spring.redis.port=6379
# Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)
spring.redis.password=
(3)对CommentService类中的方法进行修改使用@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict三个注解定制缓存管理,分别进行缓存存储、缓存更新和缓存删除的演示
package com.lagou.service;
import com.lagou.pojo.Comment;
import com.lagou.repository.CommentRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Optional;
@Service
public class CommentService {
@Autowired
private CommentRepository commentRepository;
/**
* @Cacheable: 将该方法查询结果comment存放在SpringBoot默认缓存中
* cacheNames: 起一个缓存的命名空间,对应缓存的唯一标识
* value:缓存结果 key:默认只有一个参数的情况下,key值默认就是方法参数值; 如果没有参数或者多个参数的情况:会使用SimpleKeyGenerate来为生成key
*/
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "comment", unless = "#result==null")
public Comment findCommentById(Integer id) {
Optional byId = commentRepository.findById(id);
if (byId.isPresent()) {
Comment comment = byId.get();
return comment;
}
return null;
}
// 更新方法
@CachePut(cacheNames = "comment", key = "#result.id")
public Comment updateComment(Comment comment) {
commentRepository.updateComment(comment.getAuthor(), comment.getId());
return comment;
}
// 删除方法
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "comment")
public void deleteComment(Integer id) {
commentRepository.deleteById(id);
}
}
以上 使用@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict注解在数据查询、更新和删除方法上进行了缓存管理。
其中,查询缓存@Cacheable注解中没有标记key值,将会使用默认参数值comment_id作为key进行数据保存,在进行缓存更新时必须使用同样的key;同时在查询缓存@Cacheable注解中,定义了“unless = "#result==null"”表示查询结果为空不进行缓存
控制层
package com.lagou.controller;
import com.lagou.pojo.Comment;
import com.lagou.service.CommentService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class CommentController {
@Autowired
private CommentService commentService;
@RequestMapping( "/findCommentById")
public Comment findCommentById(Integer id) {
Comment comment = commentService.findCommentById(id);
return comment;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/updateComment")
public Comment updateComment(Comment comment) {
Comment commentById = commentService.findCommentById(comment.getId());
commentById.setAuthor(comment.getAuthor());
return commentService.updateComment(commentById);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/deleteComment")
public void deleteComment(Integer id) {
commentService.deleteComment(id);
}
}
(4) 基于注解的Redis查询缓存测试
可以看出,查询用户评论信息Comment时执行了相应的SQL语句,但是在进行缓存存储时出现了IllegalArgumentException非法参数异常,提示信息要求对应Comment实体类必须实现序列化(“DefaultSerializer requires a Serializable payload but received an object of type”)。
(5)将缓存对象实现序列化。
(6)再次启动测试
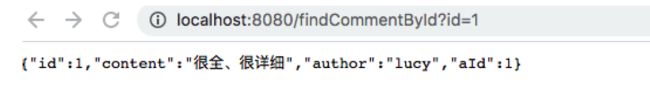
访问“http://localhost:8080/findCommentById?id=1”查询id为1的用户评论信息,并重复刷新浏览器查询同一条数据信息,查询结果
查看控制台打印的SQL查询语句
![]()
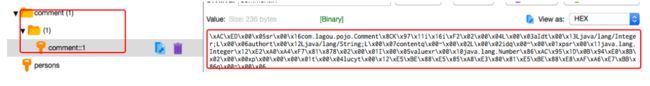
还可以打开Redis客户端可视化管理工具Redis Desktop Manager连接本地启用的Redis服务,查看具体的数据缓存效果
执行findById()方法查询出的用户评论信息Comment正确存储到了Redis缓存库中名为comment的名称空间下。其中缓存数据的唯一标识key值是以“名称空间comment::+参数值(comment::1)”的字符串形式体现的,而value值则是经过JDK默认序列格式化后的HEX格式存储。这种JDK默认序列格式化后的数据显然不方便缓存数据的可视化查看和管理,所以在实际开发中,通常会自定义数据的序列化格式
(7) 基于注解的Redis缓存更新测试。
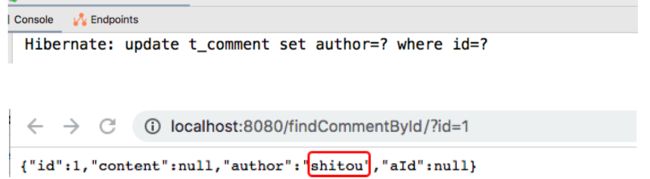
先通过浏览器访问“http://localhost:8080/updateComment/1/shitou”更新id为1的评论作者名为shitou;
接着,继续访问“http://localhost:8080/findCommentById?id=1”查询id为1的用户评论信息
可以看出,执行updateComment()方法更新id为1的数据时执行了一条更新SQL语句,后续调用findById()方法查询id为1的用户评论信息时没有执行查询SQL语句,且浏览器正确返回了更新后的结果,表明@CachePut缓存更新配置成功
(8)基于注解的Redis缓存删除测试
通过浏览器访问“http://localhost:8080/deleteComment?id=1”删除id为1的用户评论信息;
执行deleteComment()方法删除id为1的数据后查询结果为空,之前存储在Redis数据库的comment相关数据也被删除,表明@CacheEvict缓存删除成功实现
通过上面的案例可以看出,使用基于注解的Redis缓存实现只需要添加Redis依赖并使用几个注解可以实现对数据的缓存管理。另外,还可以在Spring Boot全局配置文件中配置Redis有效期,示例代码如下:
# 对基于注解的Redis缓存数据统一设置有效期为1分钟,单位毫秒
spring.cache.redis.time-to-live=60000
上述代码中,在Spring Boot全局配置文件中添加了“spring.cache.redis.time-to-live”属性统一配置Redis数据的有效期(单位为毫秒),但这种方式相对来说不够灵活
3、基于API的Redis缓存实现
在Spring Boot整合Redis缓存实现中,除了基于注解形式的Redis缓存实现外,还有一种开发中常用的方式——基于API的Redis缓存实现。这种基于API的Redis缓存实现,需要在某种业务需求下通过Redis提供的API调用相关方法实现数据缓存管理;同时,这种方法还可以手动管理缓存的有效期。
下面,通过Redis API的方式讲解Spring Boot整合Redis缓存的具体实现
(1)使用Redis API进行业务数据缓存管理。在com.lagou.service包下编写一个进行业务处理的类ApiCommentService
package com.lagou.service;
import com.lagou.pojo.Comment;
import com.lagou.repository.CommentRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Service
public class ApiCommentService {
@Autowired
private CommentRepository commentRepository;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
// 使用API方式进行缓存,先去缓存中查找,缓存中有,直接返回;没有查询数据库
public Comment findCommentById(Integer id) {
Object o = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("comment_" + id);
if (o != null) {
return (Comment) o; // 查询到数据
} else {
// 缓存中没有,从数据库中查询
Optional byId = commentRepository.findById(id);
if (byId.isPresent()) {
Comment comment = byId.get();
// 将查询结果存入到缓存中,同时还可以设置有效期
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("comment_" + id, comment, 1, TimeUnit.DAYS); // 过期时间为一天
return comment;
}
}
return null;
}
// 更新方法
public Comment updateComment(Comment comment) {
commentRepository.updateComment(comment.getAuthor(), comment.getId());
// 将更新数据进行缓存更新
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("comment_" + comment.getId(), comment, 1, TimeUnit.DAYS);
return comment;
}
// 删除方法
public void deleteComment(Integer id) {
commentRepository.deleteById(id);
redisTemplate.delete("comment_" + id);
}
}
(2)编写Web访问层Controller文件
package com.lagou.controller;
import com.lagou.pojo.Comment;
import com.lagou.service.ApiCommentService;
import com.lagou.service.CommentService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class ApiCommentController {
@Autowired
private ApiCommentService commentService;
@RequestMapping( "/findCommentById")
public Comment findCommentById(Integer id) {
Comment comment = commentService.findCommentById(id);
return comment;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/updateComment")
public Comment updateComment(Comment comment) {
Comment commentById = commentService.findCommentById(comment.getId());
commentById.setAuthor(comment.getAuthor());
return commentService.updateComment(commentById);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/deleteComment")
public void deleteComment(Integer id) {
commentService.deleteComment(id);
}
}
基于API的Redis缓存实现的相关配置。基于API的Redis缓存实现不需要@EnableCaching注解开启基于注解的缓存支持,所以这里可以选择将添加在项目启动类上的@EnableCaching进行删除或者注释
到此这篇关于SpringBoot详解整合Redis缓存方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot Redis缓存内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!