Nginx知识点总结
常用命令
./nginx 启动
./nginx -s stop 快速停止
./nginx -s quit 优雅关闭,在退出前完成已经接受的连接请求
./nginx -s reload 重新加载配置
基本配置解析
user root;
#工作线程数,最佳配为当前主机的CPU内核数
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
pid logs/nginx.pid;
# 事件驱动 每个线程的最大连接数
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
# include 引入外部的文件
# mime.types 记录了文件后缀名对应的处理类型
include mime.types;
# 如果不在记录里的文件类型使用的默认处理类型
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
# 开启数据零拷贝
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
# 连接超时时间 单位是s
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
# 监听端口
listen 80;
# 域名、主机名
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
# /是域名之后跟的内容
location / {
# 资源路径 html是相对路径
root html;
# 默认加载该路径下的文件名
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
# 出现以下错误码 跳转到/50x.html
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
nginx路径匹配规则
先精准,后头通配符,再尾通配符,最后正则
反向代理
location / {
# 反向代理到http://www.baidu.com,但不支持https
proxy_pass http://www.baidu.com
}
负载均衡
负载均衡策略
- 轮询
默认情况下使用的方式,逐一转发,适用于无状态请求,如有session认证的就不行 - ip_hash
根据客户端的ip地址转发同一台服务器,可以保持会话,但有些如移动端切换网络ip变化就不适合了
默认是根据ip进行hash,也可以指定hash的内容
如根据请求地址进行hash: hash $request_uri;
根据cookie里的jsessionid进行hash: hash $cookie_jsessionid; - least_conn
最少连接访问 - url_hash
根据用户访问的url定向转发请求 - fair
根据后端服务器响应时间转发请求,需要下载插件
# 这部分写在server上面
upstream myservers {
# 如果不使用默认策略,直接里面加入对应策略即可
# ip_hash;
# weight 是轮询权重
# down 表示不参与负载均衡
# backup 表示备用服务器,当111不能用了,112才顶上
server 192.168.110.110 weight=1 down;
server 192.168.110.111 weight=2 backup;
server 192.168.110.112 weight=3;
}
# 这部分写在server里面
location / {
proxy_pass http://myservers
}
动静分离
URLRewrite
flag标记
- last
本条规则匹配完成后,继续向下匹配新的location URI规则 - break
本条规则匹配完成即终止,不在匹配后面的如何规则 - redirect
返回302临时重定向,浏览器地址栏会显示跳转后的URL地址 - permanent
返回301永久重定向,浏览器地址栏会显示跳转后的URL地址
location / {
# 当匹配到路径规则为/2.html时,转换为真实路径/index.jsp?pageNum=2
# break为flag标记
rewrite ^/2.html$ /index.jsp?pageNum=2 break;
proxy_pass 192.168.110.1
}
#动态参数
location / {
# 当匹配到路径规则为/2.html时,转换为真实路径/index.jsp?pageNum=2
# break为
rewrite ^/([0-9]+).html$ /index.jsp?pageNum=$1 break;
proxy_pass 192.168.110.1
}
防盗链
valid_referers none | blocked | server_names | strings …;
- none
检测Referer头域不存在的情况 - blocked
检测Referer头域的值被防火墙或者代理服务器删除或伪装的情况,这种情况该头域的值不以“http://”或“https://”开头 - server_names
设置一个或多个URL,检测Referer头域的值是否是这些URL
location / {
# 可以配多个 空格隔开
valid_referers 192.168.110.111;
# 只允许192.168.110.111访问资源
if ($invalid_referer){
return 403;
}
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
# 也可以转到提示盗链资源
location / {
valid_referers 192.168.110.111;
if ($invalid_referer){
rewrite ^/ /img/x.png break;
}
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
KeepAlived
安装
yum install -y keepalived
配置文件目录
/etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
修改配置
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
notification_email {
acassen@firewall.loc
failover@firewall.loc
sysadmin@firewall.loc
}
notification_email_from Alexandre.Cassen@firewall.loc
smtp_server 192.168.200.1
smtp_connect_timeout 30
router_id LVS_DEVEL
vrrp_skip_check_adv_addr
vrrp_strict
vrrp_garp_interval 0
vrrp_gna_interval 0
}
# vrrp_test是实例名称,自定义
vrrp_instance vrrp_test {
# 当前机器的角色 MASTER是主 BACKUP是备份
state MASTER
# ens32是网卡名字,看自己的机器
interface ens32
virtual_router_id 51
# 主备竞选时的优先级
priority 100
# 间隔检测时间
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
# 虚拟的IP,可以有多个,这里一个就行了
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.200.16
}
}
其他的机器都相同的配置
除了优先级微调一下
然后都启动keepalived
systemctl start keepalived
这是启动前的ip
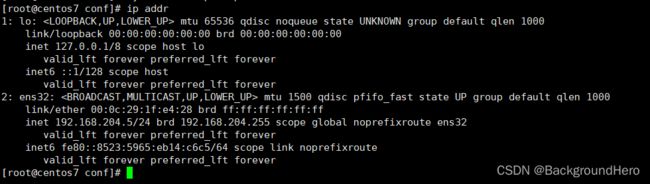
这是启动后的ip

如果当前机器挂了
与192.168.200.16会漂移到与当前机器同组的机器上
挂掉目录命令
init 0
使用sticky模块完成对Nginx的负载均衡
使用参考
tengine中有session_sticky模块我们通过第三方的方式安装在开源版本中
sticky是第三方模块,需要重新编译Nginx,他可以对Nginx这种静态文件服务器使用基于cookie的负载均衡
1. 下载模块
项目官网
https://bitbucket.org/nginx-goodies/nginx-sticky-module-ng/src/master/
另外一个版本
https://github.com/bymaximus/nginx-sticky-module-ng
下载
https://bitbucket.org/nginx-goodies/nginx-sticky-module-ng/get/1.2.6.zip
2.上传解压
3.重新编译Nginx
依赖openssl-devel
进到源码目录重新编译
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --add-module=/root/nginx-goodies-nginx-sticky-module-ng-c78b7dd79d0d
执行make
如遇报错修改源码
打开 ngx_http_sticky_misc.c文件
在12行添加
#include 备份之前的nginx程序
mv /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx.old
把编译好的Nginx程序替换到原来的目录里
cp objs/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/
升级检测
make upgrade
检查程序中是否包含新模块
nginx -V
配置方法
upstream httpget {
# sticky的原理是在第一次请求是添加个名为router的cookie,可以通过name指定,expires配置过期时间
# 而后每次访问都会对其进行hash
sticky name=route expires=6h;
server 192.168.44.102;
server 192.168.44.103;
}
和上游保持KeepAlive
server中配置
# 连接超时时间 单位是s 连接建立之后,多长时间没有活跃就会被关闭掉
# 为0即关闭
keepalive_timeout 65;
# 一个tcp连接总时长,默认1h,超过后会强制失效
keepalive_time 1h;
# 默认60s,系统中有耗时操作,超过了该值则会强制断开连接
send_timeout: 60;
# 默认是1000,一个tcp复用中,可以并发接收的请求个数
keepalive_requests: 1000;
# 配置http版本号
# 默认使用http1.o协议,需要在request中增加"connection: keep-alive" header才能够支持,而HTTP1.1默认支持。
proxy_http_version 1.1;
# 清除close信息 让nginx和上游服务器进行keepalive连接
proxy_set_header Connection "" ;
upstream中配置
# 向上游服务器的保留连接数
keepalive 100;
# 连接超时时间 单位是s 连接建立之后,多长时间没有活跃就会被关闭掉
# 为0即关闭
keepalive_timeout 65;
# 默认是1000,一个tcp复用中,可以并发接收的请求个数
keepalive_requests: 1000;
缓冲区
proxy_requset_buffering
是否完全读到请求体之后再向上游服务器发送请求
proxy_buffering
是否缓冲上游服务器数据
proxy_buffers 32 64k;
缓冲区大小 32个 64k大小内存缓冲块
proxy_buffer_size
header缓冲区大小
proxy_requset_buffering on;
proxy_buffering on;
proxy_buffer_size 64k;
proxy_buffers 32 128k;
proxy_busy_buffers_size 8k;
proxy_max_temp_file_size 1024m;
proxy_temp_file_write_size 8k
当启用从代理服务器到临时文件的响应的缓冲时,一次限制写入临时文件的数据的大小。 默认情况下,大小由proxy_buffer_size和proxy_buffers指令设置的两个缓冲区限制。 临时文件的最大大小由proxy_max_temp_file_size指令设置。
proxy_max_temp_file_size 1024m;
临时文件最大值
proxy_temp_path
# 1 2表示储存时文件夹的深度
proxy_temp_path /spool/nginx/proxy_temp 1 2;
a temporary file might look like this:
/spool/nginx/proxy_temp/7/45/00000123457
对客户端的配置
也就是写在http里的
client_body_buffer_size
对客户端请求中的body缓冲区大小
默认32位8k 64位16k
如果请求体大于配置,则写入临时文件
client_header_buffer_size
设置读取客户端请求体的缓冲区大小。 如果请求体大于缓冲区,则将整个请求体或仅将其部分写入临时文件。 默认32位8K。 64位平台16K。
client_max_body_size 1000M;
默认1m,如果一个请求的大小超过配置的值,会返回413 (request Entity Too Large)错误给客户端
将size设置为0将禁用对客户端请求正文大小的检查。
client_body_timeout
指定客户端与服务端建立连接后发送 request body 的超时时间。如果客户端在指定时间内没有发送任何内容,Nginx 返回 HTTP 408(Request Timed Out)
client_header_timeout
客户端向服务端发送一个完整的 request header 的超时时间。如果客户端在指定时间内没有发送一个完整的 request header,Nginx 返回 HTTP 408(Request Timed Out)。
client_body_temp_path path [level1 [level2 [level3`]]]
在磁盘上客户端的body临时缓冲区位置
client_body_in_file_only on;
把body写入磁盘文件,请求结束也不会删除
client_body_in_single_buffer
尽量缓冲body的时候在内存中使用连续单一缓冲区,在二次开发时使用$request_body读取数据时性能会有所提高
client_header_buffer_size
设置读取客户端请求头的缓冲区大小
如果一个请求行或者一个请求头字段不能放入这个缓冲区,那么就会使用large_client_header_buffers
large_client_header_buffers
设置最大读取客户端请求头的缓冲区大小
默认8k
获取客户端真实的IP地址
location里添加
proxy_set_head X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
如果经过了多级代理
可以在后面追加,最终得到的一个列表,代表经过的所有ip集合
GZIP
作用域 http, server, location
GZIP静态压缩
- gzip on;
开关,默认关闭
- gzip_buffers 32 4k|16 8k
两个参数分别代表 缓冲块块数和每个缓存块大小
32位建议 32 4k
64位建议 16 8k
缓冲区大小
- gzip_comp_level 1;
压缩等级 1-9,数字越大压缩比越高,同时压缩时间也多
- gzip_http_version 1.1;
使用gzip的最小版本
- gzip_min_length
设置将被gzip压缩的响应的最小长度。 长度仅由“Content-Length”响应报头字段确定。
- gzip_proxied 多选
off 为不做限制
只在作为反向代理时有效,针对上游服务器返回的头信息进行压缩
expired - 启用压缩,如果header头中包含 “Expires” 头信息
no-cache - 启用压缩,如果header头中包含 “Cache-Control:no-cache” 头信息
no-store - 启用压缩,如果header头中包含 “Cache-Control:no-store” 头信息
private - 启用压缩,如果header头中包含 “Cache-Control:private” 头信息
no_last_modified - 启用压缩,如果header头中不包含 “Last-Modified” 头信息
no_etag - 启用压缩 ,如果header头中不包含 “ETag” 头信息
auth - 启用压缩 , 如果header头中包含 “Authorization” 头信息
any - 无条件启用压缩(常用)
- gzip_vary on;
增加一个header,适配老的浏览器 Vary: Accept-Encoding
- gzip_types
哪些mime类型的文件进行压缩
- gzip_disable
禁止某些浏览器使用gzip,建议不配,正则影响性能
示例
gzip on;
gzip_buffers 16 8k;
gzip_comp_level 6;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_min_length 256;
gzip_proxied any;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascript text/css application/xml;
gzip_types
text/xml application/xml application/atom+xml application/rss+xml application/xhtml+xml image/svg+xml
text/javascript application/javascript application/x-javascript
text/x-json application/json application/x-web-app-manifest+json
text/css text/plain text/x-component
font/opentype application/x-font-ttf application/vnd.ms-fontobject
image/x-icon;
gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]\.(?!.*SV1)";
GZIP动态压缩缺点,开启后无法使用send_file,但GZIP静态压缩可以
GZIP静态压缩
就是提前将资源压缩好
官方文档
需要重新编译nginx
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx/ --with-http_gzip_static_module
# 编译
make
# 进入到编译好的文件夹中
cd objs
# 复制里面nginx替换当前的nginx 当然可以提前备份一份
cp ./nginx /usr/local/nginx/nginx
然后加上以下内容
gunzip on;
gzip_static always;
Brotli
安装
-
官网
https://github.com/google/ngx_brotlihttps://codeload.github.com/google/brotli/tar.gz/refs/tags/v1.0.9
-
下载 两个项目
-
解压缩
模块化编译
./configure --with-compat --add-dynamic-module=/root/ngx_brotli-1.0.0rc --prefix=/usr/local/nginx/
或
--add-dynamic-module=brotli目录
-
make
-
将
ngx_http_brotli_filter_module.songx_http_brotli_static_module.so拷贝到/usr/local/nginx/modules/ -
复制nginx主程序
-
配置文件中添加
load_module "/usr/local/nginx/modules/ngx_http_brotli_filter_module.so";
load_module "/usr/local/nginx/modules/ngx_http_brotli_static_module.so";
brotli on;
brotli_static on;
brotli_comp_level 6;
brotli_buffers 16 8k;
brotli_min_length 20;
brotli_types text/plain text/css text/javascript application/javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss application/json image/jpeg image/gif image/png;
- 测试
默认http协议是没有br的,https才有
curl -H 'Accept-Encoding: gzip' -I http://localhost
合并客户端请求
将多个同类型资源的请求压缩成一个请求
Concat模块
Tengine
Nginx官方介绍
git地址
- 安装
下载源码解压缩编译安装,和其他插件一样
- 配置
concat on;
concat_max_files 30;
- 使用
前端加载资源时,发送合并请求
??a.css,b.css
SSI合并服务器端文件
官方文档
配置
ssi
on开启ssl,off关闭,作用域 location
ssi_min_file_chunk
向磁盘存储并使用sendfile发送,文件大小最小值
ssi_last_modified
是否保留lastmodified,最后修改时间,客户端会判断是否修改过从而判断是否要修改缓存
ssi_silent_errors
不显示逻辑错误
ssi_value_length
限制脚本参数最大长度
ssi_types
默认text/html;如果需要其他mime类型 需要设置
SSL模板命令
-
include file
静态文件直接引用
<!--# include file="footer.html" --> -
include virtual
可以指向location,而不一定是具体文件
-
include wait
阻塞请求
-
include set
在virtual基础上设置变量
-
set
设置临时变量
-
block
可以声明一个ssi的命令块,里面可以包裹其他命令
-
config errmsg
在模板中配置报错情况
-
config timefmt
日期格式化
-
echo
直接输出变量
- var变量名称
- encoding 是否使用特殊编码格式
- default 变量没有值的时候使用默认值
-
if
逻辑判断
资源静态同步
rsync
官网地址
remote synchronize是一个远程数据同步工具,可通过 LAN/WAN 快速同步多台主机之间的文件。也可以使用 rsync 同步本地硬盘中的不同目录。
rsync 是用于替代 rcp 的一个工具,rsync 使用所谓的 rsync算法 进行数据同步,这种算法只传送两个文件的不同部分,而不是每次都整份传送,因此速度相当快。
rsync 基于inotify 开发
Rsync有三种模式:
- 本地模式(类似于cp命令)
- 远程模式(类似于scp命令)
- 守护进程(socket进程:是rsync的重要功能)
rsync 常用选项
| 选项 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| -a | 包含-rtplgoD |
| -r | 同步目录时要加上,类似cp时的-r选项 |
| -v | 同步时显示一些信息,让我们知道同步的过程 |
| -l | 保留软连接 |
| -L | 加上该选项后,同步软链接时会把源文件给同步 |
| -p | 保持文件的权限属性 |
| -o | 保持文件的属主 |
| -g | 保持文件的属组 |
| -D | 保持设备文件信息 |
| -t | 保持文件的时间属性 |
| –delete | 删除DEST中SRC没有的文件 |
| –exclude | 过滤指定文件,如–exclude “logs”会把文件名包含logs的文件或者目录过滤掉,不同步 |
| -P | 显示同步过程,比如速率,比-v更加详细 |
| -u | 加上该选项后,如果DEST中的文件比SRC新,则不同步 |
| -z | 传输时压缩 |
安装
两端安装
yum install -y rsync
密码文件
创建文件/etc/rsync.password
内容
hello:123
修改权限
chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password
修改配置
auth users = sgg
secrets file = /etc/rsyncd.pwd
开机启动
在/etc/rc.local文件中添加
rsync --daemon
- 修改权限
echo “sgg:111” >> /etc/rsyncd.passwd
查看远程目录
rsync --list-only 192.168.44.104::www/
拉取数据到指定目录
rsync -avz rsync://192.168.44.104:873/www
rsync -avz 192.168.44.104::www/ /root/w
使用SSH方式
rsync -avzP /usr/local/nginx/html/ [email protected]:/www/
客户端免密
客户端只放密码
echo "111" >> /etc/rsyncd.passwd
此时在客户端已经可以配合脚本实现定时同步了
如何实现推送?
修改配置
rsync -avz --password-file=/etc/rsyncd.passwd.client /usr/local/nginx/html/ rsync://[email protected]:/www
--delete 删除目标目录比源目录多余文件
实时推送
推送端安装inotify
依赖
yum install -y automake
wget http://github.com/downloads/rvoicilas/inotify-tools/inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/inotify
make && make install
监控目录
/usr/local/inotify/bin/inotifywait -mrq --timefmt '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S' --format '%T %w%f %e' -e close_write,modify,delete,create,attrib,move //usr/local/nginx/html/
简单自动化脚本
#!/bin/bash
/usr/local/inotify/bin/inotifywait -mrq --timefmt '%d/%m/%y %H:%M' --format '%T %w%f %e' -e close_write,modify,delete,create,attrib,move //usr/local/nginx/html/ | while read file
do
rsync -az --delete --password-file=/etc/rsyncd.passwd.client /usr/local/nginx/html/ [email protected]::ftp/
done
inotify
常用参数
| 参数 | 说明 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| -r | –recursive | #递归查询目录 |
| -q | –quiet | #打印很少的信息,仅仅打印监控事件信息 |
| -m | –monitor | #始终保持事件监听状态 |
| –excludei | #排除文件或目录时,不区分大小写 | |
| –timefmt | #指定事件输出格式 | |
| –format | #打印使用指定的输出类似格式字符串 | |
| -e | –event[ -e|–event … ]accessmodifyattribcloseopenmove_tomove createdeleteumount | #通过此参数可以指定要监控的事件 #文件或目录被读取#文件或目录的内容被修改#文件或目录属性被改变#文件或目录封闭,无论读/写模式#文件或目录被打开#文件或目录被移动至另外一个目录#文件或目录被移动另一个目录或从另一个目录移动至当前目录#文件或目录被创建在当前目录#文件或目录被删除#文件系统被卸载 |
多级缓存
浏览器缓存
什么时候可以用缓存?
- 不常改变的内容
- 过期时间
- 针对post/get请求都可以
- 存储位置
- 磁盘使用空间限制
观察京东缓存及加载速度
-
deskcache
字面理解是从内存中,其实也是字面的含义,这个资源是直接从内存中拿到的,不会请求服务器一般已经加载过该资源且缓存在了内存当中,当关闭该页面时,此资源就被内存释放掉了,再次重新打开相同页面时不会出现from memory cache的情况
-
memorycache
是从磁盘当中取出的,也是在已经在之前的某个时间加载过该资源,不会请求服务器但是此资源不会随着该页面的关闭而释放掉,因为是存在硬盘当中的,下次打开仍会from disk cache
-
Age
是CDN添加的属性表示在CDN中缓存了多少秒
- via
用来标识CDN缓存经历了哪些服务器,缓存是否命中,使用的协议
Nginx默认缓存
Nginx版本不同会默认配置
强制缓存与协商缓存
强制缓存:直接从本机读取,不请求服务器
协商缓存:发送请求header中携带Last-Modified,服务器可能会返回304 Not Modified
浏览器强制缓存
- cache-control
http1.1的规范,使用max-age表示文件可以在浏览器中缓存的时间以秒为单位
| 标记 | 类型 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| public | 响应头 | 响应的数据可以被缓存,客户端和代理层都可以缓存 |
| private | 响应头 | 可私有缓存,客户端可以缓存,代理层不能缓存(CDN,proxy_pass) |
| no-cache | 请求头 | 可以使用本地缓存,但是必须发送请求到服务器回源验证 |
| no-store | 请求和响应 | 应禁用缓存 |
| max-age | 请求和响应 | 文件可以在浏览器中缓存的时间以秒为单位 |
| s-maxage | 请求和响应 | 用户代理层缓存,CDN下发,当客户端数据过期时会重新校验 |
| max-stale | 请求和响应 | 缓存最大使用时间,如果缓存过期,但还在这个时间范围内则可以使用缓存数据 |
| min-fresh | 请求和响应 | 缓存最小使用时间, |
| must-revalidate | 请求和响应 | 当缓存过期后,必须回源重新请求资源。比no-cache更严格。因为HTTP 规范是允许客户端在某些特殊情况下直接使用过期缓存的,比如校验请求发送失败的时候。那么带有must-revalidate的缓存必须校验,其他条件全部失效。 |
| proxy-revalidate | 请求和响应 | 和must-revalidate类似,只对CDN这种代理服务器有效,客户端遇到此头,需要回源验证 |
| stale-while-revalidate | 响应 | 表示在指定时间内可以先使用本地缓存,后台进行异步校验 |
| stale-if-error | 响应 | 在指定时间内,重新验证时返回状态码为5XX的时候,可以用本地缓存 |
| only-if-cached | 响应 | 那么只使用缓存内容,如果没有缓存 则504 getway timeout |
在浏览器和服务器端验证文件是否过期的时候,浏览器在二次请求的时候会携带IF-Modified-Since属性
-
Expires
过期时间
expires 30s; #缓存30秒 expires 30m; #缓存30分钟 expires 2h; #缓存2小时 expires 30d; #缓存30天
协商缓存
-
last-modified
-
etag
http1.1支持
在HTTP协议中If-Modified-Since和If-None-Match分别对应Last-Modified和ETag
Entity Tag 的缩写,中文译过来就是实体标签的意思.
HTTP中并没有指定如何生成ETag,哈希是比较理想的选择。
在计算Etag的时候,会产生CPU的耗费,所以也可以用时间戳,但这样直接使用Last-Modified即可。
ETag 用来校验用户请求的资源是否有变化,作用和lastmodified很像,区别是lastmodified精确到秒,ETag可以用hash算法来生成更精确的比对内容。
当用户首次请求资源的时候返回给用户数据和200状态码并生成ETag,再次请求的时候服务器比对ETag,没有发生变化的话返回304
Cache-Control直接是通过不请求来实现,而ETag是会发请求的,只不过服务器根据请求的东西的内容有无变化来判断是否返回请求的资源
总结:
-
cache-control expires 强制缓存
页面首次打开,直接读取缓存数据,刷新,会向服务器发起请求
-
etag lastmodify 协商缓存
没发生变化 返回304 不发送数据
last-modified 与ssi的冲突
需要先关闭ssi才能使用
浏览器缓存原则
-
多级集群负载时last-modified必须保持一致
-
还有一些场景下我们希望禁用浏览器缓存。比如轮训api上报数据数据
-
浏览器缓存很难彻底禁用,大家的做法是加版本号,随机数等方法。
-
只缓存200响应头的数据,像3XX这类跳转的页面不需要缓存。
-
对于js,css这类可以缓存很久的数据,可以通过加版本号的方式更新内容
-
不需要强一致性的数据,可以缓存几秒
-
异步加载的接口数据,可以使用ETag来校验。
-
在服务器添加Server头,有利于排查错误
-
分为手机APP和Client以及是否遵循http协议
-
在没有联网的状态下可以展示数据
-
流量消耗过多
-
提前下发 避免秒杀时同时下发数据造成流量短时间暴增
-
兜底数据 在服务器崩溃和网络不可用的时候展示
-
临时缓存 退出即清理
-
固定缓存 展示框架这种,可能很长时间不会更新,可用随客户端下发
- 首页有的时候可以看做是框架 应该禁用缓存,以保证加载的资源都是最新的
-
父子连接 页面跳转时有一部分内容不需要重新加载,可用从父菜单带过来
-
预加载 某些逻辑可用判定用户接下来的操作,那么可用异步加载那些资源
-
漂亮的加载过程 异步加载 先展示框架,然后异步加载内容,避免主线程阻塞
GEOip
1 下载数据库
官网需注册登录
下载数据库
maxmind.com
2 安装依赖
官方git
https://github.com/maxmind/libmaxminddb
下载后执行编译安装之后
$ echo /usr/local/lib >> /etc/ld.so.conf.d/local.conf
$ ldconfig
Nginx模块
https://github.com/leev/ngx_http_geoip2_module
更完整的配置可参考官方文档
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_geoip_module.html#geoip_proxy
Nginx配置
geoip2 /root/GeoLite2-ASN_20220524/GeoLite2-ASN.mmdb {
$geoip2_country_code country iso_code;
}
add_header country $geoip2_country_code;
正向代理与反向代理缓存
正向代理配置
proxy_pass $scheme://$host$request_uri;
resolver 8.8.8.8;
代理https请求
需要第三方模块
https://github.com/chobits/ngx_http_proxy_connect_module
配置
server {
listen 3128;
# dns resolver used by forward proxying
resolver 8.8.8.8;
# forward proxy for CONNECT request
proxy_connect;
proxy_connect_allow 443 563;
proxy_connect_connect_timeout 10s;
proxy_connect_read_timeout 10s;
proxy_connect_send_timeout 10s;
# forward proxy for non-CONNECT request
location / {
proxy_pass http://$host;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
}
}
proxy缓存
官网解释
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_proxy_module.html#proxy_cache
配置
http模块:
proxy_cache_path /ngx_tmp levels=1:2 keys_zone=test_cache:100m inactive=1d max_size=10g ;
location模块:
add_header Nginx-Cache "$upstream_cache_status";
proxy_cache test_cache;
proxy_cache_valid 168h;
proxy_cache_use_stale
默认off
在什么时候可以使用过期缓存
可选error | timeout | invalid_header | updating | http_500 | http_502 | http_503 | http_504 | http_403 | http_404 | http_429 | off
proxy_cache_background_update
默认off
运行开启子请求更新过期的内容。同时会把过期的内容返回给客户端
proxy_no_cache proxy_cache_bypass
指定什么时候不使用缓存而直接请求上游服务器
proxy_no_cache $cookie_nocache $arg_nocache$arg_comment;
proxy_no_cache $http_pragma $http_authorization;
如果这些变量如果存在的话不为空或者不等于0,则不使用缓存
proxy_cache_convert_head
默认 on
是否把head请求转换成get请求后再发送给上游服务器 以便缓存body里的内容
如果关闭 需要在 cache key 中添加 $request_method 以便区分缓存内容
proxy_cache_lock
默认off
缓存更新锁
proxy_cache_lock_age
默认5s
缓存锁超时时间
断点续传缓存 range
当有完整的content-length之后即可断点续传
在反向代理服务器中需向后传递header
proxy_set_header Range $http_range;
proxy_cache_key中增加range
proxy_cache_max_range_offset
range最大值,超过之后不做缓存,默认情况下 不需要对单文件较大的资源做缓存
proxy_cache_methods
默认 head get
proxy_cache_min_uses
默认1
被请求多少次之后才做缓存
proxy_cache_path
path 指定存储目录
以cache_key取md5值
- levels=1:2
目录层级数及目录名称位数
取mdb5后几位
TMPFS
- use_temp_path
默认创建缓存文件时,先向缓冲区创建临时文件,再移动到缓存目录
是否使用缓冲区
- inactive
指定时间内未被访问过的缓存将被删除
缓存清理
purger
需要第三方模块支持
https://github.com/FRiCKLE/ngx_cache_purge
配置
location ~ /purge(/.*) {
proxy_cache_purge test_cache $1;
}
自定义cachekey
proxy_cache_key $uri;
proxy_cache_key
默认$scheme$proxy_host$request_uri
缓存的key
proxy_cache_revalidate
如果缓存过期了,向上游服务器发送“If-Modified-Since” and “If-None-Match来验证是否改变,如果没有就不需要重新下载资源了
proxy_cache_valid
可以针对不容http状态码设置缓存过期时间
不设置状态码会默认200, 301, 302
proxy_cache_valid 200 302 10m;
proxy_cache_valid 301 1h;
proxy_cache_valid any 1m;
any指其他任意状态码
Nginx内存缓存
strace
一般应用为静态文件元数据信息缓存
sendfile执行过程
epoll_wait(8, [{EPOLLIN, {u32=1904243152, u64=140709327827408}}, {EPOLLIN, {u32=1904242704, u64=140709327826960}}], 512, 25215) = 2
recvfrom(10, "GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: 192.168.44"..., 1024, 0, NULL, NULL) = 475
stat("/usr/local/nginx//html/index.html", {st_mode=S_IFREG|0644, st_size=1429, ...}) = 0
open("/usr/local/nginx//html/index.html", O_RDONLY|O_NONBLOCK) = 11
fstat(11, {st_mode=S_IFREG|0644, st_size=1429, ...}) = 0
writev(10, [{iov_base="HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nServer: nginx/1"..., iov_len=263}], 1) = 263
sendfile(10, 11, [0] => [1429], 1429) = 1429
write(4, "192.168.44.1 - - [27/May/2022:14"..., 193) = 193
close(11)
open_file_cache
open_file_cache max=500 inactive=60s
open_file_cache_min_uses 1;
open_file_cache_valid 60s;
open_file_cache_errors on
max缓存最大数量,超过数量后会使用LRU淘汰
inactive 指定时间内未被访问过的缓存将被删除
pen_file_cache_min_uses
被访问到多少次后会开始缓存
open_file_cache_valid
间隔多长时间去检查文件是否有变化
open_file_cache_errors
对错误信息是否缓存
Nginx外置缓存缓存
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_memcached_module.html
error_page
指定状态码
error_page 404 =302 http://www.atguigu.com;
默认指向location
匿名location
nginx + memcached
memcached安装
yum -y install memcached
默认配置文件在
/etc/sysconfig/memcached
查看状态
memcached-tool 127.0.0.1:11211 stats
nginx配置
upstream backend {
# server 192.168.44.102 weight=8 down;
server 192.168.44.104:8080;
}
location / {
set $memcached_key "$uri?$args";
memcached_pass 127.0.0.1:11211;
add_header X-Cache-Satus HIT;
add_header Content-Type 'text/html; charset=utf-8'; # 强制响应数据格式为html
# root html;
}
nginx + redis
Redis安装
7.0下载地址
https://codeload.github.com/redis/redis/tar.gz/refs/tags/7.0.0
安装
依赖
yum install -y tcl-devel
解压
make
make install
redis2-nginx-module
redis2-nginx-module是一个支持 Redis 2.0 协议的 Nginx upstream 模块,它可以让 Nginx 以非阻塞方式直接防问远方的 Redis 服务,同时支持 TCP 协议和 Unix Domain Socket 模式,并且可以启用强大的 Redis 连接池功能。
https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/modules/redis2/
https://github.com/openresty/redis2-nginx-module
redis快速安装
yum install epel-release
yum install -y redis
redis2-nginx-module 安装
test
location = /foo {
default_type text/html;
redis2_query auth 123123;
set $value 'first';
redis2_query set one $value;
redis2_pass 192.168.199.161:6379;
}
get
location = /get {
default_type text/html;
redis2_pass 192.168.199.161:6379;
redis2_query auth 123123;
set_unescape_uri $key $arg_key; # this requires ngx_set_misc
redis2_query get $key;
}
set
# GET /set?key=one&val=first%20value
location = /set {
default_type text/html;
redis2_pass 192.168.199.161:6379;
redis2_query auth 123123;
set_unescape_uri $key $arg_key; # this requires ngx_set_misc
set_unescape_uri $val $arg_val; # this requires ngx_set_misc
redis2_query set $key $val;
}
pipeline
set $value 'first';
redis2_query set one $value;
redis2_query get one;
redis2_query set one two;
redis2_query get one;
redis2_query del key1;
list
redis2_query lpush key1 C;
redis2_query lpush key1 B;
redis2_query lpush key1 A;
redis2_query lrange key1 0 -1;
集群
upstream redis_cluster {
server 192.168.199.161:6379;
server 192.168.199.161:6379;
}
location = /redis {
default_type text/html;
redis2_next_upstream error timeout invalid_response;
redis2_query get foo;
redis2_pass redis_cluster;
}
Stream模块
http://nginx.org/en/docs/stream/ngx_stream_core_module.html
限流
QPS限制
官方文档
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_limit_req_module.html
测试工具
https://jmeter.apache.org/
配置
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=test:10m rate=15r/s;
limit_req zone=req_zone_wl burst=20 nodelay;
日志
ngx_http_log_module
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_log_module.html
ngx_http_empty_gif_module
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_empty_gif_module.html
json
log_format ngxlog json '{"timestamp":"$time_iso8601",'
'"source":"$server_addr",'
'"hostname":"$hostname",'
'"remote_user":"$remote_user",'
'"ip":"$http_x_forwarded_for",'
'"client":"$remote_addr",'
'"request_method":"$request_method",'
'"scheme":"$scheme",'
'"domain":"$server_name",'
'"referer":"$http_referer",'
'"request":"$request_uri",'
'"requesturl":"$request",'
'"args":"$args",'
'"size":$body_bytes_sent,'
'"status": $status,'
'"responsetime":$request_time,'
'"upstreamtime":"$upstream_response_time",'
'"upstreamaddr":"$upstream_addr",'
'"http_user_agent":"$http_user_agent",'
'"http_cookie":"$http_cookie",'
'"https":"$https"'
'}';
errorlog
http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#error_log
日志分割
1.脚本
2.Logrotate
重试机制
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_proxy_module.html#proxy_next_upstream
max_fails
最大失败次数
0为标记一直可用,不检查健康状态
fail_timeout
失败时间
当fail_timeout时间内失败了max_fails次,标记服务不可用
fail_timeout时间后会再次激活次服务
proxy_next_upstream
proxy_next_upstream_timeout
重试最大超时时间
proxy_next_upstream_tries
重试次数,包括第一次
proxy_next_upstream_timeout时间内允许proxy_next_upstream_tries次重试
主动健康检查
tengine版
https://github.com/yaoweibin/nginx_upstream_check_module
nginx商业版
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_upstream_hc_module.html
配置
upstream backend {
# server 192.168.44.102 weight=8 down;
server 192.168.44.104:8080;
server 192.168.44.105:8080;
check interval=3000 rise=2 fall=5 timeout=1000 type=http;
check_http_send "HEAD / HTTP/1.0\r\n\r\n";
check_http_expect_alive http_2xx http_3xx;
}
location /status {
check_status;
access_log off;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
root html;
}
Openresty
Lua
Lua 是由巴西里约热内卢天主教大学(Pontifical Catholic University of Rio de Janeiro)里的一个研究小组于1993年开发的一种轻量、小巧的脚本语言,用标准 C 语言编写,其设计目的是为了嵌入应用程序中,从而为应用程序提供灵活的扩展和定制功能。
官网:http://www.lua.org/
IDE
EmmyLua插件
https://github.com/EmmyLua/IntelliJ-EmmyLua
https://emmylua.github.io/zh_CN/
LDT 基于eclipse
https://www.eclipse.org/ldt/
Lua基础语法
hello world
print("hello world!")
保留关键字
and break do else elseif end false for function if in local nil not or repeat return then true until while
注释
-- 两个减号是行注释
--[[
这是块注释
这是块注释.
--]]
变量
数字类型
Lua的数字只有double型,64bits
你可以以如下的方式表示数字
num = 1024
num = 3.0
num = 3.1416
num = 314.16e-2
num = 0.31416E1
num = 0xff
num = 0x56
字符串
可以用单引号,也可以用双引号
也可以使用转义字符‘\n’ (换行), ‘\r’ (回车), ‘\t’ (横向制表), ‘\v’ (纵向制表), ‘\’ (反斜杠), ‘\”‘ (双引号), 以及 ‘\” (单引号)等等
下面的四种方式定义了完全相同的字符串(其中的两个中括号可以用于定义有换行的字符串)
a = 'alo\n123"'
a = "alo\n123\""
a = '\97lo\10\04923"'
a = [[alo
123"]]
空值
C语言中的NULL在Lua中是nil,比如你访问一个没有声明过的变量,就是nil
布尔类型
只有nil和false是 false
数字0,‘’空字符串(’\0’)都是true
作用域
lua中的变量如果没有特殊说明,全是全局变量,那怕是语句块或是函数里。
变量前加local关键字的是局部变量。
控制语句
while循环
local i = 0
local max = 10
while i <= max do
print(i)
i = i +1
end
if-else
local function main()
local age = 140
local sex = 'Male'
if age == 40 and sex =="Male" then
print(" 男人四十一枝花 ")
elseif age > 60 and sex ~="Female" then
print("old man!!")
elseif age < 20 then
io.write("too young, too simple!\n")
else
print("Your age is "..age)
end
end
-- 调用
main()
for循环
sum = 0
for i = 100, 1, -2 do
sum = sum + i
end
函数
function myPower(x,y)
return y+x
end
power2 = myPower(2,3)
print(power2)
function newCounter()
local i = 0
return function() -- anonymous function
i = i + 1
return i
end
end
c1 = newCounter()
print(c1()) --> 1
print(c1()) --> 2
print(c1())
返回值
name, age,bGay = "yiming", 37, false, "[email protected]"
print(name,age,bGay)
function isMyGirl(name)
return name == 'xiao6' , name
end
local bol,name = isMyGirl('xiao6')
print(name,bol)
Table
key,value的键值对 类似 map
local function main()
dog = {name='111',age=18,height=165.5}
dog.age=35
print(dog.name,dog.age,dog.height)
print(dog)
end
main()
数组
local function main()
arr = {"string", 100, "dog",function() print("wangwang!") return 1 end}
print(arr[4]())
end
main()
遍历
arr = {"string", 100, "dog",function() print("wangwang!") return 1 end}
for k, v in pairs(arr) do
print(k, v)
end
成员函数
local function main()
person = {name='旺财',age = 18}
function person.eat(food)
print(person.name .." eating "..food)
end
person.eat("骨头")
end
main()
Openresty Nginx + Lua
Nginx是一个主进程配合多个工作进程的工作模式,每个进程由单个线程来处理多个连接。
在生产环境中,我们往往会把cpu内核直接绑定到工作进程上,从而提升性能。
安装
预编译安装
以CentOS举例 其他系统参照:http://openresty.org/cn/linux-packages.html
你可以在你的 CentOS 系统中添加 openresty 仓库,这样就可以便于未来安装或更新我们的软件包(通过 yum update 命令)。运行下面的命令就可以添加我们的仓库:
yum install yum-utils
yum-config-manager --add-repo https://openresty.org/package/centos/openresty.repo
然后就可以像下面这样安装软件包,比如 openresty:
yum install openresty
如果你想安装命令行工具 resty,那么可以像下面这样安装 openresty-resty 包:
sudo yum install openresty-resty
源码编译安装
下载
http://openresty.org/cn/download.html
最小版本基于nginx1.21
./configure
然后在进入 openresty-VERSION/ 目录, 然后输入以下命令配置:
./configure
默认, --prefix=/usr/local/openresty 程序会被安装到/usr/local/openresty目录。
依赖 gcc openssl-devel pcre-devel zlib-devel
安装:yum install gcc openssl-devel pcre-devel zlib-devel postgresql-devel
您可以指定各种选项,比如
./configure --prefix=/opt/openresty \
--with-luajit \
--without-http_redis2_module \
--with-http_iconv_module \
--with-http_postgres_module
试着使用 ./configure --help 查看更多的选项。
make && make install
服务命令
启动
Service openresty start
停止
Service openresty stop
检查配置文件是否正确
Nginx -t
重新加载配置文件
Service openresty reload
查看已安装模块和版本号
Nginx -V
测试lua脚本
在Nginx.conf 中写入
location /lua {
default_type text/html;
content_by_lua '
ngx.say("Hello, World!
")
';
}
lua-nginx-module
创建配置文件lua.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location /lua {
default_type text/html;
content_by_lua_file conf/lua/hello.lua;
}
}
在Nginx.conf下引入lua配置
include lua.conf;
创建外部lua脚本
conf/lua/hello.lua
内容:
Hello, World!ngx.say("
获取Nginx uri中的单一变量
location /nginx_var {
default_type text/html;
content_by_lua_block {
ngx.say(ngx.var.arg_a)
}
}
获取Nginx uri中的所有变量
local uri_args = ngx.req.get_uri_args()
for k, v in pairs(uri_args) do
if type(v) == "table" then
ngx.say(k, " : ", table.concat(v, ", "), "
")
else
ngx.say(k, ": ", v, "
")
end
end
在处理http请求时还可以使用
- set_by_lua
修改nginx变量
- rewrite_by_lua
修改uri
- access_by_lua
访问控制
- header_filter_by_lua
修改响应头
- boy_filter_by_lua
修改响应体
- log_by_lua
日志
代码热部署
lua_code_cache off
获取Nginx请求头信息
local headers = ngx.req.get_headers()
ngx.say("Host : ", headers["Host"], "
")
ngx.say("user-agent : ", headers["user-agent"], "
")
ngx.say("user-agent : ", headers.user_agent, "
")
for k,v in pairs(headers) do
if type(v) == "table" then
ngx.say(k, " : ", table.concat(v, ","), "
")
else
ngx.say(k, " : ", v, "
")
end
end
获取post请求参数
ngx.req.read_body()
ngx.say("post args begin", "
")
local post_args = ngx.req.get_post_args()
for k, v in pairs(post_args) do
if type(v) == "table" then
ngx.say(k, " : ", table.concat(v, ", "), "
")
else
ngx.say(k, ": ", v, "
")
end
end
http协议版本
ngx.say("ngx.req.http_version : ", ngx.req.http_version(), "
")
请求方法
ngx.say("ngx.req.get_method : ", ngx.req.get_method(), "
")
原始的请求头内容
ngx.say("ngx.req.raw_header : ", ngx.req.raw_header(), "
")
body内容体
ngx.say("ngx.req.get_body_data() : ", ngx.req.get_body_data(), "
")
Nginx缓存
Nginx全局内存缓存
lua_shared_dict shared_data 1m;
local shared_data = ngx.shared.shared_data
local i = shared_data:get("i")
if not i then
i = 1
shared_data:set("i", i)
ngx.say("lazy set i ", i, "
")
end
i = shared_data:incr("i", 1)
ngx.say("i=", i, "
")
lua-resty-lrucache
Lua 实现的一个简单的 LRU 缓存,适合在 Lua 空间里直接缓存较为复杂的 Lua 数据结构:它相比 ngx_lua 共享内存字典可以省去较昂贵的序列化操作,相比 memcached 这样的外部服务又能省去较昂贵的 socket 操作
https://github.com/openresty/lua-resty-lrucache
引用lua文件
content_by_lua_block {
require("my/cache").go()
}
自定义函数
local _M = {}
lrucache = require "resty.lrucache"
c, err = lrucache.new(200) -- allow up to 200 items in the cache
ngx.say("count=init")
if not c then
error("failed to create the cache: " .. (err or "unknown"))
end
function _M.go()
count = c:get("count")
c:set("count",100)
ngx.say("count=", count, " --
")
if not count then
c:set("count",1)
ngx.say("lazy set count ", c:get("count"), "
")
else
c:set("count",count+1)
ngx.say("count=", count, "
")
end
end
return _M
打开lua_code_cache
lua-resty-redis访问redis
https://github.com/openresty/lua-resty-redis
常用方法
local res, err = red:get("key")
local res, err = red:lrange("nokey", 0, 1)
ngx.say("res:",cjson.encode(res))
创建连接
red, err = redis:new()
ok, err = red:connect(host, port, options_table?)
timeout
red:set_timeout(time)
keepalive
red:set_keepalive(max_idle_timeout, pool_size)
close
ok, err = red:close()
pipeline
red:init_pipeline()
results, err = red:commit_pipeline()
认证
local res, err = red:auth("foobared")
if not res then
ngx.say("failed to authenticate: ", err)
return
end
local redis = require "resty.redis"
local red = redis:new()
red:set_timeouts(1000, 1000, 1000) -- 1 sec
local ok, err = red:connect("127.0.0.1", 6379)
if not ok then
ngx.say("failed to connect: ", err)
return
end
ok, err = red:set("dog", "an animal")
if not ok then
ngx.say("failed to set dog: ", err)
return
end
ngx.say("set result: ", ok)
local res, err = red:get("dog")
if not res then
ngx.say("failed to get dog: ", err)
return
end
if res == ngx.null then
ngx.say("dog not found.")
return
end
ngx.say("dog: ", res)
redis-cluster支持
https://github.com/steve0511/resty-redis-cluster
redis2-nginx-module
redis2-nginx-module是一个支持 Redis 2.0 协议的 Nginx upstream 模块,它可以让 Nginx 以非阻塞方式直接防问远方的 Redis 服务,同时支持 TCP 协议和 Unix Domain Socket 模式,并且可以启用强大的 Redis 连接池功能。
test
location = /foo {
default_type text/html;
redis2_query auth 123123;
set $value 'first';
redis2_query set one $value;
redis2_pass 192.168.199.161:6379;
}
get
location = /get {
default_type text/html;
redis2_pass 192.168.199.161:6379;
redis2_query auth 123123;
set_unescape_uri $key $arg_key; # this requires ngx_set_misc
redis2_query get $key;
}
set
# GET /set?key=one&val=first%20value
location = /set {
default_type text/html;
redis2_pass 192.168.199.161:6379;
redis2_query auth 123123;
set_unescape_uri $key $arg_key; # this requires ngx_set_misc
set_unescape_uri $val $arg_val; # this requires ngx_set_misc
redis2_query set $key $val;
}
pipeline
set $value 'first';
redis2_query set one $value;
redis2_query get one;
redis2_query set one two;
redis2_query get one;
redis2_query del key1;
list
redis2_query lpush key1 C;
redis2_query lpush key1 B;
redis2_query lpush key1 A;
redis2_query lrange key1 0 -1;
集群
upstream redis_cluster {
server 192.168.199.161:6379;
server 192.168.199.161:6379;
}
location = /redis {
default_type text/html;
redis2_next_upstream error timeout invalid_response;
redis2_query get foo;
redis2_pass redis_cluster;
}
lua-resty-mysql
https://github.com/openresty/lua-resty-mysql
local mysql = require "resty.mysql"
local db, err = mysql:new()
if not db then
ngx.say("failed to instantiate mysql: ", err)
return
end
db:set_timeout(1000) -- 1 sec
local ok, err, errcode, sqlstate = db:connect{
host = "192.168.44.211",
port = 3306,
database = "zhangmen",
user = "root",
password = "111111",
charset = "utf8",
max_packet_size = 1024 * 1024,
}
ngx.say("connected to mysql.
")
local res, err, errcode, sqlstate = db:query("drop table if exists cats")
if not res then
ngx.say("bad result: ", err, ": ", errcode, ": ", sqlstate, ".")
return
end
res, err, errcode, sqlstate =
db:query("create table cats "
.. "(id serial primary key, "
.. "name varchar(5))")
if not res then
ngx.say("bad result: ", err, ": ", errcode, ": ", sqlstate, ".")
return
end
ngx.say("table cats created.")
res, err, errcode, sqlstate =
db:query("select * from t_emp")
if not res then
ngx.say("bad result: ", err, ": ", errcode, ": ", sqlstate, ".")
return
end
local cjson = require "cjson"
ngx.say("result: ", cjson.encode(res))
local ok, err = db:set_keepalive(10000, 100)
if not ok then
ngx.say("failed to set keepalive: ", err)
return
end
模板实时渲染 lua-resty-template
https://github.com/bungle/lua-resty-template
如果学习过JavaEE中的servlet和JSP的话,应该知道JSP模板最终会被翻译成Servlet来执行;
而lua-resty-template模板引擎可以认为是JSP,其最终会被翻译成Lua代码,然后通过ngx.print输出。
lua-resty-template大体内容有:
l 模板位置:从哪里查找模板;
l 变量输出/转义:变量值输出;
l 代码片段:执行代码片段,完成如if/else、for等复杂逻辑,调用对象函数/方法;
l 注释:解释代码片段含义;
l include:包含另一个模板片段;
l 其他:lua-resty-template还提供了不需要解析片段、简单布局、可复用的代码块、宏指令等支持。
基础语法
l {(include_file)}:包含另一个模板文件;
l {* var *}:变量输出;
l {{ var }}:变量转义输出;
l {% code %}:代码片段;
l {# comment #}:注释;
l {-raw-}:中间的内容不会解析,作为纯文本输出;
lua代码热加载
在http模块中加入
lua_code_cache off;
reload后Nginx会提示影响性能,记得在生产环境中关掉。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-mlHZlfJp-1657948407188)(1569585068623.png)]
测试
一、初始化
-- Using template.new
local template = require "resty.template"
local view = template.new "view.html"
view.message = "Hello, World!"
view:render()
-- Using template.render
-- template.render("view.html", { message = "Hel11lo, Worl1d!" })
二、执行函数,得到渲染之后的内容
local func = template.compile("view.html")
local content = func(context)
ngx.say("xx:",content)
模板文件存放位置
nginx.conf中配置
set $template_root /usr/local/openresty/nginx/tmp;
resty.template.html
local template = require("resty.template")
local html = require "resty.template.html"
template.render([[
{% for _, person in ipairs(context) do %}
{*html.li(person.name)*} --
{% end %}
{% for _, person in ipairs(context) do %}
{*html.td{ id = person.id }(person.name)*}
{% end %}
]], {
{ id = 1, name = "Emma"},
{ id = 2, name = "James" },
{ id = 3, name = "Nicholas" },
{ id = 4 }
})
模板内容
DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>{{message}}h1>
body>
html>
多值传入
template.caching(false)
local template = require("resty.template")
local context = {
name = "lucy",
age = 50,
}
template.render("view.html", context)
模板内容
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>name:{{name}}</h1>
<h1>age:{{age}}</h1>
</body>
</html>
模板管理与缓存
模板缓存:默认开启,开发环境可以手动关闭
template.caching(true)
模板文件需要业务系统更新与维护,当模板文件更新后,可以通过模板版本号或消息通知Openresty清空缓存重载模板到内存中
template.cache = {}
完整页面
local template = require("resty.template")
template.caching(false)
local context = {
title = "测试",
name = "lucy",
description = "",
age = 40,
hobby = {"电影", "音乐", "阅读"},
score = {语文 = 90, 数学 = 80, 英语 = 70},
score2 = {
{name = "语文", score = 90},
{name = "数学", score = 80},
{name = "英语", score = 70},
}
}
template.render("view.html", context)
模板
{(header.html)}
<body>
{# 不转义变量输出 #}
姓名:{* string.upper(name) *}<br/>
{# 转义变量输出 #}
简介:{{description}}
简介:{* description *}<br/>
{# 可以做一些运算 #}
年龄: {* age + 10 *}<br/>
{# 循环输出 #}
爱好:
{% for i, v in ipairs(hobby) do %}
{% if v == '电影' then %} - xxoo
{%else%} - {* v *}
{% end %}
{% end %}<br/>
成绩:
{% local i = 1; %}
{% for k, v in pairs(score) do %}
{% if i > 1 then %},{% end %}
{* k *} = {* v *}
{% i = i + 1 %}
{% end %}<br/>
成绩2:
{% for i = 1, #score2 do local t = score2[i] %}
{% if i > 1 then %},{% end %}
{* t.name *} = {* t.score *}
{% end %}<br/>
{# 中间内容不解析 #}
{-raw-}{(file)}{-raw-}
{(footer.html)}
layout 布局统一风格
使用模板内容嵌套可以实现全站风格同一布局
lua
local template = require "resty.template"
一、
local layout = template.new "layout.html"
layout.title = "Testing lua-resty-template"
layout.view = template.compile "view.html" { message = "Hello, World!" }
layout:render()
二、
template.render("layout.html", {
title = "Testing lua-resty-template",
msg = "type=2",
view = template.compile "view.html" { message = "Hello, World!" }
})
三、
此方式重名变量值会被覆盖
local view = template.new("view.html", "layout.html")
view.title = "Testing lua-resty-template"
view.msg = "type=3"
view.message = "Hello, World!"
view:render()
四、
可以区分一下
local layout = template.new "layout.html"
layout.title = "Testing lua-resty-template"
layout.msg = "type=4"
local view = template.new("view.html", layout)
view.message = "Hello, World!"
view:render()
layout.html
{{title}}
layout
{*view*}
view.html·
msg:{{message}}
多级嵌套
lua
local view = template.new("view.html", "layout.html")
view.title = "Testing lua-resty-template"
view.message = "Hello, World!"
view:render()
view.html
{% layout="section.html" %}
msg:{{message}}
section.html
{view} - sss
layout.html
{{title}}
layout {{msg}}
{view}
Redis缓存+mysql+模板输出
lua
cjson = require "cjson"
sql="select * from t_emp"
local redis = require "resty.redis"
local red = redis:new()
red:set_timeouts(1000, 1000, 1000) -- 1 sec
local ok, err = red:connect("127.0.0.1", 6379)
if not ok then
ngx.say("failed to connect: ", err)
return
end
local res, err = red:get(sql)
if not res then
ngx.say("failed to get sql: ", err)
return
end
if res == ngx.null then
ngx.say("sql"..sql.." not found.")
--mysql查询
local mysql = require "resty.mysql"
local db, err = mysql:new()
if not db then
ngx.say("failed to instantiate mysql: ", err)
return
end
db:set_timeout(1000) -- 1 sec
local ok, err, errcode, sqlstate = db:connect{
host = "192.168.44.211",
port = 3306,
database = "zhangmen",
user = "root",
password = "111111",
charset = "utf8",
max_packet_size = 1024 * 1024,
}
ngx.say("connected to mysql.
")
res, err, errcode, sqlstate =
db:query(sql)
if not res then
ngx.say("bad result: ", err, ": ", errcode, ": ", sqlstate, ".")
return
end
--ngx.say("result: ", cjson.encode(res))
ok, err = red:set(sql, cjson.encode(res))
if not ok then
ngx.say("failed to set sql: ", err)
return
end
ngx.say("set result: ", ok)
return
end
local template = require("resty.template")
template.caching(false)
local context = {
title = "测试",
name = "lucy",
description = "",
age = 40,
hobby = {"电影", "音乐", "阅读"},
score = {语文 = 90, 数学 = 80, 英语 = 70},
score2 = {
{name = "语文", score = 90},
{name = "数学", score = 80},
{name = "英语", score = 70},
},
zhangmen=cjson.decode(res)
}
template.render("view.html", context)
模板
{(header.html)}
{# 不转义变量输出 #}
姓名:{* string.upper(name) *}
{# 转义变量输出 #}
年龄: {* age + 10 *}
{# 循环输出 #}
爱好:
{% for i, v in ipairs(hobby) do %}
{% if v == '电影' then %} - xxoo
{%else%} - {* v *}
{% end %}
{% end %}
成绩:
{% local i = 1; %}
{% for k, v in pairs(score) do %}
{% if i > 1 then %},{% end %}
{* k *} = {* v *}
{% i = i + 1 %}
{% end %}
成绩2:
{% for i = 1, #score2 do local t = score2[i] %}
{% if i > 1 then %},{% end %}
{* t.name *} = {* t.score *}
{% end %}
{# 中间内容不解析 #}
{-raw-}{(file)}{-raw-}
掌门:
{* zhangmen *}
{% for i = 1, #zhangmen do local z = zhangmen[i] %}
{* z.deptId *},{* z.age *},{* z.name *},{* z.empno *},
{% end %}
{(footer.html)}
Lua 开源项目
WAF
https://github.com/unixhot/waf
https://github.com/loveshell/ngx_lua_waf
l 防止 SQL 注入,本地包含,部分溢出,fuzzing 测试,XSS/SSRF 等 Web 攻击
l 防止 Apache Bench 之类压力测试工具的攻击
l 屏蔽常见的扫描黑客工具,扫描器
l 屏蔽图片附件类目录执行权限、防止 webshell 上传
l 支持 IP 白名单和黑名单功能,直接将黑名单的 IP 访问拒绝
l 支持 URL 白名单,将不需要过滤的 URL 进行定义
l 支持 User-Agent 的过滤、支持 CC 攻击防护、限制单个 URL 指定时间的访问次数
l 支持支持 Cookie 过滤,URL 与 URL 参数过滤
l 支持日志记录,将所有拒绝的操作,记录到日志中去
Kong 基于Openresty的流量网关
https://konghq.com/
https://github.com/kong/kong
Kong 基于 OpenResty,是一个云原生、快速、可扩展、分布式的微服务抽象层(Microservice Abstraction Layer),也叫 API 网关(API Gateway),在 Service Mesh 里也叫 API 中间件(API Middleware)。
Kong 开源于 2015 年,核心价值在于高性能和扩展性。从全球 5000 强的组织统计数据来看,Kong 是现在依然在维护的,在生产环境使用最广泛的 API 网关。
Kong 宣称自己是世界上最流行的开源微服务 API 网关(The World’s Most Popular Open Source Microservice API Gateway)。
核心优势:
l 可扩展:可以方便的通过添加节点水平扩展,这意味着可以在很低的延迟下支持很大的系统负载。
l 模块化:可以通过添加新的插件来扩展 Kong 的能力,这些插件可以通过 RESTful Admin API 来安装和配置。
l 在任何基础架构上运行:Kong 可以在任何地方都能运行,比如在云或混合环境中部署 Kong,单个或全球的数据中心。
APISIX
ABTestingGateway
https://github.com/CNSRE/ABTestingGateway
ABTestingGateway 是一个可以动态设置分流策略的网关,关注与灰度发布相关领域,基于 Nginx 和 ngx-lua 开发,使用 Redis 作为分流策略数据库,可以实现动态调度功能。
ABTestingGateway 是新浪微博内部的动态路由系统 dygateway 的一部分,目前已经开源。在以往的基于 Nginx 实现的灰度系统中,分流逻辑往往通过 rewrite 阶段的 if 和 rewrite 指令等实现,优点是性能较高,缺点是功能受限、容易出错,以及转发规则固定,只能静态分流。ABTestingGateway 则采用 ngx-lua,通过启用 lua-shared-dict 和 lua-resty-lock 作为系统缓存和缓存锁,系统获得了较为接近原生 Nginx 转发的性能。
l 支持多种分流方式,目前包括 iprange、uidrange、uid 尾数和指定uid分流
l 支持多级分流,动态设置分流策略,即时生效,无需重启
l 可扩展性,提供了开发框架,开发者可以灵活添加新的分流方式,实现二次开发
l 高性能,压测数据接近原生 Nginx 转发
l 灰度系统配置写在 Nginx 配置文件中,方便管理员配置
l 适用于多种场景:灰度发布、AB 测试和负载均衡等