4.Nginx优化,谁用谁说好
文章目录
- 一,Nginx优化
-
-
- 1.隐藏版本号
-
- 1.1 查看版本号
- 1.2 隐藏版本号
- 2. 修改用户与组
-
- 2.1 编译时指定用户和组
- 2.2 修改配置文件
- 3. 配置网页缓存时间
-
- 3.1 修改配置文件
- 4. 日志切割
-
- 4.1编写脚本进行日志切割
- 4.2 测试脚本
- 4.3 设置 crontab 任务,定期执行脚本自动进行日志分割
- 5.设置连接超时
-
- 5.1 参数配置
-
- 二、nginx深入优化
-
-
- 1.更改进程数
- 2. 配置网页压缩
-
- 2.1 压缩功能参数
- 2.2 上传图片到 /usr/local/nginx/html 目录下
- 3.盗链与防盗链
-
-
- 3.1 盗链概述
- 3.2防盗链配置文件原理
-
- 1.未开启防盗链时
- 3.3开启防盗链
-
-
一,Nginx优化
1.隐藏版本号
- 在生产环境中,需要隐藏 Nginx 版本号,以避免泄露 Nginx 的版本,使攻击者不能针对特定版本进行攻击
1.1 查看版本号
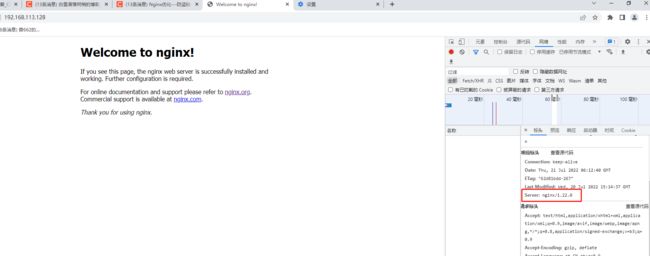
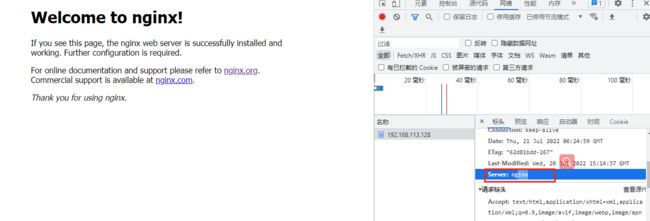
- 网页查看
f12–>网络–> ctrl+r–>选择请求–>标头
- 本地查看
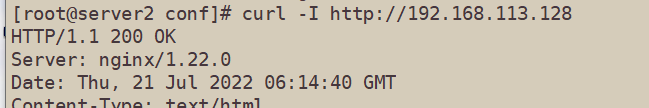
[root@server2 conf]# curl -I http://192.168.113.128
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.22.0
1.2 隐藏版本号
- 方法一:修改配置文件
[[root@server2 conf]#vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
......
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
server_tokens off; #添加,关闭版本号
......
[root@server2 conf]# nginx -t #测试配置文件语法
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@server2 conf]# systemctl restart nginx #重启服务
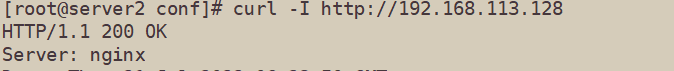
[root@server2 conf]# curl -I http://192.168.113.128 #验证是否已隐藏
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx #隐藏成功
- 方法二:修改源码文件
[root@server2 conf]# vim /opt/nginx-1.22.0/src/core/nginx.h
......
#define nginx_version 1012002
#define NGINX_VERSION "1.80.0" #修改版本号
#define NGINX_VER "mysql/" NGINX_VERSION #修改服务器类型
......
[root@server2 conf]# cd /opt/nginx-1.12.2/ #重新编译安装
root@server2 nginx-1.22.0]#
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_stub_status_module
root@server2 nginx-1.22.0]# make
root@server2 nginx-1.22.0]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
.......
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
server_tokens on; #开启版本号
[root@server2 conf]# nginx -t #检查语法
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@server2 conf]# systemctl restart nginx
[root@server2 conf]# curl -I http://192.168.113.128 #验证
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: mysql/1.80.0 #成功
2. 修改用户与组
- Nginx 运行时进程需要有用户与组的支持,用以实现对网站文件读取时进行访问控制
主进程由 root 创建,子进程由指定的用户与组创建 - Nginx 默认使用 nobody 用户账号与组账号,一般需要进行修改
- 修改 Nginx 用户和组有两种方法
1.编译安装时指定用户和组
2.修改配置文件指定用户和组
2.1 编译时指定用户和组
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx
2.2 修改配置文件
root@server2 nginx-1.22.0]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
user nginx; #第一行,去掉注释,修改为nginx
worker_processes 1;
root@server2 nginx-1.22.0]# systemctl restart nginx
root@server2 nginx-1.22.0]# ps aux |grep nginx
root 8119 0.0 0.0 20500 604 ? Ss 01:00 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nginx 8120 0.0 0.0 23028 1388 ? S 01:00 0:00 nginx: worker process #修改成功
root 8124 0.0 0.0 112676 976 pts/2 S+ 01:00 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
3. 配置网页缓存时间
- 当Nginx将网页数据返回给客户端后,可设置缓存的时间,以方便在日后进行相同内容的请求时直接返回,避免重复请求,加快了访问速度
- 一般针对静态网页设置,对动态网页不设置缓存时间;因为动态页面是一直交互的状态,若是设置动态页面缓存时间会一直占用网页的缓存空间
3.1 修改配置文件
- 在新的 location 段加入 expires 参数,指定缓存的时间,1d表示一天(若设置1.5天可指定为1d12h)
root@server2 nginx-1.22.0]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
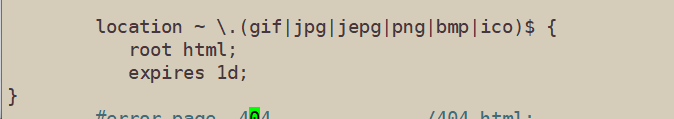
location ~ \.(gif|jpg|jepg|png|bmp|ico)$ { #加入新的location,以图片作为缓存对象
root html;
expires 1d; #指定缓存时间为1天
}
......
2.上传图片到 html 目录中,访问页面
[root@server2 nginx-1.22.0]# cd /usr/local/nginx/html/
[root@server2 html]# rz -E
rz waiting to receive.
[root@server2 html]# ls
50x.html index.html Snipaste_2022-05-23_22-04-16.png
[root@server2 html]# mv Snipaste_2022-05-23_22-04-16.png tu.jpg ##图片名过长修改
[root@server2 html]# ls
50x.html index.html tu.jpg
[root@server2 html]# systemctl restart nginx
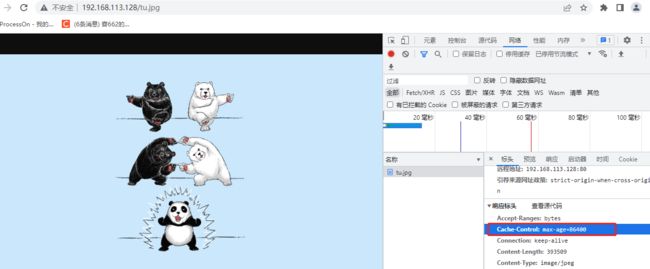
- Cache-Control: max-age=86400 表示缓存时间是86400秒(一天),在一天内访问这个页面都是用的缓存中的数据,不需要向服务器重新发出请求,可以有效减小服务器的带宽使用率
4. 日志切割
- 随着 Nginx 服务运行时间的增加,它的日志也会增加,为了能够方便知道 Nginx 的运行状态,需要时刻关注 Nginx 日志文件。过大的日志文件不利于日常监控和分析排查,因此需要定期的对日志文件进行切割
- Nginx 没有类似 Apache 的 cronlog 日志分割处理功能,但可以通过 Nginx 的信号控制功能脚本来实现日志的自动切割,并将脚本加入到 Linux 的计划任务中
- 通过Linux的计划任务周期性地进行日志切割
4.1编写脚本进行日志切割
- 设置时间变量
- 设置保存日志路径
- 将目前的日志文件进行重命名
- 重建新日志文件
- 删除时间超过30天的日志文件
- 设置cron任务,定期执行脚本自动进行日志分割
vim /opt/rzfg.sh
#!/bin/bash
#Filename:fenge.sh
day=$(date -d "-1 day" "+%Y%m%d") #-d表示设置,-1 day表示前一天
logs_path="/var/log/nginx" #日志存放的位置
pid_path="/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid"
[ -d $logs_path ] || mkdir -p $logs_path #判断是否有日志文件的目录,没有就创建
#移动访问日志到log_path,并命名test.com;脚本执行后创建日志进行命令,用时间戳的方式来标记唯一性
mv /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log ${logs_path}/test.com-access.log-$day
kill -USER1 $(cat $pid_path) #重载然后生成新的access日志
find $logs_path -mtime +30 | xargs rm -rf #删除30天前的日志
#!/bin/bash
#Filename:fenge.sh
day=$(date -d "-1 day" "+%Y%m%d")
logs_path="/var/log/nginx"
pid_path="/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid"
[ -d $logs_path ] || mkdir -p $logs_path
mv /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log ${logs_path}/test.com-access.log-$day
kill -USER1 $(cat $pid_path)
find $logs_path -mtime +30 | xargs rm -rf
4.2 测试脚本
[root@server2 opt]# vim fenge.sh
[root@server2 opt]# sh -x fenge.sh
++ date -d '-1 day' +%Y%m%d
+ day=20220720
+ logs_path=/var/log/nginx
+ pid_path=/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
+ '[' -d /var/log/nginx ']'
+ mv /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log /var/log/nginx/dxz.com-access.log-20220720
++ cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
+ kill -HUP 10900
+ find /var/log/nginx -mtime +30
+ xargs rm -rf
[root@server2 opt]# ls /var/log/nginx/
dxz.com-access.log-20220720 #成功按日期进行了日志分割
[root@server2 opt]# ls /usr/local/nginx/logs/
access.log error.log nginx.pid
[root@server2 opt]# date -s 2002-07-22 #修改时间进行测试
2002年 07月 22日 星期一 00:00:00 CST
[root@server2 opt]# bash /opt/fenge.sh
[root@server2 opt]# ls /var/log/nginx/ #成功分割
dxz.com-access.log-20020721 dxz.com-access.log-20220720
[root@server2 opt]# ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com #再同步回时间
21 Jul 15:41:23 ntpdate[11505]: step time server 120.25.115.20 offset 631121933.366082 sec
[root@server2 opt]# date
2022年 07月 21日 星期四 15:41:58 CST
4.3 设置 crontab 任务,定期执行脚本自动进行日志分割
[root@server2 opt]# crontab -e
0 2 * * * /opt/fenge.sh #添加每天凌晨 2点 执行/opt/fenge.sh 脚本,进行日志分割
[root@server2 opt]# crontab -l
0 2 * * * /opt/fenge.sh
crontab(选项)(参数)
-e:编辑该用户的计时器设置;
-l:列出该用户的计时器设置;
-r:删除该用户的计时器设置;
-u<用户名称>:指定要设定计时器的用户名称
5.设置连接超时
HTTP有一个KeepAlive摸式,它告诉web服务器在处理完一个请求后保持这个TcP连接的打开状态,若接收到来自同一客户端的其它请求,服务端会利用这个未被关闭的连接,而不需要再建立一
个连接。
KeepAlive
在一段时间内保持打开状态,它们会在这段时间内占用资源。占用过多就会影响性能。
- 为避免同一客户端长时间占用连接,造成资源浪费,可设置相应的连接超时参数,实现控制连接访问时间
5.1 参数配置
[root@server2 opt]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
http {
......
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65; #设置连接保持超时时间
Client_header_timeout 80; #等待客户端发送请求头的超时时间,超时会发送408错误
Client_body_timeout 80; #等待客户端发送请求体的超时时间
......
keepalive timeout
指定KeepAlive的超时时间(timeout)。指定每个TcP连接最多可以保持多长时间,服务器将会在这个时间后关闭连接。Nginx的默认值是65秒,有些浏览器最多只保持60秒,所以可以设定为60秒。若将它设置为0,就禁止了keepalive连接。
第二个参数(可选的)指定了在响应头Keep-Alive:timeout=time中的time值。这个头能够让些浏览器主动关闭连接,这样服务器就不必去关闭连接了。没有这个参数,Ngix不会发送Keep-Alive响应头。
二、nginx深入优化
1.更改进程数
- 在高并发环境中,需要启动更多的 Nginx 进程以保证快速响应,用以处理用户的请求,避免造成阻塞
#ps aux 命令可以查看 Nginx 运行进程的个数
[root@server2 opt]# ps -aux | grep nginx
root 10900 0.0 0.0 20616 1488 ? Ss 15:02 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nginx 11444 0.0 0.0 23120 1412 ? S 15:38 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 12020 0.0 0.0 112824 980 pts/0 S+ 16:27 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
#master process 是 Nginx 的主进程,开启了一个;worker process 是子进程,开启了一个
- 修改 Nginx 配置文件中的 work_processes 参数,一般设为 CPU 的个数或核数,在高并发的情况下可以设置为 CPU 个数或核数的2倍
#可以先查看 CPU 的核数来确定参数
[root@server2 opt]# cat /proc/cpuinfo |grep -c "physical"
8
[root@server2 opt]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
1
2 user nginx;
3 worker_processes 8; #修改为8核
4 worker_cpu_affinity 10000000 01000000 00100000 00010000 00001000 00000100 00000010 00000001;
##10000000表示启用第一个CPU内核,01000000表示启用第二个CPU内核,以此类推
-
参数设置为8,和CPU的核数相同。
-
运行进程数设置多一些,响应客户端访问请求时,Nginx 就不会启动新的进程提供服务,从而减小了系统的开销,提升了服务的速度
-
修改完成后,重启服务,再使用 ps aux 命令查看运行进程数的变化情况
[root@server2 conf]# ps -aux |grep nginx
root 12557 0.0 0.0 20576 676 ? Ss 16:48 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nginx 12558 0.0 0.0 23104 1376 ? S 16:48 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 12559 0.0 0.0 23104 1376 ? S 16:48 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 12560 0.0 0.0 23104 1376 ? S 16:48 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 12561 0.0 0.0 23104 1376 ? S 16:48 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 12562 0.0 0.0 23104 1376 ? S 16:48 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 12563 0.0 0.0 23104 1376 ? S 16:48 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 12564 0.0 0.0 23104 1376 ? S 16:48 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 12565 0.0 0.0 23104 1376 ? S 16:48 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 12570 0.0 0.0 112828 976 pts/0 S+ 16:48 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
#开启了一个主进程和八个子进程,设置的参数成功生效了
#默认情况下,Nginx 的多个进程可能更多地跑在一个 CPU 上,可以分配不同的进程给不同的 CPU 处理,
#以充分利用硬件多核多 CPU 。
#在一台 8 核的 CPU 服务器上,设置每个进程分别由不同的 CPU 核心处理,来达到 CPU 的性能最大化。
2. 配置网页压缩
- Nginx 的 ngx_http_gzip_module 压缩模块提供了对文件内容压缩的功能,允许 Nginx 服务器将输出内容发送到客户端之前进行压缩,以节约网站的带宽,提升用户的访问体验
- 默认 Nginx 已安装该模块,只需要在配置文件中加入相应的压缩功能参数对压缩性能进行优化即可
2.1 压缩功能参数
[root@server2 conf]# vim/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
http {
......
gzip on;
#开启gzip压缩功能
gzip_min_length 1k;
#用于设置允许压缩的页面最小字数
gzip_buffers 4 16k;
#表示申请4个单位为16KB的内存作为压缩结果流缓存,默认值是申请与原始数据大小相同的内存空间来存储gzip压缩结果
gzip_http_version 1.1;
#用于识别http协议版本,默认是1.1,目前大部分浏览器已支持gzip压缩,但处理很慢,也比较消耗CPU资源
gzip_comp_level 6;
#用来指定gzip压缩比,压缩比1最小,处理速度最快;压缩比为9最大,传输速度快,但处理速度最慢,使用默认即可
gzip_vary on;
#该选项可以让前端的缓存服务器缓存经过gzip压缩的页面
gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascript text/css image/jpg image/jpeg image/png image/gif application/xml text/javascript application/x-httpd-php application/javascript application/json;
#压缩类型,表示哪些网页文档启用压缩功能
......
}
gzip on;
gzip_min_length 1k;
gzip_buffers 4 16k;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_comp_level 6;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascript text/css image/jpg image/jpeg image/png image/gif application/xml text/javascript application/x-httpd-php application/javascript application/json;
2.2 上传图片到 /usr/local/nginx/html 目录下
[root@server2 conf]# cd /usr/local/nginx/html/
[root@server2 html]# ls
50x.html index.html
[root@server2 html]# rz -E
rz waiting to receive.
[root@server2 html]# ls
1.jpg 50x.html index.html
[root@server2 html]# vim index.html
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
<h1>享受孤独就会变强 </h1>
<img src="1.jpg"/>
</body>
</html>
重启服务访问页面
root@server2 html]# systemctl restart nginx
3.盗链与防盗链
- 盗链是一种恶意行为,在互联网上广泛存在;在企业网站中,一般都要配置防盗链功能,以避免网站内容被非法盗用,造成经济损失,也避免不必要的带宽浪费
3.1 盗链概述
盗链是指服务提供商自己不提供服务的内容,通过技术手段绕过其它有利益的最终用户界面(如广告),直接在自己的网站上向最终用户提供其它服务提供商的服务内容,骗取最终用户的浏览和点击率,受益者不提供资源或提供很少的资源,而真正的服务提供商却得不到任何的收益
- 测试配置所需环境
盗链端http: 192.168.113.129
服务端nginx:192.168.113.128
3.2防盗链配置文件原理
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
http{
.........
server{
.....
location ~*\(jpglgiflswf)$ {
valid referers none blocked *.kgc.com kgc.com;
if ($invalid referer )
rewrite ^/http://www.kgc.com/error.png:
#return 403;
}
}
....}
....}
-
~*.(jpg|gifIswf)$:这段正则表达式表示匹配不区分大小写,以.jpg或.gif或.swf结尾的文件;
-
valid referers:设置信任的网站,可以正常使用图片;
-
none:允许没有http refer的请求访问资源(根据Referer的定义,它的作用是指示一个请求是从哪里链接过来的,如果直接在浏览器的地址栏中输入一个资源的URL地址,那么这种请求是不会包含Referer字段的),如http:Lw,kgc,com/game,jpg我们使用http:Lw.kgc,com访问显示的图片,可以理解成ttp:L,kgc,com/game,jpg这个请求是从http:Lwww,kgc,com这个链接过来的。
-
blocked:允许不是http:/开头的,不带协议的请求访问资源;
-
*.kgc.com:只允许来自指定域名的请求访问资源,如http:Lwww.kgc,com
-
if语句:如果链接的来源域名不在valid referers.所列出的列表中,invalid referer.为true,则执行后而的操作,即进行重写
-
或返回403页面
1.未开启防盗链时
使用另外一台服务器192.168.113.129做盗链网站
#安装httpd
yum install -y httpd
#切换至/var/www/html
cd /var/www/html
[root@localhost html]# vim index.html
<html>
<body>
<img src="http://www.xtz.com/1.jpg"/>
</body>
</html>
#添加域名映射
#盗链网站
echo "192.168.113.129 www.xtj1.com" >>/etc/hosts
#目标网站
echo "192.168.113.128 www.xtj.com" >>/etc/hosts
#在Web源主机(192.168.113.128)添加域名解析
[root@server2 html]# vim /etc/hosts
192.168.113.128 www.xtj.com
#在Web源主机(192.168.113.128)添加图片
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
可以填字例:<h1> </h1>
<img src="1.jpg"/>
</body>
</html>
- 在盗链网站重启httpd(192.168.113.129)
systemctl start httpd
验证:占用的是源主机的资源
3.3开启防盗链
编辑配置文件
注意:因为location匹配原则为匹配即停止,所以将上面的location注释了
[root@server2 html]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
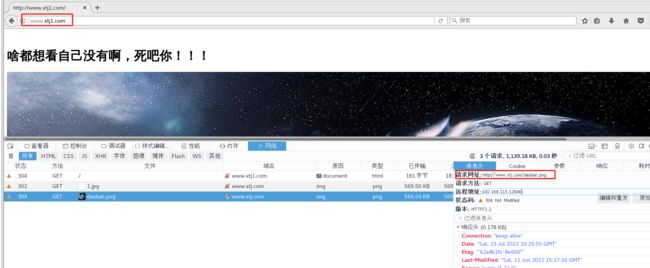
location ~* \.(jpg|gif|swf)$ {
valid_referers none blocked *.xtj.com xtj.com;
if ( $invalid_referer ) {
rewrite / http://www.xtj.com/daoban.png;
}
}
#检查语法是否有错
nginx -t
#将盗图图片拖进去
cd /usr/local/nginx/html/
[root@server2 html]# ls
1.jpg 50x.html daoban.png index.html
#重启服务
systemctl restart nginx.service
验证:
源主机
盗链网站访问