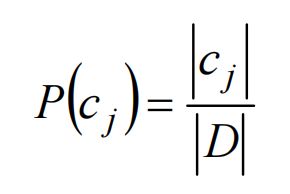机器学习 朴素贝叶斯之邮件分类
目录
一.贝叶斯算法:
1.先验概率:
2.后验概率:
3.贝叶斯定理:
4.概率模型:
二.朴素贝叶斯分类器:
1.朴素贝叶斯分类:
2.拉普拉斯修正:
3.防溢出策略:
4.垃圾邮件分类:
三.利用朴素贝叶斯分类对于电子邮件分类
1.使用的数据集:
2.相关代码:
3.运行结果:
贝叶斯方法是以贝叶斯原理为基础,使用概率统计的知识对样本数据集进行分类。由于其有着坚实的数学基础,贝叶斯分类算法的误判率是很低的。贝叶斯方法的特点是结合先验概率和后验概率,即避免了只使用先验概率的主观偏见,也避免了单独使用样本信息的过拟合现象。贝叶斯分类算法在数据集较大的情况下表现出较高的准确率,同时算法本身也比较简单。
朴素贝叶斯方法是在贝叶斯算法的基础上进行了相应的简化,即假定给定目标值时属性之间相互条件独立。也就是说没有哪个属性变量对于决策结果来说占有着较大的比重,也没有哪个属性变量对于决策结果占有着较小的比重。虽然这个简化方式在一定程度上降低了贝叶斯分类算法的分类效果,但是在实际的应用场景中,极大地简化了贝叶斯方法的复杂性。
一.贝叶斯算法:
需要了解贝叶斯算法,首先我们需要了解一下先验概率和后验概率;
1.先验概率:
2.后验概率:
3.贝叶斯定理:
4.概率模型:
那么我们如何应用贝叶斯定理到机器上,首先要在机器要建立一个概率模型;
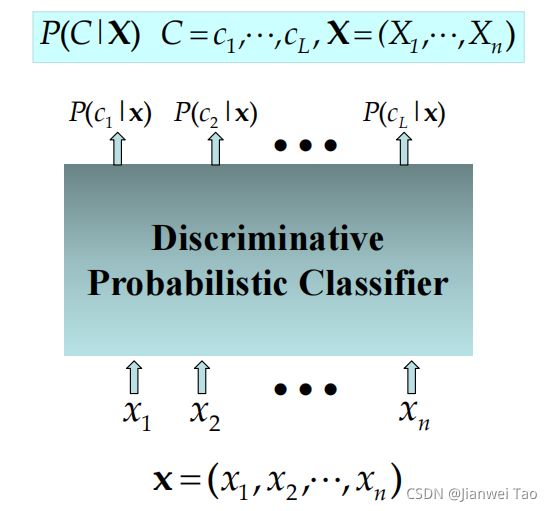
在机器学习中,通常分为
判别式模型:
判别模型之所以称为“判别”模型,是因为其根据X“判别”Y,由数据直接学习决策函数Y=f(X)或者条件概率分布作为预测的模型。
生成式模型:
生成模型之所以称为“生成”模型,是因为利用训练数据学习P(X|Y)和P(Y)的估计,得到联合概率分布,然后求得后验概率分布,再利用它进行分类。
在机器学习中任务是从属性X预测标记Y,判别模型求的是P(Y|X),即后验概率;而生成模型最后求的是P(X,Y),即联合概率。本文中的朴素贝叶斯属于生成式模型。
二.朴素贝叶斯分类器:
1.朴素贝叶斯分类:
朴素贝叶斯分类器采用了属性条件独立性假设,即所有属性都是条件独立的,联合概率就等于每个单独属性概率的乘积。
记P(C=c|X=x)为P(c|x),基于属性条件独立性假设,贝叶斯公式可重写为:
其中d为属性数目。
2.拉普拉斯修正:
![]()
3.防溢出策略:
4.垃圾邮件分类:
利用25封侮辱性邮件和25封非侮辱性文件对朴素贝叶斯分类器进行测试,其中49封作为训练数据,随机抽取10个作为测试集:
构建词向量:
def loadDataSet():
postingList=[['my', 'dog', 'has', 'flea', 'problems', 'help', 'please'],
['maybe', 'not', 'take', 'him', 'to', 'dog', 'park', 'stupid'],
['my', 'dalmation', 'is', 'so', 'cute', 'I', 'love', 'him'],
['stop', 'posting', 'stupid', 'worthless', 'garbage'],
['mr', 'licks', 'ate', 'my', 'steak', 'how', 'to', 'stop', 'him'],
['quit', 'buying', 'worthless', 'dog', 'food', 'stupid']]
classVec = [0,1,0,1,0,1] #1表示侮辱性文字,0代表正常言论
return postingList,classVec
#创建一个包含在所有文档中出现的不重复词的列表
def createVocabList(dataSet):
vocabSet = set([]) #创建空的集合
for document in dataSet:
vocabSet = vocabSet | set(document) #求两个集合的并集
return list(vocabSet)
#根据vocabList词汇表,将每个inputSet词条向量化,向量的每个值为1或0,分别表示该词有或者没有出现在词汇表中
#输入变量:词汇表,某个文档
def setOfWords2Vec(vocabList, inputSet):
#创建一个其中所含元素都为0的向量
returnVec = [0]*len(vocabList)
for word in inputSet:
if word in vocabList:
returnVec[vocabList.index(word)] = 1
else:
print("the word: %s is not in my Vocabulary!" % word)
return returnVec
#朴素贝叶斯词袋模型
def bagOfWords2VecMN(vocabList, inputSet):
returnVec = [0]*len(vocabList)
for word in inputSet:
if word in vocabList:
#每个词在词袋中可以出现多次。出现则累加
returnVec[vocabList.index(word)] += 1
return returnVec朴素贝叶斯分类训练:
#朴素贝叶斯分类器训练函数
'''
函数说明:朴素贝叶斯分类器训练函数
:param trainMatrix: 文档矩阵
:param trainCategory: 文档类别标签向量
:return: 非侮辱类的条件概率数组,侮辱类的条件概率数组,文档属于侮辱类的概率
'''
def trainNB0(trainMatrix,trainCategory):
numTrainDocs = len(trainMatrix) #训练集的数量,如6个元素
#print("数量为:",numTrainDocs)
numWords = len(trainMatrix[0]) #每个词条向量的长度,如每一个都是32维
#print("长度为:", numWords)
#sum(trainCategory)表示将标签向量中的(0,1)相加,即得到1的个数(也就是侮辱性文档数目)
#标签中“1”表示侮辱,“0”表示非侮辱,所以是统计文档属于侮辱类的概率
pAbusive = sum(trainCategory)/float(numTrainDocs)
#zeros()创建的数组,其元素值均为0
# p0Num = zeros(numWords)
# p1Num = zeros(numWords)
# p0Denom = 0.0
# p1Denom = 0.0
# #ones()函数可以创建任意维度和元素个数的数组,其元素值均为1
# #创建numpy.ones数组,词条出现数初始化为1,拉普拉斯平滑方法(为了防止与0相乘)
p0Num = ones(numWords)
p1Num = ones(numWords)
# #分母初始化为2,拉普拉斯平滑方法
p0Denom = 2.0
p1Denom = 2.0
for i in range(numTrainDocs):
if trainCategory[i] ==1:
#统计属于侮辱类的条件概率所需的数据,即P(w0/1),P(w1/1)......
p1Num += trainMatrix[i] #数组相加
#print("p1Num:",p1Num)
p1Denom += sum(trainMatrix[i]) #sum():将trainMatrix[i]中所有元素相加
#print("p1Denom:",p1Denom)
else:
#统计属于非侮辱类的条件概率所需的数据,即P(w0/0),P(w1/0)......
p0Num += trainMatrix[i]
p0Denom +=sum(trainMatrix[i])
#print("p0Denom:",p0Denom)
p1Vect = log(p1Num/p1Denom) #p1Num中的每一项取对数
p0Vect = log(p0Num/p0Denom) #非侮辱性邮件中单词出现的概率
return p0Vect,p1Vect,pAbusive朴素贝叶斯分类函数:
#朴素贝叶斯分类函数
'''
函数说明:朴素贝叶斯分类函数
:param vec2Classify: 要分类的向量
:param p0Vec: 非侮辱类的条件概率数组
:param p1Vec: 侮辱类的条件概率数组
:param pClass1: 文档属于侮辱类的概率
:return: 0->表示非侮辱类文档;1->表示侮辱类文档
'''
def classifyNB(vec2Classify,p0Vec,p1Vec,pClass1):
#两个向量对应元素相乘,然后求和
p1 = sum(vec2Classify * p1Vec) +log(pClass1)
p0 = sum(vec2Classify * p0Vec) +log(1-pClass1)
if p1>p0:
return 1
else:
return 0数据测试:
#利用单条数据测试
def testingNB():
listOPosts,listClasses = loadDataSet()
# 创建一个包含在所有文档中出现的不重复词的列表
myVocabList = createVocabList(listOPosts)
trainMat=[]
for postinDoc in listOPosts:
trainMat.append(setOfWords2Vec(myVocabList,postinDoc))
p0V,p1V,pAb = trainNB0(array(trainMat),array(listClasses))
testEntry=['love','my','dalmation']
thisDoc = array(setOfWords2Vec(myVocabList,testEntry))
print(testEntry,'分类结果为:',classifyNB(thisDoc,p0V,p1V,pAb))
testEntry = ['stupid','garbage']
thisDoc = array(setOfWords2Vec(myVocabList, testEntry))
print(testEntry, '分类结果为:', classifyNB(thisDoc, p0V, p1V, pAb))
#文件解析函数
def textParse(bigString): #input is big string, #output is word list
import re #正则表达式工具
#分割数据,其分隔符是除单词、数字外任意的字符串
listOfTokens = re.split(r'\W*', bigString)
#单词全部转小写,过滤没用的短字符串
return [tok.lower() for tok in listOfTokens if len(tok) > 2]
#垃圾邮件测试函数
def spamTest():
docList = [] #存放每个邮件的单词向量
classList = [] #存放邮件对应的标签
fullText = []
for i in range(1, 26):
#读取侮辱类(spam中存储)邮件,并生成单词向量
wordList = textParse(open('./email/spam/%d.txt' % i).read())
docList.append(wordList) #将单词向量存放到docList中
fullText.extend(wordList)
classList.append(1) #存放对应的类标签,侮辱类为1
# 读取非侮辱类(ham中存储)邮件,并生成单词向量
wordList = textParse(open('./email/ham/%d.txt' % i).read())
docList.append(wordList) #将单词向量存放到docList中
fullText.extend(wordList)
classList.append(0) #存放对应的类标签,非侮辱类为0
#由所有的单词向量生成词库
# xx = len(docList)
# yy = list(range(xx))
# print(xx,yy)
vocabList = createVocabList(docList)
trainSet = list(range(50)) #产生0-49的50个数字
testIndex = [] #存放测试数据的下标
for i in range(10):
#从0-49之间随机生成一个下标
randIndex = int(random.uniform(0, len(trainSet)))
testIndex.append(trainSet[randIndex]) #提取对应的数据作为测试数据
del(trainSet[randIndex]) #删除对应的数据,避免下次再选中
trainDataSet = [] #存放训练数据(用于词集方法)
trainClasses = [] #存放训练数据标签(用于词集方法)
trainDataSet1 = [] #存放训练数据(用于词袋方法)
trainClasses1 = [] #存放训练数据标签(用于词袋方法)
for docIndex in trainSet:
#提取训练数据(词集方法)
trainDataSet.append(setOfWords2Vec(vocabList, docList[docIndex]))
#提取训练数据标签
trainClasses.append(classList[docIndex])
#提取训练数据(词袋方法)
trainDataSet1.append(bagOfWords2VecMN(vocabList, docList[docIndex]))
trainClasses1.append(classList[docIndex])
#开始训练
p0V, p1V, pSpam = trainNB0(array(trainDataSet), array(trainClasses))
errorCount = 0 #统计测试时分类错误的数据个数
p0V_1, p1V_1, pSpam1 = trainNB0(array(trainDataSet1), array(trainClasses1))
errorCount1 = 0
#开始测试分类器
for Index in testIndex: # classify the remaining items
#print("classification:", Index)
wordVector = setOfWords2Vec(vocabList, docList[Index]) #数据预处理
# 测试分类器,如果分类不正确,错误个数加1
if classifyNB(array(wordVector), p0V, p1V, pSpam) != classList[Index]:
errorCount += 1
wordVector1 = bagOfWords2VecMN(vocabList, docList[Index]) #数据预处理
if classifyNB(array(wordVector1), p0V_1, p1V_1, pSpam1) != classList[Index]:
errorCount1 += 1
#输出分类错误率
# print('词集方法(set)的错误率: ', float(errorCount) / len(testIndex))
# print('词库方法(bag)的错误率: ', float(errorCount1) / len(testIndex))
error = (float(errorCount) / len(testIndex))
return error
def TestCount():
numTests = 10
errorSum = 0.0
for k in range(numTests):
result = spamTest()
print("第%d次测试(词集方法)的错误率为: %f" % (k + 1, result))
errorSum += result
print("在%d次测试之后,平均错误率为: %f" % (numTests, errorSum / float(numTests)))运行结果:
三.利用朴素贝叶斯分类对于电子邮件分类
使用朴素贝叶斯模型将电子邮件分类为垃圾邮件或普通邮件。
1.使用的数据集:
普通邮件:
垃圾邮件:

2.相关代码:
import math
import os
import re
from collections import Counter
class Spamfilter:
"""A naive Bayesian spam filter"""
def __init__(self, training_dir):
""" inits Spamfilter with training data
:param training_dir: path of training directory with subdirectories
'/ham' and '/spam'
"""
print("Training filter with known ham ...")
self.ham_table = dict(Counter(dir_tokens(training_dir + "ham/")))
print("Training filter with known spam...")
self.spam_table = dict(Counter(dir_tokens(training_dir + "spam/")))
self.uniq_h_toks = len(self.ham_table)
self.uniq_s_toks = len(self.spam_table)
self.total_h_toks = sum(self.ham_table.values())
self.total_s_toks = sum(self.spam_table.values())
self.tok_arr = sorted(
list(self.ham_table.keys()) + list(self.spam_table.keys())
)
self.freq_tab = self.create_frequency_table()
self.file_count = 0
self.count_spam = 0
self.count_ham = 0
self.spam_list = []
self.ham_list = []
def create_frequency_table(self):
""" Generates token frequency table from training emails
:return: dict{k,v}: spam/ham frequencies
k = (str)token, v = {spam_freq: , ham_freq:, prob_spam:, prob_ham:}
"""
freq_table = {}
for tok in self.tok_arr:
entry = {}
s_freq = self.spam_table.get(tok, 0)
entry["spam_freq"] = s_freq
h_freq = self.ham_table.get(tok, 0)
entry["ham_freq"] = h_freq
s_prob = (s_freq + 1 / float(self.uniq_s_toks)) / (self.total_s_toks + 1)
entry["prob_spam"] = s_prob
h_prob = (h_freq + 1 / float(self.uniq_h_toks)) / (self.total_h_toks + 1)
entry["prob_ham"] = h_prob
freq_table[tok] = entry
return freq_table
def prob_spam(self, token):
"""calculates the probability that 'token' is found in spam emails
:param token: (str)
:return: (float) probability 'token' is spam based on training emails
"""
val = self.freq_tab.get(token)
if val is not None:
return val["prob_spam"]
return (1.0 / self.uniq_s_toks) / (self.total_s_toks + 1)
def prob_ham(self, token):
"""calculates the probability that 'token' is found in ham emails
:param token: (str)
:return: (float) probability 'token' is ham based on training emails
"""
val = self.freq_tab.get(token)
if val is not None:
return val["prob_ham"]
return (1.0 / self.uniq_h_toks) / (self.total_h_toks + 1)
def prob_msg_spam(self, filepath):
"""Calculates the probability that a message is spam
:param filepath: (str) path of email
:return: (float) probability message is spam
"""
toks = file_tokens(filepath)
sm = 0
for tok in toks:
sm += math.log10(self.prob_spam(tok))
return sm
def prob_msg_ham(self, filepath):
"""Calculates the probability that a message is ham
:param filepath: (str) path of email
:return: (float) probability message is ham
"""
toks = file_tokens(filepath)
sm = 0
for tok in toks:
sm += math.log10(self.prob_ham(tok))
return sm
def classify(self, filepath):
"""classifies a file as spam or ham based on training data
:param filepath:
:return: (boolean) True->spam, False->ham
"""
self.file_count += 1
if self.prob_msg_spam(filepath) > self.prob_msg_ham(filepath):
self.count_spam += 1
self.spam_list.append(filepath)
return True
else:
self.count_ham += 1
self.ham_list.append(filepath)
return False
def classify_all(self, dir_path, known_type="spam"):
"""Classifies all emails in a testing directory and maintains count of errors
:param dir_path: path of testing directory
:param known_type: str: the known type of testing directory
"""
self.ham_list = []
self.spam_list = []
self.file_count = 0
self.count_spam = 0
self.count_ham = 0
print("\nClassifying all emails found in directory: ./" + dir_path)
try:
for f in os.listdir(dir_path):
self.classify(dir_path + f)
if known_type == "spam":
correct = self.count_spam / float(self.file_count)
else:
correct = self.count_ham / float(self.file_count)
print("Total spam:{:8d}".format(self.count_spam))
print("Total ham: {:8d}".format(self.count_ham))
print("Correctly classified: {:6.2f}%".format(correct * 100))
except FileNotFoundError as e:
print("ERROR: classify_all() failed " + str(e))
def clean_table(self, min_freq):
"""Removes entries from frequency table if they are deemed poor indicators.
or if combined spam/ham frequency is below 'min_freq'
:param min_freq: if total token count below threshold, delete from table
"""
rm_keys = []
for k, v in self.freq_tab.items():
if (
v["spam_freq"] + v["ham_freq"] < min_freq
or 0.45 < (v["prob_spam"] / (v["prob_spam"] + v["prob_ham"])) < 0.55
):
rm_keys.append(k)
for k in rm_keys:
print("deleting " + str(k) + " from freq table in clean()")
del self.freq_tab[k]
def print_table_info(self):
""" Print training info:
- unique tokens in ham and spam, number of emails in training set"""
print("\n=======================================")
print("TRAINING AND FREQUENCY TABLE INFO")
print("=======================================")
print("Unique tokens in spam messages:{:8d}".format(len(self.spam_table)))
print("Unique tokens in ham messages: {:8d}".format(len(self.ham_table)))
print("Unique tokens in ALL messages: {:8d}".format(len(self.freq_tab)))
print("Num spam e-mails:{:22d}".format(len(os.listdir("emails/testing/spam/"))))
print("Num ham e-mails: {:22d}".format(len(os.listdir("emails/testing/ham/"))))
def tokens(text, tok_size=3):
""" Returns a list of all substrings contained in 'text' of size 'tok_size'
:param text: (string) text to tokenize
:param tok_size: length of substrings
:return: (list) tokens of 'text'
"""
return [text[i : i + tok_size] for i in range(len(text) - tok_size + 1)]
def clean_split(in_str):
""" Removes all non-alphanum chars and splits string at whitespace, downcase
:param in_str: (str) target string
:return: (list) cleaned strings
"""
return re.sub(r"[^\s\w]|_", "", in_str).lower().split()
def file_tokens(filepath):
""" tokenizes all strings contained in 'filepath' after removing \
all non-alphanum chars and splitting strings at whitespace
:param filepath: path of target file
:return: list of tokens
"""
toks = []
try:
with open(filepath, encoding="utf8", errors="ignore") as fp:
for line in fp:
words = clean_split(line)
toks.extend(words)
except FileNotFoundError as e:
print("Error:" + str(e))
return [x for x in toks if len(x) < 10]
def dir_tokens(dir_path):
""" tokenizes all files contained in 'dir_path'
:param dir_path: directory containing files to be tokenized
:return: list of tokens
"""
dir_toks = []
try:
filenames = os.listdir(dir_path)
for f in filenames:
dir_toks.extend(file_tokens(dir_path + f))
except FileNotFoundError as e:
print("Error:" + str(e))
return dir_toks
if __name__ == "__main__":
spamfilter = Spamfilter("emails/training/")
spamfilter.print_table_info()
spamfilter.classify_all("emails/testing/spam/", "spam")
spamfilter.classify_all("emails/testing/ham/", "ham")3.运行结果:
邮件信息:
spam(垃圾邮件)判断: