Jenkins自动化部署
1 、安装Jenkins 。本文采用Linux 部署war包形式。
Jenkins下载地址:(https://get.jenkins.io/war-stable/2.346.2/jenkins.war)
Tomcat:https://mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/apache/tomcat/tomcat-9/v9.0.65/bin/ (选版本)
2 Linux需要安装git maven。
2.1 安装git :yum -y install git
验证git git --version
2.2 安装maven
wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/maven/maven-3/3.6.0/binaries/apache-maven-3.6.0-bin.tar.gz
tar -zxvf apache-maven-3.6.0-bin.tar.gz -C /usr/local
cd /usr/local
mv apache-maven-3.6.0 maven
vim /etc/profile
配置maven环境变量
MAVEN_HOME=/usr/local/maven
PATH=$MAVEN_HOME/bin:$PATH
刷新环境变量配置
source /etc/profile
mkdir -p /usr/local/maven/repository
vim /usr/local/maven/conf/settings.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<settings xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.2.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.2.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.2.0.xsd">
<localRepository>/usr/local/maven/repository</localRepository>
<pluginGroups>
<!-- pluginGroup
| Specifies a further group identifier to use for plugin lookup.
<pluginGroup>com.your.plugins</pluginGroup>
-->
</pluginGroups>
<!-- proxies
| This is a list of proxies which can be used on this machine to connect to the network.
| Unless otherwise specified (by system property or command-line switch), the first proxy
| specification in this list marked as active will be used.
|-->
<proxies>
<!-- proxy
| Specification for one proxy, to be used in connecting to the network.
|
<proxy>
<id>optional</id>
<active>true</active>
<protocol>http</protocol>
<username>proxyuser</username>
<password>proxypass</password>
<host>proxy.host.net</host>
<port>80</port>
<nonProxyHosts>local.net|some.host.com</nonProxyHosts>
</proxy>
-->
</proxies>
<!-- servers
| This is a list of authentication profiles, keyed by the server-id used within the system.
| Authentication profiles can be used whenever maven must make a connection to a remote server.
|-->
<servers>
<!-- server
| Specifies the authentication information to use when connecting to a particular server, identified by
| a unique name within the system (referred to by the 'id' attribute below).
|
| NOTE: You should either specify username/password OR privateKey/passphrase, since these pairings are
| used together.
|
<server>
<id>deploymentRepo</id>
<username>repouser</username>
<password>repopwd</password>
</server>
-->
<!-- Another sample, using keys to authenticate.
<server>
<id>siteServer</id>
<privateKey>/path/to/private/key</privateKey>
<passphrase>optional; leave empty if not used.</passphrase>
</server>
-->
</servers>
<!-- mirrors
| This is a list of mirrors to be used in downloading artifacts from remote repositories.
|
| It works like this: a POM may declare a repository to use in resolving certain artifacts.
| However, this repository may have problems with heavy traffic at times, so people have mirrored
| it to several places.
|
| That repository definition will have a unique id, so we can create a mirror reference for that
| repository, to be used as an alternate download site. The mirror site will be the preferred
| server for that repository.
|-->
<mirrors>
<!-- mirror
| Specifies a repository mirror site to use instead of a given repository. The repository that
| this mirror serves has an ID that matches the mirrorOf element of this mirror. IDs are used
| for inheritance and direct lookup purposes, and must be unique across the set of mirrors.
|
<mirror>
<id>mirrorId</id>
<mirrorOf>repositoryId</mirrorOf>
<name>Human Readable Name for this Mirror.</name>
<url>http://my.repository.com/repo/path</url>
</mirror>
-->
<mirror>
<id>aliyunmaven</id>
<mirrorOf>*</mirrorOf>
<name>阿里云公共仓库</name>
<url>https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/public</url>
</mirror>
</mirrors>
<!-- profiles
| This is a list of profiles which can be activated in a variety of ways, and which can modify
| the build process. Profiles provided in the settings.xml are intended to provide local machine-
| specific paths and repository locations which allow the build to work in the local environment.
|
| For example, if you have an integration testing plugin - like cactus - that needs to know where
| your Tomcat instance is installed, you can provide a variable here such that the variable is
| dereferenced during the build process to configure the cactus plugin.
|
| As noted above, profiles can be activated in a variety of ways. One way - the activeProfiles
| section of this document (settings.xml) - will be discussed later. Another way essentially
| relies on the detection of a system property, either matching a particular value for the property,
| or merely testing its existence. Profiles can also be activated by JDK version prefix, where a
| value of '1.4' might activate a profile when the build is executed on a JDK version of '1.4.2_07'.
| Finally, the list of active profiles can be specified directly from the command line.
|
| NOTE: For profiles defined in the settings.xml, you are restricted to specifying only artifact
| repositories, plugin repositories, and free-form properties to be used as configuration
| variables for plugins in the POM.
|
|-->
<profiles>
<!-- profile
| Specifies a set of introductions to the build process, to be activated using one or more of the
| mechanisms described above. For inheritance purposes, and to activate profiles via <activatedProfiles/>
| or the command line, profiles have to have an ID that is unique.
|
| An encouraged best practice for profile identification is to use a consistent naming convention
| for profiles, such as 'env-dev', 'env-test', 'env-production', 'user-jdcasey', 'user-brett', etc.
| This will make it more intuitive to understand what the set of introduced profiles is attempting
| to accomplish, particularly when you only have a list of profile id's for debug.
|
| This profile example uses the JDK version to trigger activation, and provides a JDK-specific repo.
<profile>
<id>jdk-1.4</id>
<activation>
<jdk>1.4</jdk>
</activation>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>jdk14</id>
<name>Repository for JDK 1.4 builds</name>
<url>http://www.myhost.com/maven/jdk14</url>
<layout>default</layout>
<snapshotPolicy>always</snapshotPolicy>
</repository>
</repositories>
</profile>
-->
<profile>
<id>jdk-1.8</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
<jdk>1.8</jdk>
</activation>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.8</maven.compiler.compilerVersion>
</properties>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring</id>
<url>https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/spring</url>
<releases>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</releases>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
</profile>
<!--
| Here is another profile, activated by the system property 'target-env' with a value of 'dev',
| which provides a specific path to the Tomcat instance. To use this, your plugin configuration
| might hypothetically look like:
|
| ...
| <plugin>
| <groupId>org.myco.myplugins</groupId>
| <artifactId>myplugin</artifactId>
|
| <configuration>
| <tomcatLocation>${tomcatPath}</tomcatLocation>
| </configuration>
| </plugin>
| ...
|
| NOTE: If you just wanted to inject this configuration whenever someone set 'target-env' to
| anything, you could just leave off the <value/> inside the activation-property.
|
<profile>
<id>env-dev</id>
<activation>
<property>
<name>target-env</name>
<value>dev</value>
</property>
</activation>
<properties>
<tomcatPath>/path/to/tomcat/instance</tomcatPath>
</properties>
</profile>
-->
</profiles>
<!-- activeProfiles
| List of profiles that are active for all builds.
|
<activeProfiles>
<activeProfile>alwaysActiveProfile</activeProfile>
<activeProfile>anotherAlwaysActiveProfile</activeProfile>
</activeProfiles>
-->
</settings>
开始部署Jenkins
把下载的Jenkins部署到tomcat目录下的webapps
然后到bin目录下运行
启动命令 sh startup.sh
停止命令 sh shutdown.sh
*如无法执行则执行 chmod 755 .sh(需在bin目录下执行)
然后浏览器访问对应服务器的地址。
http://127.0.0.1:8080/jenkins
初始化会比较慢。需等待一小会

通过 cat 查看该文件的密码输入(这里还会让你下载一些插件,直接跳过即可)
然后创建对应的用户登录即可。

然后配置镜像文件。需要目录下执行
/root/.jenkins/updates(对应Jenkins的目录)
sed -i 's/https:\/\/updates.jenkins.io\/download/http:\/\/mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn\/jenkins/g' default.json & sed -i 's/www.google.com/www.baidu.com/g' default.json
修改成功后
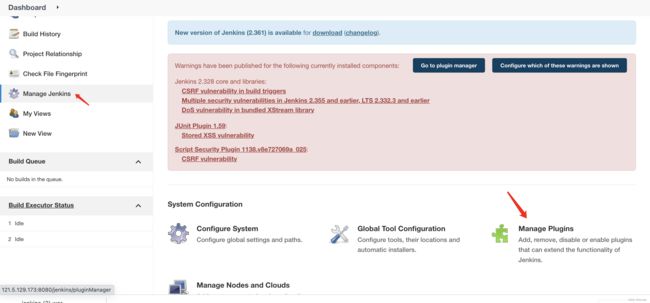
安装的插件有 git、maven、git Parameter
安装3个插件完成后点击即重启Jenkins
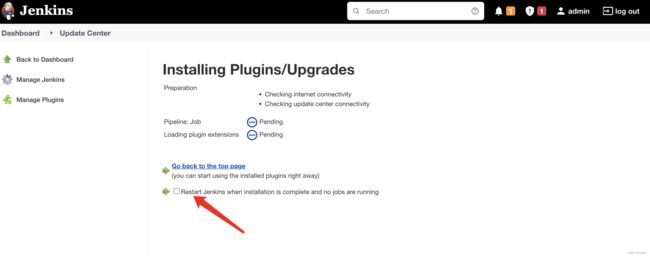
然后开始配置项目
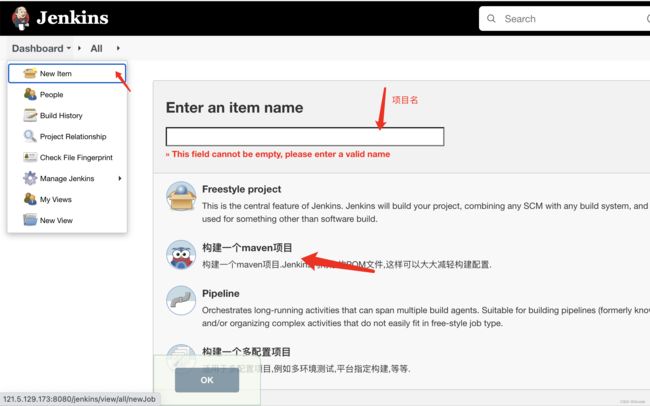
该项需安装git Parameter (动态选择分支)
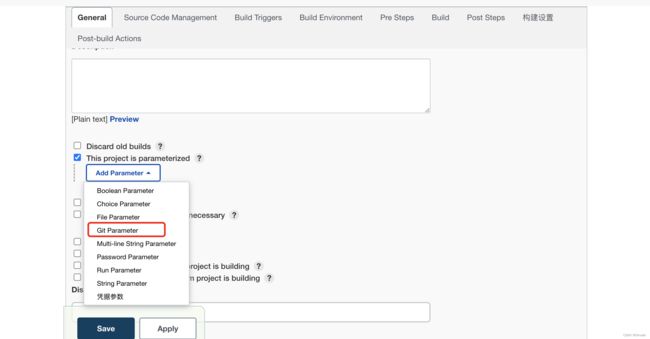

配置git项目地址
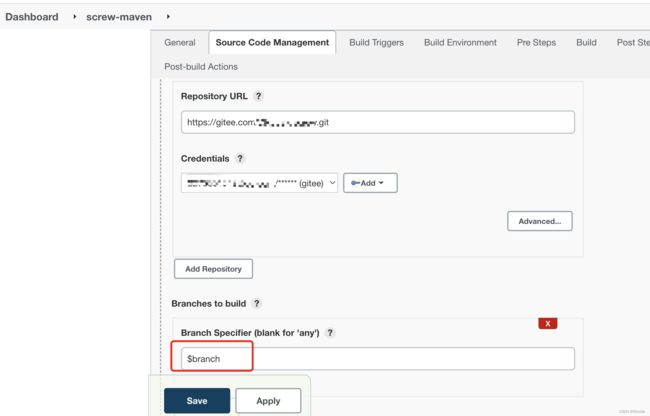
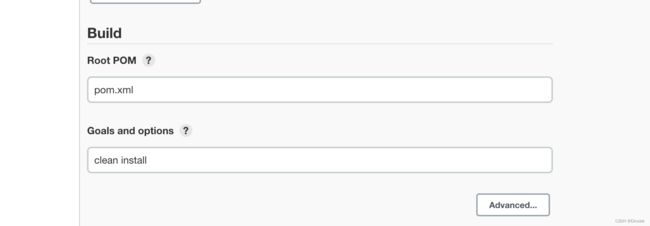
执行maven命令 clear install
添加shell脚本
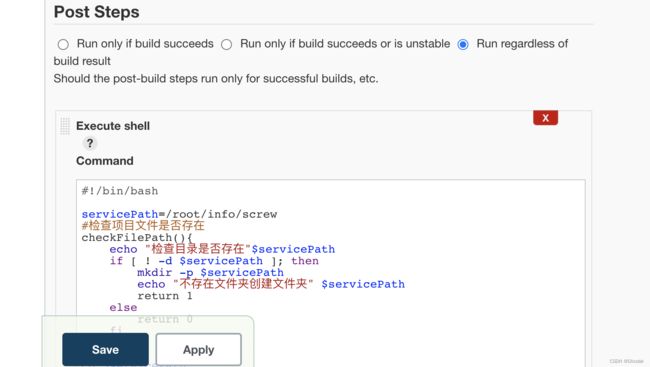
脚本内容:
#!/bin/bash
#项目根目录
servicePath=/root/info/screw
#检查项目文件是否存在
checkFilePath(){
echo "检查目录是否存在"$servicePath
if [ ! -d $servicePath ]; then
mkdir -p $servicePath
echo "不存在文件夹创建文件夹" $servicePath
return 1
else
return 0
fi
}
cd $servicePath
checkFilePath $servicePath
sh $servicePath/stop &
echo "杀死服务"
sleep 1s
time=$(date "+%Y%m%d%H%M%S")
echo "当前时间"$time
cp demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar $servicePath/bak/
servicePath=$servicePath/bak/
echo "改变后"$servicePath
checkFilePath $servicePath/
cd $servicePath
mv demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT$time.jar
servicePath=/root/info/screw
echo "再次变更$servicePath"
cd $servicePath
cp /root/.jenkins/workspace/screw-maven/target/demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar $servicePath
sh $servicePath/start &
echo "发布成功 ---》demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar"
start脚本都需要给权限(chmod 755 start)
nohup java -agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=7774 -Xms512m -Xmx1024m -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -XX:HeapDumpPath=/root/info/dump/ -jar demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar > /dev/null 2>&1 &
echo "screw starting..."
stop 脚本都需要给权限(chmod 755 start)
#!/bin/sh
ID=`ps -ef| grep 'demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar'|grep -v 'grep'|awk '{print $2}'`
for pid in $ID
do
kill -9 $pid
echo "kill demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar pid:$pid"
done
注意:
在使用jenkins进行自动化部署服务的过程中,发现调用服务器的shell命令无法正常启动tomcat,但是构建日志显示是成功执行的,而手动在服务器却是可以正常启动tomcat。
原因:jenkins默认在build结束后会kill掉所有的衍生进程
所以还需要在Tomcat的bin目录下修改catalina.sh
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Dhudson.util.ProcessTree.disable=true";
其它方案可参考该文章(https://www.cnblogs.com/qianjinyan/p/11239984.html)
至此已完结!
