vuex简介
文章目录
- vuex概念
- vuex的使用情况
- vuex的工作原理
-
- 工作原理讲解
- 实例
- 搭建vuex开发环境
-
- 安装
- 配置
- 设置store、使得vc可以看见store
-
- 使vm,vc可以读取store属性
- 创建store,管理vuex
- 脚手架加载文件顺序问题
- Vuex的开发者工具
- vuex的配置
-
- vuex的初始化数据status配置
- vuex的actions配置
- vuex的mutations配置
- vuex的getters配置及使用
- 求和案例
-
- 纯vue实现
- vuex实现
-
- 组件中读取vuex中的数据:
- 组件中修改vuex中的数据:
- 四个map方法的使用
-
- mapState
- mapGetters
- mapActions
- mapMutations
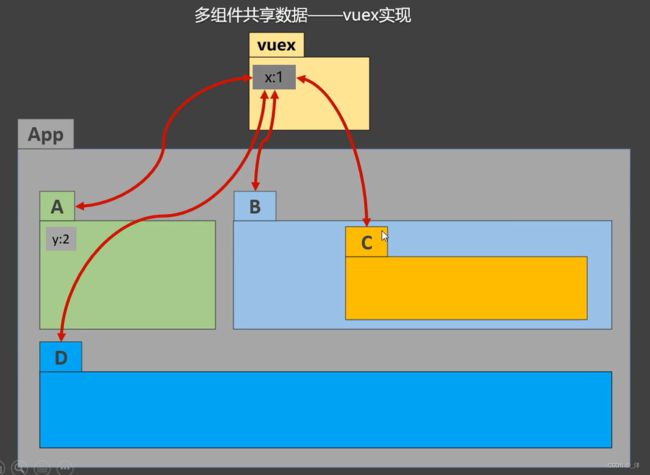
- 多组件数据共享数据
- vuex模块化
-
- src/store/index.js文件模块化写法
- 组件使用map方法获取store上的变量
-
- 方法一:接收`countOptions`和`personOptions`
- 方法二:使用`namespaced:true`
- 组件不使用map方法获取store上的变量
- 将src/store/index.js拆分成不同的文件
- 模块化的优点
- 使用actions向服务器发送请求
vuex概念
vuex是专门在Vue中实现集中式状态(数据)管理的一个Vue插件,对vue应用中
多个组件的共享状态(数据)进行集中式的管理(读/写)。
vuex也是一种组件间通信的方式,且适用于任意组件间通信。
引入:
需求:组件B、C、D 都需要获取和修改组件A上的数据X。
如果使用全局事件总线实现:
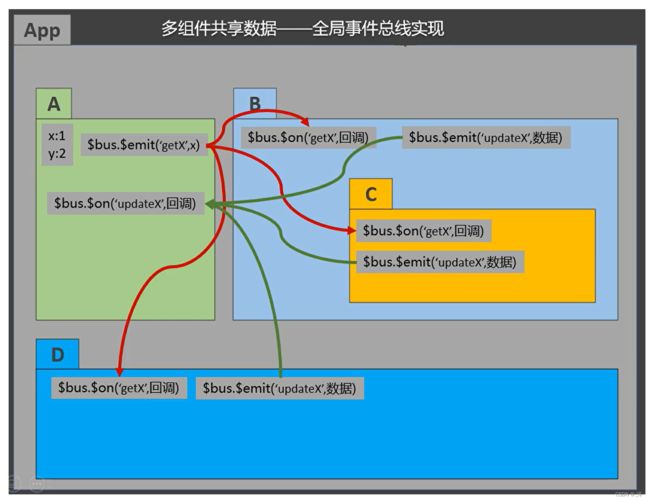
这时候我们就会想既然所有组件都要使用组件A中的数据我们为什么不直接把组件A中的数据提取出来作为公共数据呢,这就引入了vuex。
vuex不属于任何一个组件,里面存储的是组件公用的数据,任何组件都可以获取和修改vuex中的数据:
vuex的使用情况
- 多个组件依赖于同—状态 (即多个组件需要使用同一个数据)
- 来自不同组件的行为需要变更同一状态 (即不同组件的函数需要修改同一个数据)
所以只要用到共享数据就可以使用vuex。
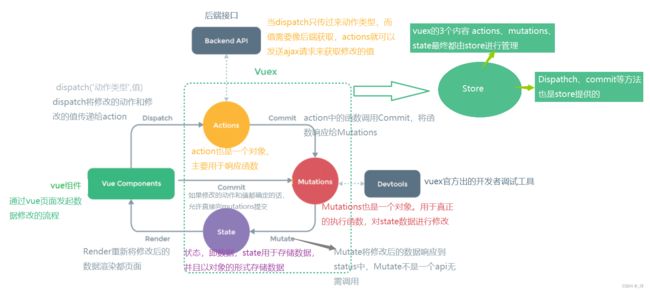
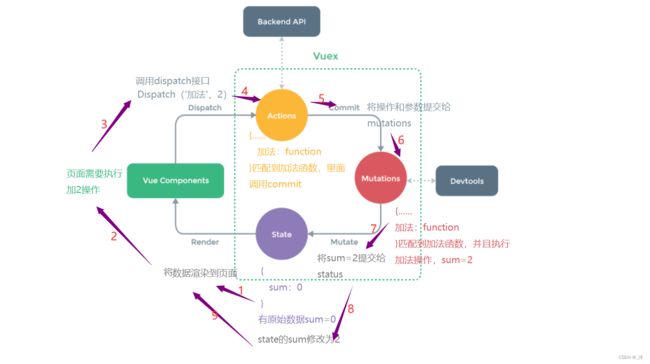
vuex的工作原理
工作原理讲解
-
如果vue组件的请求有任何的业务逻辑时也必须调用actions
-
联想:
可以将Vue Components看作顾客,Actions看作服务员,Mutations看作厨师来理解他们的关系。如果顾客不知道点什么菜(不知道参数),可以呼叫服务员来确定点菜菜单,再交由后厨(vue组件需要dispatch给actions再commit给mutation);如果顾客知道点什么菜(已知参数)就无需服务员了,直接让后厨做即可(vue组件直接commit给mutation);如果顾客知道点什么菜(已知参数)但是菜的口味需要特殊标明(有业务逻辑),还是需要通过服务员交由后厨。 -
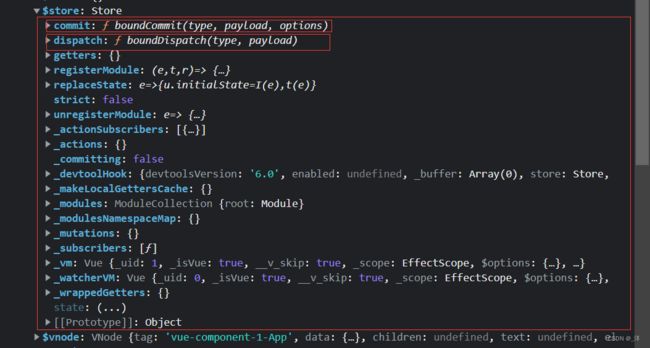
在开发中,因为vue组件需要调用dispatch函数,而dispatch函数在store身上,所以需要设置使vc(组件实例对象)可以看见store。
实例
搭建vuex开发环境
搭建vuex开发环境需要四步:
- 安装 :
npm i vuex - 配置:
Vue.use(Vuex) - 设置store
- 使得vc可以看见store
安装
执行命令 npm i vuex
暗转的时候需要注意一个版本问题:
vue2中,要用vuex的3版本
vue3中,,要用vuex的4版本
配置
在main.js中输入:
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
设置store、使得vc可以看见store
使vm,vc可以读取store属性
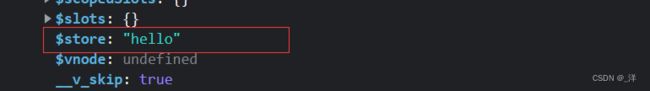
配置好vuex之后,就可以在创建vue实例对象的时候配置store配置项,
new Vue({
el: "#root",
store:"hello",
render: h => h(App),
beforeCreate() {
Vue.prototype.$bus = this
}
})
创建store,管理vuex
在src文件夹下创建store/index.js文件:
(创建store一定要在Vue.use(Vuex)之后,由于脚手架的文件执行顺序问题在main.js无法确保调用store/indxs.js在Vue.use(Vuex)之后调用,所以将main.js的Vue.use(Vuex)写在store/index.js文件中)
// 该文件用于创建vuex中最为核心的store
// 引入vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 准备actions——用于相应组件中的动作
const actions= {}
//准备mutations—用于操作数据(state)
const mutations = {}
//准备state—用于存储数据
const state = {}
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建并暴露store
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions: actions,
mutations: mutations,
state: state
})
main.js
/**
* 该文件是整个项目的入口文件
*/
// 引入vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入App
import App from './App.vue'
// 引入插件
import vueResource from 'vue-resource'
// 引入store
import store from './store/index'
// 关闭vue生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.use(vueResource)
// 创建vue实例对象
new Vue({
el: "#root",
store,
render: h => h(App),
beforeCreate() {
Vue.prototype.$bus = this
}
})
脚手架加载文件顺序问题
vue的脚手架会先扫描文件寻找所有的import语句,并先执行该文件的所有import语句。
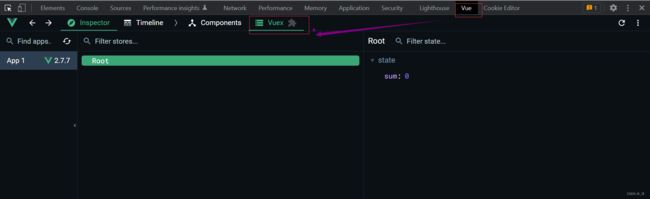
Vuex的开发者工具
vuex的配置
vuex的初始化数据status配置
store/index.js
//准备state—用于存储数据
const state = {
sum:0,//初始数据
}
// 创建并暴露store
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: state,
})
vuex的actions配置
store/index.js
const actions = {
//action方法
jiaOdd(context, value) {
console.log("actions中的jiaOdd 被调用了")
if(context.state.sum%2)
context.commit('JIA',value)
},
jiaWait(context, value) {
console.log("actions中的jiaWait 被调用了")
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('JIA',value)
},500)
}
}
// 创建并暴露store
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions: actions,
})
vuex的mutations配置
store/index.js
//准备mutations—用于操作数据(state)
const mutations = {
// mutations的操作数据
JIA(state, value) {
console.log("mutations中的JIA被调用了")
state.sum+=value
},
JIAN(state, value) {
console.log("mutations中的JIAN被调用了")
state.sum-=value
}
}
// 创建并暴露store
export default new Vuex.Store({
s mutations: mutations,
})
vuex的getters配置及使用
- 概念:当state中的数据需要经过加工后再使用时,可以使用getters加工。
- 在store.js中追加 getters配置
store/index.js
// 准备getters—用于state数据加工
const getters = {
bigSum(state) {
return state.sum*10
}
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
getters:getters
})
- getters数据读取:
$store.getters.bigSum
求和案例
纯vue实现
Count.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>当前求和为{{sum}}h1>
<select v-model="n">
<option :value="1">1option>
<option :value="2">2option>
<option :value="3">3option>
select>
<button @click="increment">+button>
<button @click="decrement">-button>
<button @click="incrementOdd">当前求和为奇数再加button>
<button @click="incrementWait">等一等再加button>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'CountVue',
data() {
return {
n: 1,//用户选择的数据
sum:1,//当前的和
}
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.sum += this.n
},
decrement() {
this.sum -= this.n
},
incrementOdd() {
if (this.sum % 2) {
this.sum += this.n
}
},
incrementWait() {
setTimeout(() => {
this.sum += this.n
},500)
}
}
}
script>
<style>
button{
margin: 5px;
}
style>
app.vue
<template>
<div>
<Count>Count>
div>
template>
<script>
import Count from "@/components/Count";
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
Count
}
}
script>
<style lang="css">
style>
vuex实现
Count.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>当前求和为{{$store.state.sum}}h1>
<select v-model="n">
<option :value="1">1option>
<option :value="2">2option>
<option :value="3">3option>
select>
<button @click="increment">+button>
<button @click="decrement">-button>
<button @click="incrementOdd">当前求和为奇数再加button>
<button @click="incrementWait">等一等再加button>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'CountVue',
data() {
return {
n: 1,//用户选择的数据
}
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.$store.commit('JIA',this.n)
},
decrement() {
this.$store.commit('JIAN', this.n)
},
incrementOdd() {
this.$store.dispatch('jiaOdd', this.n)
},
incrementWait() {
this.$store.dispatch('jiaWait', this.n)
}
}
}
script>
<style>
button{
margin: 5px;
}
style>
App.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>当前求和为{{$store.state.sum}}h1>
<select v-model="n">
<option :value="1">1option>
<option :value="2">2option>
<option :value="3">3option>
select>
<button @click="increment">+button>
<button @click="decrement">-button>
<button @click="incrementOdd">当前求和为奇数再加button>
<button @click="incrementWait">等一等再加button>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'CountVue',
data() {
return {
n: 1,//用户选择的数据
}
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.$store.commit('JIA',this.n)
},
decrement() {
this.$store.commit('JIAN', this.n)
},
incrementOdd() {
this.$store.dispatch('jiaOdd', this.n)
},
incrementWait() {
this.$store.dispatch('jiaWait', this.n)
}
}
}
script>
<style>
button{
margin: 5px;
}
style>
store/index.js
// 该文件用于创建vuex中最为核心的store
// 引入vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 准备actions——用于相应组件中的动作
const actions = {
// jia: function () {} 简写为
// jia(context, value) {
// console.log("actions中的jia被调用了")
// // context:将store中我们可能用到的方法包中成函数放到context中
// // value是传过来的数据
// context.commit('JIA',value)
// },
// jian(context, value) {
// console.log("actions中的jian 被调用了")
// context.commit('JIAN',value)
// },
jiaOdd(context, value) {
console.log("actions中的jiaOdd 被调用了")
if(context.state.sum%2)
context.commit('JIA',value)
},
jiaWait(context, value) {
console.log("actions中的jiaWait 被调用了")
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('JIA',value)
},500)
}
}
//准备mutations—用于操作数据(state)
const mutations = {
JIA(state, value) {
console.log("mutations中的JIA被调用了")
state.sum+=value
},
JIAN(state, value) {
console.log("mutations中的JIAN被调用了")
state.sum-=value
}
}
//准备state—用于存储数据
const state = {
sum:0,//当前的和
}
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建并暴露store
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions: actions,
mutations: mutations,
state: state
})
组件中读取vuex中的数据:
$store.state.sum
组件中修改vuex中的数据:
$store.dispatch('action中的方法名’,数据)或$store.commit( 'mutations中的方法名' ,数据)
四个map方法的使用
由于在vuex中取数据需要这样写 $store.state.变量名,比较麻烦为了更简便的写法vuex为我们提供了map方法
mapState
两种写法:(在computed中编写)
- 对象写法:
...mapState({计算属性名 : 'state中变量的名' }), - 数组写法:(前提是获取的计算属性名称和state中变量的名称一致)
...mapState(['state中变量的名' ]), - 作用: 借助mapState生成计算属性,从State中读取数据
...是ES6语法是说将mapState对象中的键值对直接放到中computed
eg:store/index.js:
const state = {
sum: 0,//当前的和
name: 'yang',
age: 18
}
组件获取并应用数据:
<template>
<div>
<h1>当前求和为{{sum}}h1>
<h1>姓名:{{name}}h1>
<h1>年龄:{{age}}h1>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'CountVue',
computed: {
// 手动获取数据
/*sum(){
return this.$store.state.sum
},
name(){
return this.$store.state.name
},
age(){
return this.$store.state.age
}*/
// 借助mapState生成计算属性,从state中读取数据(对象写法)
// ...是ES6语法是说将mapState对象中的键值对直接放到中computed
...mapState({ sum: 'sum', name: 'name', age: 'age' }),
// 借助mapState生成计算属性,从state中读取数据(数组写法)
// 数组写法的前提是获取的计算属性名称和state中变量的名称一致
...mapState(['sum', 'name', 'age' ])
}
}
script>
mapGetters
两种写法:(在computed中编写)
- 对象写法:
...mapGetters({计算属性名 : 'getter中函数的名' }), - 数组写法:(前提是获取的计算属性名称和getter中函数的名称一致)
...mapGetters(['getter中函数的名' ]), - 作用: 借助mapGetters生成计算属性,从Getters中读取数据
...是ES6语法是说将mapGetters对象中的键值对直接放到中computed
eg:store/index.js:
// 准备getters—用于state数据加工
const getters = {
bigSum(state) {
return state.sum*10
}
}
组件获取并应用数据:
<template>
<div>
<h1>数据放大10倍{{bigSum}}h1>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'CountVue',
computed: {
/*
// 手写
bigSum() {
return this.$store.getters.bigSum;
}
*/
// 对象写法
...mapGetters({bigSum:'bigSum'}),
// 数组写法
...mapGetters(['bigSum']),
}
}
script>
mapActions
两种写法:(在methods中编写)
- 对象写法:
...mapActions({方法 : 'Actions中函数的名' }), - 数组写法:(前提是获取的方法名称和Actions中的函数名称一致)
...mapActions(['Actions函数的名' ]), - 作用:借助mapActions生成对应的方法,方法中会调用dispatch去联系actions
...是ES6语法是说将mapActions对象中的键值对直接放到中methods
需要注意的是如果需要传递参数需要在组件模板使用方法的时候传递参数
eg:store/index.js:
const actions = {
incrementOdd(context, value) {
console.log("actions中的jiaOdd 被调用了")
if(context.state.sum%2)
context.commit('increment',value)
},
incrementWait(context, value) {
console.log("actions中的jiaWait 被调用了")
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('increment',value)
},500)
}
}
组件获取并应用数据:
<template>
<div>
<button @click="incrementOdd(n)">当前求和为奇数再加button>
<button @click="incrementWait(n)">等一等再加button>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'CountVue',
data() {
return {
n: 1,//用户选择的数据
}
},
methods: {
// 手动写
/*
incrementOdd() {
this.$store.dispatch('jiaOdd', this.n)
},
incrementWait() {
this.$store.dispatch('jiaWait', this.n)
}*/
// 借助mapActions生成对应的方法,方法中会调用dispatch去联系actions(对象写法)
...mapActions({
incrementOdd: 'incrementOdd', incrementWait: 'incrementWait'
}),
// 借助mapActions生成对应的方法,方法中会调用dispatch去联系actions(数组写法)
...mapActions(['incrementOdd', 'incrementWait'])
},
}
script>
mapMutations
两种写法:(在methods中编写)
- 对象写法:
...mapMutations({方法 : 'Mutations中函数的名' }), - 数组写法:(前提是获取的方法名称和Mutations中的函数名称一致)
...mapMutations['Mutations函数的名' ]), - 作用:借助mapMutations生成对应的方法,方法中会调用commit去联系mutations
...是ES6语法是说将mapMutations对象中的键值对直接放到中methods
需要注意的是如果需要传递参数需要在组件模板使用方法的时候传递参数
eg:store/index.js:
//准备mutations—用于操作数据(state)
const mutations = {
increment(state, value) {
console.log("mutations中的JIA被调用了")
state.sum+=value
},
decrement(state, value) {
console.log("mutations中的JIAN被调用了")
state.sum-=value
}
}
组件获取并应用数据:
<template>
<div>
<button @click="increment(n)">+button>
<button @click="decrement(n)">-button>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'CountVue',
data() {
return {
n: 1,//用户选择的数据
}
},
methods: {
// 手动写
/* increment() {
this.$store.commit('JIA',this.n)
},
decrement() {
this.$store.commit('JIAN', this.n)
},*/
// 借助mapMutations生成对应的方法,方法中会调用commit去联系mutations(对象写法)
...mapMutations({ increment: 'increment', decrement:'decrement'}),
// 借助mapMutations生成对应的方法,方法中会调用commit去联系mutations(数组写法)
...mapMutations(['increment', 'decrement']),
},
}
script>
mapActions与mapMutations使用时,若需要传递参数需要:在模板中绑定事件时传递好参数,否则参数是事件对象。
多组件数据共享数据
<template>
<div>
<Count>Count>
<hr/>
<Person/>
div>
template>
<script>
import Count from "@/components/Count";
import Person from "@/components/Person";
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
Count,
Person
},
mounted() {
console.log(this)
}
}
script>
<style lang="css">
style>
Count.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>当前求和为{{sum}}h1>
<h1>数据放大10倍{{bigSum}}h1>
<select v-model="n">
<option :value="1">1option>
<option :value="2">2option>
<option :value="3">3option>
select>
<button @click="increment(n)">+button>
<button @click="decrement(n)">-button>
<button @click="incrementOdd(n)">当前求和为奇数再加button>
<button @click="incrementWait(n)">等一等再加button>
<h3 style="color:red">下方组件的总人数是:{{ personList.length }}h3>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapState,mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'CountVue',
data() {
return {
n: 1,//用户选择的数据
}
},
methods: {
// 借助mapMutations生成对应的方法,方法中会调用commit去联系mutations(对象写法)
...mapMutations({ increment: 'increment', decrement:'decrement'}),
// 借助mapMutations生成对应的方法,方法中会调用commit去联系mutations(数组写法)
...mapMutations(['increment', 'decrement']),
// 借助mapActions生成对应的方法,方法中会调用dispatch去联系actions(对象写法)
...mapActions({
incrementOdd: 'incrementOdd', incrementWait: 'incrementWait'
}),
// 借助mapActions生成对应的方法,方法中会调用dispatch去联系actions(数组写法)
...mapActions(['incrementOdd', 'incrementWait'])
},
computed: {
// 借助mapState生成计算属性,从state中读取数据(对象写法)
...mapState({ sum: 'sum', name: 'name', age: 'age', personList :'personList'}),
// 借助mapState生成计算属性,从state中读取数据(数组写法)
...mapState(['sum', 'name', 'age','personList']),
/*************************************************************** */
// 借助mapGetters生成计算属性,从Getters中读取数据(对象写法)
...mapGetters({bigSum:'bigSum'}),
// 借助mapGetters生成计算属性,从Getters中读取数据(数组写法)
...mapGetters(['bigSum']),
}
}
script>
<style>
button{
margin: 5px;
}
style>
Person.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>人员列表h1>
请输入人员名字:<input v-model="name" />
<button @click="personAdd">添加button>
<ul>
<li v-for="person in personList" :key="person.id">{{ person.name }}li>
ul>
<h3 style="color:red">上方组件的sum是:{{sum }}h3>
div>
template>
<script>
import { nanoid } from "nanoid"
export default {
name: 'PersonVue',
data() {
return {
name:''
}
},
computed:{
personList(){
return this.$store.state.personList
},
sum() {
return this.$store.state.sum
}
},
methods:{
personAdd(){
const personObj = { id: nanoid(), name: this.name }
this.$store.commit('personAdd', personObj)
this.name=''
}
}
}
script>
src/store/index.js
// 该文件用于创建vuex中最为核心的store
// 引入vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 准备actions——用于相应组件中的动作
const actions = {
incrementOdd(context, value) {
console.log("actions中的jiaOdd 被调用了")
if(context.state.sum%2)
context.commit('increment',value)
},
incrementWait(context, value) {
console.log("actions中的jiaWait 被调用了")
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('increment',value)
},500)
}
}
//准备mutations—用于操作数据(state)
const mutations = {
increment(state, value) {
console.log("mutations中的JIA被调用了")
state.sum+=value
},
decrement(state, value) {
console.log("mutations中的JIAN被调用了")
state.sum-=value
},
personAdd(state, value) {
console.log("mutations中的personAdd被调用了")
state.personList.unshift(value)
}
}
//准备state—用于存储数据
const state = {
sum: 0,//当前的和
personList: [{
id:'001',name:'张三'
}]
}
// 准备getters—用于state数据加工
const getters = {
bigSum(state) {
return state.sum*10
}
}
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建并暴露store
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions: actions,
mutations: mutations,
state: state,
getters:getters
})
vuex模块化
在vuex的index.js文件中最好将服务于不同组件的数据放到不同的模块中
src/store/index.js文件模块化写法
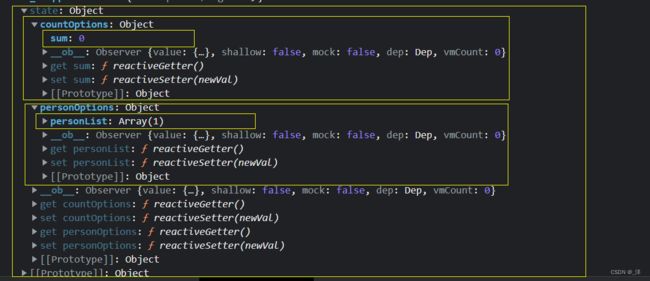
所以上述的src/store/index.js文件可以调整为:
定义countOptions和personOptions对象分别配置两个组件的vuex
// 该文件用于创建vuex中最为核心的store
// 引入vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
const countOptions = {
namespaced:true,//设置namespaced为true,为了让组件中的map方法能够识别该配置
actions: {
incrementOdd(context, value) {
console.log("actions中的jiaOdd 被调用了")
if(context.state.sum%2)
context.commit('increment',value)
},
incrementWait(context, value) {
console.log("actions中的jiaWait 被调用了")
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('increment',value)
},500)
}
},
mutations: {
increment(state, value) {
console.log("mutations中的JIA被调用了")
state.sum+=value
},
decrement(state, value) {
console.log("mutations中的JIAN被调用了")
state.sum-=value
},
},
state: {
sum: 0,//当前的和
},
getters: {
bigSum(state) {
return state.sum*10
}
}
}
const personOptions = {
namespaced:true,//设置namespaced为true,为了让组件中的map方法能够识别该配置
actions: {},
mutations: {
personAdd(state, value) {
console.log("mutations中的personAdd被调用了")
state.personList.unshift(value)
}
},
state: {
personList: [{
id:'001',name:'张三'
}]
},
getters:{}
}
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建并暴露store
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
countOptions: countOptions,
personOptions:personOptions,
}
})
组件使用map方法获取store上的变量
使用组件化的写法,那么原来获取变量的方法就不适用了。以maoState为例
...mapState(['sum', 'name', 'age','personList']),
mapState获取的是state中有的数据,可是按如上模块化写法$store.state中只有countOptions和personOptions,而变量的具体值在countOptions和personOptions中, 所以不能按原来的方法写。
方法一:接收countOptions和personOptions
eg:Count.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>当前求和为{{countOptions.sum}}h1>
<h3 style="color:red">下方组件的总人数是:{{ personOptions.personList.length }}h3>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapState,mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'CountVue',
computed: {
// 借助mapState生成计算属性,从state中读取数据(数组写法)
...mapState(['countOptions','personOptions']),
},
}
script>
方法二:使用namespaced:true
当在vuex中配是的时候,如果添加namespaced:true配置,就可以通过参数直接获取该组件的配置。
格式:...mapState('组件配置名', ['变量']),
eg:Count.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>当前求和为{{sum}}h1>
<h3 style="color:red">下方组件的总人数是:{{personList.length }}h3>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapState,mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'CountVue',
computed: {
// 借助mapState生成计算属性,从state中读取数据(数组写法)
...mapState('countOptions', ['sum']),
...mapState('personOptions', ['personList']),
},
}
script>
其他的 mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions 也可以使用该方法获取值。
组件不使用map方法获取store上的变量
- 传统的获取state值得方法:
return this.$store.state.personList
模块化后就应该写成:return this.$store.state.personOptions.personList - 传统的获取getters值得方法:
return this.$store.firstPersonName
模块化后就应该写成:return this.$store.getters['personOptions/firstPersonName'] - 传统的获取actions值得方法:
this.$store.dispatch('addPersonWang', personObj)
模块化后就应该写成:this.$store.dispatch('personOptions/addPersonWang', personObj) - 传统的获取mutations值得方法:
this.$store.commit('personAdd', personObj)
模块化后就应该写成:this.$store.commit('personOptions/personAdd', personObj)
即前面都需要添加组件的配置名。
eg:Person.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>人员列表h1>
请输入人员名字:<input v-model="name" />
<button @click="personAdd">添加button>
<button @click="addPersonWang">添加一个姓王的人button>
<ul>
<li v-for="person in personList" :key="person.id">{{ person.name }}li>
ul>
<h3>列表中第一个人的名字是:{{firstPersonName}}h3>
<h3 style="color:red">上方组件的sum是:{{sum }}h3>
div>
template>
<script>
import { nanoid } from "nanoid"
export default {
name: 'PersonVue',
data() {
return {
name:''
}
},
computed:{
personList(){
return this.$store.state.personOptions.personList
},
sum() {
return this.$store.state.countOptions.sum
},
firstPersonName() {
return this.$store.getters[`personOptions/firstPersonName`]
}
},
methods:{
personAdd(){
const personObj = { id: nanoid(), name: this.name }
this.$store.commit('personOptions/personAdd', personObj)
this.name=''
},
addPersonWang() {
const personObj = { id: nanoid(), name: this.name }
this.$store.dispatch('personOptions/addPersonWang', personObj)
this.name = ''
}
}
}
script>
将src/store/index.js拆分成不同的文件
拆分成index.js、count.js、person.js
index.js:
// 该文件用于创建vuex中最为核心的store
// 引入vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import countOptions from './count'
import personOptions from './person'
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建并暴露store
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
countOptions: countOptions,
personOptions:personOptions,
}
})
count.js:
export default {
namespaced:true,//设置namespaced为true,为了让组件中的map方法能够识别该配置
actions: {
incrementOdd(context, value) {
console.log("actions中的jiaOdd 被调用了")
if(context.state.sum%2)
context.commit('increment',value)
},
incrementWait(context, value) {
console.log("actions中的jiaWait 被调用了")
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('increment',value)
},500)
}
},
mutations: {
increment(state, value) {
console.log("mutations中的JIA被调用了")
state.sum+=value
},
decrement(state, value) {
console.log("mutations中的JIAN被调用了")
state.sum-=value
},
},
state: {
sum: 0,//当前的和
},
getters: {
bigSum(state) {
return state.sum*10
}
}
}
person.js:
export default {
namespaced:true,//设置namespaced为true,为了让组件中的map方法能够识别该配置
actions: {
// 只添加姓王的人
addPersonWang(context, value) {
if (value.name.indexOf('王') === 0) {
context.commit('personAdd',value)
} else {
alert('添加的人不姓王')
}
}
},
mutations: {
personAdd(state, value) {
console.log("mutations中的personAdd被调用了")
state.personList.unshift(value)
}
},
state: {
personList: [{
id:'001',name:'张三'
}]
},
getters: {
firstPersonName(state) {
return state.personList[0].name
}
}
}
模块化的优点
让代码更好维护,让多种数据分类更加明确。
使用actions向服务器发送请求
eg:
actions: {
addPersonServer(context) {
axios.get('https://api.uixsj.cn/hitokoto/get?type=social').then(
response => {
context.commit('personAdd',{id:nanoid(),name:response.data})
},
error =>{
console.log(error.message)
}
)
}
},