对于研究过内核的人肯定以为整个.net 最终开始是IISAPIRuntime.ProcessReuqest()然后调用ISAPIRuntime.ProcessRequest(IntPtr ecb, int iWRTyp)
其实还有一种方式,当你在使用.net 时,会自动在C:\WINDOWS\assembly的方件夹再次生成一个WebDev.WebHost
Microsoft.VisualStudio.WebHost.Server.Start()是整个的开始

 public Server(int port, string virtualPath, string physicalPath, bool requireAuthentication)
public Server(int port, string virtualPath, string physicalPath, bool requireAuthentication)
 {
{
 this.port = port;
this.port = port;
 this.vritualPath = virtualPath;
this.vritualPath = virtualPath;
 this.physicalPath = physicalPath.EndsWith(@"\", StringComparison.Ordinall) ? physicalPath : (physicalPath + @"\");
this.physicalPath = physicalPath.EndsWith(@"\", StringComparison.Ordinall) ? physicalPath : (physicalPath + @"\");
 this.requireAuthentication= requireAuthentication;
this.requireAuthentication= requireAuthentication;
 this.onSocketAccept = new WaitCallback(this.OnSocketAccept); //设置回调函数,asp.net 2.0流程的最终开始
this.onSocketAccept = new WaitCallback(this.OnSocketAccept); //设置回调函数,asp.net 2.0流程的最终开始
 this.onStart = new WaitCallback(this.OnStart);
this.onStart = new WaitCallback(this.OnStart);
 this.appManager = ApplicationManager.GetApplicationManager();
this.appManager = ApplicationManager.GetApplicationManager();
 this.ObtainProcessToken();
this.ObtainProcessToken();
 }
}
即,asp.net 流程开始时,会生成Server类,创建对应的Host,使用socket连接,然后
在OnSocketAccept的回调方法里会执行 host.ProcessRequest(conn);
host.ProcessRequest --> new Request(this, conn).Process();
此处会调过HttpRuntime.ProcessRequest (HttpWorkRequest wr) //此时wr必不是IsApiWorkRequest,而是一个SimpleWorkRequest
对ProcessRequest处理如下
HttpRuntime会先将这个请求放入RequestQueue,(队列默认有5000个请求)
如果当前线程池可用的话,立即开始一个线程处理
HttpApplication 类的一个实例在其生存期内被用于处理多个请求,但它一次只能处理一个请求,这样,成员变量才可用于存储针对每个请求的数据。
IHttpHandler applicationInstance = HttpApplicationFactory.GetApplicationInstance(extraData);


 if (applicationInstance is IHttpAsyncHandler)
if (applicationInstance is IHttpAsyncHandler)
 {
{
 IHttpAsyncHandler handler2 = (IHttpAsyncHandler) applicationInstance;
IHttpAsyncHandler handler2 = (IHttpAsyncHandler) applicationInstance;
 extraData.AsyncAppHandler = handler2;
extraData.AsyncAppHandler = handler2;

 //调用HttpApplication.BeginProcessRequest开始流程
//调用HttpApplication.BeginProcessRequest开始流程
 //_handlerCompletionCallback为异步结束时回调函数,
//_handlerCompletionCallback为异步结束时回调函数,
 //extraData为HttpContext
//extraData为HttpContext
 handler2.BeginProcessRequest(extraData, this._handlerCompletionCallback, extraData);
handler2.BeginProcessRequest(extraData, this._handlerCompletionCallback, extraData);
 }
}
 else
else
 {
{
 applicationInstance.ProcessRequest(extraData);
applicationInstance.ProcessRequest(extraData);
 this.FinishRequest(extraData.WorkerRequest, extraData, null);
this.FinishRequest(extraData.WorkerRequest, extraData, null);
 }
}


由于Asp.net 2.0东西太多,只说说大体
在Http管道中,HttpApplication是核心
下面是HttpApplication.Init()核心代码如下


 if (applicationInstance is IHttpAsyncHandler)
if (applicationInstance is IHttpAsyncHandler)
 {
{
 IHttpAsyncHandler handler2 = (IHttpAsyncHandler) applicationInstance;
IHttpAsyncHandler handler2 = (IHttpAsyncHandler) applicationInstance;
 extraData.AsyncAppHandler = handler2;
extraData.AsyncAppHandler = handler2;

 //调用HttpApplication.BeginProcessRequest开始流程
//调用HttpApplication.BeginProcessRequest开始流程
 //_handlerCompletionCallback为异步结束时回调函数,
//_handlerCompletionCallback为异步结束时回调函数,
 //extraData为HttpContext
//extraData为HttpContext
 handler2.BeginProcessRequest(extraData, this._handlerCompletionCallback, extraData);
handler2.BeginProcessRequest(extraData, this._handlerCompletionCallback, extraData);
 }
}
 else
else
 {
{
 applicationInstance.ProcessRequest(extraData);
applicationInstance.ProcessRequest(extraData);
 this.FinishRequest(extraData.WorkerRequest, extraData, null);
this.FinishRequest(extraData.WorkerRequest, extraData, null);
 }
}


返回用户当前是否启用Url重写,再也不用手动处理URL重写啦
UrlMappingsSection urlMappings = RuntimeConfig.GetAppConfig().UrlMappings;
flag = urlMappings.IsEnabled && (urlMappings.UrlMappings.Count > 0);
 context.ConfigurationPath
=
context.Request.ApplicationPathObject;
context.ConfigurationPath
=
context.Request.ApplicationPathObject;
 using
(HttpContextWrapper wrapper
=
new
HttpContextWrapper(context))
using
(HttpContextWrapper wrapper
=
new
HttpContextWrapper(context))
 {
{
 //初始化所有的模块
//初始化所有的模块
 this.InitModules();
this.InitModules();


 this._context = context;
this._context = context;
 this._hideRequestResponse = true;
this._hideRequestResponse = true;
 //初始化自身
//初始化自身
 this.Init();
this.Init();
 this._hideRequestResponse = false;
this._hideRequestResponse = false;
 this._context = null;
this._context = null;
 ArrayList steps = new ArrayList();
ArrayList steps = new ArrayList();
 //验证路径
//验证路径
 steps.Add(new ValidatePathExecutionStep(this));
steps.Add(new ValidatePathExecutionStep(this));
 if (flag)
if (flag)
 {
{
 // asp.net 2.0内置URL重写功能
// asp.net 2.0内置URL重写功能
 steps.Add(new UrlMappingsExecutionStep(this));
steps.Add(new UrlMappingsExecutionStep(this));
 }
}
 steps.Add(new MapHandlerExecutionStep(this));
steps.Add(new MapHandlerExecutionStep(this));


 steps.Add(new CallHandlerExecutionStep(this));
steps.Add(new CallHandlerExecutionStep(this));


 steps.Add(new CallFilterExecutionStep(this));
steps.Add(new CallFilterExecutionStep(this));


 steps.CopyTo(this._execSteps);
steps.CopyTo(this._execSteps);
 this._resumeStepsWaitCallback = new WaitCallback(this.ResumeStepsWaitCallback);
this._resumeStepsWaitCallback = new WaitCallback(this.ResumeStepsWaitCallback);

HttpApplication.BeginProcessRequest()时会调用HttpApplication.ResumeSteps()
就是对上面IExecutionStep进行依次的处理
在MapHandlerExecutionStep时,会根据如何配置取出对应的工厂
Asp.net 2.0 根 Web.config
 <
httpHandlers
>
<
httpHandlers
>
 <
add path
=
"
*.aspx
"
verb
=
"
*
"
type
=
"
System.Web.UI.PageHandlerFactory
"
validate
=
"
True
"
/>
<
add path
=
"
*.aspx
"
verb
=
"
*
"
type
=
"
System.Web.UI.PageHandlerFactory
"
validate
=
"
True
"
/>
 </
httpHandlers
>
</
httpHandlers
>

今天只谈.aspx
上面都是大家知道的,没什么意思啦
咱来点有意思的
搞.net 的人都知道.aspx会使用PageHandlerFactory .GetHandlerHelper()返回一个IHttpHandler
大家有没有发现
GethandlerHelper() 里有下面的方法
Page page = BuildManager.CreateInstanceFromVirtualPath(virtualPath, typeof(Page), context, true, true) as Page;


 internal static object CreateInstanceFromVirtualPath(VirtualPath virtualPath, Type requiredBaseType, HttpContext context, bool allowCrossApp, bool noAssert)
internal static object CreateInstanceFromVirtualPath(VirtualPath virtualPath, Type requiredBaseType, HttpContext context, bool allowCrossApp, bool noAssert)
 {
{
 //BuildResult
//BuildResult
 // BuildResultCompiledAssemblyBase
// BuildResultCompiledAssemblyBase
 // BuildResultCompiledType
// BuildResultCompiledType
 //BuildResult
//BuildResult
 // BuildResultNoCompileTemplateControl
// BuildResultNoCompileTemplateControl
 // BuildResultNoCompilePage
// BuildResultNoCompilePage
 ITypedWebObjectFactory factory = GetVirtualPathObjectFactory(virtualPath, context, allowCrossApp, noAssert); //注意此时是什么对象,下面再谈
ITypedWebObjectFactory factory = GetVirtualPathObjectFactory(virtualPath, context, allowCrossApp, noAssert); //注意此时是什么对象,下面再谈
 i f (factory == null)
i f (factory == null)
 {
{
 return null;
return null;
 }
}
 Util.CheckAssignableType(requiredBaseType, factory.InstantiatedType);
Util.CheckAssignableType(requiredBaseType, factory.InstantiatedType);
 using (ClientImpersonationContext context2 = new ClientImpersonationContext(context))
using (ClientImpersonationContext context2 = new ClientImpersonationContext(context))
 {
{
 return factory.CreateInstance();
return factory.CreateInstance();
 }
}
 }
}

其实这个Page是一个BuildRequest,asp.net 2.0在第一次请求时会对dll再一次的编译,
举个例子你写了一个webForm1.aspx,里面有一个Button,
此时.net 会从webForm1.axp派生出一个新的类
如下


 //[CompilerGlobalScope]
//[CompilerGlobalScope]
 //public class webform1_aspx : WebForm1, IRequiresSessionState, IHttpHandler
//public class webform1_aspx : WebForm1, IRequiresSessionState, IHttpHandler
 //{
//{
 // // Fields
// // Fields
 // private static object __fileDependencies;
// private static object __fileDependencies;
 // private static bool __initialized;
// private static bool __initialized;


 ..
..
 // protected override void FrameworkInitialize()
// protected override void FrameworkInitialize()
 // {
// {
 // base.FrameworkInitialize();
// base.FrameworkInitialize();
 // this.__BuildControlTree(this); //此处创建控件树,(CtronlBuilder的作用在这里!!!!!!!!!!!)
// this.__BuildControlTree(this); //此处创建控件树,(CtronlBuilder的作用在这里!!!!!!!!!!!)
 // base.AddWrappedFileDependencies(__fileDependencies);
// base.AddWrappedFileDependencies(__fileDependencies);
 // base.Request.ValidateInput();
// base.Request.ValidateInput();
 // }
// }
 // public override int GetTypeHashCode()
// public override int GetTypeHashCode()
 // {
// {
 // return 0x579d6af1;
// return 0x579d6af1;
 // }
// }
 // public override void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context)
// public override void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context)
 // {
// {
 // base.ProcessRequest(context);
// base.ProcessRequest(context);
 // }
// }
 //}
//}
当您请求WebForm1时
ITypedWebObjectFactory.GetType() 是BuildResultCompiledTemplateType它是BuildResultCompiledType的实现
ITypedWebObjectFactory.CreateInstance()就是BuildResultCompiledType.CreateInstance()
它会使用
ObjectFactoryCodeDomTreeGenerator.GetFastObjectCreationDelegate(this.ResultType);
在新生成的程序集中Asp命名空间下有这个类呀,直接new webform1_aspx ()
也就是说,此时你请求webform1,实际调用的是新生所在webform1_aspx ()
下面会依次执行
CallHandlerExecutionStep 处理输出流
CallFilterExecutionStep()调用webform1_aspx.ProcessRequest()
...
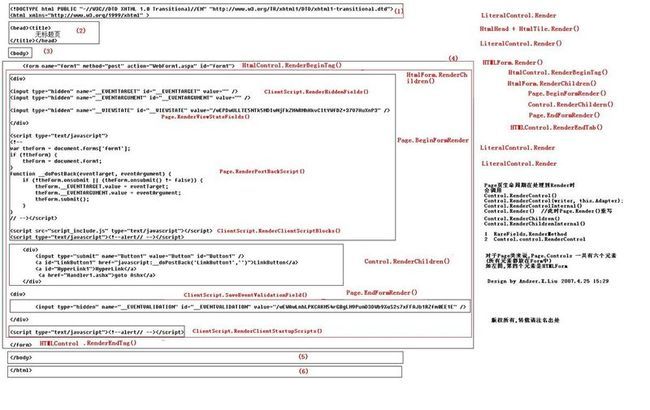
下面说一下,你请求的webForm1_aspx是如何转成html的即,Render时的顺序:
原理如下图