SpringBoot Web开发
SpringBoot Web开发
文章目录
- SpringBoot Web开发
-
- 1. 静态资源访问
-
- 1.1 静态资源目录
- 1.2 静态资源访问前缀
- 2. 自定义 Favicon
- 3. 欢迎页支持
- 4. Rest映射原理
- 5. 请求映射原理
- 6. 常用注解
-
- 6.1 @PathVariable
- 6.2 @RequestHeader
- 6.3 @RequestParam
- 6.4 @CookieValue
- 6.5 @RequestAttribute
- 6.6 @RequestBody
- 7. 视图解析与模板引擎
-
- 7.1 视图解析
- 7.2 模板引擎-Thymeleaf
- 7.3 Thymeleaf 基本语法
- 7.4 Thymeleaf使用
-
- 7.4.1 引入Stater
- 7.4.2 SprinBoot自动配置Thymeleaf
- 7.4.3 页面开发
- 8. 拦截器
-
- 8.1 实现HandlerInterceptor接口
- 8.2 注册拦截器
- 8.3 拦截器原理
- 9. 文件上传
1. 静态资源访问
1.1 静态资源目录
- 只要静态资源放在类路径下: called
/static(or/publicor/resourcesor/META-INF/resources - 访问 : 当前项目根路径/ + 静态资源名
- 原理: 静态映射/**。
但是需要注意: 请求进来,先去找Controller看能不能处理。不能处理的所有请求又都交给静态资源处理器。静态资源也找不到则响应404页面。
修改默认的资源访问目录:
resources:
# 配置是数组的形式,可以定义多个目录
static-locations: [classpath:/test/]
1.2 静态资源访问前缀
spring:
mvc:
static-path-pattern: /res/**
当前项目 + static-path-pattern + 静态资源名
例如:http://localhost:8080/res/xxx.jpg
2. 自定义 Favicon
将Favicon放到静态资源目录下即可。
3. 欢迎页支持
-
静态资源路径下 index.html
-
- 可以配置静态资源路径
- 但是不可以配置静态资源的访问前缀。否则导致 index.html不能被默认访问
- 可以配置静态资源路径
-
通过controller进行设置
4. Rest映射原理
根据源码分析直接得出结论:
Rest原理(表单提交要使用REST的时候)
-
表单提交会带上 _method=PUT
-
请求过来被
HiddenHttpMethodFilter拦截 -
- 请求是否正常,并且是POST
-
-
- 获取到**_method**的值。
- 兼容以下请求;PUT.DELETE.PATCH
- 原生request(post),包装模式requesWrapper重写了getMethod方法,返回的是传入的值。
- 过滤器链放行的时候用wrapper。以后的方法调用getMethod是调用requesWrapper的
- 获取到**_method**的值。
-
补充:
Rest使用客户端工具,如PostMan直接发送Put、delete等方式请求,无需Filter。
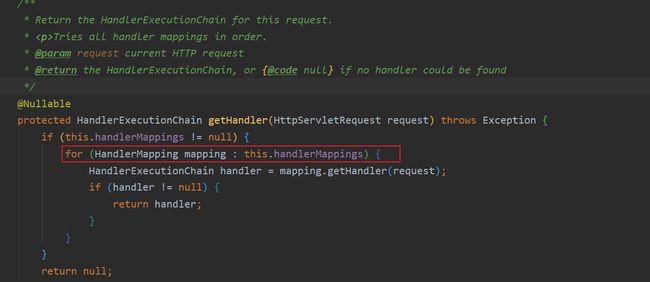
5. 请求映射原理
实际上执行功能的类是DispatcherServlet中的doDispatch方法实现功能。
在doDispatch方法中调用了getHandler方法获取应该处理请求的Handler或Controller:
通过循环依次遍历:
6. 常用注解
6.1 @PathVariable
@PathVariable用于映射URL绑定的占位符,使用@RequestMapping URI template 样式映射时,例如:xxx/{paramId},可通过 @Pathvariable注解绑定它传过来的值到方法的参数上。
@GetMapping("/getUser/{userId}")
public String getUserId(@PathVariable("userId") Integer userId) {
return "userId = " + userId;
}
6.2 @RequestHeader
@RequestHeader 是获取请求头中的数据,通过指定参数 value 的值来获取请求头中指定的参数值。
@GetMapping("/getHeader")
public String getHeader(@RequestHeader("User-Agent") String userAgent) {
return "User-Agent: " + userAgent;
}
6.3 @RequestParam
@RequestParam获取请求参数
@GetMapping("/getParam")
public String getParam(@RequestParam("userId") Integer userId) {
return "userId = " + userId;
}
6.4 @CookieValue
获取Cookie值
@GetMapping("/getCookieValue")
public String getCookieValue(@CookieValue("_ga") String _ga, @CookieValue Cookie cookie) {
return "success";
}
6.5 @RequestAttribute
获取request域属性
@Controller
public class RequestController {
@GetMapping("/goto")
public String goToPage(HttpServletRequest request){
request.setAttribute("msg","成功了...");
request.setAttribute("code",200);
return "forward:/success"; //转发到 /success请求
}
@GetMapping("/params")
public String testParam(Map<String,Object> map,
Model model,
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response){
map.put("hello","world666");
model.addAttribute("world","hello666");
request.setAttribute("message","HelloWorld");
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("c1","v1");
response.addCookie(cookie);
return "forward:/success";
}
///@RequestAttribute在这个方法被使用
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/success")
public Map success(@RequestAttribute(value = "msg",required = false) String msg,
@RequestAttribute(value = "code",required = false)Integer code,
HttpServletRequest request){
Object msg1 = request.getAttribute("msg");
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Object hello = request.getAttribute("hello");
Object world = request.getAttribute("world");
Object message = request.getAttribute("message");
map.put("reqMethod_msg",msg1);
map.put("annotation_msg",msg);
map.put("hello",hello);
map.put("world",world);
map.put("message",message);
return map;
}
}
6.6 @RequestBody
获取请求体,注意是POST请求。
@PostMapping("/getRequestBody")
public String getRequestBody(@RequestBody String body) {
return body;
}
7. 视图解析与模板引擎
在视图解析层面:SpringBoot默认不支持 JSP,需要引入第三方模板引擎技术实现页面渲染。
7.1 视图解析
视图的处理方式有三种:
- 转发
- 重定向
- 自定义视图
视图解析的流程:
1、目标方法处理的过程中,所有数据都会被放在 ModelAndViewContainer 里面。包括数据和视图地址。
2、方法的参数是一个自定义类型对象(从请求参数中确定的),把他重新放在ModelAndViewContainer
3、任何目标方法执行完成以后都会返回 ModelAndView(数据和视图地址)。
4、processDispatchResult 处理派发结果(页面改如何响应)
-
1、render(mv, request, response); 进行页面渲染逻辑
-
- 1、根据方法的String返回值得到 View 对象【定义了页面的渲染逻辑】
-
-
- 1、所有的视图解析器尝试是否能根据当前返回值得到View对象
- 2、得到了 redirect:/main.html --> Thymeleaf new RedirectView()
- 3、ContentNegotiationViewResolver 里面包含了下面所有的视图解析器,内部还是利用下面所有视图解析器得到视图对象。
- 4、view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response); 视图对象调用自定义的render进行页面渲染工作
- 1、所有的视图解析器尝试是否能根据当前返回值得到View对象
-
-
-
-
- RedirectView 如何渲染【重定向到一个页面】
- 1、获取目标url地址
- 2、response.sendRedirect(encodedURL);
- RedirectView 如何渲染【重定向到一个页面】
-
-
7.2 模板引擎-Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf is a modern server-side Java template engine for both web and standalone environments.
Thymeleaf是用于Web和独立环境的现代服务器端Java模板引擎。
— 官方文档
7.3 Thymeleaf 基本语法
① 表达式
| 表达式名字 | 语法 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| 变量取值 | ${...} |
获取请求域、session域、对象等值 |
| 选择变量 | *{...} |
获取上下文对象值 |
| 消息 | #{...} |
获取国际化等值 |
| 链接 | @{...} |
生成链接 |
| 片段表达式 | ~{...} |
jsp:include 作用,引入公共页面片段 |
② 字面量
- 文本文字(Text literals): ‘one text’, ‘Another one!’,…
- 数字文本(Number literals): 0, 12, 3.0, 12.3,…
- 布尔文本(Boolean literals): true, false
- 空(Null literal): null
- 文字标记(Literal tokens): one , sometext
③ 文本操作
- 字符串连接(String concatenation):
+ - 文本替换(Literal substitutions):
|The name is ${name}|
<div th:class="'content'">...div>
<span th:text="|Welcome to our application, ${user.name}!|">
//Which is equivalent to:
<span th:text="'Welcome to our application, ' + ${user.name} + '!'">
<span th:text="${onevar} + ' ' + |${twovar}, ${threevar}|">
④ 数学运算
- 二元运算符(Binary operators): + , - , * , / , %
⑤ 布尔运算
- 运算符: and , or
- 一元运算: ! , not
⑥ 比较运算
- 比较: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )
- 等式: == , != ( eq , ne )
⑦ 条件运算符
-
If-then:
(if) ? (then) -
If-then-else:
(if) ? (then) : (else) -
Default:
(value) ?: (defaultvalue)
⑧ 设置属性值-th:attr
- 设置单个值
<form action="subscribe.html" th:attr="action=@{/subscribe}">
<fieldset>
<input type="text" name="email" />
<input type="submit" value="Subscribe!" th:attr="value=#{subscribe.submit}"/>
fieldset>
form>
- 设置多个值
<img src="../images/xxx.png" th:attr="src=@{/images/xxx.png},title=#{logo},alt=#{logo}" />
- 以上两个的代替写法
th:xxxx
<img src="../images/xxx.png" th:attr="src=@{/images/xxx.png},title=#{logo},alt=#{logo}" />
⑨ 迭代
使用th:each
<tr th:each="prod : ${prods}">
<td th:text="${prod.name}">Onionstd>
<td th:text="${prod.price}">2.41td>
<td th:text="${prod.inStock}? #{true} : #{false}">yestd>
tr>
<tr th:each="prod,iterStat : ${prods}" th:class="${iterStat.odd}? 'odd'">
<td th:text="${prod.name}">Onionstd>
<td th:text="${prod.price}">2.41td>
<td th:text="${prod.inStock}? #{true} : #{false}">yestd>
tr>
⑩ 条件运算
<a href="comments.html"
th:href="@{/product/comments(prodId=${prod.id})}"
th:if="${not #lists.isEmpty(prod.comments)}">viewa>
<div th:switch="${user.role}">
<p th:case="'admin'">User is an administratorp>
<p th:case="#{roles.manager}">User is a managerp>
<p th:case="*">User is some other thingp>
div>
7.4 Thymeleaf使用
7.4.1 引入Stater
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>
7.4.2 SprinBoot自动配置Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf 的自动配置类:ThymeleafAutoConfiguration :
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ThymeleafProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnClass({ TemplateMode.class, SpringTemplateEngine.class })
@AutoConfigureAfter({ WebMvcAutoConfiguration.class, WebFluxAutoConfiguration.class })
public class ThymeleafAutoConfiguration { }
自动配好的策略:
- 所有thymeleaf的配置值都在 ThymeleafProperties
- 配置好了 SpringTemplateEngine
- 配好了 ThymeleafViewResolver
- 我们只需要直接开发页面
7.4.3 页面开发
首先要引入名称空间:
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
8. 拦截器
实现拦截请求功能的方式有两种:
- 第一种是通过filter过滤器
- 第二种就是配置
HandlerInterceptor实现拦截器。
实现拦截器的大致流程:
- 实现
HandlerInterceptor接口 - 注册自定义拦截器
- 指定拦截规则(注意:如果是拦截所有,那么静态资源也会被拦截)
假设一个业务场景:
一个后台管理系统,第一次进入时需要登录,也就是说没有登录却访问主页面的请求会被拦截住。实现这个功能的方式就是通过拦截器来拦截没有登录的请求。
8.1 实现HandlerInterceptor接口
实现HandlerInterceptor接口重写其中的方法:
preHandle:方法执行之前拦截postHandle:方法执行之拦截afterCompletion:页面渲染完成之后执行
注意: 要在自定义的拦截器实现类上标记@Component注解,将其添加到容器中。
package com.jc.admin.interceptor;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class loginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
/**
* 方法执行之前拦截
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
Object loginUser = session.getAttribute("loginUser");
if (loginUser != null) {
log.info("用户已经登录,执行放行操作");
return true;
}
// 用户没有登录,将请求转发到登录页
session.setAttribute("msg", "请先登录!");
// 获取请求调度程序,然后进行请求转发
request.getRequestDispatcher("/").forward(request, response);
return false;
}
/**
* 方法执行之后拦截
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @param modelAndView
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
log.info("后置处理方法执行");
}
/**
* 页面渲染完成之后执行
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @param ex
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
log.info("视图渲染后方法执行");
}
}
8.2 注册拦截器
注册拦截器这一步需要在配置类中进行,同时配置类需要实现addInterceptors方法。
package com.jc.admin.config;
import com.jc.admin.interceptor.LoginInterceptor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class AdminWebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Autowired
LoginInterceptor loginInterceptor;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(loginInterceptor)
.addPathPatterns("/**") // 添加要拦截的内容
.excludePathPatterns("/","/login", "/css/**", "/fonts/**", "/images/**", "/js/**");// 排除要拦截的内容
}
}
8.3 拦截器原理
- 根据当前请求,找到
HandlerExecutionChain(可以处理请求的handler以及handler的所有 拦截器) - 先来顺序执行 所有拦截器的
preHandle()方法。- 如果当前拦截器
preHandle()返回为true。则执行下一个拦截器的preHandle() - 如果当前拦截器返回为
false。直接倒序执行所有已经执行了的拦截器的afterCompletion();。
- 如果当前拦截器
- 如果任何一个拦截器返回
false,直接跳出不执行目标方法。 - 所有拦截器都返回
true,才执行目标方法。 - 倒序执行所有拦截器的
postHandle()方法。 - 前面的步骤有任何异常都会直接倒序触发
afterCompletion()。 - 页面成功渲染完成以后,也会倒序触发
afterCompletion()。
9. 文件上传
在Controller层的方法参数中放置MultipartFile类型的属性。
- 页面中上传文件的表单:
<form role="form" th:action="@{/upload}" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputEmail1">邮箱label>
<input type="email" name="email" class="form-control" id="exampleInputEmail1" placeholder="Enter email">
div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputPassword1">名字label>
<input type="text" name="username" class="form-control" id="exampleInputPassword1" placeholder="Password">
div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputFile">头像label>
<input type="file" name="headerImg" id="exampleInputFile">
div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputFile">生活照label>
<input type="file" name="photos" multiple>
div>
<div class="checkbox">
<label>
<input type="checkbox"> Check me out
label>
div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">提交button>
form>
- **实现文件上传的Controller: **
@Controller
public class FormController {
@PostMapping("/upload")
public String upload(@RequestParam("email") String email,
@RequestParam("username") String username,
@RequestPart("headerImg") MultipartFile headerImg,
@RequestPart("photos") MultipartFile[] photos) throws IOException {
if (!headerImg.isEmpty()) {
// 保存文件操作:保存到本地或者OSS
String filename = headerImg.getOriginalFilename();
headerImg.transferTo(new File("E:\\springboot-study\\uploadfile" + filename));
}
if (photos.length > 0) {
for (MultipartFile photo : photos) {
String filename = photo.getOriginalFilename();
photo.transferTo(new File("E:\\springboot-study\\uploadfile" + filename));
}
}
return "main";
}
}
- 通过修改配置文件可以自定义上传问价大小(如果上传超过阈值的文件,会抛出异常)
# 上传文件最大大小
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=10MB
# 一次请求中上传的所有文件最大大小
spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=100MB